Abstract
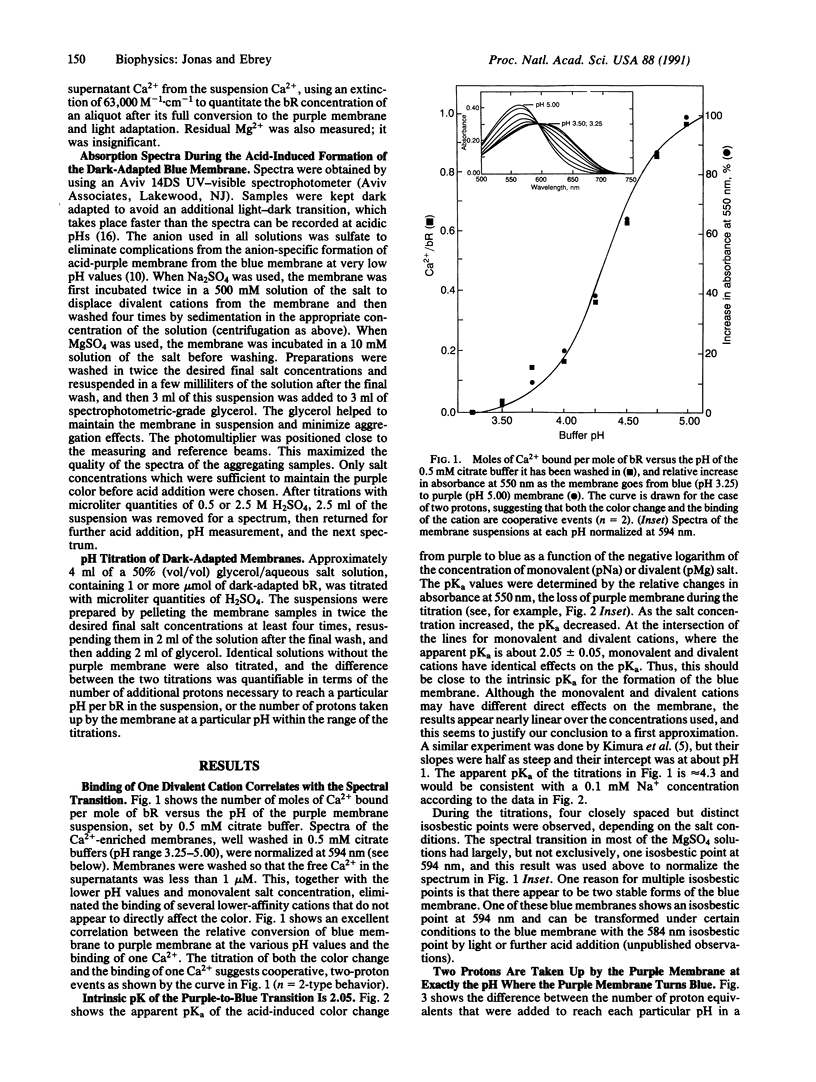
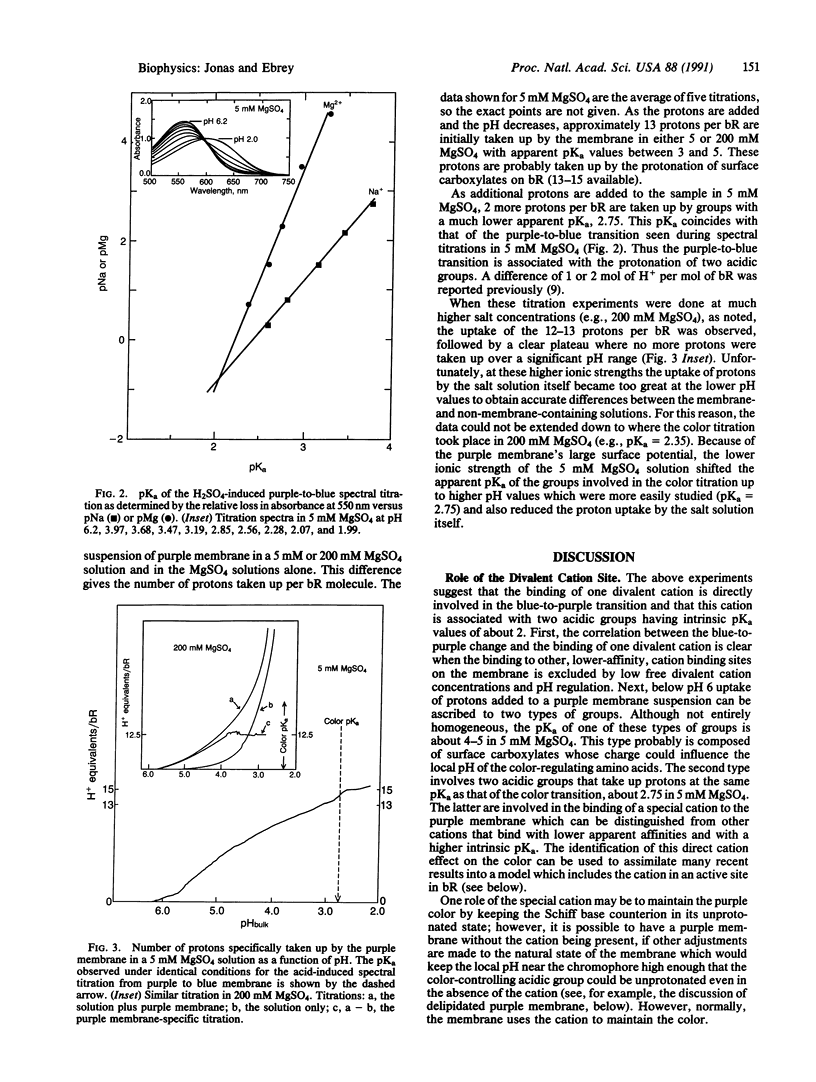
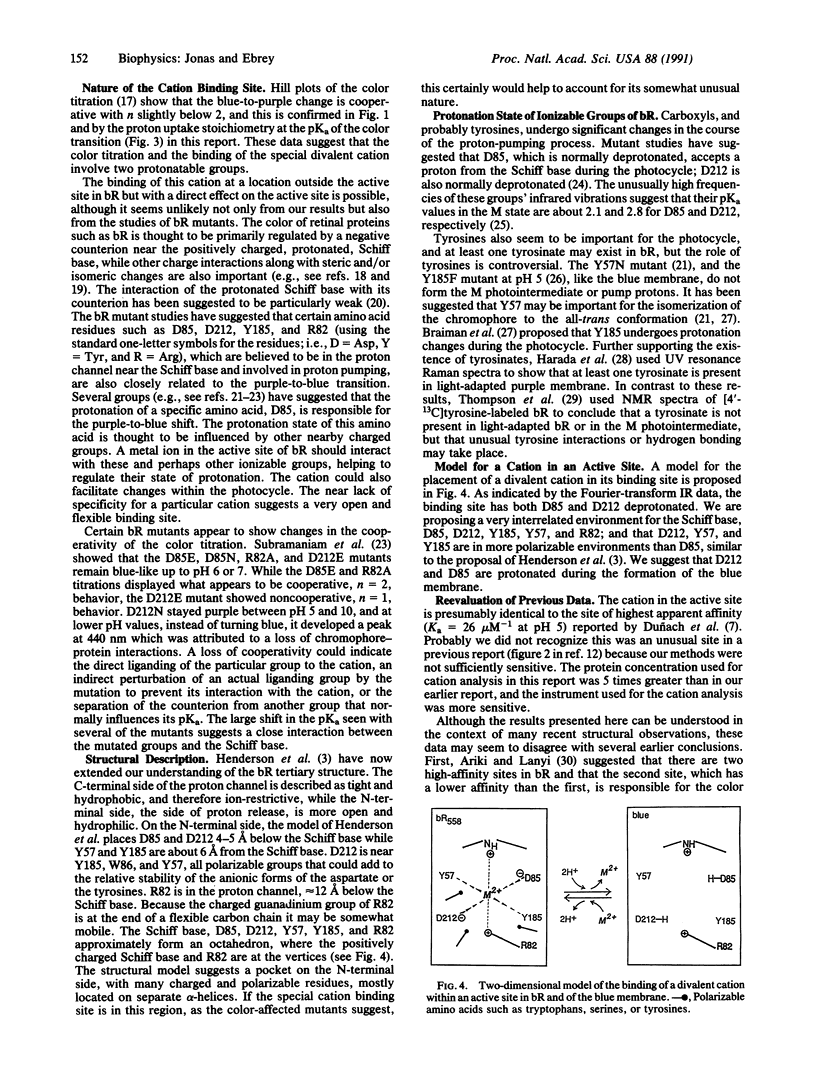
We have characterized a unique divalent cation binding site on bacteriorhodopsin which controls the blue-to-purple transition in the purple membrane of Halobacterium halobium. To identify this site we first showed the correlation between the binding of one Ca2+ per bacteriorhodopsin and the amount of blue membrane converted to purple membrane. When the free Ca2+ was reduced below 1 microM, and the pH was set below 5.0 with 0.5 mM citrate, only binding to this high-affinity site was observed, and we could separate its effect from the effect of other divalent cations binding to the membrane under other conditions. Second, the titration of purple membrane showed that protons are taken up in two distinct steps, about 13 with a pKa of 4-5 and an additional 2 protons with a pKa of 2.75, in 5 mM MgSO4. The latter is identical to the pKa for the purple-to-blue transition in 5 mM MgSO4. Taken together, these observations strongly suggest a direct role for cations in the regulation of the bacteriorhodopsin color under normal conditions. We have also found that the intrinsic pKa for the purple-to-blue transition is about 2.05, suggesting this is the pKa of the group or groups that, when protonated, lead to the blue membrane. Previously published data can now be interpreted to suggest that the cation regulates an active site near the retinal chromophore. A binding site for the divalent cation that includes Asp-212 and interactions with the protonated Schiff base, Asp-85, Tyr-57, Tyr-185, and Arg-82 is proposed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ariki M., Lanyi J. K. Characterization of metal ion-binding sites in bacteriorhodopsin. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8167–8174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braiman M. S., Mogi T., Marti T., Stern L. J., Khorana H. G., Rothschild K. J. Vibrational spectroscopy of bacteriorhodopsin mutants: light-driven proton transport involves protonation changes of aspartic acid residues 85, 96, and 212. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 15;27(23):8516–8520. doi: 10.1021/bi00423a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braiman M. S., Mogi T., Stern L. J., Hackett N. R., Chao B. H., Khorana H. G., Rothschild K. J. Vibrational spectroscopy of bacteriorhodopsin mutants: I. Tyrosine-185 protonates and deprotonates during the photocycle. Proteins. 1988;3(4):219–229. doi: 10.1002/prot.340030403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. H., Chen J. G., Govindjee R., Ebrey T. Cation binding by bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):396–400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. H., Jonas R., Melchiore S., Govindjee R., Ebrey T. G. Mechanism and role of divalent cation binding of bacteriorhodopsin. Biophys J. 1986 Mar;49(3):731–739. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83699-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer U., Oesterhelt D. Chromophore equilibria in bacteriorhodopsin. Biophys J. 1979 Nov;28(2):211–230. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85172-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R., Baldwin J. M., Ceska T. A., Zemlin F., Beckmann E., Downing K. H. Model for the structure of bacteriorhodopsin based on high-resolution electron cryo-microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 20;213(4):899–929. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80271-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas R., Koutalos Y., Ebrey T. G. Purple membrane: surface charge density and the multiple effect of pH and cations. Photochem Photobiol. 1990 Dec;52(6):1163–1177. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1990.tb08455.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khorana H. G. Bacteriorhodopsin, a membrane protein that uses light to translocate protons. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7439–7442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura Y., Ikegami A., Stoeckenius W. Salt and pH-dependent changes of the purple membrane absorption spectrum. Photochem Photobiol. 1984 Nov;40(5):641–646. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1984.tb05353.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowery P. C., Lozier R. H., Chae Q., Tseng Y. W., Taylor M., Stoeckenius W. Effect of acid pH on the absorption spectra and photoreactions of bacteriorhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1979 Sep 18;18(19):4100–4107. doi: 10.1021/bi00586a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muccio D. D., Cassim J. Y. Interpretations of the effects of pH on the spectra of purple membrane. J Mol Biol. 1979 Dec 15;135(3):595–609. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90166-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Stoeckenius W. Rhodopsin-like protein from the purple membrane of Halobacterium halobium. Nat New Biol. 1971 Sep 29;233(39):149–152. doi: 10.1038/newbio233149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Tittor J. Two pumps, one principle: light-driven ion transport in halobacteria. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Feb;14(2):57–61. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90044-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno K., Takeuchi Y., Yoshida M. Effect of light-adaptation on the photoreaction of bacteriorhodopsin from Halobacterium halobium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Dec 23;462(3):575–582. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(77)90102-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto H., Marti T., Holz M., Mogi T., Stern L. J., Engel F., Khorana H. G., Heyn M. P. Substitution of amino acids Asp-85, Asp-212, and Arg-82 in bacteriorhodopsin affects the proton release phase of the pump and the pK of the Schiff base. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1018–1022. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renthal R., Wallace B. Carbodiimides inhibit the acid-induced purple-to-blue transition of bacteriorhodopsin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Oct 3;592(3):621–625. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(80)90105-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soppa J., Otomo J., Straub J., Tittor J., Meessen S., Oesterhelt D. Bacteriorhodopsin mutants of Halobacterium sp. GRB. II. Characterization of mutants. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):13049–13056. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. L., McCain D. A., Nakanishi K., Okabe M., Shimizu N., Rodman H., Honig B., Bogomolni R. A. Chromophore/protein interaction in bacterial sensory rhodopsin and bacteriorhodopsin. Biophys J. 1986 Feb;49(2):479–483. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83657-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramaniam S., Marti T., Khorana H. G. Protonation state of Asp (Glu)-85 regulates the purple-to-blue transition in bacteriorhodopsin mutants Arg-82----Ala and Asp-85----Glu: the blue form is inactive in proton translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1013–1017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szundi I., Stoeckenius W. Effect of lipid surface charges on the purple-to-blue transition of bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3681–3684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warshel A., Ottolenighi M. Kinetic and spectroscopic effects of protein-chromophore electrostatic interactions in bacteriorhodopsin. Photochem Photobiol. 1979 Aug;30(2):291–293. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1979.tb07149.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groot H. J., Harbison G. S., Herzfeld J., Griffin R. G. Nuclear magnetic resonance study of the Schiff base in bacteriorhodopsin: counterion effects on the 15N shift anisotropy. Biochemistry. 1989 Apr 18;28(8):3346–3353. doi: 10.1021/bi00434a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



