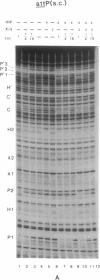
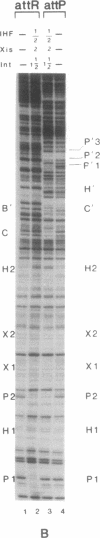
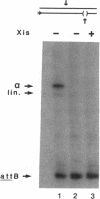
Abstract
The virally encoded Xis protein is one of the components in the site-specific recombination reactions of bacteriophage lambda. It is required for excisive recombination and inhibits integrative recombination. The mechanism of Xis inhibition of the integration reaction was investigated by methylation protection assays (footprinting analyses) in conjunction with recombination assays. Xis is shown to mediate the formation of a specific attP looped structure involving cooperative and competitive long-range interactions among integrase, integration host factor, and Xis proteins. This higher-order structure precludes supercoiled attP from engaging in the productive partner interactions that lead to execution of the first strand exchange in integrative recombination. In addition to its previously characterized role in excision, Xis-induced DNA bending is postulated to act as a regulatory switch (in an alternative loop mechanism) that converts the attP intasome from an integrative-competent complex to a nonreactive one.
Full text
PDF
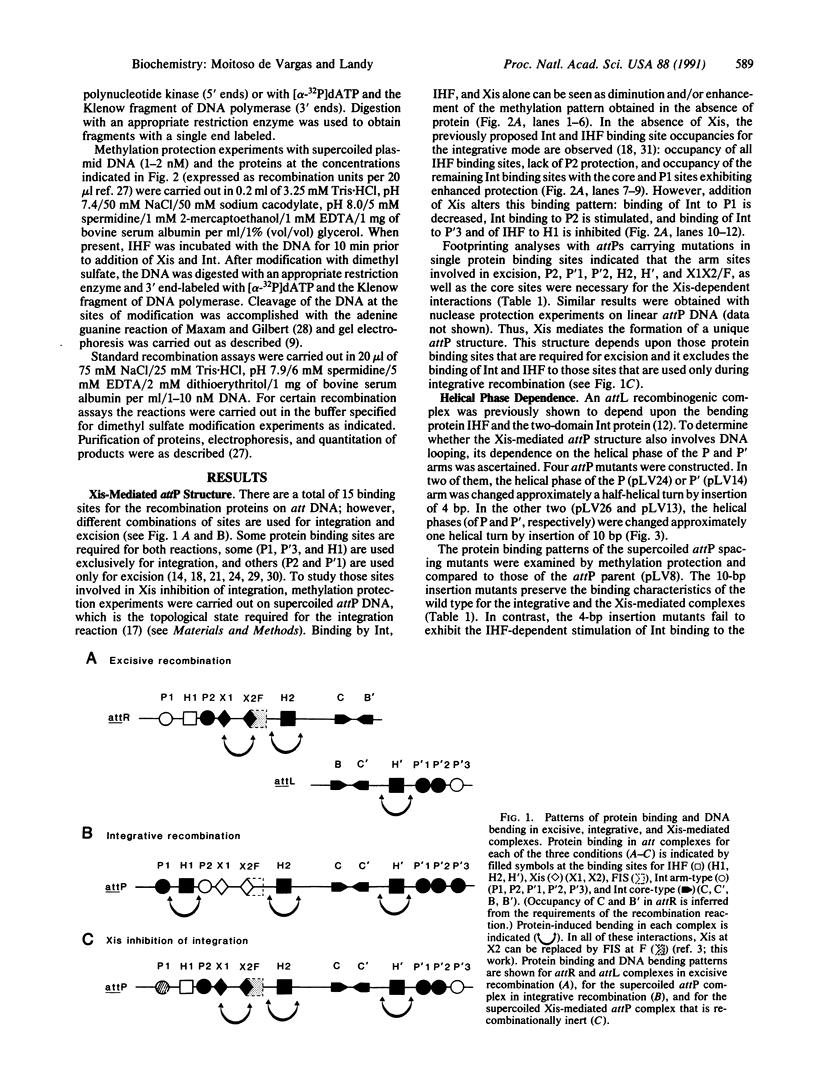


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abremski K., Gottesman S. Purification of the bacteriophage lambda xis gene product required for lambda excisive recombination. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9658–9662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer C. E., Hesse S. D., Gumport R. I., Gardner J. F. Mutational analysis of integrase arm-type binding sites of bacteriophage lambda. Integration and excision involve distinct interactions of integrase with arm-type sites. J Mol Biol. 1986 Dec 5;192(3):513–527. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90273-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Better M., Lu C., Williams R. C., Echols H. Site-specific DNA condensation and pairing mediated by the int protein of bacteriophage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5837–5841. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Better M., Wickner S., Auerbach J., Echols H. Role of the Xis protein of bacteriophage lambda in a specific reactive complex at the attR prophage attachment site. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):161–168. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90506-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushman W., Thompson J. F., Vargas L., Landy A. Control of directionality in lambda site specific recombination. Science. 1985 Nov 22;230(4728):906–911. doi: 10.1126/science.2932798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig N. L., Nash H. A. The mechanism of phage lambda site-specific recombination: site-specific breakage of DNA by Int topoisomerase. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):795–803. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90112-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franz B., Landy A. Interactions between lambda Int molecules bound to sites in the region of strand exchange are required for efficient Holliday junction resolution. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 20;215(4):523–535. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(05)80165-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman S. D., Nash H. A. Functional replacement of a protein-induced bend in a DNA recombination site. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):251–254. doi: 10.1038/341251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith J. D., Nash H. A. Genetic rearrangement of DNA induces knots with a unique topology: implications for the mechanism of synapsis and crossing-over. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3124–3128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu P. L., Ross W., Landy A. The lambda phage att site: functional limits and interaction with Int protein. Nature. 1980 May 8;285(5760):85–91. doi: 10.1038/285085a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi Y., Nash H. A. Nicking-closing activity associated with bacteriophage lambda int gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3760–3764. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S., Moitoso de Vargas L., Nunes-Düby S. E., Landy A. Mapping of a higher order protein-DNA complex: two kinds of long-range interactions in lambda attL. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):773–781. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90143-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitts P. A., Nash H. A. Bacteriophage lambda site-specific recombination proceeds with a defined order of strand exchanges. J Mol Biol. 1988 Nov 5;204(1):95–107. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90602-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landy A. Dynamic, structural, and regulatory aspects of lambda site-specific recombination. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:913–949. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K., Gellert M., Nash H. A. Involement of supertwisted DNA in integrative recombination of bacteriophage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1978 May 25;121(3):375–392. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90370-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K., Weisberg R., Enquist L., Mizuuchi M., Buraczynska M., Foeller C., Hsu P. L., Ross W., Landy A. Structure and function of the phage lambda att site: size, int-binding sites, and location of the crossover point. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 1):429–437. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moitoso de Vargas L., Kim S., Landy A. DNA looping generated by DNA bending protein IHF and the two domains of lambda integrase. Science. 1989 Jun 23;244(4911):1457–1461. doi: 10.1126/science.2544029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moitoso de Vargas L., Pargellis C. A., Hasan N. M., Bushman E. W., Landy A. Autonomous DNA binding domains of lambda integrase recognize two different sequence families. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):923–929. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90107-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash H. A. Integrative recombination of bacteriophage lambda DNA in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1072–1076. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash H. A., Robertson C. A. Heteroduplex substrates for bacteriophage lambda site-specific recombination: cleavage and strand transfer products. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3523–3533. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08518.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunes-Düby S. E., Matsumoto L., Landy A. Half-att site substrates reveal the homology independence and minimal protein requirements for productive synapsis in lambda excisive recombination. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):197–206. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90881-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunes-Düby S. E., Matsumoto L., Landy A. Site-specific recombination intermediates trapped with suicide substrates. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):779–788. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90336-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pargellis C. A., Nunes-Düby S. E., de Vargas L. M., Landy A. Suicide recombination substrates yield covalent lambda integrase-DNA complexes and lead to identification of the active site tyrosine. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7678–7685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock T. J., Nash H. A. Knotting of DNA caused by a genetic rearrangement. Evidence for a nucleosome-like structure in site-specific recombination of bacteriophage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1983 Oct 15;170(1):1–18. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80224-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. Gene regulation by proteins acting nearby and at a distance. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):697–701. doi: 10.1038/322697a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. How eukaryotic transcriptional activators work. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):683–689. doi: 10.1038/335683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richet E., Abcarian P., Nash H. A. Synapsis of attachment sites during lambda integrative recombination involves capture of a naked DNA by a protein-DNA complex. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):9–17. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90526-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richet E., Abcarian P., Nash H. A. The interaction of recombination proteins with supercoiled DNA: defining the role of supercoiling in lambda integrative recombination. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1011–1021. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90700-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson C. A., Nash H. A. Bending of the bacteriophage lambda attachment site by Escherichia coli integration host factor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 15;263(8):3554–3557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W., Landy A. Bacteriophage lambda int protein recognizes two classes of sequence in the phage att site: characterization of arm-type sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7724–7728. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W., Landy A. Patterns of lambda Int recognition in the regions of strand exchange. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):261–272. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90355-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. F., Landy A. Empirical estimation of protein-induced DNA bending angles: applications to lambda site-specific recombination complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9687–9705. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. F., Moitoso de Vargas L., Koch C., Kahmann R., Landy A. Cellular factors couple recombination with growth phase: characterization of a new component in the lambda site-specific recombination pathway. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):901–908. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90516-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. F., Snyder U. K., Landy A. Helical-repeat dependence of integrative recombination of bacteriophage lambda: role of the P1 and H1 protein binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6323–6327. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. F., Waechter-Brulla D., Gumport R. I., Gardner J. F., Moitoso de Vargas L., Landy A. Mutations in an integration host factor-binding site: effect on lambda site-specific recombination and regulatory implications. J Bacteriol. 1986 Dec;168(3):1343–1351. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1343-1351.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. F., de Vargas L. M., Skinner S. E., Landy A. Protein-protein interactions in a higher-order structure direct lambda site-specific recombination. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 5;195(3):481–493. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90177-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winoto A., Chung S., Abraham J., Echols H. Directional control of site-specific recombination by bacteriophage lambda. Evidence that a binding site for Int protein far from the crossover point is required for integrative but not excisive recombination. J Mol Biol. 1986 Dec 5;192(3):677–680. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90286-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]