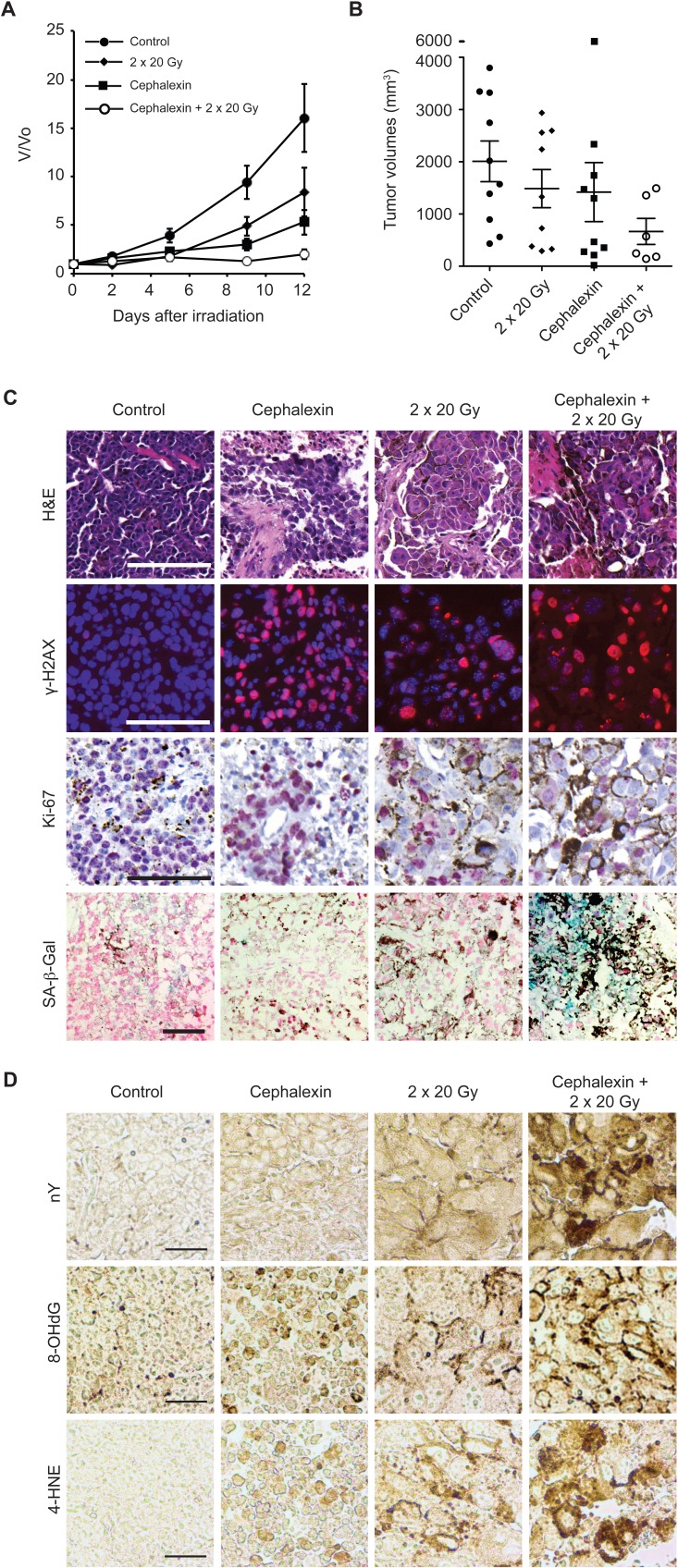
Figure 6. Cephalexin combined with radiation suppresses tumor growth and induces oxidative stress in B16.SIY tumors.
A. Tumor bearing mice were treated for 12 days with cephalexin (30 mg/kg twice daily by gavage) alone or in combination with two doses of 20 Gy. Groups were control (n = 10), 20 + 20 Gy (n = 10), cephalexin (n = 10), and cephalexin + 20 Gy + 20 Gy (n = 6). Combined treatment suppressed tumor growth compared to either treatment alone. B. Scatter plot of individual tumors in corresponding treatment groups at day 12 showing the distribution of tumor volumes and the presence of experimental outliers. Means ± SEM are shown. C. Cephalexin combined with IR produced marked tissue destruction and loss of cellularity. Combined treatment increases DNA damage, suppresses proliferation and induces senescence in B16.SIY tumors. H&E staining revealed extensive tissue destruction 7 days post combined treatment. Treatment with cephalexin + IR further increased the number of γ-H2AX positive cells, decreased the number of Ki-67 positive cells and enhanced SA-β-Gal staining compared to either treatment alone. Representative images are shown. Scale bar 100 μm. D. Cephalexin plus IR induce oxidative damage in vivo. Tissue sections were examined by immunohistochemistry for oxidative damage to proteins (protein damage marker nitrotyrosine, nY), DNA (DNA damage marker 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine, 8-OHdG), or lipids (lipid damage marker 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal, 4-HNE). Compared to control, both cephalexin and radiation increased staining for each oxidative stress marker while the combination produced an increase in each marker suggesting interactive effects. Representative images are shown. Scale bar 100 μm.