Abstract
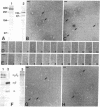
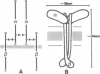
Electrophoretically pure and functionally intact human placental insulin receptor was studied by electron microscopy with negative-staining techniques. The quaternary structure of the detergent-solubilized receptor was determined. The receptor had the shape of a letter T approximately 24 nm in height and 18 nm in width with a thickness of the stem and the crossbar of 3-4 nm. No consistent change in ultrastructure of the receptor could be detected after the addition of insulin alone or insulin and Mn2+/Mg2+/ATP. After partial reduction of the alpha 2 beta 2 heterotetrameric receptor into alpha beta heterodimers, the electron micrographs showed a clear reduction in average size of the molecule with disappearance of the T profiles characteristic of the alpha 2 beta 2 heterotetramers. By incubation of the heterodimers in a phosphorylation medium containing insulin, a reassociation to molecules with molecular weights of the alpha 2 beta 2 heterotetramer took place judged from SDS/PAGE. Electron microscopy showed that the molecule formed larger aggregates, and only a few solitary T-shaped copies were seen.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Böni-Schnetzler M., Scott W., Waugh S. M., DiBella E., Pilch P. F. The insulin receptor. Structural basis for high affinity ligand binding. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):8395–8401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P. The nature and regulation of the insulin receptor: structure and function. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:357–381. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.002041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebina Y., Ellis L., Jarnagin K., Edery M., Graf L., Clauser E., Ou J. H., Masiarz F., Kan Y. W., Goldfine I. D. The human insulin receptor cDNA: the structural basis for hormone-activated transmembrane signalling. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):747–758. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90334-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita-Yamaguchi Y., Choi S., Sakamoto Y., Itakura K. Purification of insulin receptor with full binding activity. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):5045–5049. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gammeltoft S., Van Obberghen E. Protein kinase activity of the insulin receptor. Biochem J. 1986 Apr 1;235(1):1–11. doi: 10.1042/bj2350001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfine I. D. The insulin receptor: molecular biology and transmembrane signaling. Endocr Rev. 1987 Aug;8(3):235–255. doi: 10.1210/edrv-8-3-235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. D., Wong M. L., Rutter W. J. Properties of the insulin receptor ectodomain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7516–7520. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopp F., Meyer H. E., Reinauer H. Insulin receptor protein rendered visible in triton X-114 membranes. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1985 Jul;366(7):695–698. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1985.366.2.695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronnett G. V., Knutson V. P., Kohanski R. A., Simpson T. L., Lane M. D. Role of glycosylation in the processing of newly translated insulin proreceptor in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4566–4575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Bell J. R., Chen E. Y., Herrera R., Petruzzelli L. M., Dull T. J., Gray A., Coussens L., Liao Y. C., Tsubokawa M. Human insulin receptor and its relationship to the tyrosine kinase family of oncogenes. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):756–761. doi: 10.1038/313756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vretblad P. Purification of lectins by biospecific affinity chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 May 20;434(1):169–176. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(76)90047-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilden P. A., Morrison B. D., Pessin J. E. Relationship between insulin receptor subunit association and protein kinase activation: insulin-dependent covalent and Mn/MgATP-dependent noncovalent association of alpha beta heterodimeric insulin receptors into an alpha 2 beta 2 heterotetrameric state. Biochemistry. 1989 Jan 24;28(2):785–792. doi: 10.1021/bi00428a056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]