Abstract
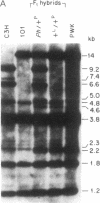
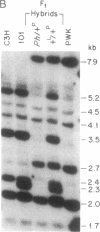
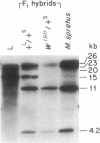
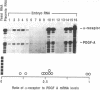
Platelet-derived growth factor receptors are composed of two subunits (alpha and beta) that associate with one another to form three functionally active dimeric receptor species. The two subunits are encoded by separate loci in humans and other species. In this study, we used conventional interspecific backcross mapping and an analysis of a deletional mutation to establish close linkage between the alpha-subunit gene (Pdgfra) and the dominant spotting (W) locus on mouse chromosome 5. Further, by analyzing the restriction fragment length polymorphisms in interspecific F1 hybrids, we were able to demonstrate that the closely associated patch (Ph) locus carries a deletion in Pdgfra. This observation was confirmed by both DNA and RNA analysis of 10.5-day fetuses produced from crosses between Ph heterozygotes. Out of 16 fetuses analyzed, Pdgfra genomic sequences were absent and no mRNA for the receptor was detected in 6 fetuses that were developmentally abnormal (the presumptive Ph homozygotes). We also determined that the deletion associated with the Ph mutation does not extend into the coding sequences of the adjacent Kit gene, by analysis of the genomic DNA from both the interspecific F1 hybrids and the presumptive Ph homozygotes. The absence of Pdgfra genomic sequences and the lack of detectable message associated with the Ph mutation should make this mutant a valuable asset for understanding the role of the receptor alpha subunit during mammalian development.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chabot B., Stephenson D. A., Chapman V. M., Besmer P., Bernstein A. The proto-oncogene c-kit encoding a transmembrane tyrosine kinase receptor maps to the mouse W locus. Nature. 1988 Sep 1;335(6185):88–89. doi: 10.1038/335088a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geissler E. N., Cheng S. V., Gusella J. F., Housman D. E. Genetic analysis of the dominant white-spotting (W) region on mouse chromosome 5: identification of cloned DNA markers near W. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9635–9639. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geissler E. N., Ryan M. A., Housman D. E. The dominant-white spotting (W) locus of the mouse encodes the c-kit proto-oncogene. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):185–192. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90020-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronwald R. G., Adler D. A., Kelly J. D., Disteche C. M., Bowen-Pope D. F. The human PDGF receptor alpha-subunit gene maps to chromosome 4 in close proximity to c-kit. Hum Genet. 1990 Aug;85(3):383–385. doi: 10.1007/BF00206767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loutit J. F., Cattanach B. M. Haematopoietic role for Patch (Ph) revealed by new W mutant (Wct) in mice. Genet Res. 1983 Aug;42(1):29–39. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300021467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon M. F., Glenister P. H. A new allele sash (Wsh) at the W-locus and a spontaneous recessive lethal in mice. Genet Res. 1982 Jun;39(3):315–322. doi: 10.1017/s001667230002098x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon M. F., Glenister P. H., Loutit J. F., Evans E. P., Peters J. A presumed deletion covering the W and Ph loci of the mouse. Genet Res. 1984 Oct;44(2):161–168. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300026367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui T., Heidaran M., Miki T., Popescu N., La Rochelle W., Kraus M., Pierce J., Aaronson S. Isolation of a novel receptor cDNA establishes the existence of two PDGF receptor genes. Science. 1989 Feb 10;243(4892):800–804. doi: 10.1126/science.2536956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercola M., Melton D. A., Stiles C. D. Platelet-derived growth factor A chain is maternally encoded in Xenopus embryos. Science. 1988 Sep 2;241(4870):1223–1225. doi: 10.1126/science.3413486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercola M., Wang C. Y., Kelly J., Brownlee C., Jackson-Grusby L., Stiles C., Bowen-Pope D. Selective expression of PDGF A and its receptor during early mouse embryogenesis. Dev Biol. 1990 Mar;138(1):114–122. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(90)90181-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nocka K., Majumder S., Chabot B., Ray P., Cervone M., Bernstein A., Besmer P. Expression of c-kit gene products in known cellular targets of W mutations in normal and W mutant mice--evidence for an impaired c-kit kinase in mutant mice. Genes Dev. 1989 Jun;3(6):816–826. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.6.816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nocka K., Tan J. C., Chiu E., Chu T. Y., Ray P., Traktman P., Besmer P. Molecular bases of dominant negative and loss of function mutations at the murine c-kit/white spotting locus: W37, Wv, W41 and W. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1805–1813. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08305.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qiu F. H., Ray P., Brown K., Barker P. E., Jhanwar S., Ruddle F. H., Besmer P. Primary structure of c-kit: relationship with the CSF-1/PDGF receptor kinase family--oncogenic activation of v-kit involves deletion of extracellular domain and C terminus. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):1003–1011. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02907.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappolee D. A., Brenner C. A., Schultz R., Mark D., Werb Z. Developmental expression of PDGF, TGF-alpha, and TGF-beta genes in preimplantation mouse embryos. Science. 1988 Sep 30;241(4874):1823–1825. doi: 10.1126/science.3175624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reith A. D., Rottapel R., Giddens E., Brady C., Forrester L., Bernstein A. W mutant mice with mild or severe developmental defects contain distinct point mutations in the kinase domain of the c-kit receptor. Genes Dev. 1990 Mar;4(3):390–400. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.3.390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. M., Look A. T., Roussel M. F., Sherr C. J. Tandem linkage of human CSF-1 receptor (c-fms) and PDGF receptor genes. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):655–661. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90224-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell E. S. Hereditary anemias of the mouse: a review for geneticists. Adv Genet. 1979;20:357–459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searle A. G., Truslove G. M. A gene triplet in the mouse. Genet Res. 1970 Apr;15(2):227–235. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300001555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifert R. A., Hart C. E., Phillips P. E., Forstrom J. W., Ross R., Murray M. J., Bowen-Pope D. F. Two different subunits associate to create isoform-specific platelet-derived growth factor receptors. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8771–8778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan J. C., Nocka K., Ray P., Traktman P., Besmer P. The dominant W42 spotting phenotype results from a missense mutation in the c-kit receptor kinase. Science. 1990 Jan 12;247(4939):209–212. doi: 10.1126/science.1688471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truslove G. M. A new allele at the patch locus in the mouse. Genet Res. 1977 Apr;29(2):183–186. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300017249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Escobedo J. A., Kuang W. J., Yang-Feng T. L., Daniel T. O., Tremble P. M., Chen E. Y., Ando M. E., Harkins R. N., Francke U. Structure of the receptor for platelet-derived growth factor helps define a family of closely related growth factor receptors. Nature. 1986 Sep 18;323(6085):226–232. doi: 10.1038/323226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]