Abstract
p130Cas regulates cancer progression by driving tyrosine receptor kinase signaling. Tight regulation of p130Cas expression is necessary for survival, apoptosis, and maintenance of cell motility in various cell types. Several studies revealed that transcriptional and post-translational control of p130Cas are important for maintenance of its expression and activity. To explore novel regulatory mechanisms of p130Cas expression, we studied the effect of microRNAs (miRs) on p130Cas expression in human breast cancer MCF7 cells. Here, we provide experimental evidence that miR-362-3p and miR-329 perform a tumor-suppressive function and their expression is downregulated in human breast cancer. miR-362-3p and miR-329 inhibited cellular proliferation, migration, and invasion, thereby suppressing tumor growth, by downregulating p130Cas. Ectopic expression of p130Cas attenuated the inhibitory effects of the two miRs on tumor progression. Relative expression levels of miR-362-3p/329 and p130Cas between normal and breast cancer correlated inversely; miR-362-3p/329 expression was decreased, whereas that of p130Cas increased in breast cancers. Furthermore, we showed that downregulation of miR-362-3p and miR-329 was caused by differential DNA methylation of miR genes. Enhanced DNA methylation (according to methylation-specific PCR) was responsible for downregulation of miR-362-3p and miR-329 in breast cancer. Taken together, these findings point to a novel role for miR-362-3p and miR-329 as tumor suppressors; the miR-362-3p/miR-329-p130Cas axis seemingly has a crucial role in breast cancer progression. Thus, modulation of miR-362-3p/miR-329 may be a novel therapeutic strategy against breast cancer.
p130Cas/breast cancer anti-estrogen resistance 1 is a member of the Cas (Crk-associated substrate) family of adaptor proteins and has a central role in tyrosine kinase-based signaling related to cell adhesion, migration, cell cycle control, apoptosis, development, and cancer progression.1, 2 Augmented expression of p130Cas in breast cancer correlates with tamoxifen resistance and poor prognosis.3, 4 Tight regulation of p130Cas function via proteolytic cleavage or reversible phosphorylation of tyrosine residues is necessary for the maintenance of cell motility, survival, and apoptosis in various cell types.5, 6, 7, 8 Although high expression of p130Cas in primary breast tumors is linked to activation of cell proliferation and cancer progression, the detailed mechanisms governing p130Cas expression are not fully understood.
MicroRNAs (miRs) are a conserved class of small noncoding RNAs (21–25 nucleotides) that regulate gene expression by inducing mRNA degradation or by suppressing mRNA translation.9 Several pieces of experimental evidence have demonstrated that miRs perform essential regulatory functions in cancer progression.10, 11 Gain and loss of certain miR functions are responsible for cancer development because of the activation of oncogenes and silencing of tumor-suppressor genes. In breast cancer, aberrant expression of such miRs as miR-146a, miR-200, miR-34, and miR-489 has been reported to alter cell growth, stemness, apoptosis, migration, and invasion via targeting of proteins involved in those cellular pathways.12, 13, 14, 15, 16 Nonetheless, there are no reports showing miRs' directly targeting p130Cas and thus affecting breast cancer development.
In this study, we demonstrate the function of miR-362-3p and miR-329 as novel regulators of p130Cas in human breast cancer cells. Ectopic expression of miR-362-3p and miR-329 decreased cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and xenograft tumor growth by directly targeting p130Cas mRNA. In addition, we found that the expression of miR-362-3p and miR-329 is downregulated in human breast cancer compared with normal control tissues, and that downregulation of both miRs is caused by transcriptional inactivation via DNA methylation. Collectively, our results suggest that the miR-362-3p/miR-329-p130Cas axis is a possible therapeutic target in breast cancer.
Results
miR-362-3p and miR-329 are novel regulators of p130Cas expression
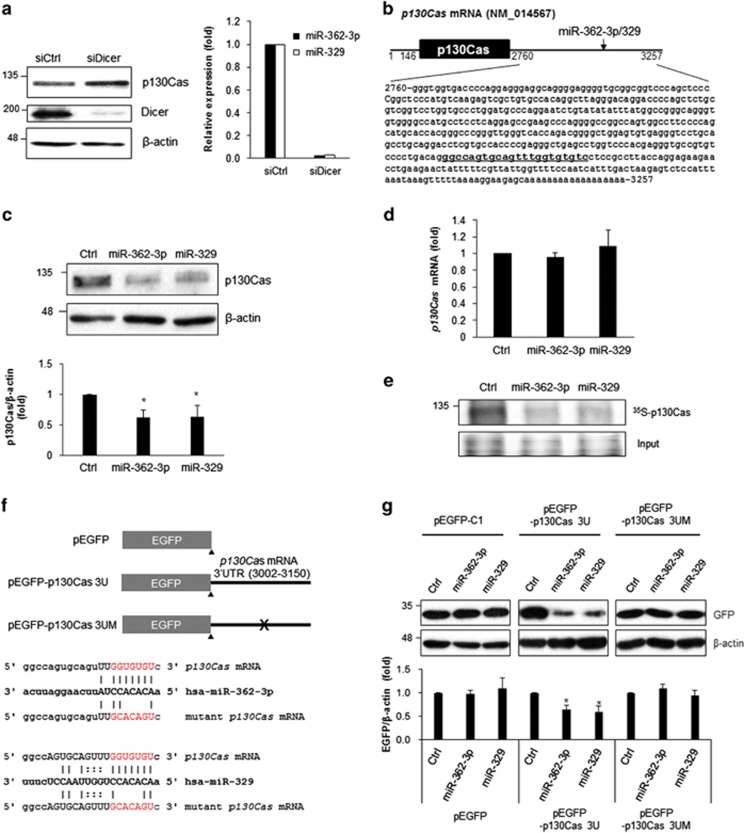
To elucidate the mechanism governing p130Cas expression, we explored miR involvement using Dicer siRNA in human breast cancer MCF7 cells. Dicer is a protein crucial for miR biogenesis because it controls the processing of precursor miRs (pre-miRs) into mature miRs.17 Downregulation of Dicer increased p130Cas expression in MCF7 cells; this result indicates that miRs were possibly involved in the regulation of p130Cas expression (Figure 1a). To identify p130Cas-targeting miRs, we performed in silico analysis using several prediction algorithms, including Targetscan, micorna.org, miRWalk, and miRanda, and found that the 3′ untranslated region (3′UTR) of human p130Cas mRNA contains a putative binding site for miR-362-3p and miR-329 (Figure 1b). Although miR-362-3p and miR-329 are generated from different chromosomes (X and 14, respectively), their seed region sequences are identical to each other. To test whether miR-362-3p and miR-329 directly target p130Cas mRNA, p130Cas levels were assessed by western blotting after transfection of miR-362-3p and miR-329 mimics into MCF7 cells. Ectopic expression of miR-362-3p and miR-329 significantly downregulated the p130Cas level (Figure 1c), but p130Cas mRNA levels were not affected by our miR transfection procedure (Figure 1d). Because p130Cas was downregulated by miR-362-3p and miR-329 without significant changes in the target mRNA levels, we assumed that miR-362-3p and miR-329 mediate translational repression of p130Cas and, accordingly, we examined de novo synthesis of p130Cas after miR overexpression. As expected, miR-362-3p and miR-329 decreased 35S-labeled p130Cas in MCF7 cells, lending support to the notion of translational repression of p130Cas by miR-362-3p and miR-329 (Figure 1e).
Figure 1.
miR-362-3p and miR-329 inhibit p130Cas expression. (a) Relative expression of p130Cas and miR-362-3p/miR-329. Forty-eight hours after transfection of control siRNA (siCtrl) or Dicer siRNA (siDicer) into MCF7 cells, total protein was isolated using RIPA buffer and the relative amount of p130Cas and Dicer were assessed by western blotting (left) or miRNA-362-3p/miR-329 levels were determined by RT-qPCR (right). U6 snRNA was used for normalization. (b) A diagram of p130Cas mRNA. A miR-binding site for miR-362-3p and miR-329 was found in the 3′-untranslated region (3′UTR) of p130Cas mRNA (underlined). (c and d) Regulation of p130Cas expression by miR-362-3p/miR-329. Forty-eight hours after transfection of miR mimics or control miR into MCF7 cells, relative level of p130Cas was determined by western blotting (c) or RT-qPCR (d) β-actin served as a loading control. GAPDH mRNA was used for normalization. (e) Translational regulation of p130Cas by miR-362-3p or miR-329. After incubation of miR-transfected cells with 35S-methionine/cysteine, the radiolabeled p130Cas protein was immunoprecipitated using p130Cas antibody, separated by SDS-PAGE and visualized using PharoseFX Plus. The representative image shows relative levels of nascent p130Cas. (f) A schematic of the EGFP reporter constructs. The 3′UTR of p130Cas mRNA containing a miR-binding site was inserted into pEGFP-C1; a mutant reporter construct lacking the miR-binding site was generated using site-directed mutagenesis. (g) Reporter analysis after miR expression. After transfection of the cells with miRs and reporter constructs along with a proper control vector, EGFP levels were assessed by western blotting. β-Actin served as a loading control. All data are presented as mean±S.D. of three independent experiments (paired t-test); *P<0.05
To confirm the regulation of p130Cas expression by miR-362-3p and miR-329, we generated EGFP reporter constructs containing a 149-bp fragment of the 3′UTR of p130Cas mRNA (positions 3002–3150; pEGFP-p130Cas 3U) or a mutant 3′UTR without the seed region for base paring with miR-362-3p or miR-329 (pEGFP-p130Cas 3UM), as shown in Figure 1f. Ectopic expression of miR-362-3p or miR-329 significantly decreased expression of the EGFP reporter containing the 3′UTR of p130Cas mRNA (EGFP-p130Cas 3U) but not EGFP control (Figure 1g). The mutant reporter, which lacks the miR-binding sites (EGFP-p130Cas 3UM) did not show the negative regulation of EGFP expression by miR-362-3p and miR-329. Taken together, these results indicated that miR-362-3p and miR-329 are novel suppressors of p130Cas and directly target the 3′UTR of p130Cas mRNA.
miR-362-3p and miR-329 inhibit tumor progression by suppressing p130Cas
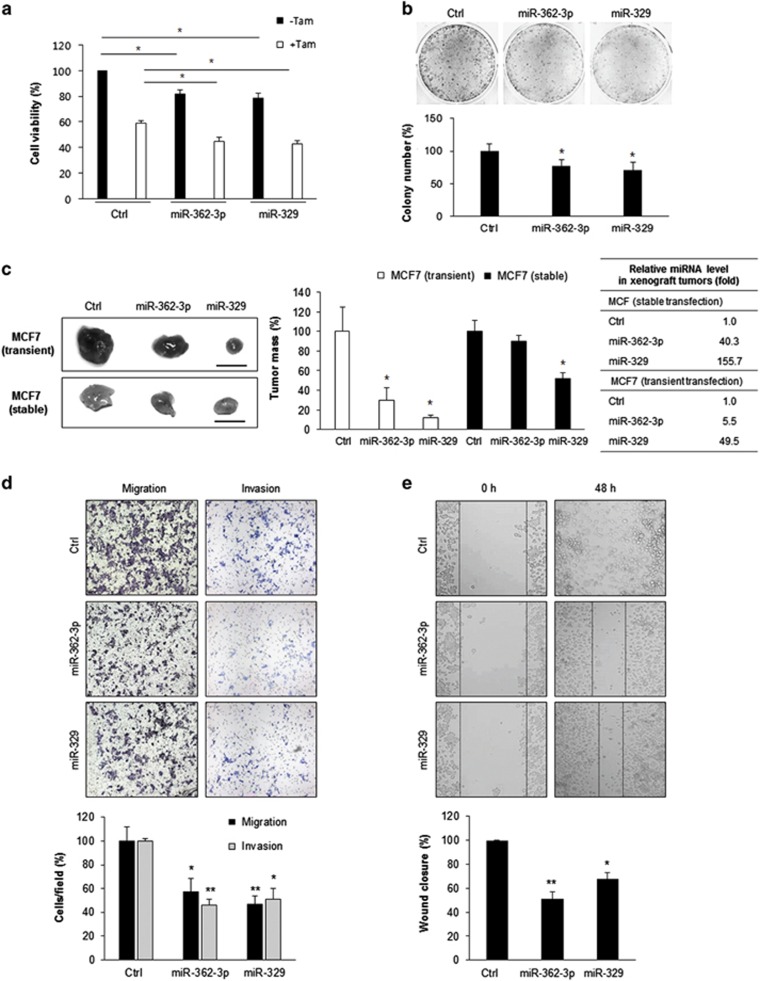
p130Cas regulates cell proliferation and cell–cell interactions, thereby participating in tumor progression.2, 5, 18 We tested whether miR-362-3p and miR-329 affect cell viability and growth. Ectopic expression of miR-362-3p and miR-329 decreased cell viability, sensitized MCF7 cells to Tamoxifen, and suppressed the colony-forming ability of MCF7 cells (Figures 2a and b); this finding indicates that miR-362-3p and miR-329 inhibit cell growth. Then, we evaluated the effects of those miRs on tumor growth in vivo on nude mice. MCF7 cells after transfection with miR-362-3p, miR-329, or control miR were transplanted into the mice as xenografts, and tumor development was assessed 4 weeks later. There were no significant changes in body weight in the three groups of mice (data now shown). Tumors expressing miR-362-3p or miR-329 mimics weighed significantly less than did the tumors expressing control miRs (Figure 2c). To further investigate the effect of miR-362-3p or miR-329 in xenograft tumor growth, we established stable MCF7 cell lines expressing miR-362-3p or miR-329 along with control plasmid and found both stable cells had lower p130Cas levels (Supplementary Figure 2). The xenograft tumors originated from stable cells expressing either miR-362-3p or miR-329 were also smaller than controls (Figure 2c). These results indicate that miR-362-3p and miR-329 (separately) suppressed the growth of xenograft tumors from MCF7 cells in vivo. Next, to determine whether miR-362-3p or miR-329 affect cell motility, we analyzed cell migration and invasiveness using Transwell chambers with or without Matrigel after transfection of miR-362-3p or miR-329 into MCF7 cells. Ectopic expression of miR-362-3p or miR-329 significantly decreased cellular migration and invasion (Figure 2d). To quantify this effect, we measured the percentage of the cells that migrated to the bottom of the Transwells after transfection with either mimics of miRs or control. Migration of the cells transfected with miR-362-3p or miR-329 was significantly less than that of control cells (P<0.05). Similarly, miR-362-3p and miR-329 inhibited migration of MCF7 cells according to a wound-healing assay (Figure 2e). Taken together, these results suggested that overexpression of miR-362-3p or miR-329 inhibited tumor progression by suppressing cell viability, colony formation, migration, invasiveness, and tumor growth of breast cancer cells.
Figure 2.
miR-362-3p and miR-329 inhibit cellular viability, growth, migration, and invasiveness. (a) Cell viability was determined by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay after 48 h transfection of miR mimics with or without tamoxifen treatment in MCF7 cells. (b) Colony formation assay. After transfection of miR mimics in MCF7 cells, 1 × 103 cells were seeded and cultured for 3 weeks. Colonies were stained with crystal violet and the number of colonies was analyzed. (c) Xenograft tumor growth assay. miR-362-3p/329 or control miR were expressed into MCF7 cells by transient or stable transfection. 2 × 106 cells were subcutaneously injected into the flank of male BALB/c nude mice and xenograft tumor mass was analyzed 4 weeks later. Relative miR expression in the xenograft tumors was assessed by RT-qPCR and fold changes were shown in the table. Scale bar, 1 cm. (d) Migration and invasion assays. MCF7 cells transfected with miR mimics or control miR were seed Boyden chamber and migrating or invading cells were stained and counted in three randomly selected visual fields. (e) Wound-healing assays. MCF7 cells transfected with miR mimics or control miR were cultured until confluence, and a scratch was made in the cell layer. After 48 h, relative wound closure was quantified as the ratio of the migration distance to control distance. The data are presented either as mean±S.D. or as a representative graph/image from three independent experiments (paired t-test); *P<0.05, **P<0.01
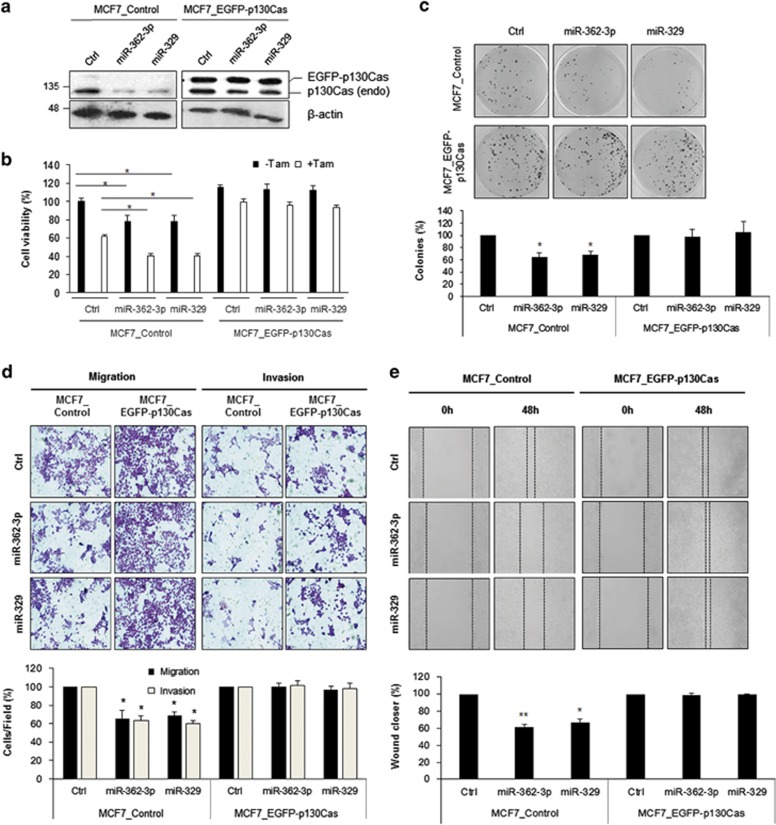
To determine whether the negative effect of miR-362-3p and miR-329 on cell growth or migration is mediated by direct targeting of p130Cas, we used MCF7 cells to establish stable cell lines expressing either EGFP-p130Cas or EGFP control (Supplementary Figure 1) and assessed cell viability using the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay with or without Tamoxifen treatment. Because miR-362-3p and miR-329 reduce p130Cas expression via the 3′UTR of its mRNA (Figures 1b and g), EGFP-p130Cas level was not affected by miR overexpression as shown in Figure 3a. Downregulation of cell viability by miR-362-3p and miR-329 was also observed in MCF7_control cells. In contrast, the negative effects of miR-362-3p and miR-329 on cell viability and chemoresistance to Tamoxifen were attenuated by ectopic p130Cas expression in MCF7_EGFP-p130Cas cells (Figure 3b). Inhibition of the colony-forming ability by miR-362-3p and miR-329 was also attenuated by p130Cas overexpression in MCF7_EGFP-p130Cas cells (Figure 3c).
Figure 3.
miR-362-3p and miR-329 regulate cell viability, growth, cell migration, and invasiveness via p130Cas. (a) Relative expression of p130Cas with or without miR-362-3p/329 in stable cell lines. Forty-eight hours after transfection of miR mimics or control miRs, relative expressions of p130Cas were determined by western blotting. (b) Cell viability was determined by MTT assay after 48 h transfection of miRs mimics with or without tamoxifen treatment in both MCF7_Control cells and MCF7_EGFP-130Cas cells. (c) Colony formation assay. MCF7_Control and MCF7_EGFP-p130Cas cells were transfected with miR mimics or control miR and 103 cells were cultured for 3 weeks, and colonies were stained with crystal violet and counted in three randomly selected visual fields. (d) Migration and invasion assays. MCF7_Control and MCF7_EGFP-p130Cas cells transfected with miR mimics or control miR were seed Boyden chamber and migrating or invading cells were stained and counted in three randomly selected visual fields. (e) Wound-healing assay. MCF7_Control and MCF7_EGFP-p130Cas cells were transfected with miR mimics or control miR and grown until confluence. A scratch was made in the cell layer, and relative wound closure was quantified as the ratio of the migration distance to control distance after 48 h. The data are presented as either mean±S.D. or a representative graph/image from three independent experiments (paired t-test); *P<0.05
We also analyzed migration and invasiveness of MCF7_EGFP-p130Cas cells. Expression of EGFP-p130Cas stimulated cell migration as reported previously.18, 19 Although miR-362-3p and miR-329 reduced the percentage of migrating cells among MCF7_control cells, this inhibition of cell migration and invasiveness by miR-362-3p and miR-329 was attenuated by EGFP-p130Cas overexpression (Figures 3d and e). Taken together, these results support our hypothesis that miR-362-3p and miR-329 inhibit cell migration or invasiveness via direct targeting of p130Cas.
Expression of miR-362-3p and miR-329 inversely correlates with p130Cas levels in human breast cancer
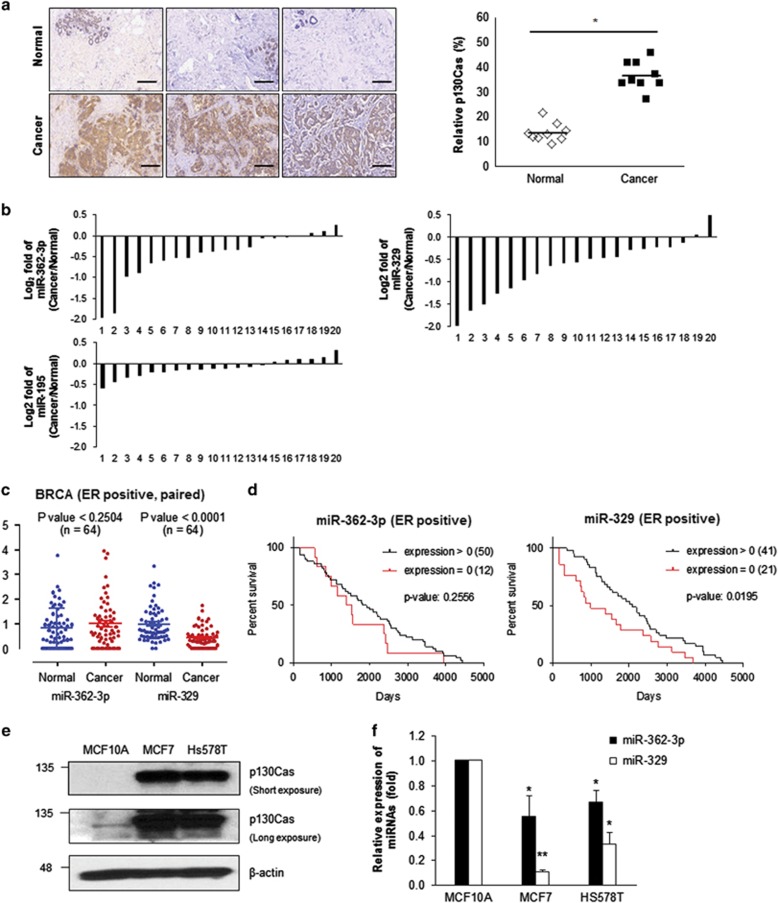
We assessed the relative p130Cas expression between breast tumors and the corresponding normal tissue. The results revealed that p130Cas levels in breast tumors were >3-fold higher than in the corresponding healthy tissues (Figure 4a). To determine whether miR-362-3p and miR-329 are differentially expressed under pathological conditions, we used real-time quantitative RT-PCR (RT-qPCR) to measure the relative expression levels of these miRs in breast tumors compared with normal control. Although there was no significant difference in miR-195 levels between the healthy control and breast cancer, both miR-362-3p and miR-329 showed lower expression levels in tumors compared with the matching control tissues (Figure 4b). In line with other reports showing downregulation of miR-329 in neuroblastoma and glioma,20, 21, 22 we found that both miR-362-3p and miR-329 were significantly downregulated in human breast cancer tissues. To confirm the observed change of miRs expression in individual patients, we processed small-RNA expression data of estrogen receptor-positive (ER-positive) patient samples from the cancer genome atlas (TCGA). There was no significant change of miR-362-3p between normal and cancer (P<0.25); however, miR-392 level was significantly lowered in paired ER-positive patients (P<0.0001) as shown in Figure 4c. To investigate the correlation between miR expression and survival of patients, we analyzed the relative survival duration among patients (Figure 4d). It appears that the patients expressing miR-329 survived longer than one with no expression (P<0.0195).
Figure 4.
Expression of miR-362-3p or miR-329 inversely correlates with p130Cas levels in human breast cancers. (a) Relative expression levels of p130Cas according to immunohistochemical analysis involving an anti-p130Cas antibody. The representative images from nine pairs of breast cancer samples with the corresponding normal tissues. Scale bar, 100 μm. (b) Relative expression levels of miRs among tissues. The log2 value of three different miRs fold change in 20 paired breast cancer specimen. (c) The expressions of miRs in ER-positive breast cancer patients. The quantities of miR-362-3p and miR-329 were plotted using the vertical scatter plots. Bars represent mean expression with standard errors. (d) The relation between survival and miRs expression. 62 patients who have a termination event were divided into two groups: patients expressing miR-362-3p or miR-329 and patients with no miR-362-3p or miR-329. The survival analysis was performed using Kaplan and Meier estimate. (e and f) Relative expression levels of p130Cas and miR-362-3p/329 in human breast MCF10A, MCF7, and Hs578T cells. p130Cas levels were determined by western blotting using p130Cas antibody (e) and miR-362-3p/329 levels were assessed by RT-qPCR (f). The data are presented as mean±S.D. of three independent experiments (paired t-test); *P<0.05, **P<0.01
To further confirm the inverse correlation between expression levels of miR-362-3p/miR-329 and p130Cas in cell culture system, we analyzed three different cell lines originating from the human breast: MCF10A (nontumorous epithelial cell line), MCF7 (adenocarcinoma), and Hs578T (carcinoma). Relative expression levels of p130Cas in MCF7 and Hs578T were higher than in MCF10A, according to western blotting (Figure 4e). On the other hand, the two breast cancer cell lines, MCF7 and Hs578T, showed significantly lower expression of miR-362-3p and miR-329 compared with MCF10A (nontumorous control; Figure 4f). Taken together, these data serve as the evidence of an inverse correlation between miR-362-3p/329 and p130Cas in human breast cancers.
Transcription of miR-362-3p and miR-329 is downregulated in human breast cancers via DNA methylation
Regulation of miR expression can be transcriptional and post-transcriptional.23 Because we uncovered downregulation of both miR-362-3p and miR-329 in human breast cancers, we decided to compare expression of the primary transcripts (pri-miRs) and precursor forms between normal and cancer tissues to determine whether downregulation of miR-362-3p and miR-329 in breast cancer is caused by transcriptional inactivation of the miR genes.
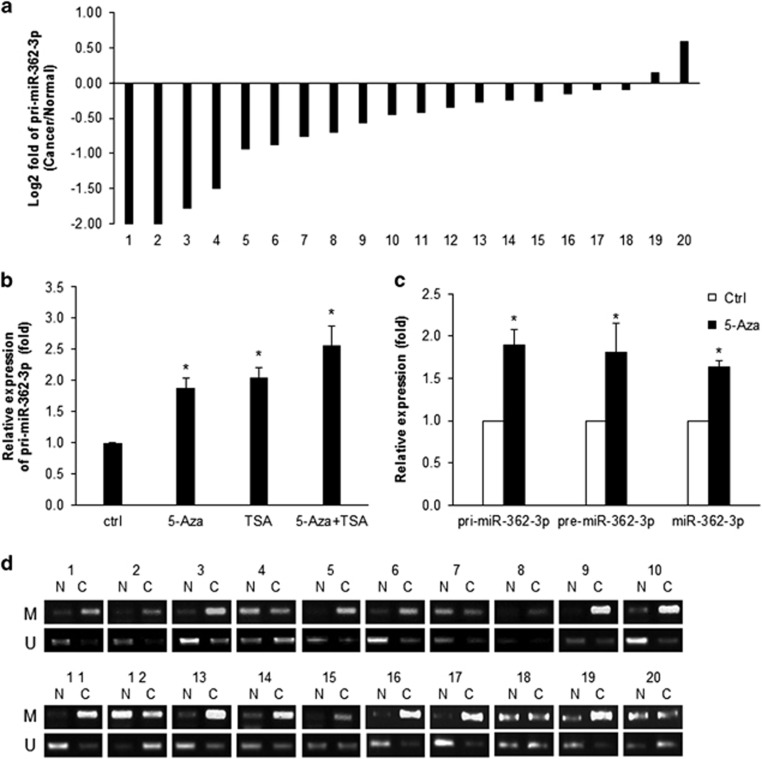
First, using RT-qPCR with specific primer sets, we compared the relative amounts of the primary transcript or precursor miR of miR-362-3p between normal and cancer tissues (Table 1). As shown in Figure 5a, both primary transcript for miR-362-3p (pri-miR-362-3p) and precursor miR-362-3p (pre-miR-362-3p) were downregulated in 18 of 20 cancer tissues; this finding indicates that downregulation of miR-362-3p in breast tumors is associated with reduced transcription of the miR-362-3p gene. Although the detailed mechanisms underlying the dysregulation of miRs in cancer have not been fully elucidated, emerging evidence supports the idea that epigenetic mechanisms such as DNA methylation control the expression of miR genes in various cancers.24, 25 To determine whether epigenetic regulation is responsible for differential expression of miR-362-3p gene, we quantified the primary transcripts of miR-362-3p in MCF7 cells after treatment with 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine (5-Aza), an inhibitor of DNA methyltransferase, or trichostatin A (TSA), an inhibitor of class I and II HDAC families. As shown in Figure 5b, the level of pri-miR-362-3p was upregulated after 5-Aza and/or TSA treatment in MCF7 cells, which indicates that the transcription of miR-362 gene could be regulated by epigenetic events. Especially, inhibition of DNA methylation by 5-Aza treatment increased primary transcript, precursor form, and mature form of miR-362-3p (Figure 5c).
Table 1. Primer sequence.
| Product name | Primer | Sequence (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|
| miR-362-3p | Forward | AACACACCTATTCAAGGATTCA |
| Reverse | mRQ 3'primer (Clontech) | |
| miR-329 | Forward | AACACACCTGGTTAACCTCTTT |
| Reverse | mRQ 3'primer (Clontech) | |
| p130Cas | Forward | ATGGGCAGTACGAGAACAGC |
| Reverse | GGCCAGGTCGTGGTCTATG | |
| Gapdh | Forward | TGCACCACCAACTGCTTAGC |
| Reverse | GGCATGGACTGTGGTCATGAG | |
| p130Cas -3U | Forward | AAAAAGATCTTAAGGGTCACCAGAC |
| Reverse | AAAAGGTACCTCTCCTGGTAAGGCG | |
| p130Cas -3UM | Forward | CAGTGCAGTTTGCACAGTCCTCCGCCTTACCA |
| Reverse | AAGGCGGAGGACTGTGCAAACTGCACTGGCCC | |
| Pri-miR-362-3p | Forward | ATATACATGAGAGTGAGACTTG |
| Reverse | TTTGAATCCTTGAATAGGTGT | |
| Pre-miR-362-3p | Forward | CTTGAATCCTTGGAACCTAG |
| Reverse | TTTGAATCCTTGAATAGGTGT | |
| Pri-miR-329 | Forward | TGCAATTCCATATTTAACAG |
| Reverse | ACTGGAAAAGAGGTTAACCAGGTGT | |
| Pre-miR-329 | Forward | UACCTGAAGAGAGGTTTTCTGGGTT |
| Reverse | ACTGGAAAAGAGGTTAACCAGGTGT | |
| miR-362-3p_Met | Forward | GCGAGCGGGGTCGACGTA |
| Reverse | CGTCTACGCGTACGCGCC | |
| miR-362-3p_Unmet | Forward | GTGAGTGGGGTTGATGTA |
| Reverse | 5CATCTACACATACACACC |
Figure 5.
Expression of miR-362-3p is regulated via DNA methylation. (a) Relative expression level of primary transcript (pri-miR-362-3p). The log2 value of pri-miR-362-3p fold change in 20 paired breast cancer specimen. (b) Relative expression levels of pri-miR-362-3p after 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine (5-Aza) and/or Trichostatin A (TSA) treatment. MCF7 cells were incubated with 2.5 μM 5-Aza for 72 h and/or with 100ng/ml TSA for 12 h. After isolation of total RNA, the expression level of pri-miR-362-3p was assessed using RT-qPCR. GAPDH mRNA was used for normalization. (c) Relative expression levels of pri-miR-362-3p, pre-miR-362-3p, and muature miR-362-3p after 5-Aza treatment were assessed by RT-qPCR. GAPDH mRNA or U6 snRNA were used for normalization of pri-/pre-miR and mature miR, respectively. (d) Methylation-specific PCR (MSP). Genomic DNA was isolated from each sample and was incubated with bisulfite for 2.5 h. The differential status of CpG islands in the promoter region of CLCN5, the host gene of miR-362-3p, was assessed by means of MSP with specific primer sets shown in Table 1. The data are presented as mean±S.D. of three independent experiments (paired t-test); *P<0.05
On the basis of these observations, we hypothesized that differential expression of miR-362-3p between normal and cancerous tissues results from the relative methylation status of the promoter region. To test this possibility, we analyzed the genomic locus of miR-362-3p. Because miR-362-3p is an intronic miR located in intron 3 of the CLCN5 gene on chromosome X (Supplementary Figure 3), we analyzed CpG islands in the promoter region of CLCN5 and performed methylation-specific PCR as described in Materials and Methods.26 As shown in Figure 5d, the amount of methylation-specific PCR products was higher in breast tumors than in normal control tissues; this result indicates that the enhanced methylation of the promoter region of CLCN5 is responsible for the downregulation of miR-362-3p in breast cancers.
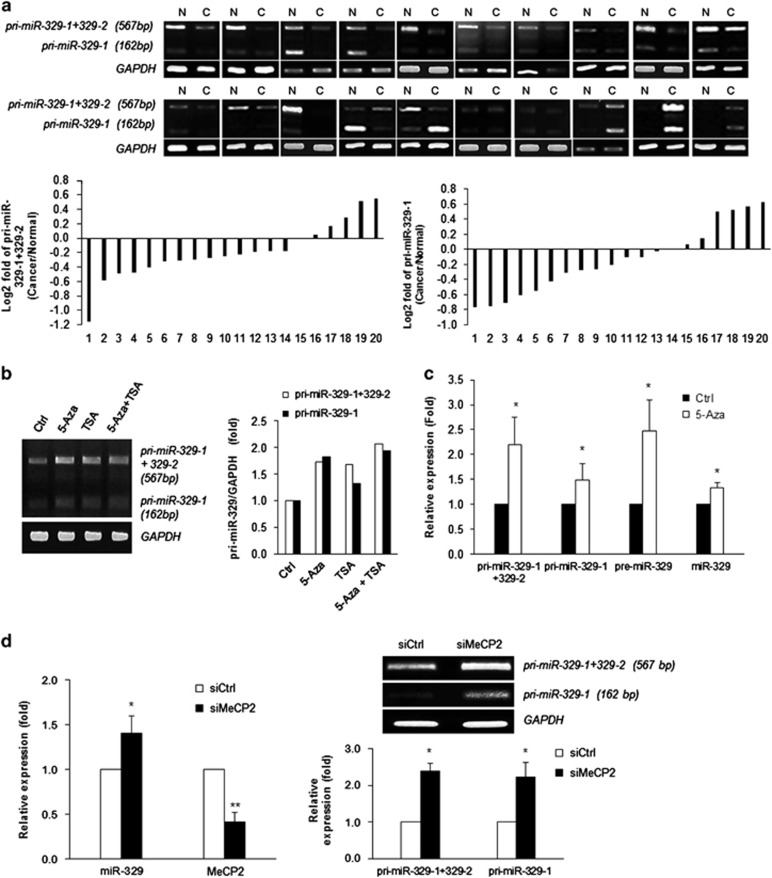
We also found that miR-329, which is encoded on chromosome 14 as two copies (miR-329-1 and miR-329-2, respectively), and the precursor sequences are identical to each other (Supplementary Figure 4). When we performed RT-PCR using the primer set listed in Table 1, the PCR products consisted of two distinct bands (pri-miR-329-1+miR-329-2 (567 bp) and pri-miR-329-1 (162 bp); Supplementary Figure 3). Relative expression levels of primary transcripts or the precursor of miR-329 were measured using conventional RT-PCR and RT-qPCR, respectively. As shown in Figure 6a, primary transcripts of both miR-329-1/miR-329-2 and pre-miR-329 were downregulated in 14 of 20 malignant breast cancer tissues; these data indicate that expression of miR-329 was inhibited in malignant breast cancer. To determine whether miR-329 gene is also controlled by epigenetic regulation, we also quantified the primary transcripts of miR-329 after treatment with 5-Aza or TSA and found an increase of miR-329 after 5-Aza or TSA (Figure 6b). Especially, 5-Aza treatment resulted in an increase of primary transcript, precursor form, and mature miR-329 as shown in Figure 6c; this finding means that DNA methylation is a possible regulatory mechanism of miR-329 expression.
Figure 6.
Expression of miR-329 is regulated by MeCP2. (a) Relative expression levels of primary transcript (pri-miR-329) in a subset of breast specimens. Total RNA was isolated from breast cancer samples or the corresponding normal tissues, and relative expression levels of pri-miR-329 were assessed using conventional RT-PCR. Pri-miR-329 (pri-miR-329-1 (162 bp) and pri-miR-329-1+pri-miR-329-2 (567 bp)) was detected as two conspicuous bands using the primer sets shown in Table 1. The log2 value shows pri-miR-329 relative fold change in 20 paired human breast specimens. (b) Relative expression level of pri-miR-329 after 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine (5-Aza) and/or Trichostatin A (TSA) treatment were determined by RT-PCR. (c) Relative expression levels of pri-miR-329, pre-miR-329, and mature miR-329 after 5-Aza treatment were determined by RT-qPCR or RT-PCR. GAPDH mRNA or U6 snRNA were used for normalization of pri-/pre-miR and mature miR, respectively. (d) Relative expression levels of miR-329 after MeCP2 silencing. Forty-eight hours after transfection of MeCP2 siRNA or control siRNA into MCF7 cells, pri-miR-329 level was analyzed by RT-PCR. The data are presented as mean±S.D. of three independent experiments (paired t-test); *P<0.05
miR-329 is one of intergenic miRs, and its promoter region has not been identified definitively. We browsed a ~10-kb region upstream of the miR-329 gene to find likely cis elements affecting miR-329 expression; however, we did not find CpG islands on that region. Recent studies showed that miR-329 is upregulated in the brain of a mouse model of Rett syndrome; these mice have mutations in the MeCP2 gene, and the MeCP2 level is elevated in neoplastic breast tissues.27, 28, 29 To test the possibility that MeCP2 is responsible for the downregulation of miR-329 in breast cancer, we assessed miR-329 expression after transfection of Mecp2 siRNA into MCF7 cells. As shown in Figure 6d, downregulation of MeCP2 resulted in upregulation of miR-329. Pri-miR-329-1 and pri-miR-329-2 were also upregulated after MeCP2 silencing; this result indicated that MeCP2 was responsible for upregulation of miR-329 in breast cancers (Figure 6d). Taken together, these data suggested that transcriptional inactivation of both miR-362-3p and miR-329 is responsible for the downregulation of both miR-362-3p and miR-329 in breast cancers.
Discussion
p130Cas functions as a major integrator of cellular signaling by interacting with various proteins including receptor tyrosine kinases, adaptor molecules, and guanine nucleotide exchange factors; p130Cas's activity is tightly regulated by phosphorylation by focal adhesion kinase or Src.19, 30, 31 Overexpression of p130Cas in breast cancer is associated with poor prognosis and with resistance to tamoxifen or adriamycin.4, 18, 32 Here, our aim was to identify the regulatory mechanism governing p130Cas expression by means of miRs. We demonstrated that miR-362-3p and miR-329 act as tumor suppressors by inhibiting p130Cas expression in human breast cancer cells. This seems to be the first study to show that the miR-362-3p/329-p130Cas axis is involved in cancer progression and to demonstrate the inverse correlation between expression levels of miR-362-3p/329 and p130Cas in breast cancer.
In this study, we show that downregulation of miR-362-3p and miR-329 facilitates cancer progression via disinhibition of p130Cas expression. Although miR-362-3p and miR-329 are encoded in an intron of the CLCN5 gene on chromosome X and in an intergenic region on chromosome 14 (14q32.31), respectively, they have identical sequences of the seed region and thereby target p130Cas mRNA. Other studies have shown differential expression of miR-362-3p in various tissues including the fetal brain of mice, estrogen receptor-positive breast tumors, gastric cancer, and melanoma as well as downregulation of miR-329 in glioma, neuroblastoma, and the mouse model of Rett syndrome.20, 22, 29, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38 The detailed mechanism, however, that governs the differential expression of the two miRs has not been fully elucidated.
Although aberrant expression of miRs is known as one of hallmarks of some diseases including cancer, the mechanism regulating miR expression under many pathological conditions remains unclear. DNA methylation is a pivotal regulatory mechanism of gene transcription, and aberrant DNA methylation in cancers often results in silencing of tumor-suppressor genes.39, 40 As shown in Figures 5b and 6c, inhibition of DNA methylation by 5-Aza enhances miR expression; this result indicates that DNA methylation is one of possible mechanisms responsible for the downregulation of miR-362-3p and miR-329 in breast cancer. Although there are CpG islands in the promoter region of the CLCN5 gene, which are likely to affect miR-362 expression, we could not find CpG islands within the ~10 kb region upstream of the miR-329 gene. Recently, several reports demonstrated that MeCP2, a protein binding a singly methylated CpG, regulates miR expression including that of miR-7b, miR-483-5p, and miR-143.41, 42, 43 Furthermore, MeCP2-deficient mice show altered miR expression, and the latter problem is responsible for the pathogenesis of Rett syndrome.29, 44 MeCP2 is also involved in suppression of miR processing by regulating formation of the DGCR8/Drosha complex in the brain.45 On the basis of the results from previous studies and our study (data not shown), we believe that upregulation of MeCP2 in breast cancer may result in downregulation of miR-329.28, 46 Further studies are needed to understand the relationship between the aberrant expression of MeCP2 and dysregulation of miRs (including miR-329) during pathological processes such as neurological diseases and cancer.
In conclusion, we present evidence that miR-362-3p and miR-329 function as tumor suppressors by directly repressing p130Cas expression in MCF7 cells; expression of these miRs is inhibited in breast cancer via DNA methylation. We found that ectopic expression of miR-362-3p or miR-329 suppresses cell growth, migration, and invasion via downregulation of p130Cas, whereas ectopic p130Cas expression attenuates the tumor-suppressive activity of both miRs in MCF7 cells. In addition, we demonstrate an inverse correlation between expression levels of miR-362-3p/329 and p130Cas and show that downregulation of miR-362-3p and miR-329 is mediated by DNA methylation of the respective miR genes. These findings demonstrate a novel role of miR-362-3p and miR-329 as tumor suppressors; the miR-362-3p/miR-329-p130Cas axis seems to have a crucial role in breast cancer progression. Thus, modulation of miR-362-3p/miR-329 may be a novel therapeutic strategy against breast cancer.
Materials and Methods
Cell culture and transfection
Human MCF7 cells were cultured in Dulbecco's modified essential medium (Hyclone, Logan, UT, USA), supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum and 1% penicillin/streptomycin at 37 °C in 5% CO2. MCF7 clones containing either pEGFP or pEGFP-p130Cas were established by sequential selecting using 0.5 mg/ml of G418 for 2 weeks. EGFP reporter plasmids were cloned by inserting 3′UTR of human p130Cas mRNA (3002–3150 bp) into pEGFP-C1 (BD Bioscience, Franklin lake, NJ, USA) as described in the previous study.47 Mutant reporter plasmid harboring mutant seed region-binding site for miRNAs was generated by site-directed mutagenesis using KOD plus mutagenesis kit (Toyobo, Osaka, Japan). Overexpression plasmids for miR-362-3p or miR-329 (Genolution Pharmarceuticals, Seoul, Korea) were transfected to MCF7 cells with control plasmid and stable clones expressing miR-362-3p or miR-329 are selected using 0.1 mg/ml Zeoicin, respectively. Plasmids, siRNAs (Genolution), and miRNAs (Bioneer, Deajeon, Korea) were transfected using Lipofectamin 2000 (Invitrogen, Calsbad, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer's instruction.
Tissue samples
Breast cancer tissues with their corresponding normal tissues were purchased from Catholic Research Tissue Specimen Bank and Super BioChips Laboratory (Seoul, Korea). This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board at the Catholic University of Korea (IRB approval number; CUMC13TISI0080).
RNA isolation and analysis
Total RNAs were isolated from frozen tissues and cell lines using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen). For the analysis of mRNA, primary transcripts of miRNAs, or precursor form of miRNAs, complementary DNA (cDNA) was synthesized by reverse transcription using ReverTra Ace qPCR RT Kit (Toyobo). For miRNA analysis, miRNA cDNA was prepared using the MiR-X miRNA First-Strand cDNA systhesis kit (Clonetech, San diego, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer's instructions. The relative abundance of each transcript was assessed by RT-qPCR using Kapa SYBR Fast qPCR kit (Kapa Biosystems, Wilmington, MA, USA) and specific primer sets on the StepOne Plus system (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). Conventional RT-PCR was also performed using Blend Taq polymerase (Toyobo) on Verti Thermal Cycler (Life Technologies, Calsbad, CA, USA). Primer sequences are listed in Table 1.
Western blot analysis
Whole-cell lysate was prepared using RIPA buffer (10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.4), 150 mM NaCl, 1% NP-40, 1 mM EDTA, and 0.1% SDS) and separated by electrophoresis in SDS-containing polyacrylamide gels, and transferred onto PVDF membrane (Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA). The blots were incubated with following antibodies against GFP (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX, USA), Dicer (Cell Signaling Technology, Inc., Danvers, MA, USA), β-actin (Abcam, Cambridge, MA, USA), p130Cas (Cas2)48 then sequentially incubated with the appropriate secondary antibodies conjugated with horseradish peroxidase (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, TX, USA). Chemoluminescent signals were visualized using NEW Clarity ECL substrate (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA).
Nascent translation assay
De novo translation of p130Cas was estimated by incubating MCF7 cells with 1 mCi L-[35S]methionine and L-[35S]cysteine (Perkin-Elmer Life Sciences, Waltham, MA, USA) for 20 min.47 After lysis with RIPA buffer, immunoprecipitation was carried out using anti-Cas2 Ab. The IP products were separated by SDS-PAGE, transferred to PVDF membranes, and visualized using PharoseFX Plus System (Bio-Rad).
Scratch wound-healing, migration, and invasion assay
Scratch wound-healing assay was performed as previously described.49 In brief, the plates with confluent MCF7 cells were wounded using a 200-μl pipette tip and cultured in low-serum (1%) DMEM for 48 h. Cell images were obtained under IX71 inverted microscope (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan). Cell migration and invasion were assayed using a Transwell chamber (BD Biosciences) with or without Matrigel. For the invasion assay, a Transwell chamber was coated with 150 μl of matrigel solution and incubated for 90 min at 37 °C. In both Transwell assays, miRNA-transfected cells were seeded in chambers with serum-free media, whereas media containing 10% FBS was added to the lower chamber. After 24 h incubation, migrated cells were fixed with 100% methanol and stained using Diff-Quik Staning kit (Sysmex, Kobe, Japan). Cell images were obtained under Axiovert 200 inverted microscope (Zeiss, Jena, Germany).
Colony-forming assay
After 48 h transfection of miRNAs, 1 × 103 cells were transferred to six-well plates and incubated for 3 weeks. Then, cells were fixed with 4% formaldehyde and stained with 0.05% crystal violet for 10 min at room temperature. After washing and drying the plates, the number of colonies was estimated by counting colonies from three random fields (100 mm2) per sample.
Measurement of cell viability
A colorimetric assay using the tetrazolium salt, MTT was used to assess cell viability after miRNA transfection and Tamoxifen treatment (5 μM, 48 h). Cells were incubated with 0.5 mg/ml of MTT for 3 h at 37 °C. The formazan crystals were dissolved with isopropanol and the absorbance at 570 nm was measured using VICTOR3 multilabel plate reader (Perkin-Elmer, Waltham, MA, USA).
Immunohistochemical staining
Tissue microarray (Super BioChips Laboratories), which contains small representative tissue samples from 10 of different cases and their corresponding non-tumor tissues, was de-paraffinized, rehydrate, and incubated with EDTA buffer (1 mM, pH 8.0) at 95 °C for antigen retrieval. All steps of IHC staining was followed as per the manufacturer's instructions (Immune Bio Science Corp., Mukilteo, WA, USA). After blocking with blocking solution, the slide was incubated with anti-p130Cas antibody (BD Biosciences) at 4 °C for overnight and further incubated with a horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibody at room temperature for 1 h. DAB was applied for color development. The strength of positivity was analyzed by panoramic MIDI slide scanner system (3D Histech Ltd., Budapest, Hungary).
Xenograft tumorigenesis
All animal experiments were performed according to approved protocols from IACUC in College of Medicine, the Catholic University of Korea. 2 × 106 cells were mixed with Matrigel (BD Biosciences) and implanted subcutaneously into the either side of the flank of BALB/c Nude mice (6-week-old, male). After 4 weeks of implant, animals were killed and tumor mass was analyzed.
Methylation-specific PCR (MSP)
MSP was performed to analyze differential methylation status of miRNA promoter regions between normal and cancer samples. Genomic DNA in each sample was extracted and treated with bisulfate using the EZ-DNA methylation kit (Zymo Research Corp., Irvine, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer's instruction. 100 ng of resulting DNA was used as the template for the nested MSP reactions. The methylation- and unmethylation-primer sets used in PCR reactions are presented in Table 1. The products were analyzed by electrophoresis using 2% agarose gels.
Analysis of miRNA expression and survival using TCGA data
miRNA expression data in breast invasive carcinoma and their corresponding clinical data were downloaded from the TCGA data portal (https://tcga-data.nci.nih.gov/tcga/). Of 1077 normal and carcinoma samples, 771 estrogen receptor positives (ER positive) and 65 normal samples including 64 paired samples were precompiled. To measure the expression level of two miRNAs (miR-362-3p and miR-329), of reads mapped to each miRNA locus, all reads with 5′ end matched to the 5′ end of the locus but with allowing 3′ end heterogeneity were summed up with the normalized read counts. The quantity of each miRNA in carcinoma samples was compared with that of normal samples using paired tests. Based on 62 ER-positive samples with a termination event and their corresponding clinical data, the survival analysis has been done using the Kaplan and Meier estimate.50 The P-values were determined using log-rank (Mantel-cox) test. To examine the effect of miRNA expression on the survival, the patients were divided into two groups: with expression of miRNAs and without expression.
Acknowledgments
We appreciated to Hyosun Tak for technical assistance. This work is supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (2012M3A9D1054517, 2012R1A5A2047939 to EKL and 2009-0093826 to WK).
Glossary
- miRs
microRNAs
- 3′UTR
3′-untranslated region
- RT-qPCR
real-time quantitative PCR
- Cas
Crk-associated substrate
- ER
estrogen receptor
- TCGA
the cancer genome atlas
- 5-Aza
5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine
- TSA
trichostatin A
- cDNA
complementary DNA
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Footnotes
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on Cell Death and Differentiation website (http://www.nature.com/cdd)
Edited by S Fulda
Supplementary Material
References
- Bouton AH, Riggins RB, Bruce-Staskal PJ. Functions of the adapter protein Cas: signal convergence and the determination of cellular responses. Oncogene 2001; 20: 6448–6458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Defilippi P, Di Stefano P, Cabodi S. p130Cas: a versatile scaffold in signaling networks. Trends Cell Biol 2006; 16: 257–263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Flier S, van der Kwast TH, Claassen CJ, Timmermans M, Brinkman A, Henzen-Logmans SC et al. Immunohistochemical study of the BCAR1/p130Cas protein in non-malignant and malignant human breast tissue. Int J Biol Markers 2001; 16: 172–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ta HQ, Thomas KS, Schrecengost RS, Bouton AH. A novel association between p130Cas and resistance to the chemotherapeutic drug adriamycin in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 2008; 68: 8796–8804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A, Pellet-Many C, Zachary IC, Evans IM, Frankel P. p130Cas: a key signalling node in health and disease. Cell Signal 2013; 25: 766–777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim W, Seok Kang Y, Soo Kim J, Shin NY, Hanks SK, Song WK. The integrin-coupled signaling adaptor p130Cas suppresses Smad3 function in transforming growth factor-beta signaling. Mol Biol Cell 2008; 19: 2135–2146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim W, Kook S, Kim DJ, Teodorof C, Song WK. The 31-kDa caspase-generated cleavage product of p130cas functions as a transcriptional repressor of E2A in apoptotic cells. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 8333–8342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donato DM, Ryzhova LM, Meenderink LM, Kaverina I, Hanks SK. Dynamics and mechanism of p130Cas localization to focal adhesions. J Biol Chem 2010; 285: 20769–20779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004; 116: 281–297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garofalo M, Croce CM. microRNAs: Master regulators as potential therapeutics in cancer. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 2011; 51: 25–43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer 2006; 6: 857–866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumaraswamy E, Wendt KL, Augustine LA, Stecklein SR, Sibala EC, Li D et al. BRCA1 regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) expression in human breast cancer cells involves microRNA-146a and is critical for its tumor suppressor function. Oncogene 2014; 34: 4333–4346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bai WD, Ye XM, Zhang MY, Zhu HY, Xi WJ, Huang X et al. MiR-200c suppresses TGF-beta signaling and counteracts trastuzumab resistance and metastasis by targeting ZNF217 and ZEB1 in breast cancer. Int J Cancer 2014; 135: 1356–1368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le MT, Hamar P, Guo C, Basar E, Perdigao-Henriques R, Balaj L et al. miR-200-containing extracellular vesicles promote breast cancer cell metastasis. J Clin Invest 2014; 124: 5109–5128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park EY, Chang E, Lee EJ, Lee HW, Kang HG, Chun KH et al. Targeting of miR-34a-NOTCH1 axis reduced breast cancer stemness and chemoresistance. Cancer Res. 2014; 74: 7573–7582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang L, He D, Yang D, Chen Z, Pan Q, Mao A et al. MiR-489 regulates chemoresistance in breast cancer via epithelial mesenchymal transition pathway. FEBS lett 2014; 588: 2009–2015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim VN, Han J, Siomi MC. Biogenesis of small RNAs in animals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2009; 10: 126–139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabodi S, Tinnirello A, Di Stefano P, Bisaro B, Ambrosino E, Castellano I et al. p130Cas as a new regulator of mammary epithelial cell proliferation, survival, and HER2-neu oncogene-dependent breast tumorigenesis. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 4672–4680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger B. A role for p130Cas in mechanotransduction. Cell 2006; 127: 879–881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao B, Tan L, He B, Liu Z, Xu R. MiRNA-329 targeting E2F1 inhibits cell proliferation in glioma cells. J Transl Med 2013; 11: 172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasayama T, Nishihara M, Kondoh T, Hosoda K, Kohmura E. MicroRNA-10b is overexpressed in malignant glioma and associated with tumor invasive factors, uPAR and RhoC. Int J Cancer 2009; 125: 1407–1413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang H, Li Q, Zhao W, Yuan D, Zhao H, Zhou Y. miR-329 suppresses the growth and motility of neuroblastoma by targeting KDM1A. FEBS Lett 2014; 588: 192–197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siomi H, Siomi MC. Posttranscriptional regulation of microRNA biogenesis in animals. Mol Cell 2010; 38: 323–332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esteller M. Epigenetic gene silencing in cancer: the DNA hypermethylome. Hum Mol Genet 2007; 16(Spec No 1): R50–R59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H, Maruyama R, Yamamoto E, Kai M. DNA methylation and microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Mol Oncol 2012; 6: 567–578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ku JL, Jeon YK, Park JG. Methylation-specific PCR. Methods Mol Biol 2011; 791: 23–32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varela MA, Roberts TC, Wood MJ. Epigenetics and ncRNAs in brain function and disease: mechanisms and prospects for therapy. Neurotherapeutics 2013; 10: 621–631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller HM, Fiegl H, Goebel G, Hubalek MM, Widschwendter A, Muller-Holzner E et al. MeCP2 and MBD2 expression in human neoplastic and non-neoplastic breast tissue and its association with oestrogen receptor status. Br J Cancer. 2003; 89: 1934–1939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urdinguio RG, Fernandez AF, Lopez-Nieva P, Rossi S, Huertas D, Kulis M et al. Disrupted microRNA expression caused by Mecp2 loss in a mouse model of Rett syndrome. Epigenetics 2010; 5: 656–663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlaepfer DD, Hauck CR, Sieg DJ. Signaling through focal adhesion kinase. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 1999; 71: 435–478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brabek J, Constancio SS, Shin NY, Pozzi A, Weaver AM, Hanks SK. CAS promotes invasiveness of Src-transformed cells. Oncogene 2004; 23: 7406–7415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Flier S, Chan CM, Brinkman A, Smid M, Johnston SR, Dorssers LC et al. BCAR1/p130Cas expression in untreated and acquired tamoxifen-resistant human breast carcinomas. Int J Cancer. 2000; 89: 465–468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang LL, Zhang Z, Li Q, Yang R, Pei X, Xu Y et al. Ethanol exposure induces differential microRNA and target gene expression and teratogenic effects which can be suppressed by folic acid supplementation. Hum Reprod 2009; 24: 562–579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu DZ, Tian Y, Ander BP, Xu H, Stamova BS, Zhan X et al. Brain and blood microRNA expression profiling of ischemic stroke, intracerebral hemorrhage, and kainate seizures. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2010; 30: 92–101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan E, Patel R, Nallur S, Ratner E, Bacchiocchi A, Hoyt K et al. MicroRNA signatures differentiate melanoma subtypes. Cell cycle 2011; 10: 1845–1852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen LL, Tobiasen H, Holm A, Schepeler T, Ostenfeld MS, Thorsen K et al. MiRNA-362-3p induces cell cycle arrest through targeting of E2F1, USF2 and PTPN1 and is associated with recurrence of colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer 2013; 133: 67–78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang P, Luo Y, Duan H, Xing S, Zhang J, Lu D et al. MicroRNA 329 suppresses angiogenesis by targeting CD146. Mol Cell Biol 2013; 33: 3689–3699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Auwera I, Limame R, van Dam P, Vermeulen PB, Dirix LY, Van Laere SJ. Integrated miRNA and mRNA expression profiling of the inflammatory breast cancer subtype. Br J Cancer 2010; 103: 532–541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones PA, Baylin SB. The fundamental role of epigenetic events in cancer. Nat Rev Genet 2002; 3: 415–428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Q, Ying J, Li J, Fan Y, Poon FF, Ng KM et al. Aberrant promoter methylation of DLEC1, a critical 3p22 tumor suppressor for renal cell carcinoma, is associated with more advanced tumor stage. J Urol 2010; 184: 731–737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han K, Gennarino VA, Lee Y, Pang K, Hashimoto-Torii K, Choufani S et al. Human-specific regulation of MeCP2 levels in fetal brains by microRNA miR-483-5p. Genes Dev 2013; 27: 485–490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann J, Chu DC, Maxwell A, Oakley F, Zhu NL, Tsukamoto H et al. MeCP2 controls an epigenetic pathway that promotes myofibroblast transdifferentiation and fibrosis. Gastroenterology 2010; 138: 705–714 14 e1-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y, Shin BC, Thamotharan S, Devaskar SU. Differential methylation of the micro-RNA 7b gene targets postnatal maturation of murine neuronal Mecp2 gene expression. Dev Neurobiol 2014; 74: 407–425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H, Tao J, Chen PJ, Shahab A, Ge W, Hart RP et al. Genome-wide analysis reveals methyl-CpG-binding protein 2-dependent regulation of microRNAs in a mouse model of Rett syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 18161–18166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng TL, Wang Z, Liao Q, Zhu Y, Zhou WH, Xu W et al. MeCP2 suppresses nuclear microRNA processing and dendritic growth by regulating the DGCR8/Drosha complex. Dev Cell 2014; 28: 547–560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirza S, Sharma G, Parshad R, Gupta SD, Pandya P, Ralhan R. Expression of DNA methyltransferases in breast cancer patients and to analyze the effect of natural compounds on DNA methyltransferases and associated proteins. J Breast Cancer 2013; 16: 23–31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim C, Kim W, Lee H, Ji E, Choe YJ, Martindale JL et al. The RNA-binding protein HuD regulates autophagosome formation in pancreatic beta cells by promoting autophagy-related gene 5 expression. J Biol Chem 2014; 289: 112–121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai R, Iwamatsu A, Hirano N, Ogawa S, Tanaka T, Mano H et al. A novel signaling molecule, p130, forms stable complexes in vivo with v-Crk and v-Src in a tyrosine phosphorylation-dependent manner. EMBO J 1994; 13: 3748–3756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang CC, Park AY, Guan JL. In vitro scratch assay: a convenient and inexpensive method for analysis of cell migration in vitro. Nat Protoc 2007; 2: 329–333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan EL, Meier P. Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Statist Assn 1958; 53: 457–481. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.