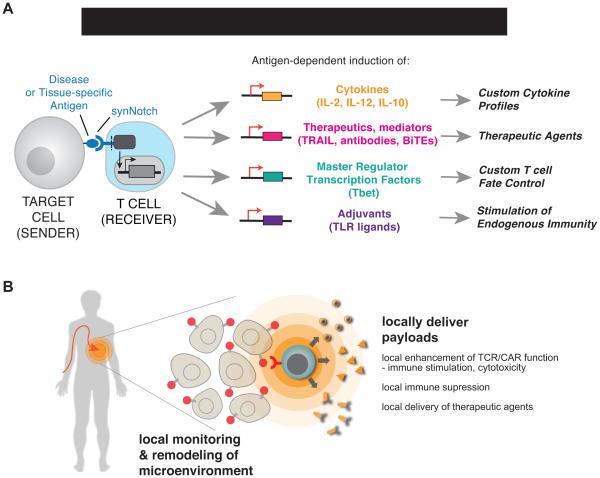
Figure 7. SynNotch Circuits Allow Versatile Reprogramming of T cells to Monitor and Selectively Modulate Their Microenvironment.
(A) synNotch receptors can drive diverse behaviors in primary human T cells. We show that synNotch receptors can drive custom cytokine production profiles, effectively deliver non-native therapeutics, and control T cell differentiation, all in an antigen-dependent and T cell activation independent manner.
(B) synNotch are sufficient to target T cells in vivo to locally produce a therapeutic payload. Future T cell therapies could utilize synNotch receptors to target T cells to disease-related or tissue-specific antigens for local delivery of therapeutics that are ineffective or toxic as systemically administered agents in humans.