Abstract
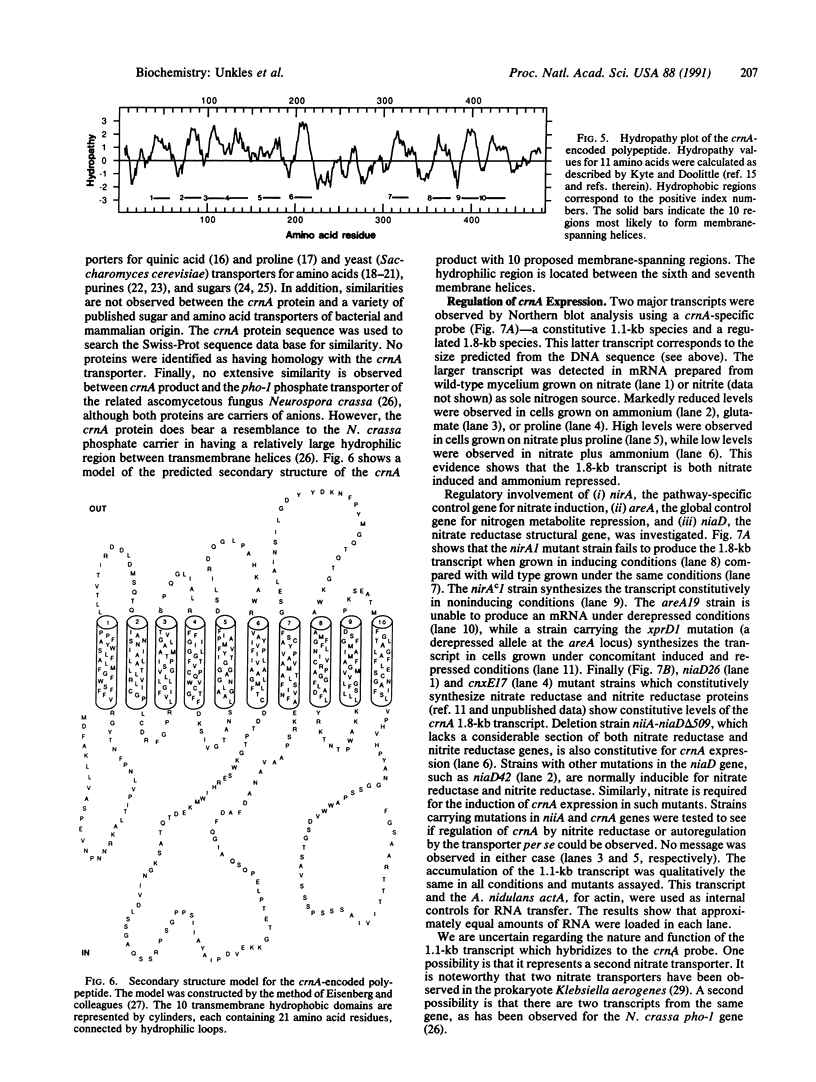
The nucleotide sequence of the Aspergillus nidulans crnA gene for the transport of the anion nitrate has been determined. The crnA gene specifies a predicted polypeptide of 483 amino acids (molecular weight 51,769). A hydropathy plot suggests that this polypeptide has 10 membrane-spanning helices with an extensive hydrophilic region between helices six and seven. No striking homology was observed between the crnA protein and other reported membrane proteins of either prokaryotic or eukaryotic organisms, indicating that the crnA transporter may represent another class of membrane protein. Northern blotting results with wild-type cells show that (i) control of crnA expression is subject to nitrate (and nitrite) induction as well as nitrogen metabolite repression and (ii) regulation of the crnA gene is exerted at the level of mRNA accumulation, most likely at transcription, in response to the nitrogen source in the growth medium. Furthermore, similar studies with mutants of nirA and areA control genes and the niaD nitrate reductase structural gene show that crnA expression is mediated by the products of nirA (nitrate induction control gene), areA (nitrogen metabolite repression control gene), and niaD (involved in autoregulation of nitrate reductase).
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arst H. N., Jr, Cove D. J. Nitrogen metabolite repression in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Nov 2;126(2):111–141. doi: 10.1007/BF00330988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownlee A. G., Arst H. N., Jr Nitrate uptake in Aspergillus nidulans and involvement of the third gene of the nitrate assimilation gene cluster. J Bacteriol. 1983 Sep;155(3):1138–1146. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.3.1138-1146.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cove D. J. Chlorate toxicity in Aspergillus nidulans. Studies of mutants altered in nitrate assimilation. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Jul 23;146(2):147–159. doi: 10.1007/BF00268083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cove D. J. Genetic studies of nitrate assimilation in Aspergillus nidulans. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 1979 Aug;54(3):291–327. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185x.1979.tb01014.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg D., Schwarz E., Komaromy M., Wall R. Analysis of membrane and surface protein sequences with the hydrophobic moment plot. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 15;179(1):125–142. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90309-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidel S., Doonan J. H., Morris N. R. Aspergillus nidulans contains a single actin gene which has unique intron locations and encodes a gamma-actin. Gene. 1988 Oct 30;70(2):283–293. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90200-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann E., Rapoport T. A., Lodish H. F. Predicting the orientation of eukaryotic membrane-spanning proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5786–5790. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins A. R., Lamb H. K., Smith M., Keyte J. W., Roberts C. F. Molecular organisation of the quinic acid utilization (QUT) gene cluster in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Oct;214(2):224–231. doi: 10.1007/BF00337715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann W. Molecular characterization of the CAN1 locus in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. A transmembrane protein without N-terminal hydrophobic signal sequence. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 25;260(21):11831–11837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes M. J. Studies on the role of the areA gene in the regulation of nitrogen catabolism in Aspergillus nidulans. Aust J Biol Sci. 1975 Jun;28(3):301–313. doi: 10.1071/bi9750301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnstone I. L., McCabe P. C., Greaves P., Gurr S. J., Cole G. E., Brow M. A., Unkles S. E., Clutterbuck A. J., Kinghorn J. R., Innis M. A. Isolation and characterisation of the crnA-niiA-niaD gene cluster for nitrate assimilation in Aspergillus nidulans. Gene. 1990 Jun 15;90(2):181–192. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90178-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jund R., Weber E., Chevallier M. R. Primary structure of the uracil transport protein of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jan 15;171(1-2):417–424. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13806.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacCabe A. P., Riach M. B., Unkles S. E., Kinghorn J. R. The Aspergillus nidulans npeA locus consists of three contiguous genes required for penicillin biosynthesis. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):279–287. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08106.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann B. J., Bowman B. J., Grotelueschen J., Metzenberg R. L. Nucleotide sequence of pho-4+, encoding a phosphate-repressible phosphate permease of Neurospora crassa. Gene. 1989 Nov 30;83(2):281–289. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90114-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nehlin J. O., Carlberg M., Ronne H. Yeast galactose permease is related to yeast and mammalian glucose transporters. Gene. 1989 Dec 28;85(2):313–319. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90423-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omata T., Ohmori M., Arai N., Ogawa T. Genetically engineered mutant of the cyanobacterium Synechococcus PCC 7942 defective in nitrate transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6612–6616. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sophianopoulou V., Scazzocchio C. The proline transport protein of Aspergillus nidulans is very similar to amino acid transporters of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Jun;3(6):705–714. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00219.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka J., Fink G. R. The histidine permease gene (HIP1) of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1985;38(1-3):205–214. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90219-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer J. R., Huffaker R. C. Kinetic evaluation, using 13N, reveals two assimilatory nitrate transport systems in Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jan;149(1):198–202. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.1.198-202.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenbol M., Jauniaux J. C., Grenson M. Nucleotide sequence of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae PUT4 proline-permease-encoding gene: similarities between CAN1, HIP1 and PUT4 permeases. Gene. 1989 Nov 15;83(1):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90413-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber E., Chevallier M. R., Jund R. Evolutionary relationship and secondary structure predictions in four transport proteins of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Mol Evol. 1988;27(4):341–350. doi: 10.1007/BF02101197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber E., Rodriguez C., Chevallier M. R., Jund R. The purine-cytosine permease gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: primary structure and deduced protein sequence of the FCY2 gene product. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Apr;4(4):585–596. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00627.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao B., Sollitti P., Marmur J. Primary structure of the maltose-permease-encoding gene of Saccharomyces carlsbergensis. Gene. 1989 Jul 15;79(2):189–197. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90201-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]