Description
A 50-year-old female, consuming mixed non-vegetarian diet, presented to our out-patient department with easy fatigability, tiredness and dyspnea of 3 months duration. On examination she had severe pallor but systemic examination of the cardiovascular, respiratory, gastrointestinal and neurological systems were within normal limits. Detailed general examination revealed hyperpigmentation of skin over the knuckles of both hands (Fig. 1). Investigations showed hemoglobin of 73 g/L with mean corpuscular volume (MCV) of 116.7 fL, mean corpuscular hemoglobin of 38.8 pg, mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration of 38.8 % and red cell distribution width of 30.6 %. She also had mild thrombocytopenia (137 × 105/µL). Total leukocyte count was 4100/µL and reticulocyte count was 4 % (Corrected reticulocyte count—1.95 %). Peripheral smear examination showed marked anisopoikilocytosis with macroovalocytes and hypersegmented neutrophils (Fig. 2). Serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) was 840 IU/L (normal <480 IU/L). Serum chemistries were within the normal range. Her plasma cyanocobalamin was 144 pg/mL (normal: 187–883 pg/mL). Gastroduodenoscopy and antral biopsy showed features of atrophic gastritis. Her serum tested positive for anti-parietal cell antibody, hence confirming the diagnosis of addisonian pernicious anemia. She symptomatically improved with parenteral hydroxycobalamine—1000 µg intra muscular (im) injection given every third day for seven injections. Her hemoglobin at 1 month follow up improved to 94 g/day and MCV 100.1 fl with improvement in thrombocytopenia (256 × 105/µL). She was put on lifelong vitamin B12 prophylaxis (1000 µg im every month) and asked to follow up yearly with complete blood count and red cell indices.
Fig. 1.

Clinical photograph showing hyperpigmentation of skin over the knuckles of fingers of both hands
Fig. 2.
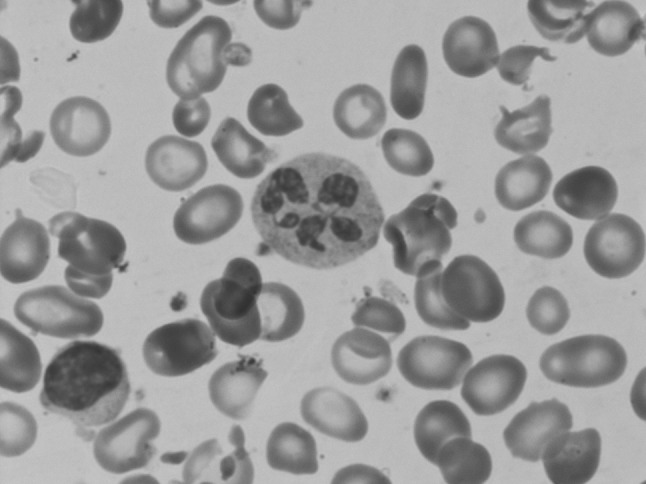
Photomicrograph of peripheral blood film, showing anisopoikilocytosis with macroovalocytes and a hypersegmented neutrophil in the centre. (magnification ×400)
Vitamin B12 deficiency is under recognized and under diagnosed even though it produces a wide array of pathological manifestations [1]. Reversible knuckle and oral mucosal pigmentation are external markers of vitamin-B12 deficiency in addition to recurrent angular stomatitis, cheilitis and rarely polymorphic cutaneous eruption [2]. This hyperpigmentation was first observed to be associated with macrocytic anemia by Dr. Bramwell Cook in 1944. He also found that both were responsive to crude liver extract [3]. Knuckle hyperpigmentation has been observed to occur in about 19.0 % patients with megaloblastic anemia and sometimes may be the only marker of vitamin-B12 deficiency [4]. It occurs as a result of reduced intracellular glutathione leading to increased melanin synthesis as well as some degree of melanocyte pigmentary incontinence and reverses with supplementation of vitamin-B12 [5]. Careful clinical examination for knuckle hyperpigmentation should be done in any patient, especially elderly individuals presenting with anemia, neurological symptoms and fatigue as it may help to clinch the clinical diagnosis of vitamin B12 deficiency.
Take Home Message
Vitamin B-12 deficiency is an under recognized, easily correctable cause of anemia, fatigue and neurological symptoms.
Knuckle hyper pigmentation is an important external marker which gives a clue to the diagnosis of Vitamin B-12 deficiency.
Careful clinical examination of this subtle and at times only clinical sign is of paramount importance to make a correct diagnosis and instituting proper treatment before serious neurological complications sets in.
Compliance with Ethical Standards
On behalf of all the co-authors (listed above) I would like to state that this work has not been submitted currently elsewhere in any other journal.
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest by any of the authors.
Ethical Approval
Conducted study did not involve any animal requiring approval for the same.
Informed Consent
Informed Consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Contributor Information
Arjun Lakshman, Email: arjunlakshman@gmail.com.
Ram V. Nampoothiri, Email: ramvnampoothiri@gmail.com
Sreejesh Sreedharanunni, Email: dr.s.sreejesh@gmail.com.
Pankaj Malhotra, Email: hematpgi@gmail.com.
Subhash Varma, Email: suvarma@gmail.com.
References
- 1.Hvas AM, Nexo E. Diagnosis and treatment of vitamin B12 deficiency—an update. Haematologica. 2006;91(11):1506–1512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kannan R, Ng MJM. Cutaneous lesions and vitamin B12 deficiency. Can Fam Physician. 2008;54(4):529–532. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Baker SJ, Ignatius M, Johnson S, Vaish SK. Pigmentation and vitamin-B12 deficiency. BMJ. 1963;2(5366):1205. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5366.1205-b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Aaron S, Kumar S, Vijayan J, Jacob J, Alexander M, Gnanamuthu C (2005) Clinical and laboratory features and response to treatment in patients presenting with vitamin B12 deficiency-related neurological syndromes. Neurol India 53(1):55–58; discussion 59 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 5.Agrawala R, Sahoo S, Choudhury A, Mohanty B, Baliarsinha A. Pigmentation in vitamin B12 deficiency masquerading Addison’s pigmentation: a rare presentation. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2013;17(7):254. doi: 10.4103/2230-8210.119591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


