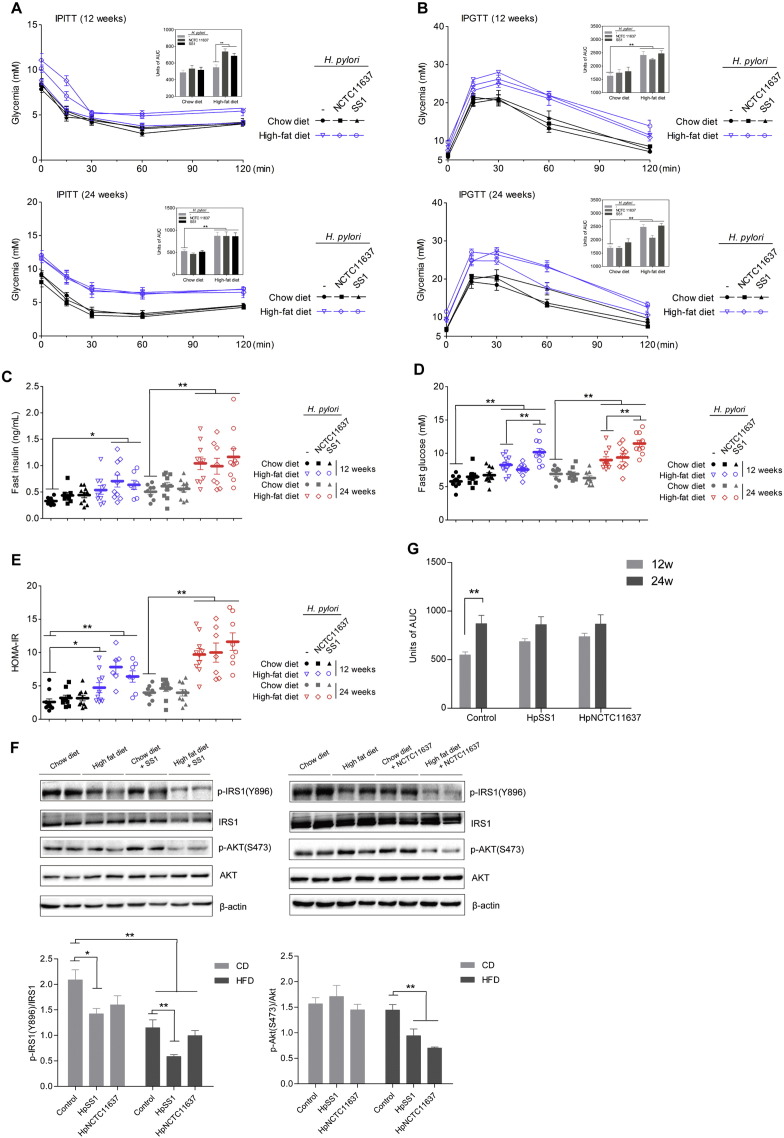
Fig. 2.
H. pylori infection promotes diet-induced IR and hyperinsulinaemia at the early stage. The intraperitoneal insulin and glucose tolerance tests were performed at different time points during the treatment (A, B). Mice were fasted overnight for plasma insulin (C), blood glucose (D) determination and the HOMA-IR index was calculated (E). Immunoblots of phosphorylated insulin receptor substrate 1 (p-IRS1) (Tyr896) and phosphorylated Akt (p-Akt) (Ser473) in the chow or HFD groups with or without H. pylori infection (F). Area under the curve for insulin tolerance tests after 12 and 24 weeks of HFD consumption in H. pylori-infected and non-infected groups (G). Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM. ⁎p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.