Abstract
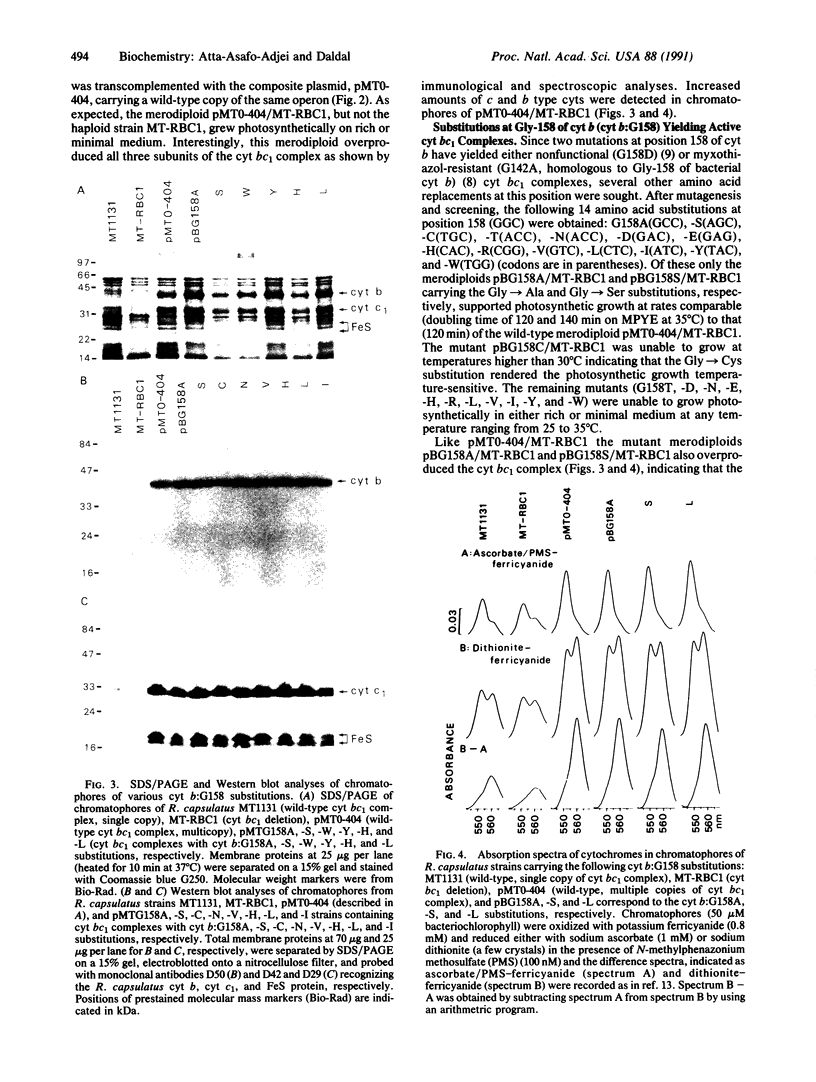
The nonphotosynthetic mutant R126 of Rhodobacter capsulatus has a cytochrome (cyt) bc1 complex (EC 1.10.2.2) with a defective quinol oxidation Qz(o,p) site but a functional quinone reduction Qc(i,n) site. Genetic analyses of this mutant have indicated that a single-base-pair change has replaced Gly-158 of cyt b with Asp. In this work, Gly-158 was changed by oligonucleotide-mediated mutagenesis to several other amino acids to define its role on quinol oxidation catalyzed by the cyt bc1 complex. The effects of the mutations were analyzed by measuring the photosynthetic growth rate of mutants and the activity of their cyt bc1 complexes. The mutants overproduced the cyt bc1 complex, assembled its subunits, and incorporated its prosthetic groups as shown by immunoblotting and optical difference spectroscopy. Of 14 amino acid residues tested at position 158 of cyt b all but alanine and serine resulted in a marked decrease of cyt bc1 activity and failed to support photosynthetic growth of R. capsulatus. The photosynthesis-competent mutants, Gly-158----Ala and Gly-158----Ser, had lower cyt bc1 complex activities that were resistant to myxothiazol, but not to stigmatellin, quinol oxidation inhibitors. These findings indicated that the specific role of Gly-158 of cyt b on quinol oxidation and myxothiazol binding may be related to the small size of its side chain and are discussed in terms of the structure and function of the quinol oxidation site of the cyt bc1 complex.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen J. P., Feher G., Yeates T. O., Komiya H., Rees D. C. Structure of the reaction center from Rhodobacter sphaeroides R-26: the protein subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6162–6166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLAYTON R. K. TOWARD THE ISOLATION OF A PHOTOCHEMICAL REACTION CENTER IN RHODOPSEUDOMONAS SPHEROIDES. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Nov 29;75:312–323. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90618-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daldal F., Cheng S., Applebaum J., Davidson E., Prince R. C. Cytochrome c(2) is not essential for photosynthetic growth of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2012–2016. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
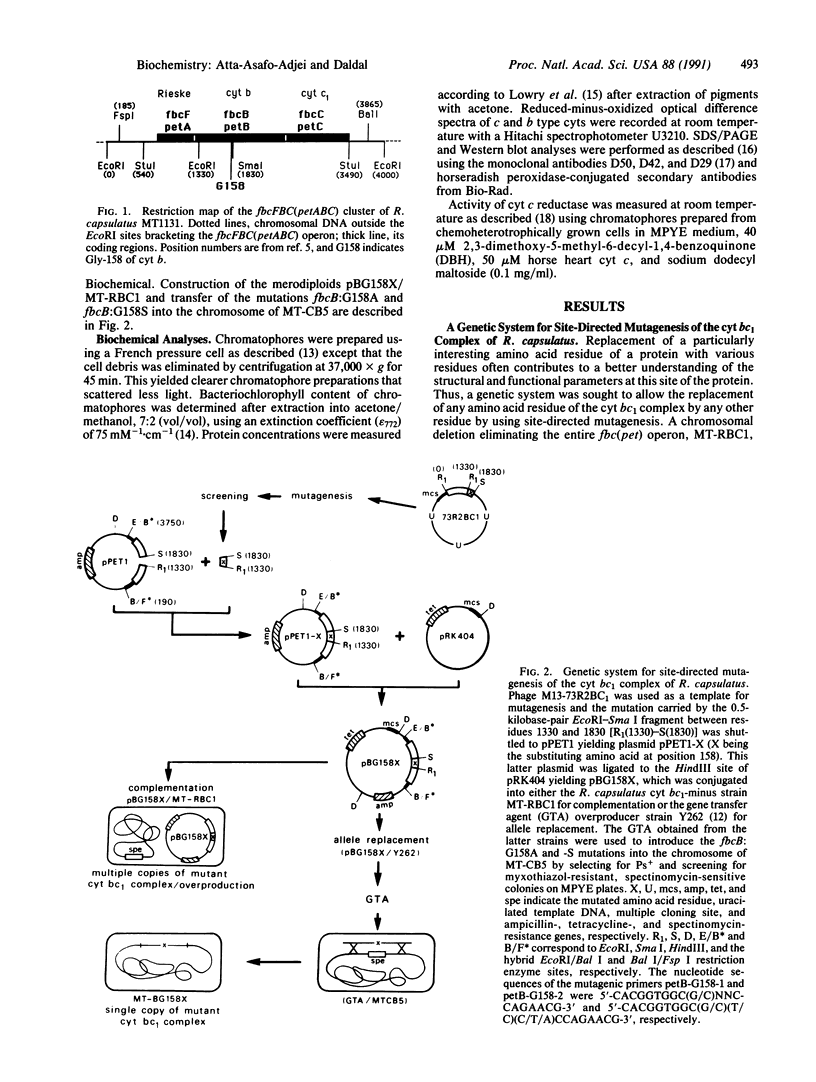
- Daldal F., Davidson E., Cheng S. Isolation of the structural genes for the Rieske Fe-S protein, cytochrome b and cytochrome c1 all components of the ubiquinol: cytochrome c2 oxidoreductase complex of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. J Mol Biol. 1987 May 5;195(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90322-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daldal F., Tokito M. K., Davidson E., Faham M. Mutations conferring resistance to quinol oxidation (Qz) inhibitors of the cyt bc1 complex of Rhodobacter capsulatus. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):3951–3961. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08578.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E., Daldal F. Primary structure of the bc1 complex of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. Nucleotide sequence of the pet operon encoding the Rieske cytochrome b, and cytochrome c1 apoproteins. J Mol Biol. 1987 May 5;195(1):13–24. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90323-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabellini N., Sebald W. Nucleotide sequence and transcription of the fbc operon from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. Evaluation of the deduced amino acid sequences of the FeS protein, cytochrome b and cytochrome c1. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Feb 3;154(3):569–579. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09437.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauska G., Nitschke W., Herrmann R. G. Amino acid identities in the three redox center-carrying polypeptides of cytochrome bc1/b6f complexes. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1988 Apr;20(2):211–228. doi: 10.1007/BF00768395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell N., Gilbert K. Mutational analysis of the mouse mitochondrial cytochrome b gene. J Mol Biol. 1988 Oct 5;203(3):607–618. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90195-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson D. E., Davidson E., Prince R. C., van den Berg W. H., Marrs B. L., Dutton P. L. Discrete catalytic sites for quinone in the ubiquinol-cytochrome c2 oxidoreductase of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. Evidence from a mutant defective in ubiquinol oxidation. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):584–591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinning I., Michel H., Mathis P., Rutherford A. W. Characterization of four herbicide-resistant mutants of Rhodopseudomonas viridis by genetic analysis, electron paramagnetic resonance, and optical spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1989 Jun 27;28(13):5544–5553. doi: 10.1021/bi00439a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trumpower B. L., Edwards C. A. Purification of a reconstitutively active iron-sulfur protein (oxidation factor) from succinate . cytochrome c reductase complex of bovine heart mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8697–8706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen H. C., Hu N. T., Marrs B. L. Characterization of the gene transfer agent made by an overproducer mutant of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jun 25;131(2):157–168. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90071-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- di Rago J. P., Coppée J. Y., Colson A. M. Molecular basis for resistance to myxothiazol, mucidin (strobilurin A), and stigmatellin. Cytochrome b inhibitors acting at the center o of the mitochondrial ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14543–14548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Jagow G., Link T. A. Use of specific inhibitors on the mitochondrial bc1 complex. Methods Enzymol. 1986;126:253–271. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(86)26026-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]