Abstract
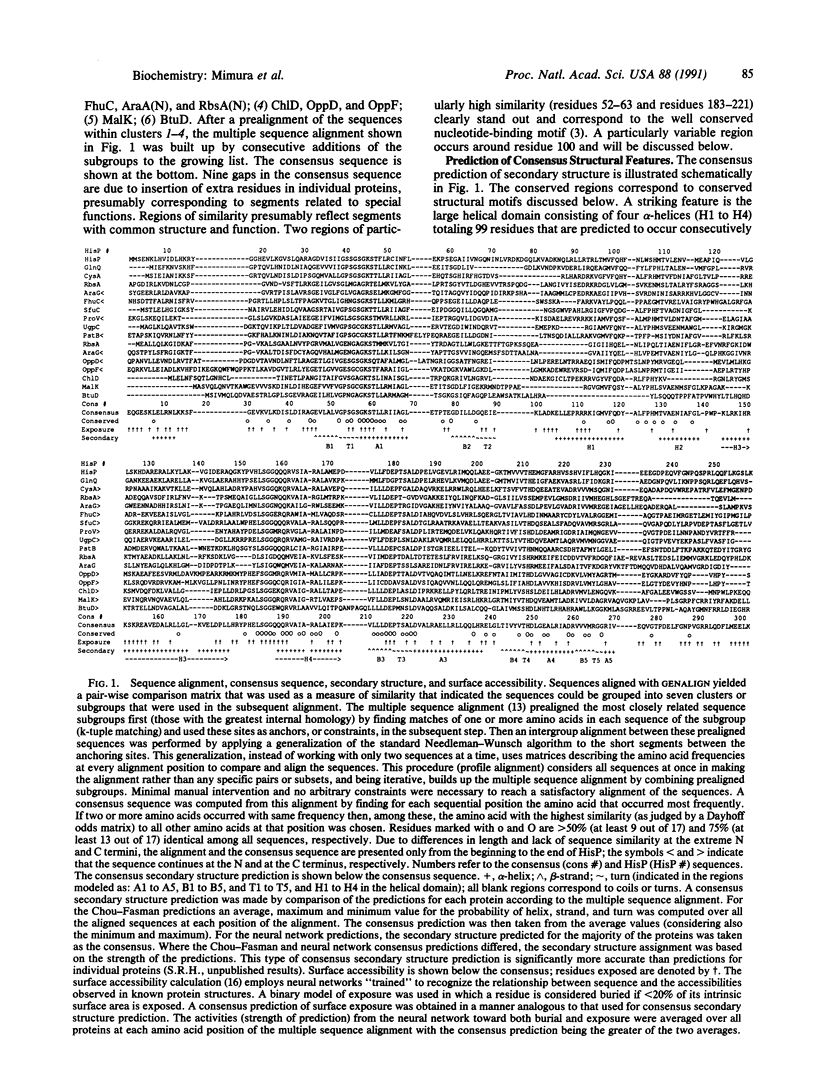
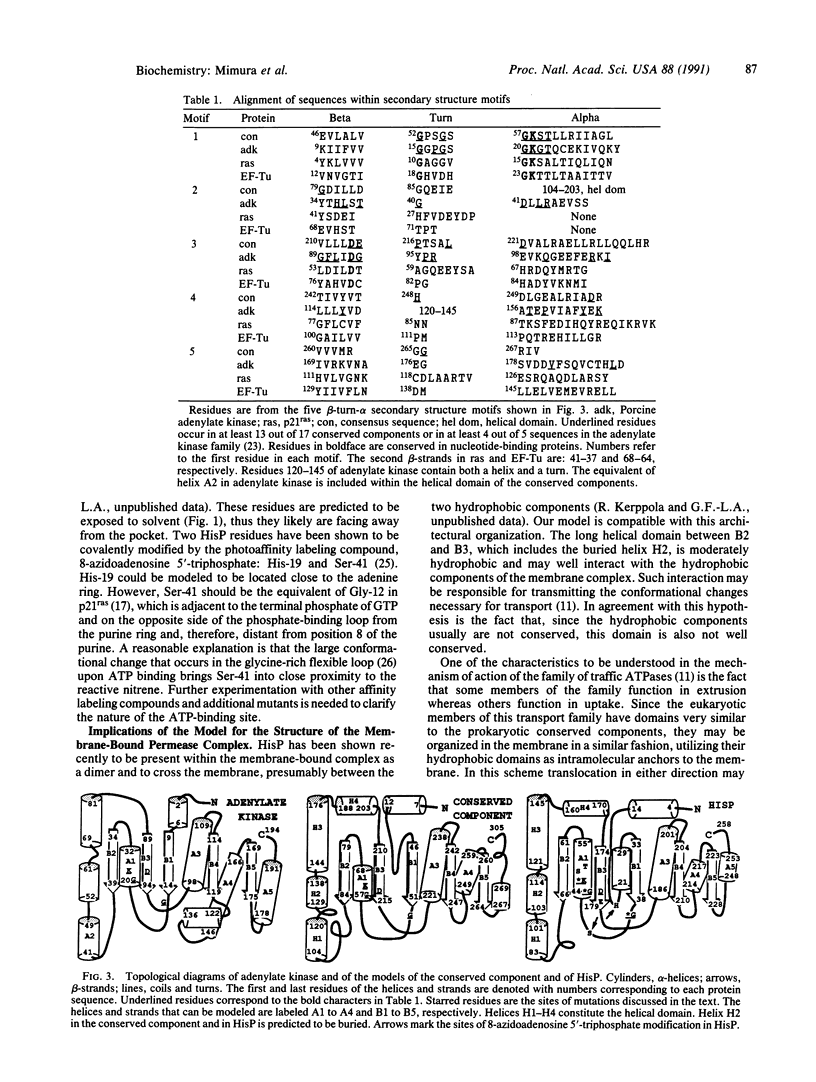
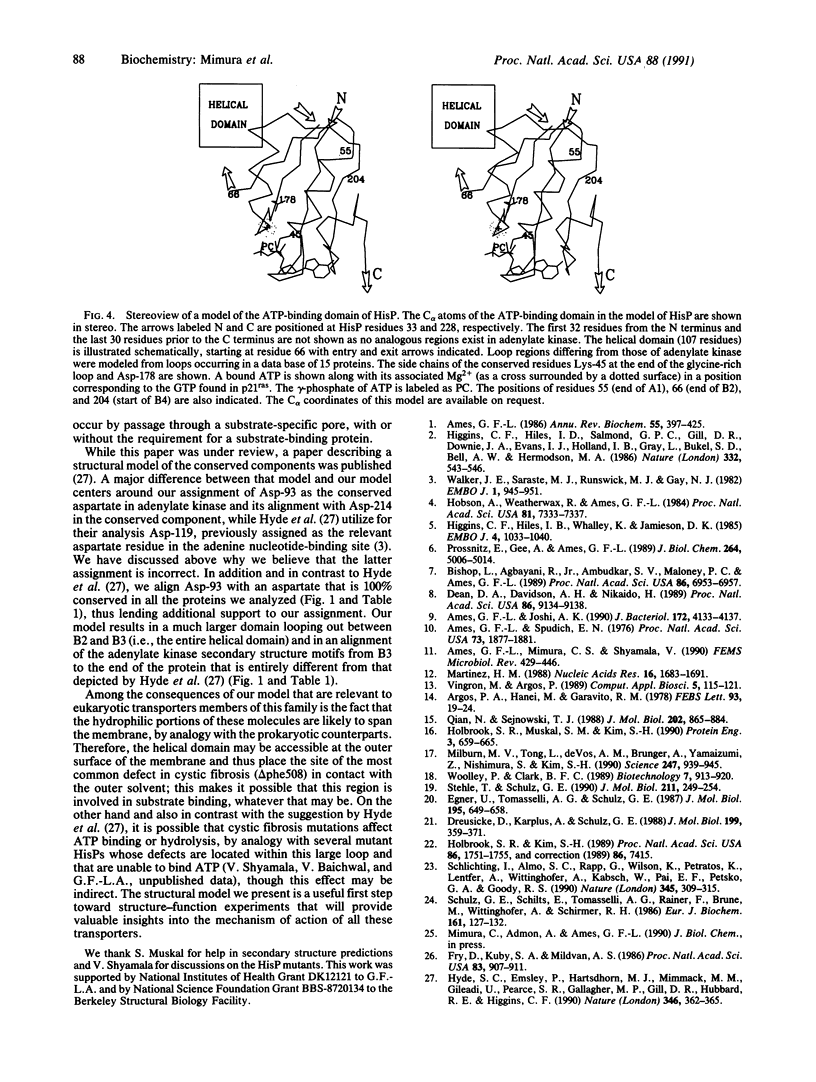
The amino acid sequences of 17 bacterial membrane proteins that are components of periplasmic permeases and function in the uptake of a variety of small molecules and ions are highly homologous to each other and contain sequence motifs characteristic of nucleotide-binding proteins. These proteins are known to bind ATP and are postulated to be the energy-coupling components of the permeases. Several medically important eukaryotic proteins, including the multidrug-resistance transporters and the protein encoded by the cystic fibrosis gene, are also homologous to this family. By multiple sequence alignment of these 17 proteins, the consensus sequence, secondary structure, and surface exposure were predicted. The secondary structural motifs that are conserved among nucleotide-binding proteins were identified in adenylate kinase, p21ras, and elongation factor Tu by superposition of their known tertiary structures. The equivalent secondary structural elements in the predicted conserved component were located. These, together with sequence information, served as guides for alignment with adenylate kinase. A model for the structure of the ATP-binding domain of the permease proteins is proposed by analogy to the adenylate kinase structure. The characteristics of several permease mutations and biochemical data lend support to the model.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames G. F. Bacterial periplasmic transport systems: structure, mechanism, and evolution. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:397–425. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.002145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames G. F., Joshi A. K. Energy coupling in bacterial periplasmic permeases. J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4133–4137. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4133-4137.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames G. F., Mimura C. S., Shyamala V. Bacterial periplasmic permeases belong to a family of transport proteins operating from Escherichia coli to human: Traffic ATPases. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1990 Aug;6(4):429–446. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1990.tb04110.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames G. F., Spurich E. N. Protein-protein interaction in transport: periplasmic histidine-binding protein J interacts with P protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1877–1881. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argos P., Hanei M., Garavito R. M. The Chou-Fasman secondary structure prediction method with an extended data base. FEBS Lett. 1978 Sep 1;93(1):19–24. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80795-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop L., Agbayani R., Jr, Ambudkar S. V., Maloney P. C., Ames G. F. Reconstitution of a bacterial periplasmic permease in proteoliposomes and demonstration of ATP hydrolysis concomitant with transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6953–6957. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean D. A., Davidson A. L., Nikaido H. Maltose transport in membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli is linked to ATP hydrolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9134–9138. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreusicke D., Karplus P. A., Schulz G. E. Refined structure of porcine cytosolic adenylate kinase at 2.1 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jan 20;199(2):359–371. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90319-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egner U., Tomasselli A. G., Schulz G. E. Structure of the complex of yeast adenylate kinase with the inhibitor P1,P5-di(adenosine-5'-)pentaphosphate at 2.6 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 5;195(3):649–658. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90188-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry D. C., Kuby S. A., Mildvan A. S. ATP-binding site of adenylate kinase: mechanistic implications of its homology with ras-encoded p21, F1-ATPase, and other nucleotide-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):907–911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. F., Hiles I. D., Whalley K., Jamieson D. J. Nucleotide binding by membrane components of bacterial periplasmic binding protein-dependent transport systems. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):1033–1039. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03735.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobson A. C., Weatherwax R., Ames G. F. ATP-binding sites in the membrane components of histidine permease, a periplasmic transport system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7333–7337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbrook S. R., Kim S. H. Molecular model of the G protein alpha subunit based on the crystal structure of the HRAS protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):1751–1755. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.1751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbrook S. R., Muskal S. M., Kim S. H. Predicting surface exposure of amino acids from protein sequence. Protein Eng. 1990 Aug;3(8):659–665. doi: 10.1093/protein/3.8.659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde S. C., Emsley P., Hartshorn M. J., Mimmack M. M., Gileadi U., Pearce S. R., Gallagher M. P., Gill D. R., Hubbard R. E., Higgins C. F. Structural model of ATP-binding proteins associated with cystic fibrosis, multidrug resistance and bacterial transport. Nature. 1990 Jul 26;346(6282):362–365. doi: 10.1038/346362a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez H. M. A flexible multiple sequence alignment program. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 11;16(5):1683–1691. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.1683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milburn M. V., Tong L., deVos A. M., Brünger A., Yamaizumi Z., Nishimura S., Kim S. H. Molecular switch for signal transduction: structural differences between active and inactive forms of protooncogenic ras proteins. Science. 1990 Feb 23;247(4945):939–945. doi: 10.1126/science.2406906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prossnitz E., Gee A., Ames G. F. Reconstitution of the histidine periplasmic transport system in membrane vesicles. Energy coupling and interaction between the binding protein and the membrane complex. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):5006–5014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian N., Sejnowski T. J. Predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins using neural network models. J Mol Biol. 1988 Aug 20;202(4):865–884. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90564-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlichting I., Almo S. C., Rapp G., Wilson K., Petratos K., Lentfer A., Wittinghofer A., Kabsch W., Pai E. F., Petsko G. A. Time-resolved X-ray crystallographic study of the conformational change in Ha-Ras p21 protein on GTP hydrolysis. Nature. 1990 May 24;345(6273):309–315. doi: 10.1038/345309a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz G. E., Schiltz E., Tomasselli A. G., Frank R., Brune M., Wittinghofer A., Schirmer R. H. Structural relationships in the adenylate kinase family. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Nov 17;161(1):127–132. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10132.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stehle T., Schulz G. E. Three-dimensional structure of the complex of guanylate kinase from yeast with its substrate GMP. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jan 5;211(1):249–254. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90024-G. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vingron M., Argos P. A fast and sensitive multiple sequence alignment algorithm. Comput Appl Biosci. 1989 Apr;5(2):115–121. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/5.2.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Saraste M., Runswick M. J., Gay N. J. Distantly related sequences in the alpha- and beta-subunits of ATP synthase, myosin, kinases and other ATP-requiring enzymes and a common nucleotide binding fold. EMBO J. 1982;1(8):945–951. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01276.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




