Activation of mast cells through IgE and antigen triggers the release of secretory granules that contain factors responsible for anaphylactic responses. Munoz et al. show that kinesin-1 regulates mast cell degranulation through PI3K-dependent formation of a kinesin-1/Slp3/Rab27b complex.
Abstract
Cross-linking of mast cell (MC) IgE receptors (FcεRI) triggers degranulation of secretory granules (SGs) and the release of many allergic and inflammatory mediators. Although degranulation depends crucially on microtubule dynamics, the molecular machinery that couples SGs to microtubule-dependent transport is poorly understood. In this study, we demonstrate that mice lacking Kif5b (the heavy chain of kinesin-1) in hematopoietic cells are less sensitive to IgE-mediated, passive, systemic anaphylaxis. After IgE-induced stimulation, bone marrow–derived MCs from Kif5b knockout mice exhibited a marked reduction in SG translocation toward the secretion site. In contrast, a lack of Kif5b did not affect cytokine secretion, early FcεRI-initiated signaling pathways, or microtubule reorganization upon FcεRI stimulation. We identified Slp3 as the critical effector linking kinesin-1 to Rab27b-associated SGs. Kinesin-1 recruitment to the Slp3/Rab27b effector complex was independent of microtubule reorganization but occurred only upon stimulation requiring phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) activity. Our findings demonstrate that PI3K-dependent formation of a kinesin-1/Slp3/Rab27b complex is critical for the microtubule-dependent movement of SGs required for MC degranulation.
Introduction
Mast cells (MCs) are granulated cells of hematopoietic lineage that house most tissues in the body. These cells are present in especially large numbers under epithelial and mucosal surfaces exposed to the external environment (such as the skin, the airways, and the intestine). Although MCs are key effectors in innate immunity, they also play a harmful role in allergies—the most serious manifestation of which is anaphylaxis (Galli et al., 2005a,b).
MCs express several receptors on their surface, including the high-affinity IgE receptor (FcεRI) responsible for allergic triggering (Beghdadi et al., 2011). Within minutes of the cross-linking of receptor-bound IgE by a specific, multivalent antigen or allergen, the MCs’ stored secretory granules (SGs) degranulate and release a variety of inflammatory mediators (including proteases, proteoglycans, lysosomal enzymes such as β-hexosaminidase, and biogenic amines such as histamine and serotonin). This is followed (within 15–30 min) by the synthesis of lipid mediators, such as leukotrienes and prostaglandins, and (after several hours) by the de novo synthesis and secretion of cytokines and chemokines that mediate the inflammatory response (Blank and Rivera, 2004; Blank et al., 2014; Wernersson and Pejler, 2014).
Degranulation is accompanied by the extensive reorganization of the cytoskeleton associated with membrane ruffling and spreading (Dráber and Dráber, 2015). The degranulation process also involves the anterograde movement of SGs toward the plasma membrane, where they fuse to release their contents. It has been shown that the FcεRI-mediated anterograde movement of SGs depends on microtubule dynamics (Nishida et al., 2005). This involves the activation of a Fyn/Gab2/RhoA signaling pathway but is independent of calcium influx (Nishida et al., 2005, 2011). Further studies have highlighted a role for ARF1 after activation by Fyn and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K; recruited via Gab2; Nishida et al., 2011). More recently, DOCK5, Nck2, and Akt (a downstream effector of PI3K) have been shown to regulate microtubule dynamics in MCs (Ogawa et al., 2014). This involved the Akt-mediated inactivation of glycogen synthase kinase 3 β (GSK3β), which promotes microtubule assembly. However, the molecular machinery that links the trafficking of SGs to microtubule dynamics in MCs has yet to be well characterized.
There are some data on the mechanism that controls the fusion between SGs and between SGs and the plasma membrane in MCs. It includes SNAREs (such as syntaxin 3 [STX3], STX4, SNAP-23, and VAMP8) and the accessory molecule Munc18-2 (Tiwari et al., 2008; Lorentz et al., 2012; Brochetta et al., 2014). The small GTPases Rab27a and (especially) Rab27b are also involved in MC degranulation (Mizuno et al., 2007). It has been shown that the GTP-bound forms of Rab27a and Rab27b recruit effectors of the synaptotagmin-like protein family (Slp1/JFC1, Slp2a, Slp3, Slp4/granuphilin, and Slp5), which are involved in the trafficking and docking of secretory vesicles in various cell types (Fukuda et al., 2002; Kuroda et al., 2002; Ménasché et al., 2008). Members of the Slp family share an N-terminal Rab27-binding Slp homology domain and a C-terminal phospholipid binding tandem C2 domain.
In cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) and in neurons, we and others have reported that the plus end movement of cytotoxic granules and synaptic vesicles, respectively, is mediated by the microtubule-dependent motor protein kinesin-1 (Arimura et al., 2009; Kurowska et al., 2012). A Rab27a/Slp3/kinesin-1 complex was shown to regulate cytotoxic granule transport in CTLs, whereas a Rab27b/Slp1/CRMP-2/kinesin-1 molecular complex is involved in the anterograde transport of synaptic vesicles in neurons (Arimura et al., 2009; Kurowska et al., 2012). Kinesin-1 (the archetypal member of the kinesin superfamily) is a tetrameric protein composed of two heavy chains (KIF5A, KIF5B, or KIF5C) and two kinesin light chains (KLCs; KLC1, KLC2, KLC3, or KLC4; Hirokawa, 1998). KIF5B and KLC1 are ubiquitously distributed and mediate the plus end–directed, microtubule-dependent transport of cargoes. The targeted inactivation of Kif5b in pancreatic β cells revealed a key role for kinesin-1 in insulin secretion (Cui et al., 2011). The study of another mouse model in which Kif5b had been specifically inactivated in myogenic cells revealed that kinesin-1 has an important role in the anterograde transport of key elements required for myofibril assembly (including α-sarcomeric actin, myosin IIB, nestin, and desmin; Wang et al., 2013).
To characterize the function of kinesin-1 in MC degranulation, we crossed the Kif5bfl/− mouse (Cui et al., 2011) with the VAV1-Cre mouse. The Kif5bfl/−;VAV1-CRE conditional knockout (cKOKif5b) offspring lack Kif5b in all their hematopoietic lineages, including MCs. These mice display no obvious abnormal development of the lymphoid and myeloid lineages. Here, we demonstrate that kinesin-1 regulates FcεRI-mediated MC degranulation both in vitro and in vivo. We further identify the molecular complex and a signaling pathway downstream of PI3K that enable SGs to be recruited to kinesin-1.
Results
Kif5b is expressed in MCs and is not required for MC differentiation
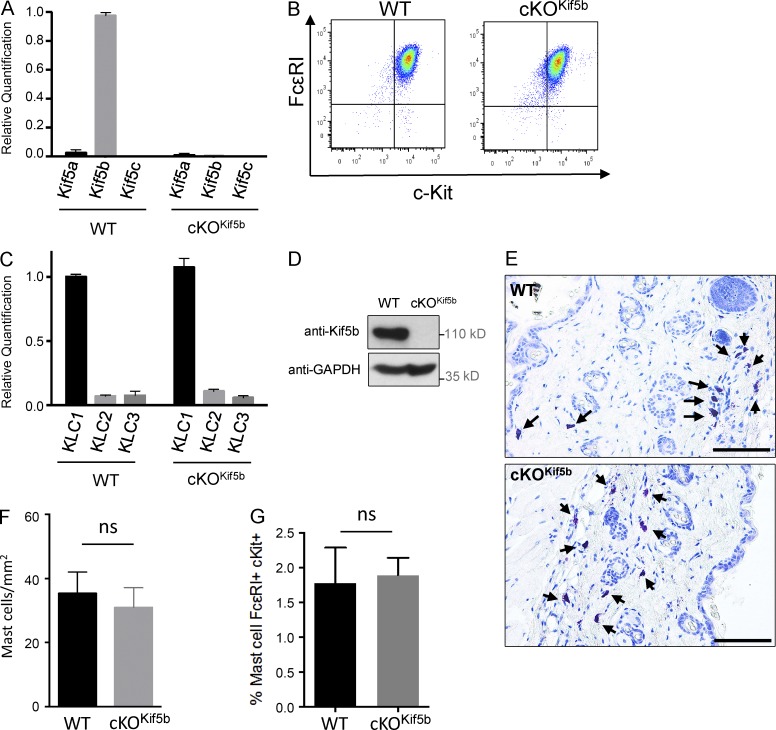
To explore the molecular machinery involved in the anterograde transport of SGs during MC degranulation, we focused on Kif5b (the gene coding for the major heavy chain isoform of kinesin-1 expressed in murine MCs; Fig. 1 A). We generated the cKOKif5b mouse model, which lacks Kif5b in all hematopoietic cell lineages. In the absence of Kif5b, bone marrow progenitors differentiated normally into MCs in the presence of IL-3 and stem cell factor. Expression levels of the MC-specific markers FcεRI and c-Kit were similar when comparing wild-type (WT) and cKOKif5b bone marrow–derived MCs (BMMCs; Fig. 1 B). We confirmed that Kif5b was absent in cKOKif5b BMMCs, and we did not observe compensatory up-regulation of the other isoforms (Fig. 1 A). As kinesin-1 is a tetramer composed of two heavy chains and two light chains, we analyzed light chain expression in BMMCs. Quantitative real-time PCR assays of the three KLCs (KLC1, KLC2, and KLC3) showed that KLC1 was the main isoform present in BMMCs (Fig. 1 C). We next confirmed the absence of Kif5b protein in cKOKif5b BMMCs (Fig. 1 D). In vivo, WT and cKOKif5b samples did not differ significantly in terms of the MC counts in the skin of the back (in a toluidine blue staining; Fig. 1, E and F) or in the peritoneal cavity (detected using flow cytometry; Fig. 1 G). This finding indicates that kinesin-1 is not essential for MC survival or tissue targeting. Collectively, these results show that Kif5b deficiency does not affect MC development in vitro or in vivo.
Figure 1.
Kif5 expression in BMMCs and cKOKif5b MC maturation. (A) Relative quantification of Kif5a, Kif5b, and Kif5c transcripts by real-time PCR in BMMCs from WT and cKOKif5b mice. Transcript levels for each sample were expressed as a proportion of the mean value for Kif5b. The data are representative of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. (B) Expression of FcεRI and c-Kit on BMMCs from WT and cKOKif5b mice, as determined by flow cytometry. (C) Relative quantification of KLC1, KLC2, and KLC3 transcripts by real-time PCR in BMMCs from cKOKif5b and WT mice. Transcript levels for each sample were expressed as a proportion of the mean value for KLC1. The data are representative of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. (D) WT and cKOKif5b BMMC lysates were separated by SDS-PAGE and were immunoblotted with anti-Kif5b and anti-GAPDH antibodies. The blots are representative of three independent experiments. (E) Toluidine blue staining of MCs in the back skin of WT and cKOKif5b mice. Arrows indicate MCs. Bars, 100 µm. (F) The corresponding absolute MC counts per millimeter squared (mean ± SD). Three histological sections per animal were analyzed for WT (n = 3) and cKOKif5b (n = 3) mice. (G) Flow cytometry determination of the proportion of c-Kit– and FcεRI-expressing peritoneal MCs obtained from WT (n = 5) and cKOKif5b (n = 5) mice. Error bars represent SD. ns, not significant.
Kinesin-1 regulates SG degranulation in MCs in vitro and in vivo
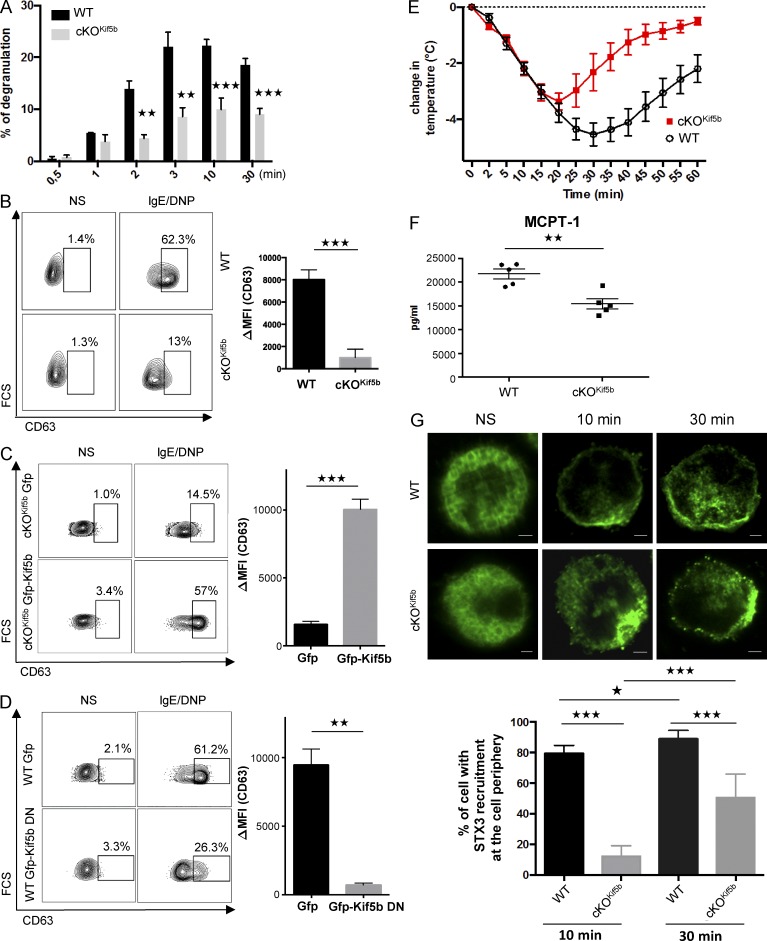
To determine the role of kinesin-1 in stimulus–secretion coupling in MCs, WT and cKOKif5b BMMCs were sensitized with anti–DNP-IgE antibody before stimulation with DNP–human serum albumin (HSA). Time course experiments showed that within minutes, FcεRI-mediated BMMC activation induced degranulation (as measured by the release of β-hexosaminidase from SGs). Kif5b-deficient BMMCs exhibited a markedly impaired ability to degranulate upon FcεRI activation (Fig. 2 A). Likewise, when degranulation was assessed by measuring the exposure of CD63 at the cell surface upon IgE/Ag stimulation as described previously (Brochetta et al., 2014), we confirmed that Kif5b-deficient BMMCs expressed much lower levels than WT cells (Fig. 2 B). We also performed rescue experiments by reexpression of Kif5b in mutant BMMCs. As expected, reintroduction of Kif5b corrected the defective degranulation in Kif5b-deficient BMMCs (Fig. 2 C). Conversely, expression of a dominant-negative (DN) mutant of Kif5b (GFP-Kif5b DN; Kimura et al., 2005) lacking the kinesin ATPase motor domain of kinesis heavy chain in WT BMMCs inhibited IgE/Ag-stimulated secretion (Fig. 2 D).
Figure 2.
The absence of Kif5b impairs MC degranulation in vitro and in vivo. (A) Release of β-hexosaminidase from IgE-sensitized WT and cKOKif5b BMMCs, as induced by 20 ng/ml DNP-HSA and determined at the indicated time points. Results are quoted as the mean ± SD of 10 experiments. (B) IgE-sensitized WT and cKOKif5b BMMCs were either not stimulated or were stimulated with 20 ng/ml DNP-HSA for 10 min. Cells were fixed, and the cell surface expression of CD63 (as a surrogate marker of degranulation) was determined by flow cytometry (left) and quantified (ΔMFI CD63+; right). (C) GFP or GFP-Kif5b was transfected in Kif5b-deficient BMMCs. GFP+ BMMCs were then assessed for CD63 expression using flow cytometry (left), and expression was quantified (ΔMFI CD63+; right). (D) GFP or GFP-Kif5b DN was transfected in WT BMMCs. GFP+ BMMCs were then assessed for CD63 expression using flow cytometry (left), and expression was quantified (ΔMFI CD63+; right). (E) WT (n = 5) and cKOKif5b (n = 5) mice were passively sensitized with 1 µg/g anti-DNP IgE antibody. 24 h later, mice were challenged with (500 µg) DNP-HSA. Systemic anaphylaxis was determined from the change in body temperature. (F) Serum MCPT-1 levels in WT (n = 5) and cKOKif5b (n = 5) mice, measured 60 min after the DNP-HSA challenge. (G, top) IgE-sensitized WT and cKOKif5b BMMCs were plated on fibronectin-coated glass coverslips and then stimulated by the addition of 20 ng/ml DNP-HSA for the indicated times. NS, nonstimulated. Cells were then fixed, permeabilized, and stained with anti-STX3. Bars, 2 µm. (Bottom) The percentage of cells with STX3 recruitment to the periphery of the cell. In each individual experiment in the nonstimulated condition (n = 3), stimulated condition for 10 min (n = 3), and stimulated condition for 30 min (n = 3), >100 cells distributed in different areas of the glass coverslip were counted. Statistical analyses were performed using unpaired t tests. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.005; ***, P < 0.0001.
To assess kinesin-1’s role in MC degranulation in vivo, we performed passive systemic anaphylaxis experiments. 24 h after sensitization with anti-DNP IgE antibody, WT and cKOKif5b mice were challenged with DNP-HSA. The body temperature was recorded, and the serum level of MC-specific protease-1 (MCPT-1) was assayed as an index of the severity of the anaphylactic response. As shown in Fig. 2 E, the body temperature drop was less pronounced in cKOKif5b mice than in WT mice (notably during the later phases). Likewise, cKOKif5b mice had lower serum levels of MCPT-1 at 60 min (relative to WT mice), indicating that Kif5b-deficient MCs were impaired in their capacity to degranulate in vivo (Fig. 2 F).
To explore whether or not the absence of kinesin-1 in BMMCs affected SG translocation, we compared the distribution of SGs in resting cells and stimulated cells (at 10 and 30 min) using an anti-STX3 antibody. In resting BMMCs, there was no difference in the SG distribution between WT and cKOKif5b samples (Fig. 2 G). In stimulated BMMCs, however, we observed a marked difference. 10 min after stimulation through FcεRI, at least 80% of STX3 was located at the cell periphery in WT BMMCs (indicating significant SG translocation and fusion with the plasma membrane), whereas only 15% of STX3 was found at the cell periphery in cKOKif5b BMMCs (Fig. 2 G). After 30 min of activation, the proportion of cKOKif5b BMMCs in which SGs had reached the cell periphery had risen to 50%, but was still lower than in WT BMMCs (Fig. 2 G). These results indicate that kinesin-1 is the molecular motor that enables SGs to translocate to the plasma membrane and secrete their contents.
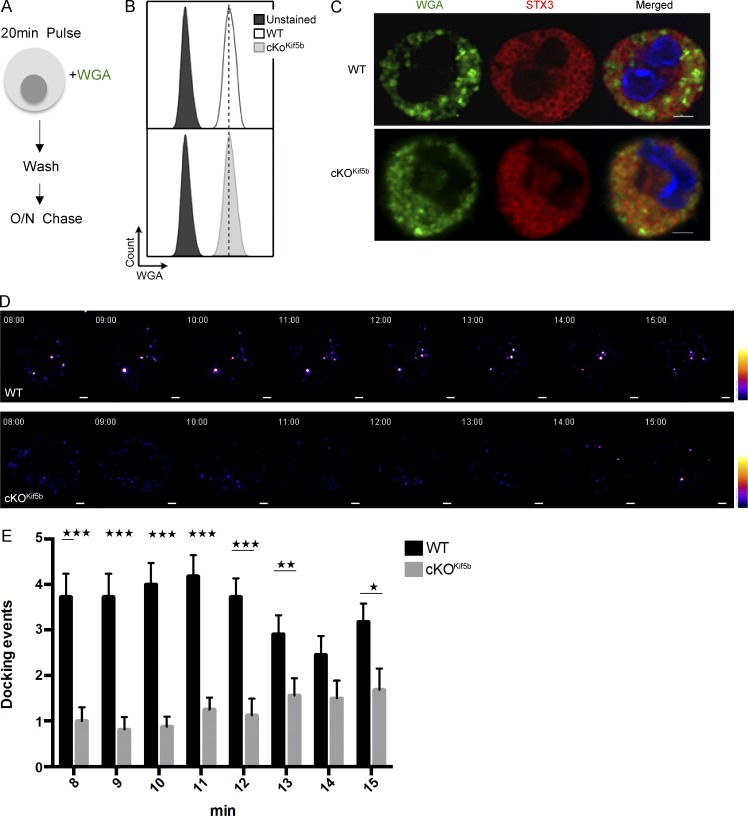
To confirm and extend these findings, we used live cell imaging with total internal reflection fluorescence (TIRF) microscopy to analyze the time course of SG recruitment to the plasma membrane upon FcεRI activation. We found that after a brief period of endocytosis, WGA (previously used to label cytotoxic granules in CTLs; Sepulveda et al., 2015) constitutes a valuable marker of SGs in live BMMCs. The BMMCs were pulsed for 20 min with Alexa Fluor 488 (green)–conjugated WGA and then chased for 18 h (Fig. 3 A). WGA uptake was similar in WT and cKOKif5b BMMCs (Fig. 3 B). The WGA was present in the lumen of STX3-positive SGs (Fig. 3 C) and so probably labeled intraluminal vesicles (as previously shown for cytotoxic granules; Sepulveda et al., 2015). Upon WGA loading, BMMCs were sensitized with anti–DNP-IgE antibody and placed on fibronectin-coated glass coverslips. Immediately after the addition of DNP-HSA, TIRF microscopy images were acquired for 15 min. In WT BMMCs, SG docking events were first viewed 8 min after stimulation and continued until the end of the acquisition (Video 1 and Fig. 3, D and E). In contrast, very few SG docking events were detectable in cKOKif5b BMMCs until 13 min after stimulation. However, the number of docking events in cKOKif5b BMMCs was much lower than in WT BMMCs (Video 2 and Fig. 3, D and E). These results indicate that kinesin-1 controls translocation of SGs to the secretion site.
Figure 3.
The dynamic recruitment of SGs to the plasma membrane upon FcεRI activation is impaired in the absence of Kif5b. (A) Schematic representation of the WGA labeling protocol for BMMCs. WT and cKOKif5b BMMCs were pulsed with Alexa Fluor 488–conjugated WGA and washed. An 18-h chase was then performed. (B) According to flow cytometry, WGA uptake was equivalent in WT and cKOKif5b BMMCs. (C) WT and cKOKif5b BMMCs were labeled with WGA-488 and plated on fibronectin-coated glass coverslips. Cells were then fixed, permeabilized, and stained with anti-STX3. (D) TIRF video microscopy was performed on IgE-sensitized WT and cKOKif5b BMMCs labeled with WGA-488 (green) and then plated on fibronectin-coated glass coverslips. The addition of 20 ng/ml DNP-HSA represents t = 0 of the acquisition. Representative series of images are shown every minute, from 8 to 15 min. A pseudocolor scale from blue (very weak intensity) to white (highest intensity) was used to indicate the intensity of TIRF staining. A WGA-containing granule was defined by a minimum of a square of 3 × 3 pixels (1 pixel = 0.16 µm) of strong intensity signal (orange to white intensity). Also see Videos 1 and 2. (E) The number of docking events per cell acquired with TIRF microscopy, from 8 min to 15 min of the acquisition. Statistical analyses were performed using unpaired t tests. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.005; ***, P < 0.0001. 20 cells were analyzed for each condition in a total of four independent experiments. Error bars represent mean ± SD. Bars, 2 µm.
Kinesin-1 is not essential for early signaling and cytokine secretion upon FcεRI stimulation
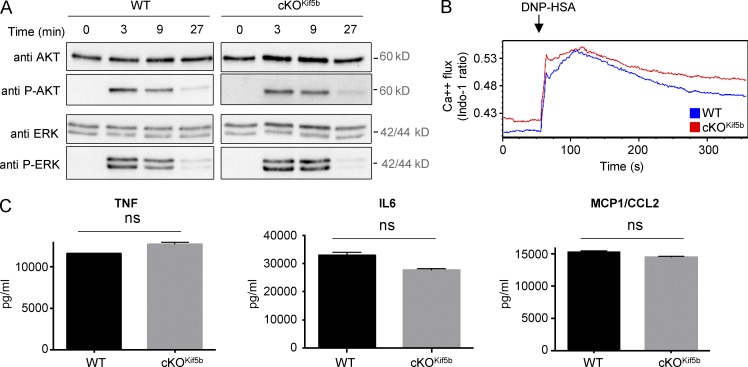
We next looked at whether functional kinesin-1 was required for early signaling pathways. WT and Kif5b-deficient BMMCs did not differ significantly in terms of Erk and Akt phosphorylation (Fig. 4 A) or calcium influx (Fig. 4 B). These results indicate that the degranulation defect observed in the Kif5b-deficient BMMCs is not caused by impaired signaling downstream of FcεRI activation.
Figure 4.
Proximal signaling and cytokine secretion upon FcεRI activation is not affected in Kif5b-deficient BMMCs. (A) IgE-sensitized WT and cKOKif5b BMMCs were stimulated with DNP-HSA for the indicated times, lysed, and then assayed for total and phosphorylated Akt and Erk by Western blotting. Data are representative of two independent experiments. (B) IgE-sensitized WT and cKOKif5b BMMCs were loaded with indo-1 and stimulated with DNP-HSA. The fluorescence emission ratio for Ca2+-bound/Ca2+-free indo-1 was measured for the indicated period of time. Similar results were obtained in three independent experiments. (C) TNF, IL-6, and CCL2 (MCP1) secretion were determined in ELISA. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD of triplicate samples and are representative of two independent experiments. ns, not significant.
Because FcεRI receptor aggregation also leads to de novo synthesis and secretion of cytokines, we next sought to determine whether or not Kif5b-deficient BMMCs could produce and secrete proinflammatory cytokines such as TNF, IL-6, and CCL2 (also known as MCP1). After 3 h of stimulation through FcεRI, there were no apparent differences in cytokine secretion between WT and Kif5b-deficient BMMCs (Fig. 4 C). These results indicate that kinesin-1 is not essential for cytokine secretion upon FcεRI activation.
Characterization of the kinesin-1–dependent transport machinery in MCs
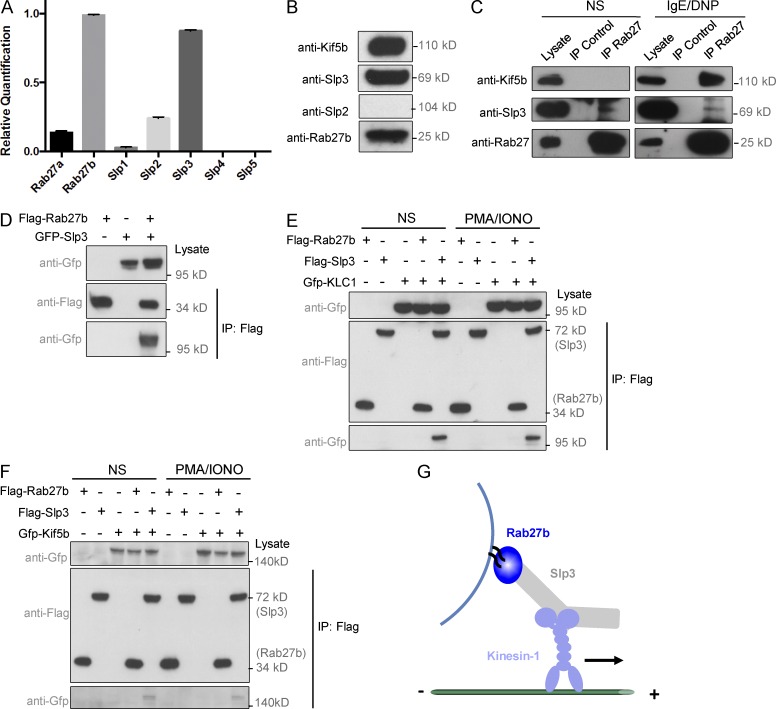
Given that kinesin-1 has been shown to regulate the transport of Rab27/Slp-associated vesicles on microtubules, and that Rab27b is involved in MC degranulation (Mizuno et al., 2007; Arimura et al., 2009; Kurowska et al., 2012), we further explored the molecular machinery of kinesin-1–dependent SG transport in MCs. In line with literature data on defective secretion by MCs in Rab27b mice but not in Rab27a knockout mice (Mizuno et al., 2007), we found that Rab27b was the main Rab27 family member expressed in BMMCs, whereas Rab27a was only expressed at low levels (Fig. 5 A). When the expression of the five members of the Slp family was analyzed, only Slp3 was found to be highly expressed in BMMCs; Slp2 was expressed to a much lesser extent (Fig. 5 A). Because Slp2 protein could not be detected in BMMC lysate (Fig. 5 B), we investigated Slp3’s contribution to the kinesin-1–dependent transport machinery. Fig. 5 C shows that Slp3 coimmunoprecipitated with Rab27b in both unstimulated and FcεRI-stimulated cells. Interestingly, Kif5b coimmunoprecipitated with Rab27b strongly in stimulated cells but not at all in unstimulated cells (Fig. 5 C).
Figure 5.
Characterization of the kinesin-1–dependent transport machinery in MCs. (A) Relative quantification of Rab27a, Rab27b, Slp1, Slp2, Slp3, Slp4, and Slp5 transcripts in BMMCs, using real-time PCRs. Transcript levels for each sample were expressed as a proportion of the mean value for Rab27b. (B) BMMCs were lysed and then analyzed by Western blotting with anti-Kif5b, anti-Slp2, anti-Slp3, and anti-Rab27 antibodies. (C) IgE-sensitized WT BMMCs were either not stimulated (NS) or were stimulated with 20 ng/ml DNP-HSA for 10 min and then lysed. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated (IP) with a polyclonal anti-Rab27 antibody or with an isotype control antibody. The immunoblots were analyzed using anti-Kif5b, anti-Slp3, and anti-Rab27 antibodies. (D) Flag-Rab27b and GFP-Slp3 were coexpressed in HEK 293T cells. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag antibody (M2 beads) and then separated by SDS-PAGE. Coprecipitated Rab27b and Slp3 were immunoblotted with anti-Flag and anti-GFP. (E) Flag-Rab27b, -Slp3, and GFP-KLC1 were coexpressed in HEK 293T cells. Cells were either not stimulated or were stimulated with PMA/ionomycin, and then cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag antibody (M2 beads) and separated by SDS-PAGE. Coprecipitated Rab27b or Slp3 and KLC1 were immunoblotted with anti-Flag and anti-GFP. (F) Flag-Rab27b, -Slp3, and GFP-Kif5b were coexpressed into HEK 293T cells. Cells were either not stimulated or were stimulated with PMA/ionomycin, and then cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag antibody (M2 beads) and separated by SDS-PAGE. Coprecipitated Rab27b or Slp3 and Kif5b were immunoblotted with anti-Flag and anti-GFP antibodies. Data in C–F are representative of three independent experiments. (G) Schematic diagram of the heterotrimeric protein transport complex involved in the translocation of SGs upon activation.
To understand which proteins in the complex were able to interact with each other, we overexpressed different combinations of tagged proteins in HEK 293T cells. The strong interactions between Rab27b and Slp3 and between Slp3 and KLC1 were confirmed (Fig. 5, D and E). No interaction between Rab27b and the kinesin-1 light or heavy chains was observed (Fig. 5, E and F). In contrast, Kif5b and Slp3 showed a weak interaction (Fig. 5 F), although it was not clear whether this occurred directly or required endogenous KLC1 expressed in HEK 293T cells. In contrast to the results in MCs (Fig. 5 C), activation of HEK 293T by PMA/ionomycin did not modulate the interaction between Slp3 and kinesin-1 (Fig. 5, E and F). These data suggest that the interaction between Slp3 and kinesin-1 does not require additional modifications. Because MC activation promotes Slp3/Kif5b complex formation, this determines kinesin-1’s ability to access Slp3 (Fig. 5 G).
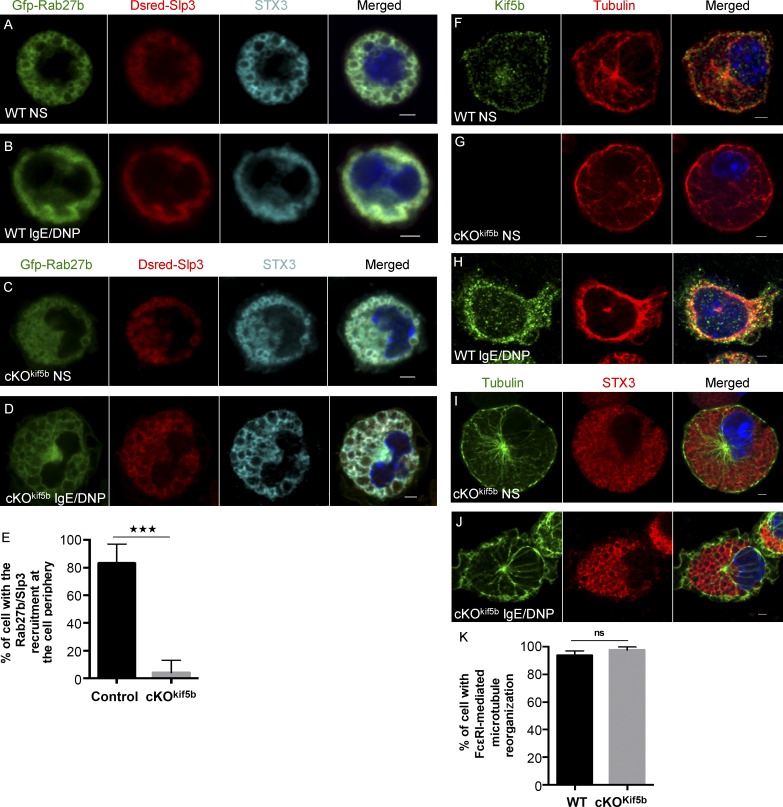
We next investigated the subcellular localization of the kinesin-1–dependent transport machinery. To this end, we engineered BMMCs to coexpress GFP-Rab27b and Dsred-Slp3. In WT BMMCs, strong overlap of the two fluorescence signals (Dsred-Slp3/GFP-Rab27b; 73.90 ± 2.54% overlap) was observed for the SGs labeled by STX3 (STX3/(GFP-Rab27b/Dsred-Slp3); 73.22 ± 5.56% overlap; Fig. 6 A). Upon FcεRI activation, the Rab27b/Slp3 complexes (DRed-Slp3/GFP-Rab27b; 80.92 ± 2.6% overlap) were recruited to the cell periphery and colocalized with STX3 (STX3/(GFP-Rab27b/Dsred-Slp3); 70.9 ± 4.7% overlap; Fig. 6 B). In Kif5b-deficient BMMCs, translocation of the Rab27b/Slp3 complex to the cell periphery was dramatically impaired upon activation (Fig. 6, C–E), as had been observed for STX3 (Fig. 2 D). This finding further supports the critical role of kinesin-1 in the transport of Rab27b/Slp3-associated SGs to the cell periphery.
Figure 6.
Subcellular localization of the kinesin-1–dependent transport machinery in MCs. (A–D) Confocal microscopy of WT or Kif5b-deficient BMMCs transfected with GFP-Rab27b and Dsred-Slp3 and labeled with anti-STX3 antibody in resting cells (A and C) or in cells stimulated by the addition of 20 ng/ml DNP-HSA for 10 min (B and D). (E) The statistical analysis of experiments in B and D was performed using an unpaired t test. ***, P < 0.0001. More than 30 cells were counted per setting. (F–J) IgE-sensitized WT (F and H) and cKOKif5b (G, I, and J) BMMCs were plated on fibronectin-coated glass coverslips and either were not stimulated (F, G, and I) or were stimulated by the addition of 20 ng/ml DNP-HSA for 10 min (H and J). Cells were then fixed, permeabilized, and stained with an anti-tubulin antibody and an anti-Kif5b or anti-STX3 antibody. Bars, 2 µm. All images of single cells are representative of >100 cells observed over at least three independent experiments. (K) Statistical analysis of microtubule reorganization at the plasma membrane identified by filopodia-like extension shape in experiments in H and J was performed using an unpaired t test. More than 100 cells were counted per setting. NS, not stimulated.
The endogenous Kif5b was mainly distributed along the microtubules, with strong labeling beneath the plasma membrane and (to a lesser extent) in the cytosol and around the microtubule-organizing center (Fig. 6 F). The Kif5b-deficient MCs did not display any Kif5b labeling, confirming the antibody’s specificity (Fig. 6 G). Upon FcεRI activation, Kif5b in WT cells was predominantly recruited to the peripheral tubulin ring beneath the plasma membrane (an area of the cell that is rich in newly formed microtubules leading to filopodia-like extensions; Fig. 6 H). Microtubule organization did not seem to be affected by the absence of Kif5b in either unstimulated or stimulated cells (Fig. 6, G and I–K), and microtubules formed normally upon FcεRI activation (Fig. 6, J and K).
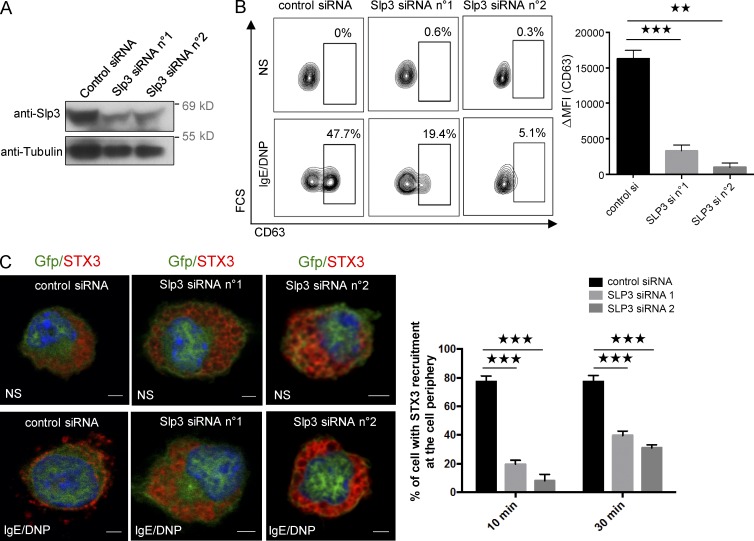
Because our results indicated that Slp3 links Rab27b-associated SGs to kinesin-1 upon FcεRI activation, we further analyzed Slp3’s involvement in SG secretion by using siRNAs to specifically knock down Slp3 in BMMCs. The high efficacy of Slp3 knockdown was confirmed by Western blotting (Fig. 7 A). The BMMCs’ ability to degranulate after Slp3 knockdown was assessed by measuring the membrane expression of CD63. Likewise, Slp3 silencing substantially impaired SG secretion (Fig. 7 B). We next looked at whether the secretion defect resulting from Slp3 silencing was also associated with a defect in SG translocation. In unstimulated Slp3-silenced BMMCs, STX3’s localization was essentially the same as in BMMCs expressing control siRNA (Fig. 7 C). In contrast, Slp3-silenced BMMCs were unable to translocate their STX3-containing SGs to the plasma membrane upon stimulation through FcεRI, whereas translocation did occur in BMMCs expressing control siRNA (Fig. 7 C). These data demonstrate that Slp3 is part of the molecular machinery that couples microtubule dynamics and SG translocation to the plasma membrane upon FcεRI activation.
Figure 7.
Role of Slp3 in SG degranulation. (A) BMMCs were electroporated with siRNAs targeting Slp3 (n°1 or n°2) or with control siRNA. Transfected BMMCs were lysed and analyzed by Western blotting using anti-Slp3 and antitubulin as a loading control. (B) Control or Slp3 siRNA n°1 or Slp3 siRNA n°2 was cotransfected with GFP alone. GFP+ BMMCs were then assessed for CD63 expression using flow cytometry (left), and expression was quantified (ΔMFI CD63+; right). (C, left) BMMCs were electroporated with siRNAs targeting Slp3 (n°1 or n°2) or with control siRNA, along with GFP. IgE-sensitized electroporated BMMCs were either not stimulated, or were stimulated with 20 ng/ml DNP-HSA for 10 min. Cells were fixed, permeabilized, and stained with anti-STX3 antibody. Bars, 2 µm. (Right) In each individual experiment in the nonstimulated condition (n = 2), stimulated condition for 10 min (n = 2), and stimulated condition for 30 min (n = 2), >30 cells distributed in different areas of the glass coverslip were counted. Statistical analyses were performed using unpaired t tests. **, P < 0.005; ***, P < 0.0001. MFI, mean fluorescence intensity.
The formation of kinesin-1–dependent transport machinery is regulated by PI3K
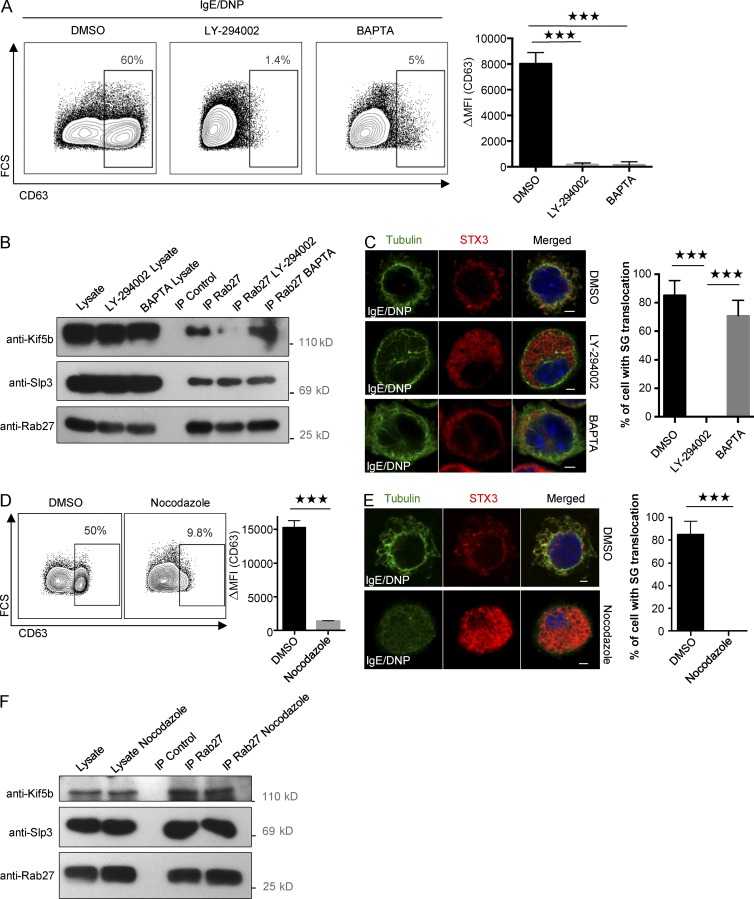
The results described previously suggested the existence of an active mechanism for recruitment of the kinesin-1–dependent transport machinery to SGs. To identify possible signaling pathways, we performed experiments with two specific inhibitors of PI3K and intracellular calcium flux (LY-294002 and BAPTA; Nishida et al., 2005, 2011). Both drugs severely impaired degranulation (Fig. 8 A). When assessing Kif5b recruitment to the granular Slp3/Rab27b effector complex upon FcεRI activation, we found that BAPTA had no effect; in contrast, treatment with LY-294002 completely disrupted Kif5b/Slp3 complex formation (Fig. 8 B). To determine whether PI3K blockade affects the coupling of SGs to microtubule-dependent translocation, we analyzed the drugs’ effect on the relocation of SG-associated STX3 to the plasma membrane upon FcεRI activation. In agreement with the uncoupling observed previously, LY-294002 dramatically impaired SG translocation to the plasma membrane, but BAPTA had no effect (Fig. 8 C; Nishida et al., 2005). As it had previously been shown that PI3K controls microtubule formation (Nishida et al., 2005), we looked at whether recruitment of kinesin-1 to the transport machinery required microtubule formation. To this end, we disrupted microtubule formation using nocodazole. As expected, nocodazole strongly impaired SG secretion (Fig. 8 D) and the translocation of SG-associated STX3 to the plasma membrane (Fig. 8 E). Interestingly, treatment with nocodazole had no effect on Kif5b/Slp3 complex formation after stimulation via FcεRI (Fig. 8 F). Taken as a whole, these results indicate that the coupling between kinesin-1 and its granular effector complex is independent of the microtubule network but does require PI3K activity.
Figure 8.
Kinesin-1–dependent transport machinery formation requires the activation of PI3K. (A) IgE-sensitized BMMCs were preincubated in normal medium containing DMSO (control), 100 µM PI3K inhibitor LY-294002, or 20 mM intracellular calcium chelator BAPTA, and then stimulated with 20 ng/ml DNP-HSA for 10 min. Cells were fixed and incubated with anti-CD63 antibody before flow cytometry analysis (left), and expression was quantified (ΔMFI CD63+; right). (B) IgE-sensitized BMMCs were preincubated in normal medium containing DMSO, LY-294002, or BAPTA. BMMCs were stimulated with 20 ng/ml DNP-HSA for 10 min and then lysed. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated (IP) with a polyclonal anti-Rab27 antibody or with isotype control antibody. The immunoblots were analyzed using anti-Kif5b, anti-Slp3, and anti-Rab27 antibodies. Data are representative of three independent experiments. (C, left) IgE-sensitized BMMCs were preincubated in medium containing DMSO, 100 µM LY-294002, or 20 mM BAPTA. BMMCs were stimulated with 20 ng/ml DNP-HSA for 10 min. Cells were fixed, permeabilized, and stained with anti-STX3 and antitubulin antibodies. (Right) More than 100 cells were counted per setting. (D) IgE-sensitized BMMCs were preincubated in normal medium containing DMSO (control) or 20 µM nocodazole and then stimulated with 20 ng/ml DNP-HSA for 10 min. Cells were fixed and incubated with anti-CD63 antibody before flow cytometry analysis (left), and expression was quantified (ΔMFI CD63+; right). (E) IgE-sensitized BMMCs were preincubated in medium containing DMSO or nocodazole. BMMCs were stimulated with 20 ng/ml DNP-HSA for 10 min. Cells were fixed, permeabilized, and stained with anti-STX3 and antitubulin antibodies (left). Bars, 2 µm. (Right) More than 100 cells were counted per setting. Statistical analyses were performed using unpaired t tests. ***, P < 0.0001. (F) IgE-sensitized BMMCs were preincubated in normal medium containing DMSO or 20 µM nocodazole. BMMCs were stimulated with 20 ng/ml DNP-HSA for 10 min before lysis. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with a polyclonal anti-Rab27 antibody or with isotype control antibody. The immunoblots were analyzed using anti-Kif5b, anti-Slp3, and anti-Rab27 antibodies. Data are representative of three independent experiments. Error bars represent mean ± SD. MFI, mean fluorescence intensity.
Discussion
MC activation by IgE and antigens triggers the release of SGs containing the preformed mediators responsible for anaphylactic responses. Although microtubule dynamics are known to have a critical role in SG movement (Nishida et al., 2005, 2011; Ogawa et al., 2014), little is known about the molecular machinery that couples SGs to the microtubule cytoskeleton and drives the granules toward the secretion site after MC activation. Here, we provide evidence that the Kif5b heavy chain isoform of kinesin-1 is the key motor protein regulating the translocation of SGs to the plasma membrane upon FcεRI activation (and thus enabling anaphylactic degranulation) in vitro and in vivo. In contrast, Kif5b is not essential for the activation of proximal signaling pathways or the secretion of cytokines upon FcεRI stimulation. We further demonstrated that the kinesin-1 motor protein links microtubules to SGs through a newly characterized molecular machinery (composed of granule-associated Rab27b and the Slp3 adapter protein). We found that formation of this complex is highly regulated in MCs and requires stimulation through a PI3K-dependent pathway.
Several lines of evidence suggest that Kif5b is critical for SG secretion upon FcεRI activation. A lack of Kif5b dramatically impaired (a) the release of β-hexosaminidase enzyme stored in SGs, (b) the degranulation ability of BMMCs (as quantified by cell surface CD63 expression), (c) the subcellular translocation of granule-associated STX3 to the cell periphery, (d) the dynamic recruitment of SGs to the plasma membrane, and (e) the anaphylactic response in in vivo passive systemic anaphylaxis experiments. In contrast, calcium influx, proximal signaling pathways, microtubule reorganization, and cytokine secretion were independent of Kif5b function.
It is noteworthy that in the absence of Kif5b, the release of granule contents was only partially impaired in vitro and in vivo. This partial impairment may be caused by the particular type of secretion that occurs in MCs. Indeed, MCs use a degranulation process called compound or multivesicular exocytosis, during which granules undergo fusion with each other before reaching the plasma membrane (Röhlich et al., 1971). These sequential fusion events may facilitate the release of the contents of several SGs by limiting vesicle trafficking before fusion with the plasma membrane. Degranulation in MCs also occurs through SGs that have already docked at the plasma membrane and thus may not require active movement. Furthermore, we cannot rule out the possibility that kinesin family members other than kinesin-1 may regulate SG transport in MCs or partially compensate for the loss of kinesin-1.
MC activation also leads to the synthesis and secretion of cytokines and chemokines. Our data show that the secretion of TNF, IL-6, and MCP1 was not affected in Kif5b-deficient BMMCs. When considered together with data on SNARE proteins, SNARE accessory proteins, and actin regulatory proteins (such as VAMP8, Munc18-2, and Coronin1b; Tiwari et al., 2008; Föger et al., 2011; Brochetta et al., 2014), our results emphasize that cytokine secretion and SG secretion in MCs use different vesicle trafficking pathways.
To more precisely characterize the SG transport machinery, we focused on effectors of granule-localized Rab27b. This protein has previously been reported to affect MC degranulation and was also shown to link to proteins interacting with kinesins, notably through Slp adapters (Mizuno et al., 2007; Arimura et al., 2009; Kurowska et al., 2012). Among the various Slp members endogenously expressed in MCs, Slp3 was the most highly expressed. Slp3 interacted with Rab27b, and both proteins colocalized on SGs and were translocated to the plasma membrane of MCs upon FcεRI-mediated stimulation. The critical role of Slp3 in SG secretion was further demonstrated by the drastic impairment of SG secretion in Slp3-silenced cells, which resulted from a defect in SG translocation (closely mimicking the Kif5b deficiency). These data strongly suggest that Slp3 has a critical functional role in the translocation of SGs during MC degranulation.
Most interestingly, the Rab27b/Slp3 complexes in resting MCs localized to SGs labeled by STX3 but did not interact with kinesin-1. Furthermore, the recruitment of kinesin-1 to the Rab27b/Slp3 complex required MC activation. The molecular mechanism underlying kinesin-1’s interaction with the cargo receptor molecule Slp3 has not been described. Previous studies have revealed an autoinhibitory conformational mechanism used by a variety of kinesin motors, including kinesin-1 (Verhey and Hammond, 2009). The motor protein adopts a folded conformation in which nonmotor domains come into contact with the motor domain, thus blocking binding to and movement on microtubules (Verhey and Hammond, 2009). The release of autoinhibition involves cargo binding and cellular activation, which change the molecular motor’s phosphorylation status (Donelan et al., 2002; Verhey and Hammond, 2009). It has been reported that fasciculation and elongation protein-ζ1 and Jun N-terminal kinase–interacting protein 1 regulate kinesin-1 microtubule mobility by binding to inhibitory regions of kinesin-1 (Blasius et al., 2007). Similarly, phosphorylation during cell division has been shown to remove the conformational autoinhibition of members of the kinesin-5 and -7 families (Cahu et al., 2008; Espeut et al., 2008). In pancreatic β cells, elevated intracellular calcium levels induce the dephosphorylation of Kif5b by calcineurin, which thus promotes insulin secretion (Donelan et al., 2002). Overexpression of Slp3, KLC1, or Kif5b in HEK 293T cells showed that Slp3 interacts with kinesin-1 through an activation-independent mechanism. One can reasonably hypothesize that kinesin-1 adopts an autoinhibitory conformation in resting MCs, making it inaccessible for Slp3.
To identify possible signaling effectors for the formation of the kinesin-1–dependent transport complex machinery, we used specific inhibitor compounds to disrupt PI3K activation or calcium flux in response to MC activation through FcεRI. Our results show that Slp3/Kif5b complexes were not formed in the absence of PI3K activity. In contrast, complex formation was independent of intracellular calcium elevation. Our results are in agreement with a previous study showing that SG translocation to the plasma membrane is independent of calcium but depends on the dynamic reorganization of microtubules (Nishida et al., 2005). However, calcium is required for the release of SGs and controls the fusion between the SGs and the plasma membrane. Previous studies have shown that PI3K (through recruitment to the Gab2 adapter protein) has an important role in the regulation of microtubule dynamics and SG translocation in IgE-stimulated MCs (Nishida et al., 2011; Ogawa et al., 2014). This process involved the regulation of microtubule dynamics via phosphorylation and inactivation of GSK3β through Akt (a downstream effector of PI3K and ARF1; Ogawa et al., 2014). Interestingly, a previous study indicated that active GSK3 inhibited anterograde transport in neurons through the phosphorylation of KLC2 (Morfini et al., 2002). However, further studies are now required to identify which of the signaling molecules downstream of PI3K regulate kinesin-1’s accessibility to cargo receptors like Slp3. This may require investigation of kinesin-1’s phosphorylation status under unstimulated and stimulated conditions to establish whether this posttranslational modification modulates kinesin-1’s access to its cargo receptor (as has been shown for kinesin-5 and -7 families; Cahu et al., 2008; Espeut et al., 2008).
Because Kif5b deficiency did not affect microtubule organization and microtubule formation upon FcεRI-mediated stimulation, we conclude that the impairment in SG translocation is solely due to defective mobility. Interestingly, disruption of the microtubule network by nocodazole did not abolish formation of the kinesin-1–dependent transport machinery upon FcεRI-mediated stimulation, suggesting that the Kif5b/Slp3 complex forms downstream of PI3K activity but is completely independent of concomitant microtubule reorganization.
In conclusion, we used a murine cKO model (lacking Kif5b in all hematopoietic lineages) to demonstrate that kinesin-1 regulates SG transport upon FcεRI activation of MCs through the recruitment of Rab27b/Slp3 complexes. This process is regulated by PI3K after IgE-mediated stimulation. The fact that cKOKif5b mice exhibited very low levels of passive, systemic anaphylaxis suggests that kinesin-1 could be a valuable target for new therapeutic approaches for controlling IgE-mediated type I immediate hypersensitivity reactions (independent of chemokine/cytokine secretion).
Materials and methods
Reagents and antibodies
Rabbit anti-STX3 and mouse monoclonal anti–DNP-IgE antibodies have been described previously (Brochetta et al., 2014). Anti–c-Kit–allophycocyanin and anti–FcεRI-FITC were purchased from eBioscience. Rabbit Akt antibody (Cell Signaling Technology), rabbit P-Akt antibody (Cell Signaling Technology), rabbit Erk1/2 antibody (Cell Signaling Technology), rabbit P-Erk1/2 antibody (Cell Signaling Technology), mouse monoclonal Kif5b antibody (BioLegend), rabbit polyclonal Kif5b (Proteintech), rabbit polyclonal Rab27 antibody (Synaptic Systems), rabbit polyclonal Slp3 antibody (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc.), mouse monoclonal α-tubulin (Abcam), mouse GAPDH antibody (EMD Millipore), purified rabbit anti–α-tubulin (Rockland), goat Alexa Fluor 555–conjugated anti–mouse IgG F(ab’)2 secondary antibodies (Invitrogen), donkey Alexa Fluor 555–conjugated anti–rabbit IgG (H+L; Invitrogen), and goat Alexa Fluor 647–conjugated anti–rabbit IgG secondary antibodies were used. The polyclonal rabbit antibody anti-Slp2 has been described previously (Ménasché et al., 2008). Alexa Fluor 488 WGA was purchased from Invitrogen. LY-294002, BAPTA, and nocodazole were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich.
Mice
VAV-Cre transgenic mice (The Jackson Laboratory) were first crossed with Kif5b+/− to generate Kif5b+/−;VAV-Cre mice. Next, Kif5b+/−;VAV-Cre mice were bred with Kif5bfl/fl mice to generate Kif5bfl/−;VAV-Cre (cKOKif5b) mutant mice and control (WT) Kif5bfl/+ littermates. Mice were genotyped by PCR using the primers described by Cui et al. (2011). Mice were maintained in pathogen-free conditions and handled according to national and institutional guidelines.
Cell culture and transfection
Bone marrow was isolated from femurs and tibias of 8–12-wk-old mice. Cells were then cultured in Iscove's modified Dulbecco's medium (Invitrogen) supplemented with 15% heat-inactivated FCS, 1% nonessential amino acids, 1 mM sodium pyruvate, 50 µM 2-ME, 100 U/ml penicillin, 100 U/ml streptomycin, 10 ng/ml IL-3, and 10 ng/ml stem cell factor (Miltenyi Biotec). After four weeks of culture, maturation of the BMMCs (c-Kit and FcεRI expression) was checked by flow cytometry. BMMCs were transfected using the NEPA21 system (Nepagen), according to the manufacturer’s protocols.
Histology
Sections from back skin were fixed in PFA, embedded in paraffin (according to routine histology laboratory techniques), and then stained with 0.1% toluidine blue solution.
Quantitative PCR
cDNA was prepared from BMMC mRNA using Superscript II and random primers (Invitrogen). Levels of KIF5A, KIF5B, KIF5C, KLC1, KLC2, KLC3, RAB27A, RAB27B, SYTL1, SYTL2, SYTL3, SYTL4, and SYTL5 transcripts were determined in quantitative PCR assays using TaqMan Gene Expression Master Mix primer (KIF5A: Mm00515265_m1; KIF5B: Mm00515276_m1; KIF5C: Mm00500464_m1; RAB27A: Mm00469997_m1; KLC1: Mm00492936_m1; KLC2: Mm00492945_m1; KLC3: Mm00461422_m1; RAB27B: Mm00472653_m1; SYTL1: Mm00473300_m1; SYTL2: Mm01317927_m1; SYTL3: Mm00473333_m1; SYTL4: Mm00489110_m1; SYTL5: Mm00624760_m1; and 18S: Mm03928990_g1; Applied Biosystems) and cDNA. Each sample was amplified in triplicate on a real-time PCR cycler (ABI 7900) and analyzed with Sequence Detection Systems software (version 2.2.2; Applied Biosystems). The relative mRNA levels were quantified using the comparative Cτ method and normalized against the mean values of ACTB as an endogenous control. Levels of KIF5A, KIF5B, and KIF5C transcripts were then expressed as a proportion of the mean value for KIF5B. Levels of RAB27A, RAB27B, SYTL1, SYTL2, SYTL3, SYTL4, and SYTL5 transcripts were expressed as a proportion of the mean value of the gene showing the highest level of expression (arbitrarily set to 1 U).
Plasmid constructs
Mouse Rab27b was cloned into pCRII-TOPO using the primers Rab27b forward (5′-CGTCGAATTCTATGACTGATGGAGACTATGATT-3′) and reverse (5′-CGGGATCCCTAGCAGGCACATTTCTTTTC-3′). These constructs were then subcloned into pEGFP-C1 (Takara Bio Inc.). Cloning of Slp3, Kif5b, and Kif5b-DN has been previously reported (Ménasché et al., 2008; Kurowska et al., 2012).
Degranulation assays
Release of SG contents was determined in a β-hexosaminidase assay. In brief, BMMCs were sensitized overnight with an anti-DNP–specific IgE. IgE-sensitized BMMCs were stimulated with 20 ng/ml DNP-HSA for the indicated time at 37°C. Cells were centrifuged at 4°C, and supernatants were incubated in citrate buffer with p-nitrophenyl–N-acetyl–β-d-glucosaminide for 60 min at 37°C. The reaction was quenched in carbonate buffer for 15 min, and the OD was determined at 405 nm. Specific release was calculated as the percentage of total β-hexosaminidase content in a Triton X-100 cell lysate, after subtraction of baseline degranulation in nontriggered cells. Degranulation of BMMCs was also evaluated by surface expression CD63 using flow cytometry. IgE-sensitized BMMCs were either not stimulated or were stimulated with 20 ng/ml DNP-HSA for 10 min. Cells were fixed in 3.7% PFA, incubated with anti-CD63 antibody (MLB International) at 4°C, and then incubated with Alexa Fluor 647–conjugated anti–rat IgG (Thermo Fisher Scientific) before flow cytometry analysis with a Fortessa system (BD).
ELISAs of IL-6, TNF, and MCP-1
BMMCs were sensitized with DNP-specific IgE overnight, washed, and then incubated for 3 h in culture medium containing 20 ng/ml DNP-HSA. Commercial ELISA kits for IL-6, TNF, and MCP-1 (eBioscience) were used according to the manufacturer’s protocols.
Immunofluorescence
BMMCs were sensitized with DNP-specific IgE overnight, plated onto fibronectin-coated glass coverslips (10 µg/ml, Sigma Aldrich) for 45 min at 37°C with 1 mM MnCl2, and then activated with 20 ng/ml DNP-HSA for the indicated times. BMMCs were fixed by incubation for 15 min on ice in 3.7% wt/vol PFA and then for a further 10 min in NH4Cl (50 mM in PBS). The cells were then incubated for 1 h with specific primary antibodies in permeabilization buffer (PBS with 1 mg/ml bovine serum albumin and 0.05% wt/vol saponin; Sigma-Aldrich), washed twice, and incubated for another hour with fluorescent-conjugated secondary antibody in permeabilization buffer. Lastly, the cells were mounted on slides in Prolong gold antifade reagent in the presence or absence of DAPI (Invitrogen). Confocal microscopy was performed with an LSM 700 system (ZEISS) and 63× NA 1.4 objective. The images were processed with the LSM Image Browser (ZEISS) and ImageJ software (version 1.43; National Institutes of Health).
Immunofluorescence analysis
BMMCs were stained for STX3 to assess the translocation of the SG upon activation. Two profiles were quantified: absence of translocation, and translocation to the cell periphery (defined by more than two thirds of the cell periphery where positive for STX3 labeling). BMMCs were stained for tubulin to assess the microtubule reorganization upon activation. Two profiles were quantified: absence of microtubule reorganization (tubulin shapes adopt a peripheral ring), and microtubule reorganization (observation of at least two filopodia-like extensions per cell were considered to be microtubule reorganization).
TIRF
The TIRF assay was performed using WGA-488–loaded BMMCs sensitized with DNP-specific IgE overnight. Cells were allowed to attach to fibronectin-coated glass coverslips (10 µg/ml; Sigma-Aldrich) before stimulation with 20 ng/ml DNP-HSA. TIRF images were then acquired for 15 min (exposure time of 200 ms). During the observation, the cells were cultured at 37°C in a 5% CO2 atmosphere. Fluorescence data were acquired with a TIRF imaging system (Eclipse Ti-E; Nikon). Images were acquired with a QuantEM 512 SC camera (Roper Technologies) and NIS-Elements AR software (version 3.1; Nikon). Image sets were processed with ImageJ software. A WGA-containing granule was defined by a minimum of a square of 3 × 3 pixels (1 pixel = 0.16 µm) of strong intensity signal, orange to white intensity from the pseudocolor scale.
Calcium flux
5 × 106 IgE-sensitized BMMCs were loaded with 5 µg indo-1 (Thermo Fisher Scientific) in RPMI medium supplemented with 10 mM Hepes, pH 7.0, for 30 min at 37°C. RPMI medium supplemented with 10 mM Hepes, pH 7.0, and 5% FCS was then added for 30 min at 37°C. Cells were washed and resuspended in RPMI medium supplemented with 5% FCS before the addition of 20 ng/ml DNP-HSA (to induce calcium flux). Calcium flux was measured by using a FACSAria flow cytometer (BD) to monitor the fluorescent emission ratio (405 nm/475 nm). Time course analyses were performed using the FlowJo software package (Tree Star).
Passive systemic anaphylaxis
A temperature probe (Bio Medic Data Systems) was implanted into the subcutaneous tissue on the back of 8-wk-old WT and cKO mice. On the next day, mice were passively sensitized i.v. using 1 µg/g anti-DNP mouse IgE antibody (H1-ε-26). 24 h later, mice were challenged by the i.v. administration of 500 µg DNP-HSA (Sigma-Aldrich). The body temperature was recorded every 5 min for 60 min using a wireless reader (DAS-7007S; Bio Medic Data Systems). At the end of the recording, blood samples were collected and the serum concentration of MCPT-1 was measured with an ELISA kit (eBioscience).
Immunoblotting and immunoprecipitation
For proximal signaling, 107 IgE-sensitized WT or cKOKif5b BMMCs stimulated with 20 ng/ml DNP-HSA for the indicated times were lysed in lysis buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.6, 150 mM NaCl, 5 mM EDTA, and 0.5% Triton X-100) supplemented with an EDTA-free protease inhibitor cocktail tablet (Roche). For the immunoprecipitation assay, 40 × 106 IgE-sensitized WT BMMCs were either not stimulated or were stimulated with 20 ng/ml DNP-HSA for 10 min. Cells were lysed in lysis buffer (50 mM Hepes, pH 7.4, 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM MgCl2, 1% Triton X-100, and 10% glycerol) supplemented with one EDTA-free protease inhibitor cocktail tablet and phosphatase inhibitors (Sigma-Aldrich). Immunoprecipitation was performed with polyclonal rabbit Rab27 antibody (Synaptic Systems). Anti-Slp3, anti-Rab27, and anti-Kif5b antibodies were used to develop the Western blots.
siRNA
Specific duplex siRNA targeting Slp3 was purchased from QIAGEN (references: n°1 = SI02899750, and n°2 = SI02899743).
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed with Prism software (version 6; GraphPad Software) using a two-tailed, unpaired t test.
Online supplemental material
Video 1 shows TIRF video microscopy of WGA-488 (green)–labeled WT BMMCs for the 15 min immediately after FcεRI activation. Video 2 shows TIRF video microscopy of WGA-488 (green)–labeled cKOKif5b BMMCs for the 15 min immediately after FcεRI activation.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the staff in Imagine Institute’s animal facility for their assistance.
This work was funded by Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale, the French National Research Agency (ANR-12-BSV1-0020-01 and ANR HLH-cytotox), an International collaboration grant from L’Agence National de la Recherche France (grant ANR-12-ISV3-0006-01) and Conacyt Mexico (Conacyt-ANR188565), the ARC Foundation (grant PJA20131200047), the European Research Council (PIDImmun, grant 249816), and Société Française d'Allergologie 2014 and 2016 (grant SFA-D.A. Moneret-Vautrin) to U. Blank and G. Ménasché. This research project has also received funding from the Investissements d’Avenir program (grant ANR-11-IDEX-0005-02, Sorbonne Paris Cite, Laboratoire d’excellence INFLAMEX). I. Munoz received a doctoral fellowship from the Ministère de l’Education Nationale de la Recherche et de la Technologie. Core facilities were partly funded by the Imagine Foundation and the French government’s Investissement d’Avenir program (grant ANR-10-IAHU-01).
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Footnotes
Abbreviations used:
- BMMC
- bone marrow–derived MC
- cKO
- conditional knockout
- CTL
- cytotoxic T lymphocyte
- DN
- dominant-negative
- HSA
- human serum albumin
- KLC
- kinesin light chain
- MC
- mast cell
- PI3K
- phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
- SG
- secretory granule
- TIRF
- total internal reflection fluorescence
- WT
- wild type
References
- Arimura N., Kimura T., Nakamuta S., Taya S., Funahashi Y., Hattori A., Shimada A., Ménager C., Kawabata S., Fujii K., et al. 2009. Anterograde transport of TrkB in axons is mediated by direct interaction with Slp1 and Rab27. Dev. Cell. 16:675–686. 10.1016/j.devcel.2009.03.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beghdadi W., Madjene L.C., Benhamou M., Charles N., Gautier G., Launay P., and Blank U.. 2011. Mast cells as cellular sensors in inflammation and immunity. Front. Immunol. 2:37 10.3389/fimmu.2011.00037 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blank U., and Rivera J.. 2004. The ins and outs of IgE-dependent mast-cell exocytosis. Trends Immunol. 25:266–273. 10.1016/j.it.2004.03.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blank U., Madera-Salcedo I.K., Danelli L., Claver J., Tiwari N., Sánchez-Miranda E., Vázquez-Victorio G., Ramírez-Valadez K.A., Macias-Silva M., and González-Espinosa C.. 2014. Vesicular trafficking and signaling for cytokine and chemokine secretion in mast cells. Front. Immunol. 5:453 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00453 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasius T.L., Cai D., Jih G.T., Toret C.P., and Verhey K.J.. 2007. Two binding partners cooperate to activate the molecular motor Kinesin-1. J. Cell Biol. 176:11–17. 10.1083/jcb.200605099 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brochetta C., Suzuki R., Vita F., Soranzo M.R., Claver J., Madjene L.C., Attout T., Vitte J., Varin-Blank N., Zabucchi G., et al. 2014. Munc18-2 and syntaxin 3 control distinct essential steps in mast cell degranulation. J. Immunol. 192:41–51. 10.4049/jimmunol.1301277 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahu J., Olichon A., Hentrich C., Schek H., Drinjakovic J., Zhang C., Doherty-Kirby A., Lajoie G., and Surrey T.. 2008. Phosphorylation by Cdk1 increases the binding of Eg5 to microtubules in vitro and in Xenopus egg extract spindles. PLoS One. 3:e3936 10.1371/journal.pone.0003936 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cui J., Wang Z., Cheng Q., Lin R., Zhang X.M., Leung P.S., Copeland N.G., Jenkins N.A., Yao K.M., and Huang J.D.. 2011. Targeted inactivation of kinesin-1 in pancreatic β-cells in vivo leads to insulin secretory deficiency. Diabetes. 60:320–330. 10.2337/db09-1078 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donelan M.J., Morfini G., Julyan R., Sommers S., Hays L., Kajio H., Briaud I., Easom R.A., Molkentin J.D., Brady S.T., and Rhodes C.J.. 2002. Ca2+-dependent dephosphorylation of kinesin heavy chain on β-granules in pancreatic β-cells: Implications for regulated b-granule transport and insulin exocytosis. J. Biol. Chem. 277:24232–24242. 10.1074/jbc.M203345200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dráber P., and Dráber P.. 2015. Membrane-cytoskeleton dynamics in the course of mast cell activation. Methods Mol. Biol. 1220:219–237. 10.1007/978-1-4939-1568-2_14 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espeut J., Gaussen A., Bieling P., Morin V., Prieto S., Fesquet D., Surrey T., and Abrieu A.. 2008. Phosphorylation relieves autoinhibition of the kinetochore motor Cenp-E. Mol. Cell. 29:637–643. 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.01.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Föger N., Jenckel A., Orinska Z., Lee K.H., Chan A.C., and Bulfone-Paus S.. 2011. Differential regulation of mast cell degranulation versus cytokine secretion by the actin regulatory proteins Coronin1a and Coronin1b. J. Exp. Med. 208:1777–1787. 10.1084/jem.20101757 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda M., Kanno E., Saegusa C., Ogata Y., and Kuroda T.S.. 2002. Slp4-a/granuphilin-a regulates dense-core vesicle exocytosis in PC12 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 277:39673–39678. 10.1074/jbc.M205349200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli S.J., Kalesnikoff J., Grimbaldeston M.A., Piliponsky A.M., Williams C.M., and Tsai M.. 2005a Mast cells as “tunable” effector and immunoregulatory cells: Recent advances. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 23:749–786. 10.1146/annurev.immunol.21.120601.141025 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli S.J., Nakae S., and Tsai M.. 2005b Mast cells in the development of adaptive immune responses. Nat. Immunol. 6:135–142. 10.1038/ni1158 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirokawa N. 1998. Kinesin and dynein superfamily proteins and the mechanism of organelle transport. Science. 279:519–526. 10.1126/science.279.5350.519 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura T., Watanabe H., Iwamatsu A., and Kaibuchi K.. 2005. Tubulin and CRMP-2 complex is transported via Kinesin-1. J. Neurochem. 93:1371–1382. 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03063.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroda T.S., Fukuda M., Ariga H., and Mikoshiba K.. 2002. The Slp homology domain of synaptotagmin-like proteins 1–4 and Slac2 functions as a novel Rab27A binding domain. J. Biol. Chem. 277:9212–9218. 10.1074/jbc.M112414200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurowska M., Goudin N., Nehme N.T., Court M., Garin J., Fischer A., de Saint Basile G., and Ménasché G.. 2012. Terminal transport of lytic granules to the immune synapse is mediated by the kinesin-1/Slp3/Rab27a complex. Blood. 119:3879–3889. 10.1182/blood-2011-09-382556 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorentz A., Baumann A., Vitte J., and Blank U.. 2012. The SNARE machinery in mast cell secretion. Front. Immunol. 3:143 10.3389/fimmu.2012.00143 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ménasché G., Ménager M.M., Lefebvre J.M., Deutsch E., Athman R., Lambert N., Mahlaoui N., Court M., Garin J., Fischer A., and de Saint Basile G.. 2008. A newly identified isoform of Slp2a associates with Rab27a in cytotoxic T cells and participates to cytotoxic granule secretion. Blood. 112:5052–5062. 10.1182/blood-2008-02-141069 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno K., Tolmachova T., Ushakov D.S., Romao M., Abrink M., Ferenczi M.A., Raposo G., and Seabra M.C.. 2007. Rab27b regulates mast cell granule dynamics and secretion. Traffic. 8:883–892. 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2007.00571.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morfini G., Szebenyi G., Elluru R., Ratner N., and Brady S.T.. 2002. Glycogen synthase kinase 3 phosphorylates kinesin light chains and negatively regulates kinesin-based motility. EMBO J. 21:281–293. 10.1093/emboj/21.3.281 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishida K., Yamasaki S., Ito Y., Kabu K., Hattori K., Tezuka T., Nishizumi H., Kitamura D., Goitsuka R., Geha R.S., et al. 2005. FcεRI-mediated mast cell degranulation requires calcium-independent microtubule-dependent translocation of granules to the plasma membrane. J. Cell Biol. 170:115–126. (published erratum appears in J. Cell Biol. 2005. 170:115–126) 10.1083/jcb.200501111 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishida K., Yamasaki S., Hasegawa A., Iwamatsu A., Koseki H., and Hirano T.. 2011. Gab2, via PI-3K, regulates ARF1 in FcεRI-mediated granule translocation and mast cell degranulation. J. Immunol. 187:932–941. 10.4049/jimmunol.1100360 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa K., Tanaka Y., Uruno T., Duan X., Harada Y., Sanematsu F., Yamamura K., Terasawa M., Nishikimi A., Côté J.F., and Fukui Y.. 2014. DOCK5 functions as a key signaling adaptor that links FcεRI signals to microtubule dynamics during mast cell degranulation. J. Exp. Med. 211:1407–1419. 10.1084/jem.20131926 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Röhlich P., Anderson P., and Uvnäs B.. 1971. Electron microscope observations on compounds 48/80-induced degranulation in rat mast cells. J. Cell Biol. 51:465–483. 10.1083/jcb.51.2.465 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sepulveda F.E., Burgess A., Heiligenstein X., Goudin N., Ménager M.M., Romao M., Côte M., Mahlaoui N., Fischer A., Raposo G., et al. 2015. LYST controls the biogenesis of the endosomal compartment required for secretory lysosome function. Traffic. 16:191–203. 10.1111/tra.12244 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari N., Wang C.C., Brochetta C., Ke G., Vita F., Qi Z., Rivera J., Soranzo M.R., Zabucchi G., Hong W., and Blank U.. 2008. VAMP-8 segregates mast cell–preformed mediator exocytosis from cytokine trafficking pathways. Blood. 111:3665–3674. 10.1182/blood-2007-07-103309 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhey K.J., and Hammond J.W.. 2009. Traffic control: regulation of kinesin motors. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 10:765–777. 10.1038/nrm2782 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Z., Cui J., Wong W.M., Li X., Xue W., Lin R., Wang J., Wang P., Tanner J.A., Cheah K.S., et al. 2013. Kif5b controls the localization of myofibril components for their assembly and linkage to the myotendinous junctions. Development. 140:617–626. 10.1242/dev.085969 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wernersson S., and Pejler G.. 2014. Mast cell secretory granules: armed for battle. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 14:478–494. 10.1038/nri3690 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.