Abstract
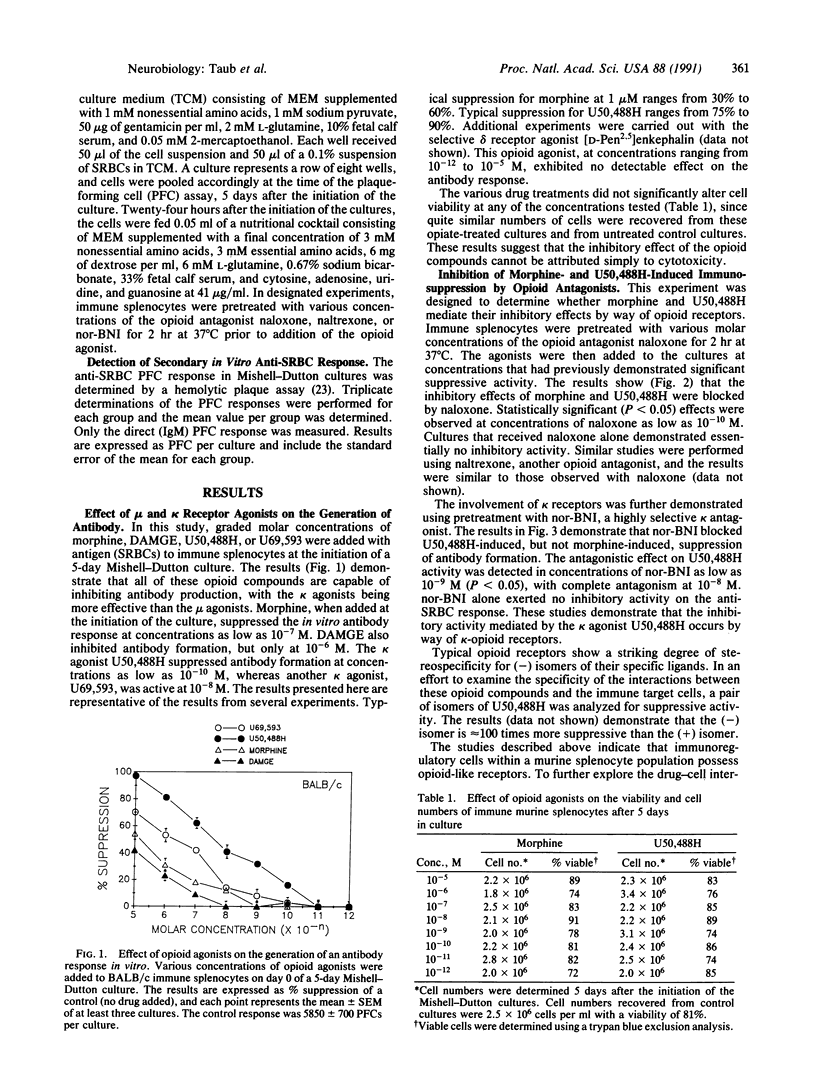
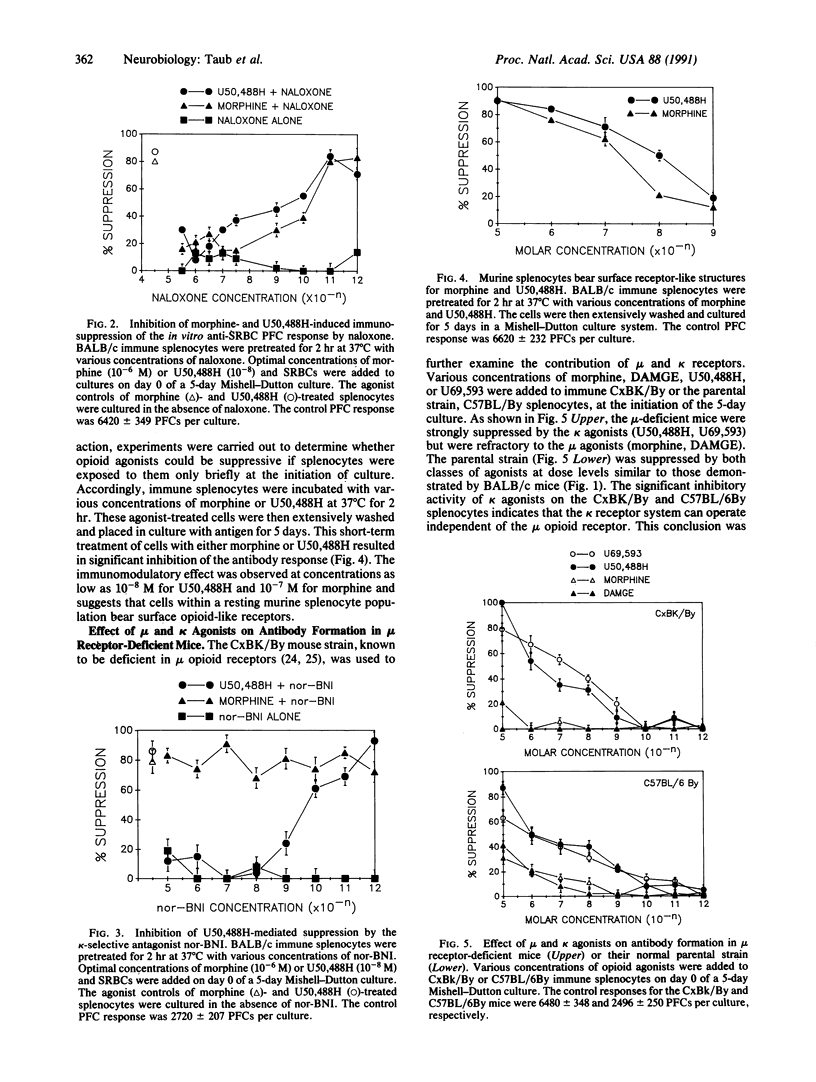
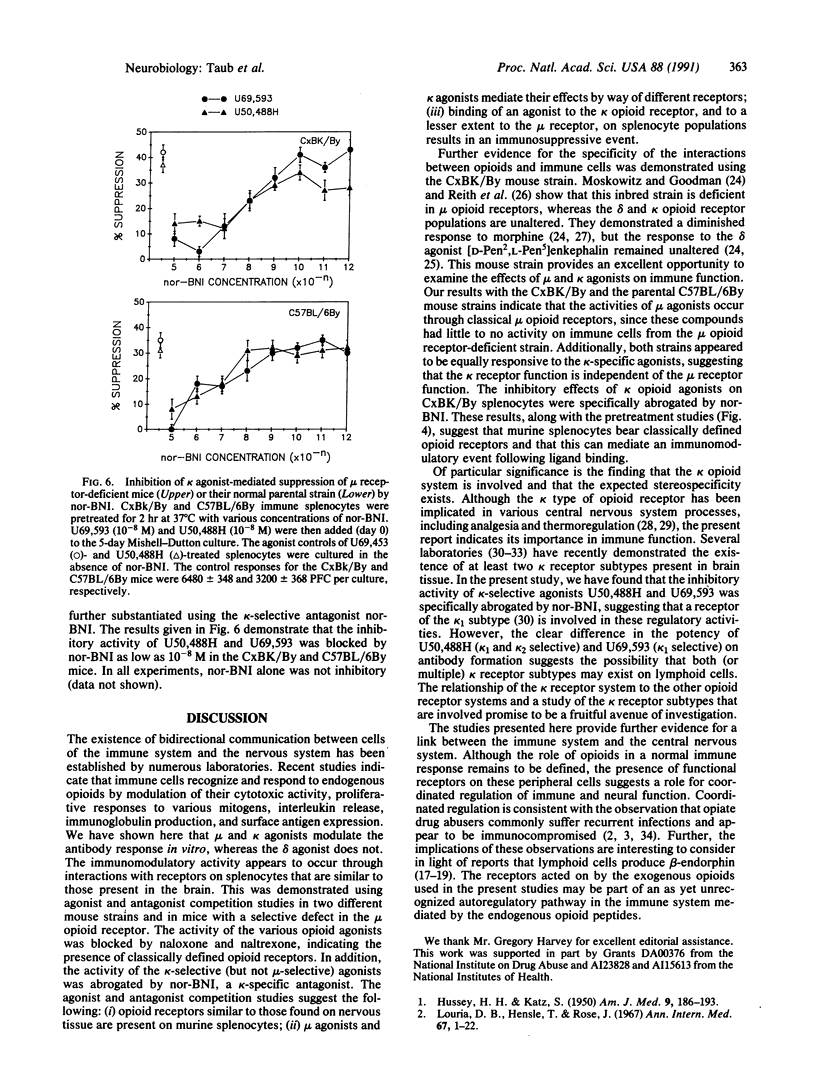
Opioids and opioid peptides have been shown by numerous laboratories to modulate various parameters of the immune response, but little attention has been given to the type of opioid receptor that might be involved. This study focuses on the in vitro influences of morphine and DAMGE (Tyr-D-Ala-Gly-N-Me-Phe-Gly-ol), mu-selective agonists, and U50,488H and U69,593, kappa-selective agonists, on the generation of antibody to sheep erythrocytes in vitro. It was found that the mu and kappa opioid agonists were able to inhibit the capacity of murine lymphoid cells to generate antibody at concentrations as low as 10(-10) M. The effects were almost completely blocked by pretreatment with naloxone or naltrexone, opioid-specific antagonists. Only the kappa-agonist activity was abrogated by pretreatment with norbinaltorphimine, a kappa-specific antagonist. The stereospecificity of the kappa effect was demonstrated using isomers of U50,488H, with the (-) form possessing significantly greater immunomodulatory activity. Additional studies, using a mu receptor-deficient mouse strain, demonstrated that only the kappa agonists were capable of suppressing antibody responses, whereas mu- and kappa-selective agonists suppressed the parent mu-responsive strain. Our results clearly indicate that mu and kappa opioid receptors are involved in regulation of lymphoid cell production of antibodies.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baran A., Shuster L., Eleftheriou B. E., Bailey D. W. Opiate receptors in mice: genetic differences. Life Sci. 1975 Aug 15;17(4):633–640. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90101-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. M., Stimmel B., Taub R. N., Kochwa S., Rosenfield R. E. Immunologic dysfunction in heroin addicts. Arch Intern Med. 1974 Dec;134(6):1001–1006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant H. U., Bernton E. W., Holaday J. W. Morphine pellet-induced immunomodulation in mice: temporal relationships. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Jun;245(3):913–920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr D. J., DeCosta B. R., Kim C. H., Jacobson A. E., Guarcello V., Rice K. C., Blalock J. E. Opioid receptors on cells of the immune system: evidence for delta- and kappa-classes. J Endocrinol. 1989 Jul;122(1):161–168. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1220161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherubin C. E. The medical sequelae of narcotic addiction. Ann Intern Med. 1967 Jul;67(1):23–33. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-67-1-23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. A., Liu L., Price M., Hersh B., Edelson M., Pasternak G. W. Kappa opiate receptor multiplicity: evidence for two U50,488-sensitive kappa 1 subtypes and a novel kappa 3 subtype. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Nov;251(2):461–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham A. J., Szenberg A. Further improvements in the plaque technique for detecting single antibody-forming cells. Immunology. 1968 Apr;14(4):599–600. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushman P., Jr, Gupta S., Grieco M. H. Immunological studies in methadone maintained patients. Int J Addict. 1977 Apr;12(2-3):241–253. doi: 10.3109/10826087709027222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUSSEY H. H., KATZ S. Infections resulting from narcotic addiction; report of 102 cases. Am J Med. 1950 Aug;9(2):186–193. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(50)90021-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUSSEY H. H., KATZ S. Infections resulting from narcotic addiction; report of 102 cases. Am J Med. 1950 Aug;9(2):186–193. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(50)90021-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappler J. W. A micro-technique for hemolytic plaque assays. J Immunol. 1974 Mar;112(3):1271–1274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lolait S. J., Lim A. T., Toh B. H., Funder J. W. Immunoreactive beta-endorphin in a subpopulation of mouse spleen macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1984 Jan;73(1):277–280. doi: 10.1172/JCI111203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louria D. B., Hensle T., Rose J. The major medical complications of heroin addiction. Ann Intern Med. 1967 Jul;67(1):1–22. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-67-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonough R. J., Madden J. J., Falek A., Shafer D. A., Pline M., Gordon D., Bokos P., Kuehnle J. C., Mendelson J. Alteration of T and null lymphocyte frequencies in the peripheral blood of human opiate addicts: in vivo evidence for opiate receptor sites on T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2539–2543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskowitz A. S., Goodman R. R. Autoradiographic analysis of mu1, mu2, and delta opioid binding in the central nervous system of C57BL/6BY and CXBK (opioid receptor-deficient) mice. Brain Res. 1985 Dec 23;360(1-2):108–116. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91226-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nock B., Rajpara A., O'Connor L. H., Cicero T. J. [3H]U-69593 labels a subtype of kappa opiate receptor with characteristics different from that labeled by [3H]ethylketocyclazocine. Life Sci. 1988;42(23):2403–2412. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(88)90195-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellis N. R., Harper C., Dafny N. Suppression of the induction of delayed hypersensitivity in rats by repetitive morphine treatments. Exp Neurol. 1986 Jul;93(1):92–97. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(86)90148-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reith M. E., Sershen H., Vadasz C., Lajtha A. Strain differences in opiate receptors in mouse brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Sep 24;74(4):377–380. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90059-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman R. B., Bykov V., de Costa B. R., Jacobson A. E., Rice K. C., Brady L. S. Interaction of endogenous opioid peptides and other drugs with four kappa opioid binding sites in guinea pig brain. Peptides. 1990 Mar-Apr;11(2):311–331. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(90)90088-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shavit Y., Depaulis A., Martin F. C., Terman G. W., Pechnick R. N., Zane C. J., Gale R. P., Liebeskind J. C. Involvement of brain opiate receptors in the immune-suppressive effect of morphine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):7114–7117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.7114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith E. M., Morrill A. C., Meyer W. J., 3rd, Blalock J. E. Corticotropin releasing factor induction of leukocyte-derived immunoreactive ACTH and endorphins. 1986 Jun 26-Jul 2Nature. 321(6073):881–882. doi: 10.1038/321881a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taub D. D., Lin Y. S., Hu S. C., Rogers T. J. Immunomodulatory activity of staphylococcal enterotoxin-B. The induction of an I-J-restricted suppressor factor. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 1;143(3):813–820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiseo P. J., Geller E. B., Adler M. W. Antinociceptive action of intracerebroventricularly administered dynorphin and other opioid peptides in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Aug;246(2):449–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tittle T. V., Rittenberg M. B. Expression of IgG memory response in vitro to thymus-dependent and thymus-independent antigens. Cell Immunol. 1978 Jan;35(1):180–190. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90138-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tubaro E., Avico U., Santiangeli C., Zuccaro P., Cavallo G., Pacifici R., Croce C., Borelli G. Morphine and methadone impact on human phagocytic physiology. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1985;7(6):865–874. doi: 10.1016/0192-0561(85)90049-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tubaro E., Borelli G., Croce C., Cavallo G., Santiangeli C. Effect of morphine on resistance to infection. J Infect Dis. 1983 Oct;148(4):656–666. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.4.656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaught J. L., Mathiasen J. R., Raffa R. B. Examination of the involvement of supraspinal and spinal mu and delta opioid receptors in analgesia using the mu receptor deficient CXBK mouse. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Apr;245(1):13–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber R. J., Pert A. The periaqueductal gray matter mediates opiate-induced immunosuppression. Science. 1989 Jul 14;245(4914):188–190. doi: 10.1126/science.2749256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wybran J., Appelboom T., Famaey J. P., Govaerts A. Suggestive evidence for receptors for morphine and methionine-enkephalin on normal human blood T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1979 Sep;123(3):1068–1070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zukin R. S., Eghbali M., Olive D., Unterwald E. M., Tempel A. Characterization and visualization of rat and guinea pig brain kappa opioid receptors: evidence for kappa 1 and kappa 2 opioid receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):4061–4065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.4061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurawski G., Benedik M., Kamb B. J., Abrams J. S., Zurawski S. M., Lee F. D. Activation of mouse T-helper cells induces abundant preproenkephalin mRNA synthesis. Science. 1986 May 9;232(4751):772–775. doi: 10.1126/science.2938259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



