Abstract
IMPORTANCE
Frailty results in decreased physiological reserve and diminished resistance to stressors; approximately 10% of those in the elderly population (those ≥65 years) are frail. High-intensity treatments and complications after hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) injure normal tissues and may increase the risk of frailty even among nongeriatric HCT patients.
OBJECTIVE
To determine the prevalence of frailty in young adult HCT patients (18- to 64-year-olds) and siblings; and the impact of frailty on subsequent mortality in HCT survivors.
DESIGN, SETTING, AND PARTICIPANTS
This cohort study, conducted in August 2015 examined 998 HCT survivors, who underwent transplant procedures between 1974 and 1998, who have survived at least 2 years after HCT, and 297 frequency-matched siblings. The study was performed at City of Hope or University of Minnesota with participants completing surveys at home or in the clinic. Hematopoietic cell transplantation survivors and siblings participating in the Bone Marrow Transplant Survivor Study (BMTSS) completed a frailty survey between February 13, 1999 and June 15, 2005 (median time since HCT: 7.9 years); HCT survivors were followed for subsequent mortality (median: 10.3 years from survey).
MAIN OUTCOMES AND MEASURES
Prevalence and predictors of frailty; impact of frailty on subsequent mortality in HCT survivors. Frailty phenotype defined as exhibiting 3 or more of the following characteristics: clinically underweight, exhaustion, low energy expenditure, slow walking speed, and muscle weakness. The national Death Index, Social Security Death Index and medical records were used for mortality assessment as of December 21, 2011.
RESULTS
The 998 HCT survivors were a mean (SD) of 42.5 (11.6) years of age, and the 297 matched siblings were 43.8 (10.9) years of age. The prevalence of frailty among young adult HCT patients exceeded 8%. The HCT survivors were 8.4 times more likely to be frail than their siblings (95%CI, 2.0–34.5; P = .003). Among HCT recipients, allogeneic HCT recipients with chronic graft-vs-host disease (GvHD) were at increased risk of frailty compared with autologous HCT (OR,15.02; 95%CI, 6.6–34.3; P < .001); resolved chronic GvHD (OR, 2.7; 95% CI, 1.1–6.9; P = .04). Cumulative incidence of subsequent all-cause mortality was 39.3%and 14.7%at 10 years for HCT recipients with and without frailty, respectively (P < .001). Frailty was associated with a 2.76-fold (95%CI, 1.7–4.4; P < .001) increased risk of subsequent mortality after adjusting for relevant prognosticators.
CONCLUSIONS AND RELEVANCE
The prevalence of frailty among young-adult HCT survivors approaches that seen in the elderly general population. Frail HCT survivors are at increased risk of subsequent mortality when compared with nonfrail survivors. This study identifies vulnerable populations needing close monitoring to anticipate and manage morbidity and prevent mortality.
Frailty is a phenotype characterized by self-reported exhaustion, weakness, low physical activity, slow walking speed, and unintentional weight loss.1 Frailty is observed most commonly in older adults; approximately 10% of individuals in the general population, 65 years or older, are frail.2 Frailty results in decreased physiological reserve and diminished resistance to stressors.3 Importantly, frailty increases the risk for adverse health outcomes. Often preceding the onset of chronic disease, it is a predictor of early mortality.1,4
Hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) is an established curative option for hematological malignant diseases. Hematopoietic cell transplantation recipients are exposed to high-intensity chemotherapy, radiation, and immunosuppressive agents, undergoing cumulative exposures from before HCT (for management of primary disease), during HCT (conditioning regimens), until after HCT (management of chronic graft vs host disease [GvHD] in allogeneic HCT recipients). These high-intensity lifetime therapeutic exposures can potentially injure normal tissues. Advances in transplantation techniques and supportive care strategies have resulted in substantial improvement in survival rates for individuals with hematological malignant diseases. More than 70% of those who survive the first 2 years after HCT are expected to become longterm survivors.5–8 Unfortunately, cure or control of underlying disease is not accompanied by full restoration of health. Hematopoietic cell transplantation survivors are at increased risk for treatment-related chronic health conditions including subsequent malignant neoplasms, cardiovascular diseases,7 adverse psychological outcomes,9 functional impairment, and activity limitation.10 High-intensity therapeutic exposures, chronic GvHD, and chronic health conditions after HCT serve as substantial stressors, increasing the risk of frailty even among nonelderly HCT survivors. We tested the hypothesis that nonelderly long-term HCT survivors (patients who have survived ≥2 years post-HCT) would be at a higher risk of frailty compared with a sibling comparison group and that frail HCT patients would be at a higher risk of subsequent mortality compared with nonfrail HCT patients.
Methods
Study Population
Study participants were drawn from the Bone Marrow Transplant Survivor Study (BMTSS), a retrospective cohort study of patients who received HCT at City of Hope (COH), Duarte, California, or University of Minnesota (UMN), Minneapolis, between 1974 and 1998 for a hematologic malignant diseases, or severe a plastic anemia (SAA), and survived at least 2 years posttransplantation, irrespective of current life status.10,11 We restricted eligibility for the current study to those who were alive between the ages of 18 and 64 years at study participation. The Human Subjects Committee at the participating institutions approved the study; written informed consent was provided according to the Declaration of Helsinki. Participants were not compensated for their participation.
Key Points.
Question
What is the prevalence of frailty in young adult (18–64 years) hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) survivors, and what is the impact of frailty on subsequent mortality?
Findings
In this study of 998 young adult HCT patients and their siblings, the prevalence of frailty was 8.4%(significantly higher than that of the siblings), approaching that seen in the elderly population (10%). Frail HCT patients had a higher risk of subsequent mortality than their siblings.
Meaning
Premature aging and frailty imposes a substantial increased risk for subsequent mortality in nonelderly HCT survivors (patients who have survived ≥2 years post-HCT) patients.
Of 1603 eligible subjects, 1438 (90%) were successfully contacted, and of those contacted, 998 (69%) participated in the study. Compared with nonparticipants, participants were older at HCT (mean age: 34 vs 29 years; P < .001), with a shorter follow- up after HCT (mean: 8.7 vs 10.5 years; P < .001). Non-Hispanic whites (803 of 1252 [64%] vs 195 of 351 [56%]), females (456 of 685 participants [67%] vs 542 of 918 nonparticipants [59%]), and autologous HCT recipients (436 of 665 [66%] vs 562 of 938 [60%]; P = .02) were more likely to participate. Participation rate did not differ by risk of relapse at HCT, or by transplanting institution, or primary diagnosis (except patients with SAA, who were less likely to participate). Hematopoietic cell transplantation patients participating in the study were asked to provide a list of all siblings interested in participating in the study. A stratified sample of siblings was invited to participate, based on the demographic distribution of HCT survivors (age at study participation [categorized into 5-year age groups], sex, race/ethnicity [non-Hispanic whites, Hispanics, African Americans, Asians], and transplanting site [City of Hope or University of Minnesota]). A total of 297 frequency-matched siblings between the ages of 18 and 64 years participated in this study.
The HCT survivors and siblings completed the BMTSS questionnaire between February 13, 1999, and June 15, 2005. This questionnaire included a self-report of physical health conditions, sociodemographic characteristics, health-risk behaviors, physical activity in the past 7 days, and whether health conditions limited their activities.7,9 Hematopoietic cell transplantation survivors also reported diagnosis and the extent of chronic GvHD and presence of active (within 12 months of study participation) chronic GvHD. Reliability and validity of the BMTSS questionnaire has been tested, and responses indicate that survivors were able to report the occurrence of adverse medical conditions with accuracy.12 The data were analyzed in August 2015.
Frailty Phenotype
As reported previously,13 the frailty phenotype was constructed from the responses provided by the HCT survivors and siblings to the BMTSS questionnaire and included the following 5 indices: (1) clinically underweight (body mass index [BMI], calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared, <18.5); (2) exhaustion (self-report of feeling tired); (3) low energy expenditure (self-report of physical activity for <2 days per week); (4) slowness (self-reported limitations in climbing stairs or walking 1 block); and (5) weakness (self-report of weakness in movement). Participants reporting the presence of 3 or more of these 5 indices were classified as frail and those reporting 2 of the 5 indices were classified as prefrail.
Clinical Characteristics
Information regarding primary diagnosis, preparative regimens, stem cell source (autologous, related or unrelated donor), graft type (bone marrow or peripheral blood stem cells), and risk of relapse at HCT (standard risk or high risk) was obtained from institutional databases. Patients transplanted in first or second complete remission after acute myeloid (AML) or lymphoid (ALL) leukemia, and Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) or non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), first chronic phase of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), and patients with SAA were considered as standard risk for relapse; the remainder were considered as high risk. Chronic physical health conditions diagnosed after HCT were captured at time of survey and graded using the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, as described previously.11 Vital status was ascertained as of December 21, 2011, using the following resources: National Death Index Plus (NDI Plus), Social Security Death Index (SSDI), medical records, and institutional long-term follow-up efforts. Information on cause of death was obtained from the NDI Plus program and medical records.
Statistical Analyses
The primary focus of the study was to (1) examine the magnitude of frailty (compared with an unexposed sibling cohort), (2) to identify the predictors of frailty among HCT survivors, and (3) to examine the risk of subsequent mortality among survivors with frailty. Descriptive statistics were calculated to characterize the study population and compared between groups with χ2 tests, exact tests, and t tests as appropriate.
Survivors vs Siblings
Comparisons between HCT survivors and siblings for frailty were conducted using unconditional logistic regression, and were reported as odds ratios (ORs) with 95% CIs. Multivariable models were adjusted for sex, age at study participation, race/ethnicity, education, annual household income, transplanting institution, health insurance status, and chronic health conditions. To account for potential within-family correlation between a survivor and sibling, a sandwich estimator of the covariance matrix was used to estimate the effects of covariates.14
Among HCT Survivors
Logistic regression was used to determine the predictors of frailty among HCT survivors. The following variables were examined for their associations with frailty in initial univariate models: a composite variable that included donor type and presence of chronic GvHD (autologous HCT [referent group], allogeneic HCT without chronic GvHD, allogeneic HCT with resolved chronic GvHD, allogeneic HCT with active chronic GvHD), sex, age at study participation (18–39 years [referent group], 40–64 years), time since HCT (2 to 4 years [referent group], 5 to 9 years, ≥ 10 years), race/ethnicity (non-Hispanic whites [referent group], others), education (college graduate/postgraduate education [referent group], less than college graduate), health insurance coverage, income (≥ $20 000/year [referent group], < $20000/year), transplanting institution, exposure to total body irradiation (TBI), primary cancer diagnosis (SAA [referent group], AML+ALL, HL+NHL, CML, multiple myeloma [MM], others), and presence of chronic health conditions. Age at study participation, sex, primary diagnosis and transplanting institution were chosen a priori to be retained in the final model. For other variables, those with P values < .05 from univariate analyses were entered simultaneously into the model to calculate ORs and corresponding 95% CIs for risk of frailty.
Impact of Post-HCT Frailty on Subsequent Mortality
Cumulative incidence of all-cause mortality was calculated from survey completion to date of death or December 31, 2011. Log-rank test was used to compare cumulative incidence of subsequent mortality by frailty phenotype. Cox regression analysis was used to first determine the univariate association between each of the following variables and subsequent mortality: frailty (no/yes); a composite variable that included donor type and presence of chronic GvHD; sex; age at study participation (18–39 years [referent group], 40–64 years); income (≥ $20 000/year [referent group], < $20 000/year); transplanting institution; risk of relapse at HCT (low risk [referent group] vs high risk); primary cancer diagnosis; and presence of chronic health conditions. Age at study participation, sex, primary cancer diagnosis and transplanting institution were chosen a priori to be retained in the final Cox regression multivariable model. For the remaining variables, associations in the univariable analysis with a P value <.05 were retained in the model to calculate hazard ratio (HR) and corresponding 95% CI for risk of subsequent mortality.
Data were analyzed using SAS statistical software (version 9.3, SAS Institute, Inc). All statistical tests were 2-sided and P-values less than .05 were considered statistically significant.
Results
Demographic and Clinical Characteristics of HCT Survivors and Siblings
The demographic characteristics of HCT survivors and siblings are presented in Table 1. Mean age at study participation (42.5 vs 43.8 years; P = .09) and having health insurance coverage (911 [93]% vs 279 [95%]; P = .10) were comparable between HCT survivors and siblings. However, siblings were more likely to be females (191 [64%] vs 456 [46%]; P < .001), non- Hispanic white (259 [88%] vs 803 [81%]; P = .004), college graduates (166 [56%] vs 486 [49%]; P < .001), and more likely to have an annual household income of $20000 or more (273 [92%] vs 801 [80%]; P < .001).
Table 1.
Demographic Characteristics of Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Survivors and Siblings
| Characteristic | No. (%)
|
P Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Survivors (n = 998) | Siblings (n = 297) | ||
| Age at enrollment, mean (SD), y | 42.5 (11.6) | 43.8 (1.9) | .09 |
|
| |||
| Sex, male | 542 (54.3) | 106 (35.7) | <.001 |
|
| |||
| Race/ethnicity | .004 | ||
|
| |||
| Non-Hispanic white | 803 (80.5) | 259 (87.2) | |
|
| |||
| Others | 195 (19.5) | 36 (12.1) | |
|
| |||
| Missing | 0 | 2 (0.7) | |
|
| |||
| Education | <.001 | ||
|
| |||
| ≥College graduate | 486 (48.7) | 166 (55.9) | |
|
| |||
| <College graduate | 508 (50.9) | 130 (43.8) | |
|
| |||
| Missing | 4 (0.3) | 1 (0.3) | |
|
| |||
| Household income, $ | <.001 | ||
|
| |||
| ≥20 000/y | 801 (80.3) | 273 (91.8) | |
|
| |||
| <20 000/y | 132 (13.2) | 12 (4.1) | |
|
| |||
| Missing | 65 (6.5) | 12 (4.1) | |
|
| |||
| Health insurance | .10 | ||
|
| |||
| No | 74 (7.4) | 14 (4.7) | |
|
| |||
| Yes | 911 (92.5) | 279 (95.2) | |
|
| |||
| Missing | 13 (1.3) | 4 (1.4) | |
|
| |||
| Grade 3/4 chronic conditions: Yes | 181 (18) | 21 (7) | <.001 |
|
| |||
| Frailty Index (composite variable) | <.001 | ||
|
| |||
| No frailty | 744 (74.6) | 275 (92.6) | |
|
| |||
| Prefrailty | 170 (17.0) | 20 (6.7) | |
|
| |||
| Frailty | 84 (8.4) | 2 (0.7) | |
|
| |||
| Frailty (individual domains) | |||
|
| |||
| Clinically underweight | 45 (4.5) | 9 (3.0) | .26 |
|
| |||
| Exhaustion | 175 (17.7) | 13 (4.4) | <.001 |
|
| |||
| Slowness | 187 (18.9) | 11 (3.7) | <.001 |
|
| |||
| Low energy expenditure | 510 (51.4) | 138 (46.5) | .14 |
|
| |||
| Weakness | 83 (8.4) | 4 (1.4) | <.001 |
|
| |||
| Age at HCT, mean (SD), y | 33.8 (13.6) | NA | NA |
|
| |||
| Interval between HCT and study, mean (SD), y | 8.7 (5.3) | NA | NA |
|
| |||
| Primary cancer diagnosis | |||
|
| |||
| Severe aplastic anemia | 53 (5.3) | NA | NA |
|
| |||
| Chronic myeloid leukemia | 232 (23.3) | NA | NA |
|
| |||
| Acute myeloid leukemia | 241 (24.2) | NA | NA |
|
| |||
| Hodgkin lymphoma | 92 (9.2) | NA | NA |
|
| |||
| Non-Hodgkin lymphoma | 191 (19.1) | NA | NA |
|
| |||
| Acute lymphoblastic leukemia | 100 (10.0) | NA | NA |
|
| |||
| Multiple myeloma | 37 (3.7) | NA | NA |
|
| |||
| Others | 52 (5.2) | NA | NA |
|
| |||
| Stem cell donor | |||
|
| |||
| Autologous HCT | 436 (43.7) | NA | NA |
|
| |||
| Allogeneic, sibling donor | 463 (46.4) | NA | NA |
|
| |||
| Allogeneic, unrelated donor | 99 (9.9) | NA | NA |
|
| |||
| Active GvHD among allogeneic HCT | |||
|
| |||
| No | 261 (46.4) | NA | NA |
|
| |||
| Active | 134 (23.8) | NA | NA |
|
| |||
| Resolved | 166 (29.5) | NA | NA |
|
| |||
| Missing | 1 (0.2) | NA | |
|
| |||
| Risk of relapse at HCT | |||
|
| |||
| High risk | 342 (34.4) | NA | NA |
|
| |||
| Preparative regimens | |||
|
| |||
| Chemotherapy-based preparative regimens | 228 (22.8) | NA | NA |
|
| |||
| Total body irradiation based | 768 (77.0) | NA | NA |
|
| |||
| Missing | 2 (0.2) | NA | NA |
Abbreviations: GvHD, graft vs host disease; HCT, hematopoietic cell transplantation; NA, not applicable.
Disease and transplant characteristics for HCT survivors are also presented in Table 1. Mean (SD) age at HCT was 33.8 (13.6) years, and the mean (SD) interval between HCT and study participation was 8.7 (5.3) years. Chronic myeloid leukemia (232 [23%]), AML (241 [24%]), NHL (191 [19%]), ALL (100 [10%]), and HL (29 [9%]) accounted for 85%of all primary diagnoses. Total body irradiation was used for 768 of the HCT recipients (77%). Of the 562 allogeneic HCT recipients, 300 (53%) had a history of chronic GvHD, and 134 (24%) reported active chronic GvHD at study participation.
Frailty Among HCT Survivors and Siblings
Overall, more survivors were identified as frail (84[8.4%]) when compared with siblings (2 [0.7%]; P < .001) (Table 1). While the prevalence of clinically underweight (45 [4.5%] vs 9 [3.0%]) and low energy expenditure (510 [51.4%] vs 138 [46.5%]) was higher among survivors than among siblings, the difference did not reach statistical significance (P = .26, P = .14, respectively) (Table 1). However, a significantly larger proportion of survivors reported exhaustion (175 [18%] vs 13 [4%]; P < .001), slowness (187 [19%] vs 11 [4%]; P < .001), and weakness (83 [8%] vs 4 [1%]; P < .001), when compared with siblings. Multivariable analysis (adjusted for age at study participation, sex, race/ethnicity, education, household income, health insurance, presence of grades 3 or 4 chronic health conditions, and transplanting institution) revealed that HCT survivors were 8.35 times more likely to be frail (95% CI, 2.0–34.5; P = .003) (Table 2) compared with siblings.
Table 2.
Risk Factors Associated With Frailty Among Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Survivors and Siblingsa
| Characteristics | Analysis, OR (95% CI) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Univariable | P Value | Multivariable | P Value | |
| Survivor-sibling comparison | ||||
| Siblings | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | ||
| HCT Survivors | 13.56 (3.2–55.4) | .003 | 8.35 (2.0–34.5) | .003 |
| Sex | ||||
| Females | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | ||
| Males | 1.16 (0.7–1.8) | .51 | 0.99 (0.6–1.6) | .96 |
| Race/ethnicity | ||||
| Non-Hispanic white | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | ||
| Other | 1.53 (0.9–2.6) | .10 | 0.75 (0.4–1.4) | .34 |
| Education | ||||
| ≥College graduate | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | ||
| <College graduate | 2.06 (1.3–3.3) | .003 | 1.93 (1.2–3.1) | .008 |
| Chronic health conditions | ||||
| Grades 0–2 | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | ||
| Grades 3–4 | 2.39 (1.5–3.9) | .005 | 2.23 (1.3–3.7) | .003 |
| Annual household income, $ | ||||
| ≥20 000 | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | ||
| <20 000 | 3.16 (1.85–5.4) | <.001 | 2.56 (1.4–4.6) | .002 |
| Income unknown | 2.77 (1.3–5.7) | .006 | 2.69 (1.2–5.9) | .02 |
| Health insurance | ||||
| No insurance | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | ||
| With insurance | 1.19 (0.5–3.0) | .71 | 2.09 (0.8–5.6) | .14 |
| Age at study participation, y | ||||
| 18–39 | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | ||
| 40–64 | 1.17 (0.7–1.9) | .50 | 1.08 (0.7–1.7) | .76 |
Abbreviations: HCT, hematopoietic cell transplantation; OR, odds ratio
The goodness of fit for the model had a C statistic of 0.77; 95%CI, 0.72–0.82.
Frailty Among HCT Survivors
Table 3 summarizes the findings from the multivariable analyses describing variables associated with increased risk for frailty among HCT survivors. Patients with low annual household income (<$ 20000 vs ≥$20 000:OR,2.01;95%CI, 1.1–3.8; P = .03), those with less than college education (OR,2.37; 95% CI, 1.4–4.1; P = .002), those with grades 3 to 4 chronic health conditions (vs grades 0–2: OR,2.05; 95% CI, 1.1–3.8; P = .02), patients with multiple myeloma (vs SAA: OR,6.38; 95% CI, 1.0–41.7; P = .05), and patients with resolved chronic GvHD (vs autologous HCT: OR,2.70; 95%CI, 1.1–6.9; P = .04), or with active chronic GvHD (vs autologous HCT: OR,15.02; 95% CI, 6.6–34.3; P < .001) were more likely to be frail.
Table 3.
Risk Factors Associated With Frailty Among Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation (HCT) Survivorsa
| Characteristics | Analysis, OR (95% CI) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Univariable | P Value | Multivariable | P Value | |
| Age at study participation, y | ||||
| 18–39 | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | ||
| 40–64 | 1.20 (0.8–1.9) | .44 | 0.93 (0.5–1.6) | .81 |
| Sex | ||||
| Females | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | ||
| Males | 0.96 (0.6–1.5) | .89 | 0.83 (0.5–1.4) | .47 |
| Race/ethnicity | ||||
| Non-Hispanic white | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | ||
| Other | 1.42 (0.8–2.4) | .19 | NA | NA |
| Education | ||||
| ≥College graduate | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | ||
| <College graduate | 1.91 (1.2–3.1) | .009 | 2.37 (1.4–4.1) | .002 |
| Chronic health conditions | ||||
| Grades 0/2 | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | ||
| Grades 3/4 | 2.06 (1.3–3.4) | .005 | 2.05 (1.1–3.8) | .02 |
| Annual household income, $ | ||||
| ≥20 000 | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | ||
| <20 000 | 2.67 (1.6–4.6) | <.001 | 2.01 (1.1–3.8) | .03 |
| Income unknown | 2.56 (1.2–5.3) | .01 | 3.28 (1.4–7.6) | .006 |
| Health insurance | ||||
| No insurance | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | ||
| With insurance | 1.29 (0.5–3.3) | .59 | NA | NA |
| Conditioning regimens | ||||
| Non-TBI containing regimens | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | ||
| TBI-containing regimens | 1.53 (0.8–2.8) | .16 | NA | NA |
| Primary diagnosis | ||||
| SAA | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | ||
| AML+ALL | 2.46 (0.6–10.6) | .23 | 1.64 (0.3–8.7) | .53 |
| HL+NHL | 1.63 (0.4–7.3) | .52 | 2.64 (0.5–14.3) | .26 |
| CML | 3.36 (0.8–14.6) | .11 | 1.76 (0.4–8.5) | .48 |
| MM | 4.93 (1.0–25.9) | .06 | 6.38 (1.0–41.7) | .05 |
| Other | 1.02 (0.1–7.5) | .98 | 1.67 (0.2–14.5) | .64 |
| Type of HCT and presence of chronic GvHD | ||||
| Autologous HCT | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | ||
| Allogeneic HCT + no chronic GvHD | 0.97 (0.5–2.1) | .93 | 1.49 (0.6–3.9) | .43 |
| Allogeneic HCT + resolved chronic GvHD | 1.71 (0.8–3.6) | .16 | 2.70 (1.1–6.9) | .04 |
| Allogeneic HCT + active chronic GvHD | 10.04 (5.6–18.1) | <.001 | 15.02 (6.6–34.3) | <.001 |
| Time since HCT, y | ||||
| 2–4 | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | ||
| 5–9 | 0.91 (0.5–1.5) | .70 | 0.96 (0.5–1.7) | .89 |
| ≥10 | 0.5 (0.3–1.0) | .051 | 0.72 (0.3–1.5) | .39 |
Abbreviations: ALL, acute lymphoid leukemia; AML, acute myeloid leukemia; CML, chronic myeloid leukemia; GvHD, graft vs host disease; HL, Hodgkin lymphoma; MM, multiple myeloma; NA, not applicable NHL, non-Hodgkin lymphoma; OR, odds ratio; SAA, severe aplastic anemia; TBI, total body irradiation.
The goodness of fit for the model had a C statistic, 0.82 (95%CI, 0.77–0.87).
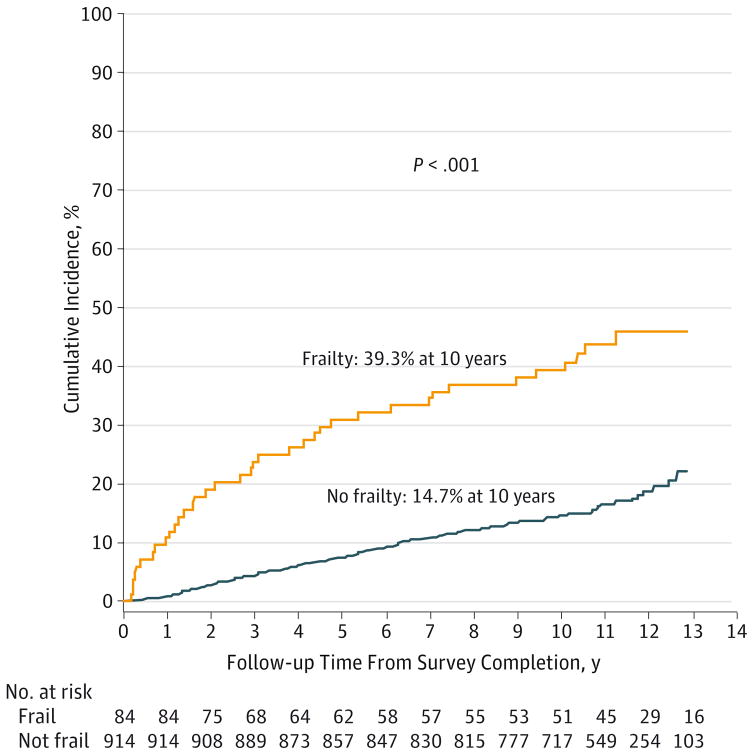
Overall Mortality
After a median follow-up of 10.3 years (range, 0.04–12.9 years) from survey completion, 182 (18%) participants had died. The 10-year cumulative incidence of all-cause mortality from survey completion was 39.3%and 14.7%(33 deaths and 131 deaths by 10 years) for patients with and without frailty (P < .001) (Figure). The 10-year cumulative incidence of relapse-related mortality was 15.5% (13 deaths by 10 years) among frail HCT recipients vs 4.5% (41 deaths by 10 years) among nonfrail individuals; P < .001). The 10-year cumulative incidence of non-relapse mortality was also higher among frail HCT recipients (23.9% [20 deaths by 10 years]) compared with nonfrail HCT recipients (10.2%[90 deaths by 10 years]; P < .001). Multivariable analysis, adjusted for type of transplant and chronic GvHD, age at study participation, sex, presence of grades 3 to 4 chronic health conditions, primary diagnosis, annual household income, and risk of relapse at transplant, revealed that frailty was associated with a 2.76-fold increased risk of subsequent death (95% CI, 1.7–4.4; P < .001, Table 4).
Figure.
Cumulative Incidence of Subsequent Mortality (From Survey Completion) by Frailty
Table 4.
Impact of Frailty on Subsequent Mortality Among Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Survivors
| Characteristics | Analysis, OR (95% CI) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Univariable | P Value | Multivariable | P Value | |
| Age at study participation, y | ||||
| 18–39 | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | ||
| 40–64 | 2.79 (2.0–4.0) | <.001 | 2.57 (1.8–3.8) | <.001 |
| Sex | ||||
| Females | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | ||
| Males | 1.39 (1.0–1.9) | .03 | 1.33 (0.97–1.8) | .07 |
| Race/ethnicity | ||||
| Non-Hispanic white | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | ||
| Other | 0.89 (0.6–1.3) | .55 | NA | NA |
| Education | ||||
| ≥College graduate | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | ||
| <College graduate | 1.24 (0.9–1.7) | .16 | NA | NA |
| Chronic health conditions | ||||
| Grades 0/2 | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | ||
| Grades 3/4 | 1.6 (1.1–2.2) | .006 | 1.40 (0.98–2.0) | .07 |
| Annual household income, $ | ||||
| ≥20 000 | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | ||
| <20 000 | 1.56 (1.1–2.3) | .02 | 1.59 (1.1–2.4) | .02 |
| Income unknown | 1.39 (0.8–2.4) | .21 | 1.14 (0.6–2.1) | .67 |
| Health insurance | ||||
| No insurance | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | ||
| With insurance | 0.95 (0.6–1.6) | .86 | NA | NA |
| Conditioning regimens | ||||
| Non-TBI containing regimens | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | ||
| TBI-containing regimens | 0.88 (0.6–1.3) | .49 | NA | NA |
| Primary diagnosis | ||||
| SAA | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | ||
| AML+ALL | 2.95 (0.9–9.3) | .06 | 1.70 (0.6–5.1) | .34 |
| HL+NHL | 3.49 (1.1–10.9) | .03 | 1.31 (0.4–4.2) | .66 |
| CML | 2.90 (0.9–9.3) | .07 | 1.44 (0.5–4.3) | .51 |
| MM | 8.91 (2.6–30.9) | .006 | 2.02 (0.5–7.6) | .30 |
| Other | 3.36 (0.9–12.3) | .07 | 1.43 (0.4–5.6) | .61 |
| Type of HCT and presence of chronic GvHD | ||||
| Autologous HCT | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | ||
| Allogeneic HCT + no chronic GvHD | 0.45 (0.29–0.69) | .002 | 0.49 (0.3–0.8) | .008 |
| Allogeneic HCT + resolved chronic GvHD | 0.43 (0.26–0.72) | .03 | 0.38 (0.2–0.7) | .004 |
| Allogeneic HCT + active chronic GvHD | 1.47 (1.0–2.1) | .03 | 0.92 (0.5–1.6) | .77 |
| Risk of relapse at HCT | ||||
| Standard | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | ||
| High | 1.61 (1.2–2.2) | .001 | 1.25 (0.8–1.8) | .23 |
| Frailty | ||||
| No | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | ||
| Yes | 3.30 (2.3–4.8) | <.001 | 2.76 (1.7–4.4) | <.001 |
Abbreviations: ALL, acute lymphoid leukemia; AML, acute myeloid leukemia; CML, chronic myeloid leukemia; GvHD, graft vs host disease; HCT, hematopoietic cell transplantation; HL, Hodgkin lymphoma; NHL, non-Hodgkin lymphoma; NA, not applicable; OR, odds ratio; SAA, severe aplastic anemia; TBI, total-body irradiation.
Discussion
Our data indicate that HCT survivors at a mean age of 42.5 years at study participation exhibit the frailty phenotype (84[8.4%]), at a rate more than 8-fold higher than among siblings, but very similar to that (10%) documented in community-based elderly populations compared with the general population (>65 years) (n = 61 500 participants).2 Among HCT recipients, patients transplanted for multiple myeloma, survivors of allogeneic HCT with chronic GvHD, those with other chronic health conditions, and those from a lower socioeconomic background are most vulnerable to having the frailty phenotype. We also demonstrate that this phenotype is associated with an increased risk for subsequent mortality. These data support the hypothesis that therapeutic exposures and the high risk of post-HCT complications constitute a substantial stressor, placing HCT survivors at risk for frailty, and provides potential evidence for premature aging in this population.
Our data indicate rates similar to those reported15 among adult survivors of childhood cancer at least 10 years from diagnosis (mean age at study, 33.6 years) where the prevalence of frailty was 13.1% among women and 2.7% among men. Among childhood cancer survivors, the prevalence of frailty also increased with age and was more prevalent among those with chronic health conditions.15 In our cohort, neither sex nor increasing age were associated with frailty risk among HCT survivors. However chronic health conditions nearly doubled the risk of frailty. This difference may be because HCT recipients carry a high burden of morbidity—the cumulative incidence of grades 3 to 5 chronic health conditions exceeds 40% 15 years after HCT10,11—and the presence and/or types of chronic health conditions experienced by HCT survivors overwhelm the potential impact of age and/or sex.
In fact, in our study, independent of the association between chronic conditions and frailty, allogeneic HCT recipients with active chronic GvHD were at a 15-fold higher risk of frailty than autologous HCT recipients, suggesting a potential role for proinflammatory pathways to the frailty phenotype.16–18 Our findings are supported by data from the Cardiovascular Health Study suggesting that frailty represents a physiologic state characterized by increased inflammation and elevated markers of coagulation (C-reactive protein, factor VIII, D-dimer),17 and by data from the literature on aging, which indicates that cellular senescence is associated with elevated levels of inflammatory markers including interleukin-6, tumor necrosis factor α, and immune cell cytokines.19 Other data20–22 suggest an association between frailty, progressive telomere shortening, and associated cellular aging, relevant in the HCT survivor population because their disease and treatment induces substantial proliferative stress.
Similar to results of a previous report,15 we found an association between frailty and subsequent mortality. Indeed, frailty was associated with a 2.7-fold higher risk of subsequent mortality, after adjusting for clinical and therapeutic prognostic factors, chronic health conditions, and chronic GvHD. These findings demonstrate the need for interventions, including personalized assessments and multidisciplinary efforts targeting both prefrail and frail individuals to improve outcomes.23–25
Study Limitations
This study needs to be considered in the setting of several potential limitations. First, although we have previously demonstrated12 that there is concordance between outcomes abstracted from medical records and self-reported outcomes, these analyses relied on self-reported measures, subject to reporting and recall bias. It is possible that HCT survivors were either unaware of or did not estimate their physical limitations accurately, which would result in either under estimating or overestimating our prevalence estimates. Second, the assessment of frailty was in the setting of a cross-sectional study design, and frailty estimates could possibly vary with time from HCT; we attempted to overcome this limitation by adjusting for time since HCT. Furthermore, our cohort included patients who underwent transplantation between 1974 and 1998. There have been significant changes in transplant strategies over the past 2 decades, including use of reduced intensity conditioning, older age of recipients, increased use of alternative donor and graft sources, and novel GvHD prophylaxis strategies. Thus, while it is important to study and report on patients transplanted in the older era, the significant changes in practice necessitate assessment of patients transplanted in the contemporary era.
Differences between our constructs and the clinical constructs used by Fried et al1 are highlighted in eTable in the Supplement. Although we carefully cross-walked questionnaire responses to a known frailty rubric, our criteria were based on self-report.26–29 We did not have performance-based measures for hand grip strength or walking speed. Because individuals are likely to have gradual changes in physical abilities, it is likely that the prevalence of these components of frailty are underestimated in this population. However, the same measures were used for the sibling comparison group—allowing for a valid comparison of the difference in magnitude of self-reported frailty between survivors and siblings. These limitations not with standing, we described frailty in a large cohort of autologous and allogeneic HCT survivors, compared the risk of frailty in these survivors to age- and sex matched siblings, and determined the impact of frailty on subsequent mortality.
Conclusions
We found that the prevalence of frailty among young adult HCT survivors is high, and approaching that observed among elderly community dwellers,2 suggesting a phenotype of accelerated aging. The costs involved in caring for a frail individual, and the significantly increased risk of subsequent mortality, suggest a critical need for developing and implementing interventions to prevent or treat frailty. Treating only medical conditions, without targeted interventions to address frailty, is likely to be insufficient for improving the adverse outcomes associated with frailty.18,25,30 Thus, for similar comorbidities, the optimal management could be very different in frail vs robust older patients.18,31 Finally, longitudinal surveillance of survivors is needed to identify those at highest risk and thus provide targeted interventions to prevent or improve adverse outcomes associated with frailty in this population.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
Funding/Support: This study was supported in part by the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society (grant 6256-13 to Dr Bhatia) and the National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute (grant R01 CA078938 to Dr Bhatia).
Footnotes
Conflict of Interest Disclosures: None reported.
Previous Presentation: This study was presented as a podium presentation at the American Society of Hematology Conference; December 7, 2015; Orlando, Florida.
Author Contributions: Dr Bhatia had full access to all of the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. Drs Arora and Sun contributed equally.
Study concept and design: Arora, Bhatia.
Acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data: All authors.
Drafting of the manuscript: Arora, Sun, Berano Teh, Bhatia.
Critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content: Arora, Ness, Wu, Francisco, Armenian, Schad, Namdar, Bosworth, Kuo, Weisdorf, Forman, Bhatia.
Statistical analysis: Sun, Bhatia.
Obtained funding: Bhatia.
Administrative, technical, or material support: Berano Teh, Wu, Francisco, Armenian, Schad, Namdar, Bosworth, Kuo, Forman, Bhatia.
Study supervision: Arora, Berano Teh, Francisco, Armenian, Forman, Bhatia.
Other: Ness.
Role of the Funder/Sponsor: The funding institutions had no role in the design and conduct of the study; collection, management, analysis, and interpretation of the data; preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript; and decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
References
- 1.Fried LP, Tangen CM, Walston J, et al. Cardiovascular Health Study Collaborative Research Group. Frailty in older adults: evidence for a phenotype. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2001;56(3):M146–M156. doi: 10.1093/gerona/56.3.m146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Collard RM, Boter H, Schoevers RA, Oude Voshaar RC. Prevalence of frailty in community-dwelling older persons: a systematic review. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2012;60(8):1487–1492. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2012.04054.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Rockwood K, Mitnitski A. Frailty defined by deficit accumulation and geriatric medicine defined by frailty. Clin Geriatr Med. 2011;27(1):17–26. doi: 10.1016/j.cger.2010.08.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hogan DB, MacKnight C, Bergman H Steering Committee, Canadian Initiative on Frailty and Aging. Models, definitions, and criteria of frailty. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2003;15(3 suppl):1–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Wong FL, Francisco L, Togawa K, et al. Long-term recovery after hematopoietic cell transplantation: predictors of quality-of-life concerns. Blood. 2010;115(12):2508–2519. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-06-225631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Naeim A, Wong FL, Pal SK, Hurria A. Oncologists’ recommendations for adjuvant therapy in hormone receptor-positive breast cancer patients of varying age and health status. Clin Breast Cancer. 2010;10(2):136–143. doi: 10.3816/CBC.2010.n.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Armenian SH, Sun CL, Francisco L, et al. Health behaviors and cancer screening practices in long-term survivors of hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT): a report from the BMT Survivor Study. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2012;47(2):283–290. doi: 10.1038/bmt.2011.60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Armenian SH, Sun CL, Shannon T, et al. Incidence and predictors of congestive heart failure after autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation. Blood. 2011;118(23):6023–6029. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-06-358226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sun CL, Francisco L, Baker KS, Weisdorf DJ, Forman SJ, Bhatia S. Adverse psychological outcomes in long-term survivors of hematopoietic cell transplantation: a report from the Bone Marrow Transplant Survivor Study (BMTSS) Blood. 2011;118(17):4723–4731. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-04-348730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Armenian SH, Sun CL, Kawashima T, et al. Long-term health-related outcomes in survivors of childhood cancer treated with HSCT versus conventional therapy: a report from the Bone Marrow Transplant Survivor Study (BMTSS) and Childhood Cancer Survivor Study (CCSS) Blood. 2011;118(5):1413–1420. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-01-331835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Sun CL, Francisco L, Kawashima T, et al. Prevalence and predictors of chronic health conditions after hematopoietic cell transplantation: a report from the Bone Marrow Transplant Survivor Study. Blood. 2010;116(17):3129–3139. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-06-229369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Louie AD, Robison LL, Bogue M, Hyde S, Forman SJ, Bhatia S. Validation of self-reported complications by bone marrow transplantation survivors. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2000;25(11):1191–1196. doi: 10.1038/sj.bmt.1702419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Bouillon K, Kivimaki M, Hamer M, et al. Measures of frailty in population-based studies: an overview. BMC Geriatr. 2013;13:64. doi: 10.1186/1471-2318-13-64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Therneau TMGP. Modeling survival data: extending the Cox model. New York: Springer-Verlag; 2000. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ness KK, Krull KR, Jones KE, et al. Physiologic frailty as a sign of accelerated aging among adult survivors of childhood cancer: a report from the St Jude Lifetime cohort study. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(36):4496–4503. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2013.52.2268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Newman AB, Gottdiener JS, McBurnie MA, et al. Cardiovascular Health Study Research Group. Associations of subclinical cardiovascular disease with frailty. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2001;56(3):M158–M166. doi: 10.1093/gerona/56.3.m158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Walston J, McBurnie MA, Newman A, et al. Cardiovascular Health Study. Frailty and activation of the inflammation and coagulation systems with and without clinical comorbidities: results from the Cardiovascular Health Study. Arch Intern Med. 2002;162(20):2333–2341. doi: 10.1001/archinte.162.20.2333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Fried LP, Ferrucci L, Darer J, Williamson JD, Anderson G. Untangling the concepts of disability, frailty, and comorbidity: implications for improved targeting and care. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2004;59(3):255–263. doi: 10.1093/gerona/59.3.m255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Tchkonia T, Zhu Y, van Deursen J, Campisi J, Kirkland JL. Cellular senescence and the senescent secretory phenotype: therapeutic opportunities. J Clin Invest. 2013;123(3):966–972. doi: 10.1172/JCI64098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Bhatia R, Van Heijzen K, Palmer A, et al. Longitudinal assessment of hematopoietic abnormalities after autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation for lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23(27):6699–6711. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.10.330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Gramatges MM, Liu Q, Yasui Y, et al. Telomere content and risk of second malignant neoplasm in survivors of childhood cancer: a report from the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20(4):904–911. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-2076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Chakraborty S, Sun CL, Francisco L, et al. Accelerated telomere shortening precedes development of therapy-related myelodysplasia or acute myelogenous leukemia after autologous transplantation for lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(5):791–798. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.17.1033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Cameron ID, Fairhall N, Langron C, et al. A multifactorial interdisciplinary intervention reduces frailty in older people: randomized trial. BMC Med. 2013;11:65. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-11-65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Gates S, Fisher JD, Cooke MW, Carter YH, Lamb SE. Multifactorial assessment and targeted intervention for preventing falls and injuries among older people in community and emergency care settings: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2008;336(7636):130–133. doi: 10.1136/bmj.39412.525243.BE. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Gill TM, Baker DI, Gottschalk M, Peduzzi PN, Allore H, Byers A. A program to prevent functional decline in physically frail, elderly persons who live at home. N Engl J Med. 2002;347(14):1068–1074. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa020423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Rochat S, Cumming RG, Blyth F, et al. Frailty and use of health and community services by community-dwelling older men: the Concord Health and Ageing in Men Project. Age Ageing. 2010;39(2):228–233. doi: 10.1093/ageing/afp257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Santos-Eggimann B, Cuénoud P, Spagnoli J, Junod J. Prevalence of frailty in middle-aged and older community-dwelling Europeans living in 10 countries. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2009;64(6):675–681. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glp012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Solfrizzi V, Scafato E, Frisardi V, et al. Italian Longitudinal Study on Aging Working Group. Frailty syndrome and all-cause mortality in demented patients: the Italian Longitudinal Study on Aging. Age (Dordr) 2012;34(2):507–517. doi: 10.1007/s11357-011-9247-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Eckel SP, Bandeen-Roche K, Chaves PH, Fried LP, Louis TA. Surrogate screening models for the low physical activity criterion of frailty. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2011;23(3):209–216. doi: 10.1007/bf03324962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Binder EF, Schechtman KB, Ehsani AA, et al. Effects of exercise training on frailty in community-dwelling older adults: results of a randomized, controlled trial. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2002;50(12):1921–1928. doi: 10.1046/j.1532-5415.2002.50601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ferrucci L, Guralnik JM, Cavazzini C, et al. The frailty syndrome: a critical issue in geriatric oncology. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2003;46(2):127–137. doi: 10.1016/s1040-8428(02)00177-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.