Correction to: Molecular Psychiatry 21, 749–757; doi:10.1038/mp.2016.49
The GWAS of neuroticism conducted within the Queensland Institute of Medical Research (QIMR) Berghofer Medical Research Institute cohort did not include covariates of age, sex, genotyping batch and 10 principal components. Adding these covariates does not substantially change the pattern of results within the meta-analysis, but P-values for the nine reported loci have changed slightly (please see revised Figure 2, Table 2A and Table 2B). Of note is that, the P-value for the index SNP rs490647 on chromosome one is now 5.0 × 10−8 (previously 3.8 × 10−8) and the P-value for the index SNP rs62353264 on chromosome four is now 5.5 × 10−8 (previously 3.7 × 10−8).
Figure 2.
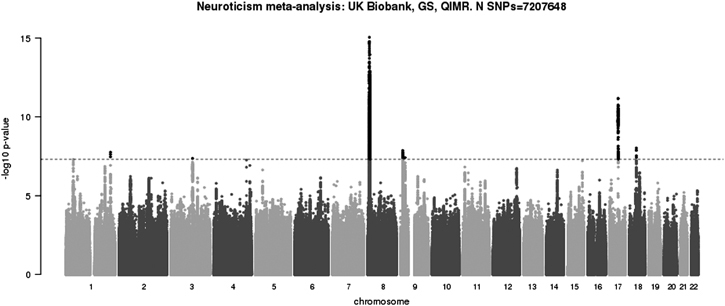
Table 2A.
Genome-wide significant index SNPs. Combined meta-analysis of UK Biobank, GS:SFHS and QIMR data sets
| Index SNP | Chr | Position | A1/A2 | Freq | BETA (SE) | P | Direction (UKBB-GS-QMIR) | Heter P | Associated region | Genes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs490647 | 1 | 37 242 743 | A/G | 0.227 | 0.091 (0.017) | 5.0 × 10−8 | +++ | 0.720 | 37 219 429–37 261 085 | GRIK3 |
| rs4653663 | 1 | 225 927 218 | A/T | 0.255 | 0.091 (0.016) | 1.8 × 10−8 | +++ | 0.095 | 225 899 639–225 947 638 | ENAH, SRP9 |
| rs12637928 | 3 | 110 184 749 | A/T | 0.490 | −0.077 (0.014) | 4.3 × 10−8 | −−− | 0.695 | 110 103 126–110 299 632 | PVRL3 (579KB distal) |
| rs62353264 | 4 | 166 085 805 | A/T | 0.986 | −0.330 (0.061) | 5.5 × 10−8 | −−+ | 0.158 | 166 063 134–166 198 156 | TMEM192, KLHL2, MSMO1 |
| rs12682352 | 8 | 8 646 246 | T/C | 0.525 | 0.115 (0.014) | 9.0 × 10−15 | +++ | 0.433 | 8 301 794–10 831 868 | More than 10 genes |
| rs12378446 | 9 | 11 369 213 | T/C | 0.791 | 0.099 (0.017) | 9.4 × 10−9 | +++ | 0.831 | 11 131 371–11 880 898 | PTRD (650KB distal) |
| rs4977844 | 9 | 23 295 899 | C/G | 0.358 | 0.083 (0.015) | 1.4 × 10−8 | +++ | 0.318 | 23 291 526–23 340 616 | ELAVL2 |
| rs111433752 | 17 | 43 857 989 | T/G | 0.790 | −0.121 (0.018) | 6.7 × 10−12 | −−− | 0.053 | 43 463 493–44 865 603 | More than 10 genes |
| rs1187264 | 18 | 35 289 647 | C/G | 0.136 | 0.118 (0.021) | 9.5 × 10−9 | +++ | 0.515 | 35 287 090–35 413 260 | CELF4 |
Abbreviations: Chr, chromosome; Freq, frequency; GS:SFHS, Generation Scotland: Scottish Family Health Study; Heter, heterogeneity; QIMR, Queensland Institute of Medical Research (QIMR) Berghofer Medical Research Institute; SNP, single-nucleotide polymorphism. Shown are linkage disequilibrium (LD)- independent genome-wide significant SNP associations for neuroticism (sorted by genomic position according to UCSC hg19/NCBI Build 37). Column A1/A2 has the SNP alleles, with the first allele (A1) the reference allele for the frequency and β columns. Frequency of allele 1 is calculated in the UK Biobank data set. Chr and Position denote the location of the index SNP. β is linear regression coefficient for allele1, and s.e. is the standard error for β. Associated region indicates range positions of SNPs with r2>0.6 with the index and any other genome-wide association study (GWAS) significant SNP at the locus. The final column indicates protein-coding reference sequence genes at the associated loci (see region plots in Supplementary Information) or where there are no genes at the associated locus, the nearest gene if <1 Mb from the locus.
Table 2B.
Association results for genome-wide significant index SNPs in UK Biobank, GS:SFHS and QIMR datasets separately
| Index SNP | Chr | Position | UK Biobank | GS:SFHS | QIMR | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BETA | s.e. | P | FRQ | BETA | s.e. | P | FRQ | BETA | s.e. | P | FRQ | |||
| rs490647 | 1 | 37 242 743 | 0.088 | 0.018 | 7.79 × 10−7 | 0.227 | 0.073 | 0.065 | 0.257 | 0.234 | 0.139 | 0.065 | 0.031 | 0.243 |
| rs4653663 | 1 | 225 927 218 | 0.079 | 0.017 | 5.12 × 10−6 | 0.255 | 0.117 | 0.062 | 0.060 | 0.260 | 0.217 | 0.062 | 0.0005 | 0.259 |
| rs12637928 | 3 | 110 184 749 | −0.074 | 0.015 | 8.76 × 10−7 | 0.490 | −0.073 | 0.055 | 0.186 | 0.506 | −0.123 | 0.056 | 0.028 | 0.491 |
| rs62353264 | 4 | 166 085 805 | −0.335 | 0.065 | 2.36 × 10−7 | 0.986 | −0.547 | 0.219 | 0.012 | 0.984 | 0.147 | 0.291 | 0.612 | 0.988 |
| rs12682352 | 8 | 8 646 246 | 0.120 | 0.015 | 1.02 × 10−15 | 0.525 | 0.0005 | 0.111 | 0.997 | 0.539 | 0.076 | 0.055 | 0.169 | 0.528 |
| rs12378446 | 9 | 11 369 213 | 0.100 | 0.019 | 9.69 × 10−8 | 0.791 | 0.123 | 0.068 | 0.071 | 0.793 | 0.065 | 0.068 | 0.342 | 0.784 |
| rs4977844 | 9 | 23 295 899 | 0.083 | 0.016 | 2.02 × 10−7 | 0.358 | 0.136 | 0.058 | 0.019 | 0.351 | 0.012 | 0.059 | 0.837 | 0.352 |
| rs111433752 | 17 | 43 857 989 | −0.109 | 0.019 | 5.19 × 10−9 | 0.790 | −0.143 | 0.073 | 0.050 | 0.806 | −0.301 | 0.078 | 0.0001 | 0.788 |
| rs1187264 | 18 | 35 289 647 | 0.123 | 0.022 | 2.36 × 10−8 | 0.136 | 0.029 | 0.081 | 0.720 | 0.136 | 0.139 | 0.081 | 0.086 | 0.132 |
Abbreviations: Chr, chromosome; FRQ, frequency; GS:SFHS, Generation Scotland: Scottish Family Health Study; QIMR, Queensland Institute of Medical Research (QIMR) Berghofer Medical Research Institute; SNP, single-nucleotide polymorphism.
PowerPoint slides
Footnotes
The online version of the original article can be found at 10.1038/mp.2016.49


