Supplement Fig. 4.
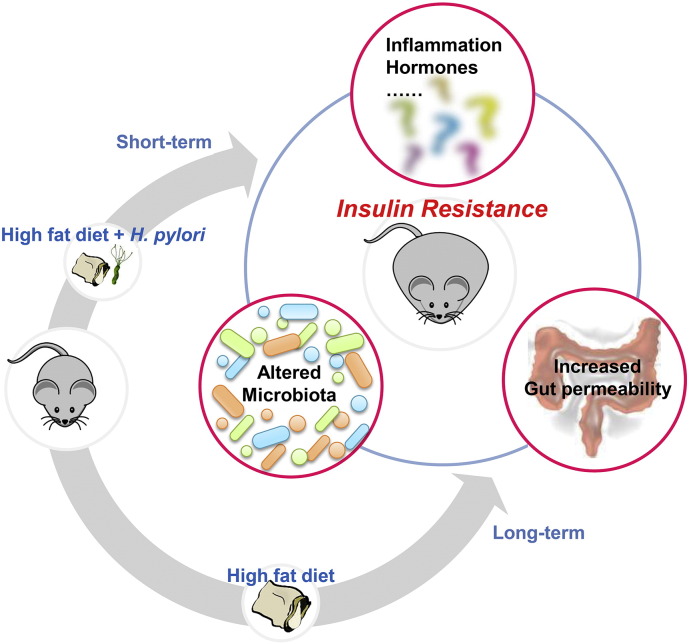
H. pylori infection aggravates HFD-induced IR in association with the gut microbiota. H. pylori-infected mice after short-term HFD displayed more severe metabolic syndrome compared to the HFD controls, the extent of which was comparable to the effect of long-term HFD. Meanwhile, there is a dynamic alteration of gut microbiota that is consistent with the overall changes of metabolic phenotype. We speculate that there may be an interaction of H. pylori, diet and gut microbiota which accelerates the development of IR and the possible mechanisms include impaired intestinal integrity, metabolic inflammation and the abnormal secretion of metabolic hormones.