Abstract
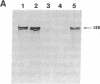
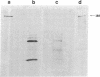
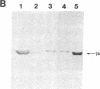
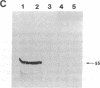
Antibodies previously used for immunofluorescence localization of a myosin heavy chain-like polypeptide to the nuclear envelope in higher eukaryotic cells crossreact with both muscle and nonmuscle isoforms of Drosophila myosin heavy chain. Analyses of Drosophila tissue culture cells and premyogenic embryos suggest that it is the nonmuscle isoform that is associated with the nuclear envelope. Further immunofluorescence and immunoelectron microscopy indicate that this polypeptide is associated with nuclear pore complexes. These data support the hypothesis put forward previously that myosin or myosin-like molecules play a role in pore complex architecture.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam S. A., Lobl T. J., Mitchell M. A., Gerace L. Identification of specific binding proteins for a nuclear location sequence. Nature. 1989 Jan 19;337(6204):276–279. doi: 10.1038/337276a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allis C. D., Waring G. L., Mahowald A. P. Mass isolation of pole cells from Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1977 Apr;56(2):372–381. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90277-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barros C., Berrios M. Is the activated spermatozoon really capacitated? J Exp Zool. 1977 Jul;201(1):65–71. doi: 10.1002/jez.1402010108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berrios M. A new design of immunofluorescence chamber. Med Lab Sci. 1989 Jul;46(3):276–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berrios M., Blobel G., Fisher P. A. Characterization of an ATPase/dATPase activity associated with the Drosophila nuclear matrix-pore complex-lamina fraction. Identification of the putative enzyme polypeptide by direct ultraviolet photoaffinity labeling. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 10;258(7):4548–4555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berrios M., Fisher P. A. A myosin heavy-chain-like polypeptide is associated with the nuclear envelope in higher eukaryotic cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;103(3):711–724. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.3.711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K., Havel C. M., Watson J. A. Isoprene synthesis in isolated embryonic Drosophila cells. II. Regulation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase activity. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):8512–8518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chardonnet Y., Dales S. Early events in the interaction of adenoviruses with HeLa cells. 3. Relationship between an ATPase activity in nuclear envelopes and transfer of core material: a hypothesis. Virology. 1972 May;48(2):342–359. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90045-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L. I., Blobel G. Identification and characterization of a nuclear pore complex protein. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):699–709. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90784-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Featherstone C., Darby M. K., Gerace L. A monoclonal antibody against the nuclear pore complex inhibits nucleocytoplasmic transport of protein and RNA in vivo. J Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;107(4):1289–1297. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.4.1289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay D. R., Newmeyer D. D., Price T. M., Forbes D. J. Inhibition of in vitro nuclear transport by a lectin that binds to nuclear pores. J Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;104(2):189–200. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.2.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher P. A., Berrios M., Blobel G. Isolation and characterization of a proteinaceous subnuclear fraction composed of nuclear matrix, peripheral lamina, and nuclear pore complexes from embryos of Drosophila melanogaster. J Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;92(3):674–686. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.3.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher P. A., Smith D. E. Affinity purification of antibodies using antigens immobilized on solid supports. Biochem Soc Trans. 1988 Apr;16(2):134–138. doi: 10.1042/bst0160134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiehart D. P., Feghali R. Cytoplasmic myosin from Drosophila melanogaster. J Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;103(4):1517–1525. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.4.1517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiehart D. P., Lutz M. S., Chan D., Ketchum A. S., Laymon R. A., Nguyen B., Goldstein L. S. Identification of the gene for fly non-muscle myosin heavy chain: Drosophila myosin heavy chains are encoded by a gene family. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):913–922. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03452.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R. L., Afzelius B. A. Nuclear membrane hydrolysis of adenosine triphosphate. Nature. 1966 Nov 5;212(5062):609–609. doi: 10.1038/212609a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin L., Fisher P. A. Immunoaffinity purification and functional characterization of interphase and meiotic Drosophila nuclear lamin isoforms. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12596–12601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConnell M., Whalen A. M., Smith D. E., Fisher P. A. Heat shock-induced changes in the structural stability of proteinaceous karyoskeletal elements in vitro and morphological effects in situ. J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1087–1098. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newmeyer D. D., Finlay D. R., Forbes D. J. In vitro transport of a fluorescent nuclear protein and exclusion of non-nuclear proteins. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2091–2102. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newmeyer D. D., Forbes D. J. Nuclear import can be separated into distinct steps in vitro: nuclear pore binding and translocation. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):641–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90402-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newmeyer D. D., Lucocq J. M., Bürglin T. R., De Robertis E. M. Assembly in vitro of nuclei active in nuclear protein transport: ATP is required for nucleoplasmin accumulation. EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):501–510. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04239.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson W. D., Mills A. D., Dilworth S. M., Laskey R. A., Dingwall C. Nuclear protein migration involves two steps: rapid binding at the nuclear envelope followed by slower translocation through nuclear pores. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):655–664. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90403-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. E., Fisher P. A. Identification, developmental regulation, and response to heat shock of two antigenically related forms of a major nuclear envelope protein in Drosophila embryos: application of an improved method for affinity purification of antibodies using polypeptides immobilized on nitrocellulose blots. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 1):20–28. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. E., Gruenbaum Y., Berrios M., Fisher P. A. Biosynthesis and interconversion of Drosophila nuclear lamin isoforms during normal growth and in response to heat shock. J Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;105(2):771–790. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.2.771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snow C. M., Senior A., Gerace L. Monoclonal antibodies identify a group of nuclear pore complex glycoproteins. J Cell Biol. 1987 May;104(5):1143–1156. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.5.1143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wozniak R. W., Bartnik E., Blobel G. Primary structure analysis of an integral membrane glycoprotein of the nuclear pore. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;108(6):2083–2092. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.6.2083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasuzumi G., Nakai Y., Tsubo I., Yasuda M., Sugioka T. The fine structure of nuclei as revealed by electron microscopy. IV. The intranuclear inclusion formation in Leydig cells of aging human testes. Exp Cell Res. 1967 Feb;45(2):261–276. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(67)90178-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasuzumi G., Tsubo I. The fine structure of nuclei as revealed by electron microscopy. 3. Adenosine triphosphatase activity in the pores of nuclear envelope of mouse choroid plexus epithelial cells. Exp Cell Res. 1966 Sep;43(2):281–292. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(66)90055-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]