Abstract
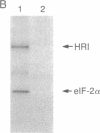
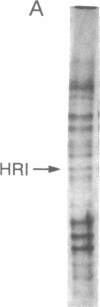
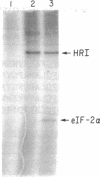
We have purified the heme-regulated eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha subunit (eIF-2 alpha) kinase (HRI) from rabbit reticulocytes for amino acid microsequencing. This kinase is a single 92-kDa polypeptide and migrates in perfect alignment with 32P-labeled HRI on SDS/PAGE. Its functions of binding ATP and of autophosphorylation and eIF-2 alpha phosphorylation are inhibited by hemin. The amino acid sequences of three tryptic peptides of HRI have been obtained. A search of the data base of the National Biomedical Research Foundation reveals that these amino acid sequences are unique and that two of these three sequences show homology to protein kinases. HRI peptide P-52 contains Asp-Phe-Gly, which is the most highly conserved short stretch of amino acids in catalytic domain VII of protein kinases. HRI peptide P-74 contains the conserved amino acid residues Asp-(Met)-Tyr-Ser-(Val)-Gly-Val found in catalytic domain IX of protein kinases [Hanks, S. K., Quinn, A. M. & Hunter, T. (1988) Science 241, 42-52]. These findings are consistent with the autokinase and eIF-2 alpha kinase activities of HRI. Synthetic HRI peptide P-74 is a very potent inhibitor of eIF-2 alpha phosphorylation by HRI. Since little is known about the function of conserved domain IX, P-74 peptide may be useful in elucidating the role of this domain of protein kinases.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamson S. D., Herbert E., Kemp S. F. Effects of hemin and other porphyrins on protein synthesis in a reticulocyte lysate cell-free system. J Mol Biol. 1969 Jun 14;42(2):247–258. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90041-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aebersold R. H., Leavitt J., Saavedra R. A., Hood L. E., Kent S. B. Internal amino acid sequence analysis of proteins separated by one- or two-dimensional gel electrophoresis after in situ protease digestion on nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):6970–6974. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.6970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almiş-Kanigür G., Kan B., Kospançali S., Bermek E. A translational inhibitor activated in rabbit reticulocyte lysates under high pO2. FEBS Lett. 1982 Aug 16;145(1):143–146. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)81223-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amesz H., Goumans H., Haubrich-Morree T., Voorma H. O., Benne R. Purification and characterization of a protein factor that reverses the inhibition of protein synthesis by the heme-regulated translational inhibitor in rabbit reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Aug 1;98(2):513–520. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13212.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRUNS G. P., LONDON I. M. THE EFFECT OF HEMIN ON THE SYNTHESIS OF GLOBIN. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Jan 18;18:236–242. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90746-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonanou-Tzedaki S. A., Smith K. E., Sheeran B. A., Arnstein H. R. Reduced formation of initiation complexes between Met-tRNAf and 40-S ribosomal subunits in rabbit reticulocyte lysates incubated at elevated temperatures. Activity of the Met-tRNAf binding factor. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Mar 15;84(2):601–610. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12203.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson J., Drevin H., Axén R. Protein thiolation and reversible protein-protein conjugation. N-Succinimidyl 3-(2-pyridyldithio)propionate, a new heterobifunctional reagent. Biochem J. 1978 Sep 1;173(3):723–737. doi: 10.1042/bj1730723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. J., Yang J. M., Petryshyn R., Kosower N., London I. M. Disulfide bond formation in the regulation of eIF-2 alpha kinase by heme. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 5;264(16):9559–9564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst V., Levin D. H., London I. M. Evidence that glucose 6-phosphate regulates protein synthesis initiation in reticulocyte lysates. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7163–7172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst V., Levin D. H., London I. M. Inhibition of protein synthesis initiation by oxidized glutathione: activation of a protein kinase that phosphorylates the alpha subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4110–4114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagard R., London I. M. Relationship between phosphorylation and activity of heme-regulated eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):866–870. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell P. J., Balkow K., Hunt T., Jackson R. J., Trachsel H. Phosphorylation of initiation factor elF-2 and the control of reticulocyte protein synthesis. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):187–200. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90330-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross M., Mendelewski J. Control of protein synthesis by hemin. An association between the formation of the hemin-controlled translational repressor and the phosphorylation of a 100 000 molecular weight protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Oct 24;520(3):650–663. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(78)90150-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross M., Rabinovitz M. Control of globin synthesis by hemin: factors influencing formation of an inhibitor of globin chain initiation in reticulocyte lysates. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Dec 6;287(2):340–352. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90383-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard G. A., Adamson S. D., Herbert E. Studies on cessation of protein synthesis in a reticulocyte lysate cell-free system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jul 16;213(1):237–240. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90028-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt T., Vanderhoff G., London I. M. Control of globin synthesis: the role of heme. J Mol Biol. 1972 May 28;66(3):471–481. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90427-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurst R., Schatz J. R., Matts R. L. Inhibition of rabbit reticulocyte lysate protein synthesis by heavy metal ions involves the phosphorylation of the alpha-subunit of the eukaryotic initiation factor 2. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 25;262(33):15939–15945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosower N. S., Vanderhoff G. A., Kosower E. M. Glutathione. 8. The effects of glutathione disulfide on initiation of protein synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jul 31;272(4):623–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer G., Cimadevilla J. M., Hardesty B. Specificity of the protein kinase activity associated with the hemin-controlled repressor of rabbit reticulocyte. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3078–3082. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudlicki W., Fullilove S., Read R., Kramer G., Hardesty B. Identification of spectrin-related peptides associated with the reticulocyte heme-controlled alpha subunit of eukaryotic translational initiation factor 2 kinase and of Mr 95,000 peptide that appears to be the catalytic subunit. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9695–9701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathe R. Synthetic oligonucleotide probes deduced from amino acid sequence data. Theoretical and practical considerations. J Mol Biol. 1985 May 5;183(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90276-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D., Ranu R. S., Ernst V., London I. M. Regulation of protein synthesis in reticulocyte lysates: phosphorylation of methionyl-tRNAf binding factor by protein kinase activity of translational inhibitor isolated from hemedeficient lysates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3112–3116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matts R. L., Levin D. H., London I. M. Effect of phosphorylation of the alpha-subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 on the function of reversing factor in the initiation of protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2559–2563. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matts R. L., Levin D. H., London I. M. Fate of reversing factor during restoration of protein synthesis by hemin or GTP in heme-deficient reticulocyte lysates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1217–1221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matts R. L., London I. M. The regulation of initiation of protein synthesis by phosphorylation of eIF-2(alpha) and the role of reversing factor in the recycling of eIF-2. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):6708–6711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell C. R., Kamper C. S., Rabinovitz M. Hemin control of globin synthesis: an assay for the inhibitor formed in the absence of hemin and some characteristics of its formation. J Mol Biol. 1971 May 28;58(1):317–327. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90249-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pain V. M., Clemens M. J. Assembly and breakdown of mammalian protein synthesis initiation complexes: regulation by guanine nucleotides and by phosphorylation of initiation factor eIF-2. Biochemistry. 1983 Feb 15;22(4):726–733. doi: 10.1021/bi00273a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pain V. M. Initiation of protein synthesis in mammalian cells. Biochem J. 1986 May 1;235(3):625–637. doi: 10.1042/bj2350625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panniers R., Henshaw E. C. A GDP/GTP exchange factor essential for eukaryotic initiation factor 2 cycling in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells and its regulation by eukaryotic initiation factor 2 phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):7928–7934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranu R. S., London I. M. Regulation of protein synthesis in rabbit reticulocyte lysates: purification and initial characterization of the cyclic 3':5'-AMP independent protein kinase of the heme-regulated translational inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4349–4353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siekierka J., Manne V., Ochoa S. Mechanism of translational control by partial phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):352–356. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siekierka J., Mauser L., Ochoa S. Mechanism of polypeptide chain initiation in eukaryotes and its control by phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of initiation factor 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2537–2540. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas N. S., Matts R. L., Petryshyn R., London I. M. Distribution of reversing factor in reticulocyte lysates during active protein synthesis and on inhibition by heme deprivation or double-stranded RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):6998–7002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.6998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. T., Cass K. H., Stellwagen E. Blue dextran-sepharose: an affinity column for the dinucleotide fold in proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):669–672. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trachsel H., Ranu R. S., London I. M. Regulation of protein synthesis in rabbit reticulocyte lysates: purification and characterization of heme-reversible translational inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3654–3658. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yue V. T., Schimmel P. R. Direct and specific photochemical cross-linking of adenosine 5'-triphosphate to an aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4678–4684. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker W. V., Schulman H. M. Stimulation of globin-chain initiation by hemin in the reticulocyte cell-free system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Feb;59(2):582–589. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.2.582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]