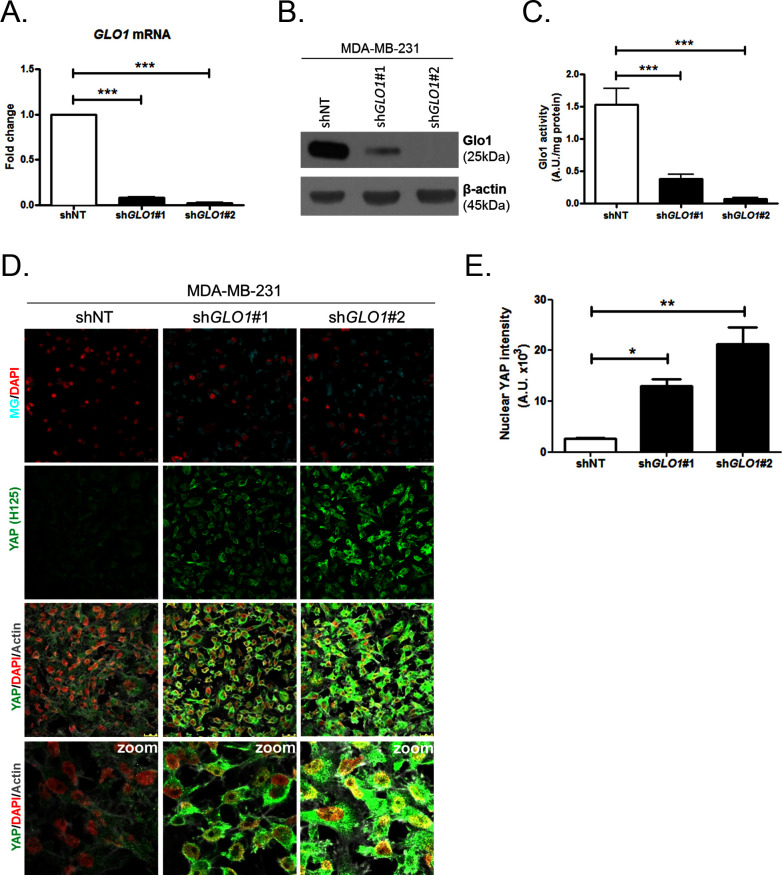
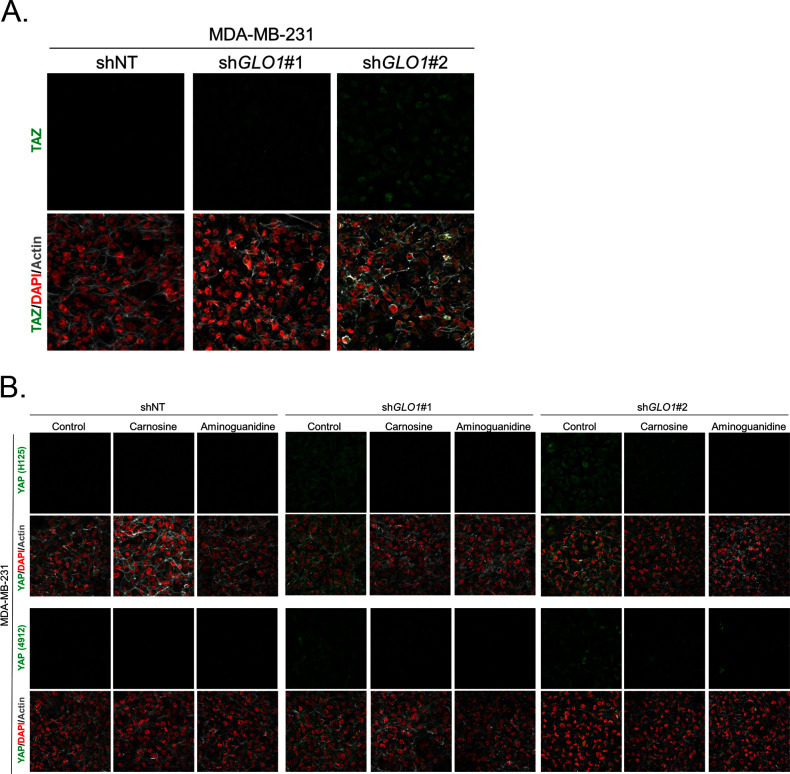
Figure 4. YAP cellular accumulation in shGLO1 MDA-MB-231 clones.
(A) GLO1 mRNA, (B) protein and (C) activity level in MDA-MB-231 shNT control and shGLO1#1 and #2. (D) YAP immunofluorescence (Santa Cruz antibody, H125) in MDA-MB-231 silenced for GLO1 (shGLO1#1 and #2) cultured from low to high density. Detection of MG was performed using MBo-specific fluorescent probe. Data are representative of three independent experiments. Magnification 630x. Zoomed pictures are shown when indicated. (E) Quantification of nuclear YAP corresponding to D experiment. All data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett post-test and shown as the mean values ± SEM of at least three independent experiments. *p<0.05, **p<0.01 and ***p<0.001.