Abstract
Introduction
The purpose of this review is to document the various types of astrocytoma that occur in the fetus and neonate, their locations, initial findings, pathology, and outcome. Data are presented that show which patients are likely to survive or benefit from treatment compared with those who are unlikely to respond.
Materials and methods
One hundred one fetal and neonatal tumors were collected from the literature for study.
Results
Macrocephaly and an intracranial mass were the most common initial findings. Overall, hydrocephalus and intracranial hemorrhage were next. Glioblastoma (GBM) was the most common neoplasm followed in order by subependymal giant cell astrocytoma (SEGA), low-grade astrocytoma, anaplastic astrocytoma, and desmoplastic infantile astrocytoma (DIA). Tumors were detected most often toward the end of the third trimester of pregnancy.
Conclusion
A number of patients were considered inoperable since their tumor occupied much of the intracranial cavity involving large areas of the brain. High-grade astrocytomas were more common than low-grade ones in this review. Fetuses and neonates with astrocytoma have a mixed prognosis ranging from as low as 20 % (GBM) to a high of 90 %. The overall survival was 47/101 or 46 %.
Keywords: Fetal astrocytoma, Neonatal astrocytoma, Perinatal astrocytoma, Intracranial hemorrhage, Congenital brain tumor
Introduction
Glial cells are the supportive elements of the central nervous system (CNS) [22]. They include astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and ependymal cells, and the corresponding tumors originating from these cells astrocytoma, oligodendroglioma, and ependymoma all of which are loosely called “glioma” [16, 22]. The term “glioma” is used interchangeably with astrocytoma to describe the more common subgroup of tumors [22].
Glioma (astrocytoma) is the leading CNS tumor in children. Low-grade gliomas are the leading pediatric CNS tumors overall and are responsible for approximately one third of cases [22, 63]. Higher grade gliomas occur less often and account for 7–11 % of cases of CNS malignancy beyond infancy [22, 28].
Low- and high-grade astrocytoma differs significantly in terms of their histological grading, site of origin, treatment, and prognosis. The various types of tumors within the group of low-grade astrocytoma are classified as WHO grade I and grade II [13, 39]. The major histological subtype in the perinatal period is the pilocytic astrocytoma, a WHO grade I tumor that is usually well circumscribed and has only a narrow margin of infiltration into the surrounding tissues [13]. Next in frequency is the fibrillary astrocytoma (WHO grade II), which has a tendency to be more infiltrative. High-grade astrocytomas are those graded III (e.g., anaplastic astrocytoma) or IV (e.g., glioblastoma) and comprise approximately 7–11 % of pediatric tumors [28]. Perinatal strocytomas vary from benign (low-grade) to malignant (high-grade) tumors [9, 18, 30, 32, 49, 51, 63, 69]. High-grade astrocytomas were more prevalent than low-grade ones in this review, 55 versus 46 % (Table 9).
Table 9.
Fetal and neonatal astrocytoma: histological type, grade versus survival (n = 101)
| Tumor | Grade | Number | Survival (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glioblastoma | IV | 45 (44.6) | 9/45 (20) |
| Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma | I | 18 (17.9) | 11/18 (61) |
| Low-grade, I–II, astrocytoma | I–II | 10 (9.90) | 9/10 (90) |
| Anaplastic astrocytoma | III | 10 (9.90) | 6/10 (60) |
| Desmoplastic infantile astrocytoma/ganglioglioma | I | 10 (9.90) | 8/10 (80) |
| Astroblastoma | ?a | 5 (4.90) | 3/5 (60) |
| Gemistocytic astrocytoma | II | 3 (2.97) | 1/3 (33.3) |
| Total | 101 (100) | 47/101 (46.5) |
aGrade has not been assigned for this tumor (39,54)
Fetal and neonatal brain tumors are rare comprising only 0.5–1.5 % of all childhood CNS tumors [68]. Astrocytoma is not only the main neuroglial tumor but also second in incidence following intracranial teratoma [12, 24, 30–32, 35, 36, 55, 76, 82, 90]. Perinatal astrocytomas occur most often outside the posterior cranial fossa and above the tentorium. Cerebral hemisphere is the main location where they tend to be large, involve more than one lobe, and displace the lateral and/or third ventricles [24, 30, 35, 36, 55, 56, 81, 82]. Intracranial mass, macrocephaly, hydrocephalus, and hemorrhage are the most common initial imaging findings [23, 27, 30, 32, 38, 51] (Tables 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, and 8). However, the leading presentation is an intracranial mass detected on routine prenatal sonograms [23, 27, 30, 32, 81]. Differential diagnosis of a brain tumor includes vascular malformation, infarction, or hemorrhage [21, 47, 83, 84].
Table 2.
Fetal and neonatal glioblastoma (n = 45)
| Female/male | 21/17 = 1.23a |
| Fetusesb | 28 |
| Neonatesc | 17 |
| Gestation (weeks) | 36, range 29–40 |
| Birth weight (g) | 3152, range 1400–4270 |
| Maternal history | |
| Maternal age (years) | 27 years, range 17–38 |
| Gravida | G1 9, G2 2, G4 1, G5 2 |
| Delivery | |
| Vaginal | 26 |
| Cesarian section | 19 |
| Termination of pregnancy | 3 |
| Initial findings | |
| Macrocephalus | 28 |
| Hydrocephalus | 27 |
| Intracranial mass on imaging | 26 |
| Intracranial hemorrhage | 13 |
| Bulging anterior fontanel | 13 |
| Stillbirth | 5 |
| Seizures | 3 |
| Dystocia | 3 |
| Increasing irritability | 3 |
| Hydramnios | 3 |
| Vomiting | 3 |
| Eye signsd | 3 |
| Facial palsy | 3 |
| Hemiparesis | 3 |
| Hypotonia | 2 |
| Breech presentation | 2 |
| Location | |
| Cerebral hemisphere, NOSe | 34 |
| Thalamus | 3 |
| Cerebellum and cerebellar-pontine angle | 2 |
| Cerebellum and basal ganglia | 2 |
| Midline suprasellar | 1 |
| Hypothalamus | 1 |
| Midline replacing most of brain | 1 |
| Cerebral hemisphere replaced by tumor | 1 |
| Tumor filled intracranial cavity replacing brain | 1 |
| Septum pellucidum and adjacent ventricle | 1 |
| Tumor characteristics | |
| Brain weight (g) | 597, range 250–850 |
| Tumor weight (g) | 20, 5.8f |
| Tumor greatest dimension (cm) | 9.6, range 5–11 |
| Treatment | |
| Patients treated | 16 (35.6) |
| Patients not treated | 29 (64.4) |
| Survival with surgical resection alone | 2/6 |
| Survival with SR + CTc | 4/4 |
| Survival with SR + XRT | 2/2 |
| Survival with SR + CT + embolization | 1/1 |
| Survival with SR + CT + XRT | 0/2 |
| Survival with CT | 0/1 |
| Outcome | |
| Fetal survival | 2/31 (6.0) |
| Neonatal survival | 7/14 (50) |
| Patients treated survived | 9/16 (56) |
| Patients not treated survived | 0/29 |
| Overall survival | 9/45 = 20 % |
Cases selected from the literature
CT chemotherapy, NOS not otherwise specified, SR surgical resection, XRT radiation therapy
aSex not stated in seven patients
bTumor discovered prenatally or on the first day of life
cTumor discovered within the first 2 months of life
dEye signs: setting sun, doll’s eyes, nystagmus
eCerebral hemisphere locations: parietal 3, frontal 2, and one each: parietal-occipital, frontal-parietal
fTumor weights were given only in two patients
gTwo of nine survivors were alive with disease
Table 3.
Fetal and neonatal subependymal giant cell astrocytoma (n = 18)
| Male/female | 14/4 = 3.5 |
| Fetusesa | 11 |
| Neonatesb | 7 |
| Gestation (weeks) | 35, range 22–40 |
| Birth weight (g) | 2653, range 2100–3600 |
| Family history of tuberous sclerosis | 1 |
| None | 9 |
| Family history not stated | 8 |
| Maternal history | |
| Maternal age | 27 years, range 17–38 |
| Gravida | G1 6, range G1–G6 |
| Delivery | |
| Vaginal | 15 |
| Cesarian section | 2 |
| Termination of pregnancy | 1 |
| Initial findings | |
| Cerebral hemisphere mass | 14 |
| Hydrocephalus | 11 |
| Concomitant cardiac rhabdomyoma | 10 |
| Seizures | 3 |
| Macrocephaly | 2 |
| Otherc | 10 |
| Location | |
| Subependyma lateral ventricle adjacent to foramen of Monro | 10 |
| Cerebral hemisphere, NOS | 4 |
| Subependyma lateral ventricle, basal ganglia, and/or thalamus | 2 |
| Within a lateral ventricle | 2 |
| Tumor characteristics | |
| Tumor greatest dimension (cm) | 4, range, 2–9 |
| Treatment | |
| Patients treated | 12d |
| Patients not treated | 5e |
| Survival with surgery alone | 9/11 (81.8)f |
| Survival SR + CT | 2/2 (100)g |
| Patients lost to follow-up | 1 |
| Outcome | |
| Fetal survival | 6/11 (54.5) |
| Neonatal survival | 5/6 (83.3)h |
| Patients treated survived | 11/12 (91.7) |
| Patients not treated survived | 1/6 (16.7) |
| Overall survivalh | 12/17 = 70.6 % |
Cases selected from the literature
CT chemotherapy, NOS not otherwise specified, SR surgical resection, XRT radiation therapy
aTumor discovered prenatally or on the first day of life
bTumor discovered within first the 2 months of life
cOther initial findings, one each: fetal hydrops, dystocia, hydramnios, lethargy, hypotonia, opisthotonus, abnormal eye movements, vomiting, hemiparesis, cyanosis, respiratory distress
dPatients treated: seven fetuses, five treated
ePatients not treated: four fetuses, five neonates
f( ) = percent
gSR + CT; one fetus and one neonate
hOne neonate was lost to follow-up
Table 4.
Fetal and neonatal “low-grade” astrocytoma (grades I and II) (n = 10)
| Male/female | 6/4 = 1.5 |
| Fetusesa | 3 |
| Neonatesb | 7 |
| Gestation (weeks) | 39, range 37–40 |
| Birth weight (g) | 2902, range 2000–3990 |
| Maternal history | |
| Maternal age (years)c | |
| Gravidac | |
| Delivery | |
| Vaginal | 9 |
| Cesarian section | 1 |
| Initial findingsd | |
| Mass discovered on imaging | 8 |
| Intracranial hemorrhage | 3 |
| Bulging anterior fontanel | 3 |
| Macrocephalus | 2 |
| Decreased movement of extremity | 2 |
| Quadraparesis | 2 |
| Hypotonia | 2 |
| Breech presentation | 2 |
| Eye signs | 2e |
| Hemiparesis | 2 |
| Breech presentation | 2 |
| Other findings | 7 |
| Location | |
| Spinal cord | 5 |
| Cerebral hemisphere | 3 |
| Optic nerve | 2 |
| Tumor characteristicsf | |
| Treatment | |
| Patients treated | 10 |
| Patients not treated | 0 |
| Survival with surgical resection alone | 9/9 |
| Survival with SR + CTc | 1/1 |
| Outcome | |
| Fetal survival | 2/3 |
| Neonatal survival | 7/7 |
| Patients with spinal cord tumors who survived with significant disabilities | 3/4 (75) |
| Overall survival | 9/10 = 90 % |
Cases selected from the literature
CT chemotherapy, SR surgical resection
aTumor discovered prenatally or on the first day of life
bTumor discovered within the first 2 months of life
cMaternal age and gravida were given only in one of ten reports
dOther initial findings, one each: hydrocephalus, dystocia, head tilt, seizures, irritability, poor feeding, vomiting
eOptic nerve tumor eye associated signs: microphthalmia, orbital cyst, proptosis, exophthalmia
fTumor characteristics such as brain weight, tumor weight, and tumor dimensions were not listed in the ten reports reviewed
Table 5.
Fetal and neonatal anaplastic astrocytoma (n = 10)
| Female/male | 5/4 = 1.25a |
| Fetusesb | 7 |
| Neonatesc | 3 |
| Gestation (weeks) | 37, range 31–40 |
| Birth weight (g) | 3873, range 3100–4700 |
| Maternal history | |
| Maternal age (years) | 28 years, range 20–33 |
| Gravida | G1 1, G2 1, NS 8 |
| Delivery | |
| Vaginal | 7 |
| Cesarian section | 3 |
| Termination of pregnancy | 1 |
| Initial findings | |
| Intracranial mass on imaging | 7 |
| Macrocephalus | 6 |
| Hydrocephalus | 6 |
| Intracranial hemorrhage | 3 |
| Bulging anterior fontanel | 3 |
| Seizures | 2 |
| Irritability | 2 |
| Other findingsd | 5 |
| Location | |
| Cerebral hemispheree | 10/10 (100) |
| Tumor characteristics | |
| Tumor greatest dimension (cm) | 9 cm, range 6–12 |
| Weightf | |
| Treatment | |
| Patients treated | 6/10 (60) |
| Patients not treated | 4/10 (40) |
| Survival with surgical resection alone | 2/2 (100) |
| Survival with SR + CTf | 3/3 (100) |
| Survival with SR + CT + XRT | 1/1 (100) |
| Outcome | |
| Fetal survival | 5/7 (71.4) |
| Neonatal survival | 1/3 (33.3) |
| Patients treated survived | 6/6 (100) |
| Patients not treated survived | 1/1 (100) |
| Overall survival | 6/10 = 60 %g |
Cases selected from the literature
CT chemotherapy, SR surgical resection, XRT radiation therapy
aSex not stated in one patient
bTumor discovered prenatally or on the first day of life
cTumor discovered on the first 2 months of life
dOther presenting findings, one each: dystocia, vomiting, palsy, hemiparesis, no recognizable cerebral structures
eCerebral hemisphere locations: one each, parietal, parietal-occipital, temporal, both cerebral hemispheres; cerebral hemisphere site, not specified, 6
fTumor weights were given only in four patients
gThree survivors were alive with disease
Table 6.
Fetal and neonatal desmoplastic infantile astrocytoma/ganglioglioma (n = 10)
| Female/male | 5/4 = 1.25a |
| Fetusesb | 1 |
| Neonatesc | 9 |
| Gestation (weeks) | 37, range 34–40 |
| Maternal historyd | |
| Delivery | |
| Vaginal | 8 |
| Cesarian section | 2 |
| Initial findings | |
| Macrocephaly | 9 |
| Intracranial mass on imaging | 7 |
| Bulging anterior fontanel | 2 |
| Seizures | 2 |
| Increasing irritability | 2 |
| Other findings | 10d |
| Location | |
| Cerebral hemisphere | 10 |
| Frontal-parietal-temporal | 5 |
| Parietal-temporal | 1 |
| Parietal-occipital | 1 |
| Frontal-temporal | 1 |
| Bilateral cerebral hemispheres | 1 |
| Cerebral hemisphere replaced by tumor | 1 |
| Tumor characteristics | |
| Tumor greatest dimension (cm) | 11.8, range 11–13 |
| Tumor diagnoses | |
| Desmoplastic infantile gangliogliomae | 7 |
| Desmoplastic infantile astrocytomaf | 3 |
| Treatment | |
| Patients treated | 10 |
| Survival with surgical resection alone | 8/9 (89)h |
| Survival with SR + CTg | 0/1 |
| Outcome | |
| Fetal survival | 1/1 |
| Neonatal survival | 7/9 (77.8) |
| Patients treated survived | 8/10 (80) |
| Overall survival | 8/10 = 80 % |
Cases selected from the literature
CT chemotherapy, DIG desmoplastic infantile astrocytoma, GBM glioblastoma, SR surgical resection
aIn one patient sex was not stated
bTumor discovered prenatally or on the first day of life
cTumor discovered within the first 2 months of life
dGravida and maternal age were not mentioned in the ten reports reviewed
eOther initial findings, one example each: hydrocephalus, vomiting, setting sun eye sign, lethargy, hemiparesis, hypotonia, malaise, intracranial hemorrhage, breech presentation, dystocia
fDesmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma: ganglion cells present in addition to astrocytic cells
gDesmoplastic infantile astrocytoma: astrocytic cells present; ganglion cells not present
hOne patient was operated upon at age 2 months for removal of DIG. Subsequently 8 years later, the tumor recurred as GBM [2]
Table 7.
Fetal and neonatal astroblastoma (n = 5)
| Male/female | 4/1 = 4 |
| Fetusesa | 4 |
| Neonatesb | 1 |
| Gestation (weeks) | 35, range 31–39 |
| Birth weight (g) | 2725, range 2500–2950 |
| Maternal history | |
| Maternal agec | – |
| Gravidac | – |
| Delivery | |
| Vaginal | 3 |
| Cesarian section | 2 |
| Initial findings | |
| Mass discovered on imaging | 5 |
| Macrocephaly | 4 |
| Hemorrhage | 3 |
| Hydrocephalus | 2 |
| Bulging anterior fontanel | 1 |
| Respiratory distress | 1 |
| Location | |
| Cerebral hemisphered | 5 |
| Cerebral hemisphere replaced by tumor | 2 |
| Tumor characteristics | |
| Tumor greatest dimension (cm) | 10, range 9–11 |
| Treatment | |
| Patients treated | 4 |
| Patients not treated | 1 |
| Survival with surgical resection alone | 0/2 |
| Survival with SR + CT | 2/2 (100) |
| Outcome | |
| Fetal survival | 1/3 (33.3)e |
| Neonatal survival | 1/1 (100) |
| Patients treated survived | 2/4 (50) |
| Patients not treated survived | 0/1 |
| Overall survival | 2/5 = 40 % |
Cases selected from the literature
aTumor discovered prenatally or on the first day of life
bTumor discovered within the first 2 months of life
cMaternal age and gravida were given for patient no. 5 (age 29, G4, P3)
dCerebral hemisphere locations: cerebral hemisphere ( frontal lobe 2, cerebral hemisphere, site NOS, 3)
eFetus lost to follow-up (presumed dead)
Table 8.
Fetal and neonatal gemistocytic astrocytoma (n = 3)
| Female/male | 2/1 |
| Fetusesa | 3 |
| Neonatesb | 0 |
| Gestation (weeks) | 35, range 32–40 |
| Birth weight (g) | 3523c |
| Maternal history | |
| Maternal age (years) | 29, range 19–36 |
| Gravida | G1, G3 |
| Delivery | |
| Vaginal | 0 |
| Cesarian section | 3 |
| Initial findings | |
| Macrocephalus | 3 |
| Hydrocephalus | 3 |
| Intracranial mass discovered on imaging | 2 |
| Intracranial hemorrhage | 2 |
| Bulging anterior fontanel | 1 |
| Seizures | 1 |
| Dystocia | 1 |
| Irritability | 1 |
| Vomiting | 1 |
| Location | |
| Cerebral hemisphere, occipital lobe | 1 |
| Cerebral hemispheres replaced by tumor | 1 |
| Tumor filled one half of intracranial cavity | 1 |
| Tumor characteristics | |
| Brain weight (g) | 654c |
| Tumor weight (g) | |
| Tumor greatest dimension (cm) | |
| Treatment and survival | |
| Patients treated | 1 (1/3) |
| Patients not treated | 2 (0/3) |
| Survival with surgical resection + chemotherapy | 1 (1/1)d |
| Outcome | |
| Fetal | 1/3 |
| Patients treated survived | 1/1 |
| Patients not treated survived | 0/2 |
| Overall survival | 1/3 = 33 % |
Cases selected from the literature
aTumor discovered before birth or on the first day of life
bTumor discovered during the first 2 months of life
cGiven for one patient only
dCombination chemotherapy using cisplatinum and vincristine. Patient had a recurrence at age 10 months
Materials and methods
Retrospective review of 101 cases including 57 fetuses and 44 neonates with astrocytoma was performed. They were collected from the literature, mostly from the archives of the National Library of Medicine (PubMed MEDLINE) and from our institution. The study was confined to fetuses with astrocytoma that were detected prenatally by imaging studies or discovered at birth and neonates with tumors occurring during the first 2 months of life. Only patients with adequate clinical and pathological data and where outcomes of pregnancy and survival were given were accepted for review. The following data were collected and tabulated: maternal age, gravida, initial presentation, and obstetric management, and the fetal data—sex of the fetus, weeks of gestation, birth weight, tumor location and dimensions, histology and grade, treatment, and outcome. Diagnosis of the various tumors was established in patients included in the study by histological confirmation of biopsy or surgical and/or postmortem specimens. Time period of patient accrual was from 1970 to 2015. Length of follow-up varied from 1 week to 1 year.
Results
One hundred one fetuses and neonates, presented with astrocytoma (Tables 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9). Most tumors were detected during the third trimester of pregnancy. They varied from low-grade, I and II, to high-grade malignancies (grades III and IV) (Tables 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, and 8). High-grade astrocytomas were more prevalent than lower grade ones, a ratio of 1.5:1. Glioblastoma was the major neoplasm, 45 or 44.6 %. Next were subependymal giant cell astrocytoma 18 (17.9 %), followed by ten examples of each anaplastic astrocytoma (9.9 %), low-grade (I–II) astrocytoma (9.9 %), and desmoplastic infantile astrocytoma/ganglioglioma (9.9 %); the two less common tumors were astroblastoma, 5 (4.9 %), and gemistocytic astrocytoma, 3 (2.97 %) examples.
Table 1.
Distribution of 101 perinatal astrocytomas
| Tumor | Number (%) |
|---|---|
| Glioblastoma | 45 (44.6) |
| Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma | 18 (17.9) |
| Low-grade, I–II, astrocytoma | 10 (9.90) |
| Anaplastic astrocytoma | 10 (9.90) |
| Desmoplastic infantile astrocytoma/ganglioglioma | 10 (9.90) |
| Astroblastoma | 5 (4.90) |
| Gemistocytic astrocytoma | 3 (2.97) |
| Total | 101 (100) |
Overall, the main presenting findings were macrocephaly and an intracranial mass followed by hydrocephalus and intracranial hemorrhage (Tables 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9). Nine percent (5/57) of the affected fetuses were stillborn. The overall survival for both fetuses and neonates was 47/101 or 46.5 %.
Glioblastoma malignant astrocytoma grade 4 (GBM)
Arises from the cerebral hemispheres and basal nuclei of fetuses, stillbirths, and infants [21, 23, 24, 30, 38, 43, 49, 68, 72]. It is the leading form of astrocytoma in this and in other similar perinatal studies [12, 15, 30, 31, 68]. GBM comprised almost half of the cases here (Tables 1, 2, and 9). An echogenic mass occupying much of one or both hemispheres accompanied by a shift of midline structures, obstructive hydrocephalus, and hemorrhage were the main prenatal ultrasound findings [21, 23, 38, 89, 93] (Table 2). Serial imaging studies showed that tumor growth developed rapidly over a surprisingly short period of time. Intracranial hemorrhage contributed also to the tumor’s rapid size increase [38, 89]. Dystocia occurred when there was a large space occupying intracranial mass. Cephalocentesis (cranial perforation) may be required for removal of the tumor before vaginal delivery could occur [1]. Large head circumference, hydrocephalus, and a bulging anterior fontanel were the main presenting findings in the neonate.
Pathology
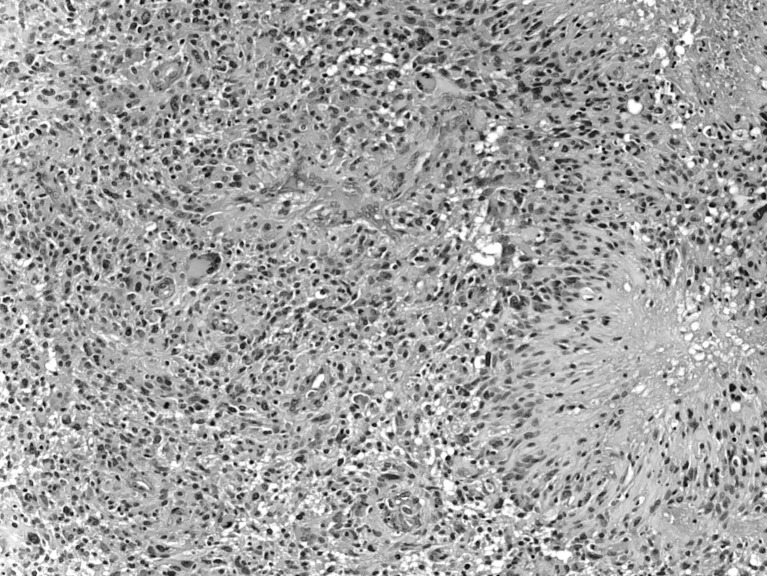
The cerebral hemisphere was the most common site of origin, namely, 34/45 or 76 % (Table 2). On gross inspection, many GBMs were large with soft pale-gray, hemorrhagic, and necrotic areas [35, 42, 82, 84]. Microscopically, they showed hypercellularity, marked pleomorphism, tumor giant cells, microvascular proliferation, and “palisading necrosis” (neoplastic spindle-shaped cells form palisades around central necrotic foci) [11, 13, 30, 39] (Fig. 1). GFAP and vimentin are immunoreactive. Some other findings include a strong nuclear expression of p53 and 10q deletions. High-grade astrocytomas were more prevalent than low-grade ones in this review.
Fig. 1.
GBMs showing hypercellularity, marked pleomorphism, tumor giant cells, microvascular proliferation, and “palisading necrosis” (neoplastic spindle-shaped cells form palisades around central necrotic foci)
Fetal and neonatal GBMs are genetically different from their adult counterparts and show a low frequency of known genetic defects [11].
Treatment and outcome
Fetuses with GBM may be born moribund or die soon after birth [1, 21, 27, 30, 49]. The prognosis for young patients with this tumor is discouraging low (Table 2). The overall survival rate was only 9 of 45 or 20 % (Tables 2 and 9). Nevertheless, cure was not always out of the question. All six patients who had surgical resection and chemotherapy [10, 11, 46, 50], one with surgical resection, embolization, and chemotherapy [74], and two of six who received surgery as the only treatment, survived [93] (Table 2). Neonatal survival of 50 % was higher than fetal, which was only 6.5 %.
Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma (SEGA) is one of the unique forms of astrocytoma. It occurs in brains of patients with tuberous sclerosis (TSC) and in those without the disease. Most are found during the first and second decades of life and only occasionally in the perinatal period [30, 31, 51, 56, 58–60, 63] (Table 3).
TSC is an autosomal-dominant inherited condition characterized by highly variable clinical manifestations including seizures, mental retardation, skin lesions, and hamartomas affecting multiple organ systems such as the heart, brain, eye, and kidney [33, 60, 73, 89] (Table 3). Brain lesions consist of subependymal nodules, white matter heterotopias, cortical tubers, and SEGA [73]. Cortical tubers and subependymal nodules are much more common than SEGA [31]. Tubers are situated throughout the white matter whereas subependymal nodules characteristically are found in or near the ventricles. The former are composed of firm, focal areas consisting of large eosinophilic cells with prominent nuclei suggesting features of both neurons and astrocytes [13, 33, 73]. Subependymal nodules have a histological appearance similar to SEGA. In some instances, there is really no well-defined cytologic difference between the two. Moreover, serial imaging and biopsy studies reveal transitions of subependymal nodules to SEGA [73]. Apparently, size of the lesion does not seem to be helpful in distinguishing between the two.
Fetuses and neonates with TSC present more often clinically with their cardiac problems, namely uncontrollable arrhythmias and intracavitary outflow obstruction due to rhabdomyoma(s), rather than manifestations of their CNS pathology [30, 31, 33, 89]. For example, 11 of 18 fetuses and neonates in the study here had 1 or more cardiac rhabdomyoma. Newborns diagnosed initially with SEGA may go on to develop other manifestations of TSC [33].
Table 3 shows that males are affected more often than females, a ratio of 3.5 to 1. Of the 18 patients with SEGA a family history of TSC was given only in one; however, a history of this disease was not mentioned in eight patients. Hydrocephalus and an intracranial mass were the main presenting findings (Table 3). SEGAs appeared on sonograms as subependymal echogenic nodules situated in the walls of lateral ventricles typically near the foramen of Monro. The tumor was nodular and of mixed signal or iso-dense to the brain, enhancing densely with contrast on CT scan. Calcifications are noted often within the tumor [51, 56, 59, 63].
Pathology
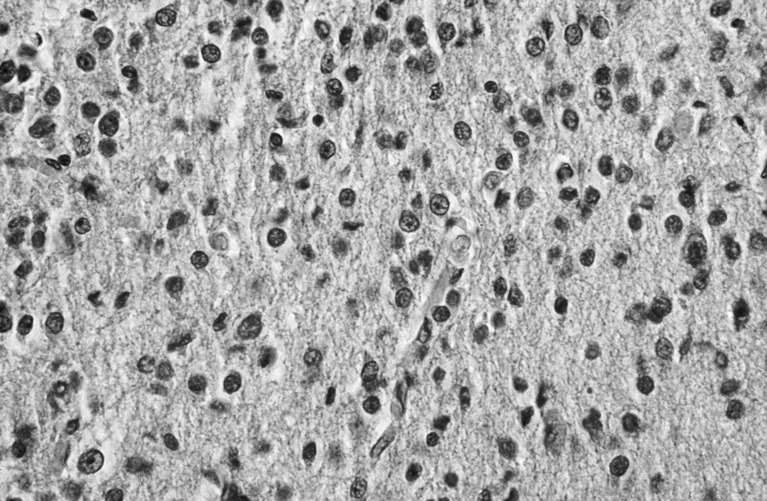
SEGAs occurred as outgrowths from within or beneath the walls of lateral ventricles. They obstructed the foramen of Monro or blocked the third ventricle producing hydrocephalus [30, 51, 56, 58]. Cerebral hemisphere was the most common site of origin occurring all 18 patients here (Table 3). Ten were located near or within the foramen of Monro obstructing it. Microscopic examination reveals large astrocytic cells with abundant pink staining cytoplasm, slightly vesicular nuclei, and prominent nucleoli (Fig. 2). Cells are surrounded by numerous fibrillary processes. The tumors are variably immunoreactive with GFAP, S-100, and β-tubulin, suggesting perhaps a mixed glial-neuronal phenotype [39]. Although histologically SEGA resembles gemistocytic astrocytoma, the latter is more infiltrative and located within the parenchyma rather than a well-demarcated, exophytic intraventricular growth. Moreover, SEGA cells tended to be larger than neoplastic gemistocytes, which also usually lack calcifications [13, 73].
Fig. 2.
Microscopic examination revealing large astrocytic cells with abundant pink staining cytoplasm, slightly vesicular nuclei, and prominent nucleoli
Treatment and outcome
Twelve of 18 SEGA patients were treated; 5 were not. One nontreated neonate was lost to follow-up. Nine of 11 infants treated with either surgical resection alone or surgery plus evorolimus chemotherapy survived [40, 51, 56, 60, 64]. Overall survival rate was 70.6 % (Table 3). Fetal deaths were five times greater than neonatal. Treatment of SEGA is discussed in detail elsewhere [92].
Low -grade astrocytoma—pilocytic astrocytoma, grade I, arises throughout the neural axis. The spinal cord, cerebral hemisphere, and optic nerve were the tumor locations in this review. Half occurred in the spinal cord [17, 53, 77], three in the cerebral hemisphere [7, 44, 70, 83, 90], and two in the optic nerve [7, 44] (Table 4). Intracranial mass on prenatal imaging was the most common presentation in the fetus whereas a spinal mass and paralysis were the main ones in the neonate (Table 4).
Pathology
Low-grade 1 pilocytic astrocytoma exists on the benign end of the histologic spectrum. The tumor consists of small bipolar and stellate-shaped cells with scanty processes forming loose and compact areas and microcysts [13, 39] (Fig. 3). Rosenthal fibers and eosinophilic granular (cytoid) bodies are characteristically but variably present. Anaplastic changes consisting of cellular and nuclear pleomorphism, nuclear hyperchromatism, neoplastic giant cells, and bizarre mitoses are absent. Mitoses are uncommon. Astrocytoma cells react strongly with GFAP and negatively with synaptophysin, neurofilament, desmin, cytokeratin, and epithelial membrane antibodies [9, 13, 30, 39].
Fig. 3.
The tumor consisting of small bipolar and stellate-shaped cells with scanty processes forming loose and compact areas and microcysts
Optic pilocytic astrocytoma originates as a fusiform or globular mass arising from the optic nerve [7, 9]. The tumor produces a dumbbell-shaped mass with cyst formations in both intraorbital and intracranial segments of the nerve. There is a significant association between optic pathway pilocytic astrocytoma and neurofibromatosis type 1 approaching 50 % in some series [9, 30, 34, 67]. This association foretells a poor prognosis.
Treatment and outcome
All three patients with low-grade I and II cerebral astrocytoma treated by surgical resection as the only form of therapy were cured [70, 83, 90]. Both neonates with optic astrocytoma survived, one received surgery only and the other surgery plus vincristine and carboplatin [7, 44]. There were five patients with spinal cord tumors, and of these, four survived. Death occurred in a 3120-g, 37-week gestation male fetus who was the product of a breech presentation. He received a subtotal resection for a spinal cord, T8–T11, tumor. Subsequently, the baby developed paralysis of both upper and lower extremities and died at age 8 weeks [17]. Overall survival for the entire low-grade astrocytoma group was 9/10 or 90 %, which is the highest figure recorded for the entire review (Tables 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9). Unfortunately, three of the four patients with spinal cord tumors who survived had serious residual disabilities. On the other hand, two with low-grade cerebral astrocytoma were left without significant ones. More detailed treatment of low-grade astrocytoma is discussed elsewhere [16, 26, 65, 79].
Anaplastic astrocytoma occurs less often in older children than the low-grade-astrocytoma whereas in the fetus and neonate, the incidence of the two is about the same (Tables 4 and 5). The term “anaplastic astrocytoma” refers to those tumors of intermediate-grade malignancy corresponding to the WHO classification grade III [13, 39].
Pathology
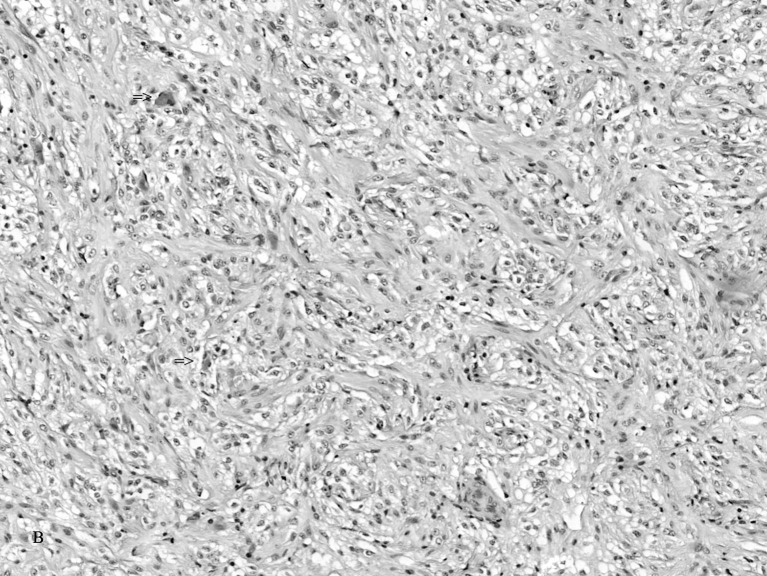
All ten anaplastic astrocytomas were located in the cerebral hemispheres [14, 18, 19, 27, 57, 69, 80, 94] (Table 5). Microscopically, they show cytoplasmic and nuclear pleomorphism, hypercellularity, mitotic activity to a degree, but lack the pallisading necrosis or vascular proliferation of GBM [18, 19, 27, 69, 78, 80, 94] (Fig. 4). However, one exception was a specimen from a stillborn fetus (therapeutic termination) whose tumor was discovered by ultrasound at 31-week gestation; intracranial hemorrhage and vascular proliferation were found along with pleomorphism, hypercellularity, and mitotic activity, suggesting perhaps an early in utero transformation to GBM [27]. GFAP and vimentin antibodies are reactive, but NSE, synaptophysin, neurofilament, desmin, cytokeratin, and epithelial membrane antigen are not.
Fig. 4.
Anaplastic astrocytomas showing cytoplasmic and nuclear pleomorphism, hypercellularity, mitotic activity to a degree, but lack the pallisading necrosis or vascular proliferation of GBM
Treatment and outcome
Six of ten patients with cerebral anaplastic astrocytomas were treated by several modalities: (1) surgical resection as the only form of therapy [18, 69], (2) surgery plus chemotherapy [19, 80, 94], and (3) surgery followed by chemotherapy and irradiation [78]. Five of six survived no matter what form of therapy was given (Table 5). Of the four patients who were not treated, one survived. Overall survival was 6/10 or 60 %.
Desmoplastic cerebral astrocytoma/desmoplastic cerebral ganglioglioma of infancy (DIAGA) occurs most often during the first year of life than at any other time [2, 4, 20, 25, 30, 45, 47, 62, 71, 81, 83, 86]. The diagnosis was made in this review in nine neonates and in one fetus (Table 6). There was a 9:1 male predominance. Tumors in seven patients were detected prenatally by ultrasound and appeared typically as a large cystic mass with a solid component situated within a cerebral hemisphere; most extended peripherally into the dura [20, 30, 45, 75, 86]. A large, intracranial hemorrhage was present also in the fetal patient obscuring the tumor and making diagnosis difficult [83].
An ongoing discussion in the literature exists regarding nosology and grading of this group of tumors [30, 39]. The question is raised whether infantile desmoplastic cerebral ganglioglioma (DIAG) and desmoplastic cerebral astrocytoma (DIA) represent the same histologic entity or two different conditions. During the perinatal period, their clinical features, pathology, treatment, and outcome are almost the same.
In addition, there is some disagreement about the WHO grading classification [30, 39]. The initial benign histology and clinical findings in the ten patients in this review are more consistent with a grade I–II tumor rather than a high-grade one. Nevertheless, it should be mentioned that some DIAGAs reported in some older children and adults have been diagnosed malignant [2, 62].
Pathology
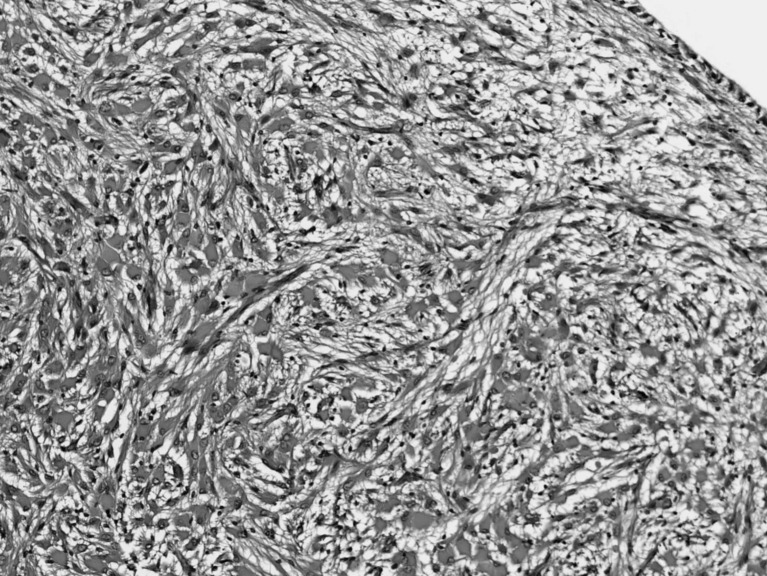
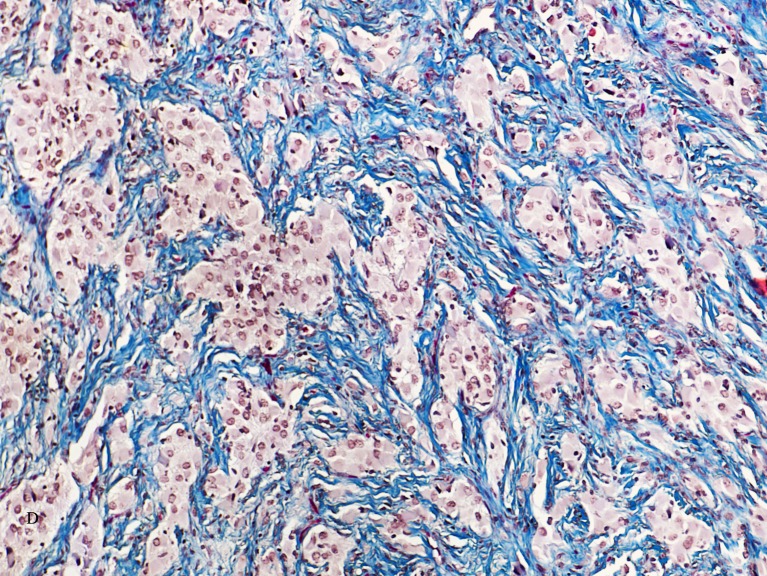
Characteristic histologic findings are a cellular, spindle cell tumor with a prominent collagenous (“desmoplastic,” fibrous) stroma composed of bipolar and spindle-shaped cells having an eosinophilic cytoplasm and cells with long processes [20, 30, 45, 83, 86] (Fig. 5). Astrocytic cells form bundles and nests separated by thick bands of collagen [4, 30, 45, 83, 86]. Lymphocytes are variably present. Reticulin stain shows thick fibers surrounding nests of individual cells. Tumor cells and their processes react with GFAP and collagen fibers stain strongly blue with Masson’s trichrome [20, 30]. Ganglion cells were present in the six DIAG tumors but not identified in the four DIAs (Table 6).
Fig. 5.
Characteristic histologic findings showing a cellular, spindle cell tumor with a prominent collagenous (desmoplastic, fibrous) stroma composed of bipolar and spindle-shaped cells having an eosinophilic cytoplasm and cells with long processes. The prominent, blue collagen component is shown by the Mallory trichrome stain.
Treatment and outcome
Eight of ten patients who were treated by surgery alone were cured [2, 4, 25, 47, 81, 88]. The male fetus listed in Table 6 was operated upon at age 2 months for removal of a DIAG. Eight years later, he died; the tumor recurred as GBM [62].
DIAGA is one of the astrocytoma groups usually associated with a relatively good prognosis overall provided that a complete resection was done; there was an 80 % survival for this group of tumors [4, 20, 45, 86] (Table 6).
Astroblastoma is a rare, controversial, supratentorial, tumor first described by Bailey and Bucy in 1930 [3]. The existence of this neoplasm has been debated ever since. The exact cell of origin has not been established [61]. Currently, it is placed in the WHO classification as a neuroepithelial tumor of uncertain origin [39]. It is exceedingly rare for less than five prenatal cases have been reported [5, 29, 35, 61, 66, 87] (Table 7).
Pathology
The dominant histologic feature is the characteristic perivascular pseudorosette [8, 66]. Two definite histological types of astroblastoma are described: low-grade and high-grade [8]. The low-grade lesion is a better differentiated tumor with more benign histologic findings, and the high-grade type has more anaplastic features and a poorer prognosis [8]. Low-grade astroblastoma consists of orderly perivascular pseudorosettes, having a papillary appearance, minimal cellular atypia, rare mitoses, and no microvascular proliferation. High-grade lesions show loss of the typical papillary architecture, areas of solid growth, increased cellularity with nuclear atypia, increased mitotic activity, and microvascular proliferation [8, 52, 85]. As one would anticipate low-grade, differentiating astroblastoma has a better prognosis than the anaplastic type [52]. At present, a WHO grade has not been assigned to this tumor [52].
The main entity in the differential diagnosis of astroblastoma is the well-differentiated ependymoma [13, 61, 66]. Clear spaces are present between the astroblastoma pseudorosettes whereas the ependymoma has a more compact architecture. There are differences in nuclear characteristics and thickness of the perivascular cytoplasmic processes as well. Astroblastomas exhibit broad foot plates opposed to tapering processes as seen in ependymomas [61]. Some tumors may resemble papillary meningioma or even a choroid plexus tumor. The main difference here is that astroblastoma is immunoreactive with GFAP whereas the meningioma is not; choroid plexus papilloma is focally GFAP positive [13].
Treatment and outcome
Treatment of astroblastoma is unsettled, largely because the rarity of the tumor precludes definitive therapeutic studies. Anaplastic histology is an important prognostic factor. Surgical resection is regarded as the preferred treatment modality; it plays a major role in managing the well-differentiated astroblastoma [52]. The precise role for irradiation and chemotherapy has not been well defined since only a few cases have been published to date [85]. However, these procedures could be considered in the treatment of the anaplastic type [52]. Prognosis is further complicated by the potential of the astroblastoma converting a more malignant form of glioma, namely GBM [8]. The clinical course is unpredictable.
Gemistocytic astrocytoma (GA) is a member of the diffuse astrocytoma group [13, 39, 41, 54]. It is much more common in older individuals where survival rates are higher than those in the fetus and neonate. Literature review uncovered only three examples of fetal GA all detected by prenatal ultrasound [6, 48, 54] (Table 8).
Pathology
Certain histologic criteria are required to make the diagnosis of GA. The main one is that a significant number of neoplastic gemistocytic astrocytes must be present in the tumor, at least 20 %, since collections of well-differentiated GA cells can mimic reactive astrocytes [39]. Although the tumor resembles SEGA, the GA cells are smaller and have a more prominent, eosinophilic cytoplasm containing an eccentric nucleus and a small nucleolus. Cells are surrounded by thick and thin cell processes. Tumor cells are reactive with GFAP and vimentin, either diffusely or focally [6, 48, 54]. There is a second atypical cellular component consisting of smaller cells with prominent, more darkly staining nuclei and scant, sometimes barely visible cytoplasm. This is the so-called growth (proliferative) fraction which is MIB-1/Ki67 reactive [13, 39]. The larger eosinophilic cells show a much lower proliferation rate than the smaller component. Perivascular lymphocyte cuffing is variably present to some degree.
All three GA patients in this review had large hemispheric tumors detected by prenatal ultrasound or on the day of birth. The first patient in Table 8, a female of 32-week gestation, died at 2 months of age without treatment [6]. The GA occupied half of the intracranial cavity. Her histology showed no necrosis, vascular proliferation, or other cellular atypical features [6]. The second patient received surgery and chemotherapy and survived [54]. The third infant lived for 6 days without treatment. Her tumor cells exhibited mild pleomorphism, increased cellularity, a low MIB-1 index (<1 %), but palisading necrosis and endothelial proliferation were noted; this tumor was designated as malignant [48].
Treatment and outcome
The only survivor, patient 2 (tumor WHO grade 2), was a full-term male with a right occipital lobe primary [54] (Table 8). Microscopically, the GA revealed atypical tumor cells and an elevated MIB-1 index of 15 %. The child was alive and well even after a relapse at age 2.5 years. He was treated by complete surgical resection and chemotherapy consisting of vincristine and cis-platinum [54]. Current therapy of GA is discussed elsewhere [22, 26, 28, 65].
GA shows a tendency to behave aggressively more than other grade I and II astrocytomas. Some may progress to anaplastic astrocytoma and eventually GBM [54].
Discussion
Astrocytoma is the foremost neuroglial tumor occurring throughout infancy and childhood and is derived from and composed of astrocytes showing varying degrees of differentiation. As a group, astrocytomas differ in their gross and histological features as well as in their site of origin and clinical manifestations [12, 15, 27, 30, 31, 37, 57, 68, 93] (Table 9 ).
Most perinatal astrocytomas occur outside the posterior cranial fossa and above the tentorium (Tables 2). When it can be determined, the cerebral hemisphere is the most common primary site. Those arising from this location tend to be large, involve more than one lobe, and displace the ventricle(s). In some instances, the brain may be almost completely replaced by tumor.
Astrocytoma typically presents in the fetus and neonate as an intracranial mass, which is the initial observation on prenatal or postnatal sonograms; hydrocephalus macrocephaly and intracranial hemorrhage, in that order, are additional presenting findings (Tables 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, and 8).
Tumors vary considerably in their microscopic appearance. Histologically, they range from benign (low-grade) to malignant (high-grade) tumors (Table 9). Here, there were 55 high-grade astrocytomas compared to 46 low-grade ones [52].
Treatment is primarily surgical, like other brain tumors in this age group [31]. Sometimes surgery is preceded by a shunt, and in selected cases followed by chemotherapy [30, 31, 37]. Usually, irradiation is contraindicated because of immaturity of the developing brain and adjacent structures. The extent and size of the tumor and the general condition of the neonate are limiting factors that can preclude surgery. Some tumors can be inoperable because of their large size or unstable condition of the infant [31].
Compliance with ethical standards
Conflict of interest
The author declares that he has no conflict of interest.
References
- 1.Anteby SO, Cohen H, Sadovsky E. Dystocia caused by fetal intracranial tumor. Obstetr Gynecol. 1974;43:50–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bader A, Heran M, Dunham C, et al. Radiological features of infantile glioblastoma and desmoplastic infantile tumors: British Columbia’s Children’s Hospital experience. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2015;16:119–125. doi: 10.3171/2014.10.PEDS13634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bailey P, Bucy PC. Astroblastomas of the brain. Acta Psychiatri Neurol. 1930;5:439–461. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1930.tb08230.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bekiesinska Figatowska M, Jurkiewicz E, Duczkowski M, et al. Congenital CNS tumors diagnosed on prenatal MRI. Neuroradiol J. 2011;24:477–481. doi: 10.1177/197140091102400402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bell JW, Osborn AG, Salzman KL, et al. Neuroradiologic characteristics of astroblastoma. Neuroradiol. 2007;49:203–209. doi: 10.1007/s00234-006-0182-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bleggi Torres LF, Pope LZ, Koerbel A, et al. November 2003: neonatal female with congenital brain tumor. Congenital gemistocytic astrocytoma. Brain pathol. 2004;14:227–228. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2004.tb00101.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bonner J, Ide CH. Astrocytoma of the optic nerve and chiasm associated with microphthalmos and orbital cyst. Brit J Ophthalmol. 1974;58:828–831. doi: 10.1136/bjo.58.9.828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bonnin JM, Rubinstein LJ. Astroblastomas: a pathological study of 23 tumors, with a postoperative follow-up in 13 patients. Neurosurg. 1989;25:6–13. doi: 10.1227/00006123-198907000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Borit A, Richardson EP. The biological and clinical behavior of pilocytic astrocytomas of the optic pathways. Brain. 1982;105:161–187. doi: 10.1093/brain/105.1.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Boukas A, Panaretos P, Cowie C, et al. Congenital glioblastoma multiforme: complete resection with long-term survival and a novel technique of contralateral cystoventriculostomy. Pediatr neurosurg. 2012;48:327–330. doi: 10.1159/000351411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Brat DJ, Shehata BM, Castellano Sanchez A, et al. Congenital glioblastoma: a clinicopathologic and genetic analysis. Brain pathol. 2007;17:276–281. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2007.00071.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Buetow PC, Smirniotopoulos JG, Done S. Congenital brain tumors: a review of 45 cases. Am J Roentgenol. 1990;155:587–593. doi: 10.2214/ajr.155.3.2167004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Burger PC, Scheithauer BW. Tumors of the central nervous system. Atlas of Tumor Pathology, 4th series, Fascicle 7. Washington, D.C.: Armed Forces Institute of Pathology; 2007. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Carstensen H, Juhler M, Bøgeskov L, Laursen H. A report of nine newborns with congenital brain tumours. Child’s Nervous System. 2006;22:1427–1431. doi: 10.1007/s00381-006-0115-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Cassart M, Bosson N, Garel C, et al. Fetal intracranial tumors: a review of 27 cases. Europe Radiol. 2008;18:2060–2066. doi: 10.1007/s00330-008-0999-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Child Astrocytoma Treatment (PDQ)- Health professional Version-National Cancer Institute (2016) February
- 17.Colby C, Rozance P, Goodwin TL, et al. Rapid deterioration of a newborn with congenital spinal cord astrocytoma. Med Pediatr Oncol. 2001;36:500–502. doi: 10.1002/mpo.1118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Connolly B, Blaser SI, Humphreys RP, Becker L. Long-term survival of an infant with ‘anaplastic’ astrocytoma. Pediatr Neurosurg. 1997;26:97–102. doi: 10.1159/000121170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Das A, Simmons C, Danielpour M. A congenital brain tumor associated with assisted in vitro fertilization. Case report. J Neurosurg. 2005;103(5 Suppl):451–253. doi: 10.3171/ped.2005.103.5.0451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.de Chadarévian JP, Pattisapu JV, Faerber EN. Desmoplastic cerebral astrocytoma of infancy. Light microscopy, immunocytochemistry, and ultrastructure. Cancer. 1990;66:173–179. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19900701)66:1<173::AID-CNCR2820660131>3.0.CO;2-H. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Dören M, Tercanli S, Gullotta F, Holzgreve W. Prenatal diagnosis of a highly undifferentiated brain tumour—a case report and review of the literature. Prenat Diagn. 1997;17:967–971. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0223(199710)17:10<967::AID-PD165>3.0.CO;2-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Estlin E, Lowis S. Astrocytoma. In: Estlin E, Lowis S, editors. CNS tumors of childhood. Clinics in Developmental Medicine No. 166. Cambridge: MacKeith Press; 2005. pp. 203–220. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Geraghty AV, Knott PD, Hanna HM. Prenatal diagnosis of fetal glioblastoma multiforme. Prenat Diagn. 1989;9:613–616. doi: 10.1002/pd.1970090903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Gerlach H, Jänisch W, Schreiber D. CNS tumors of the perinatal period (author’s transl) Zentralblatt für allgemeine Pathologie und pathologische Anatomie. 1982;126:23–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Gu S, Bao N, Yin M. Combined fontanelle puncture and surgical operation in treatment of desmoplastic infantile astrocytoma: case report and a review of the literature. J Child Neurol. 2010;25:216–221. doi: 10.1177/0883073809333542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hargrave D. Paediatric high and low grade glioma: the impact of tumour biology on current and future therapy. Brit J Neurosurg. 2009;23:351–363. doi: 10.1080/02688690903158809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Heckel S, Favre R, Gasser B, Christmann D. Prenatal diagnosis of a congenital astrocytoma: a case report and literature review. Ultras Obstet Gynecol. 1995;5:63–66. doi: 10.1046/j.1469-0705.1995.05010063.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Heideman RL, Kuttesch J, Gajjar AJ, et al. Supratentorial malignant gliomas in childhood: a single institution perspective. Cancer. 1997;80:497–504. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19970801)80:3<497::AID-CNCR18>3.0.CO;2-S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Iruretagoyena JI, Heiser T, Iskandar B, Shah D. A rare malignant fetal brain tumor. Fetal Diagn Ther. 2016;39:311–314. doi: 10.1159/000430911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Isaacs H., Jr . Brain tumors. In: Isaacs H Jr, editor. Tumors of the fetus and infant: an atlas. New York: Springer-Verlag; 2013. pp. 163–195. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Isaacs H. Fetal brain tumors: a review of 154 cases. Amer J Perinatol. 2009;26:453–466. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1214245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Isaacs H. I. Perinatal brain tumors: a review of 250 cases. Pediatr Neurol. 2002;27:249–261. doi: 10.1016/S0887-8994(02)00472-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Isaacs H. Perinatal (fetal and neonatal) tuberous sclerosis: a review. Amer J Perinatol. 2009;26:755–760. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1223267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Isaacs H. Perinatal neurofibromatosis: two case reports and review of the literature. Amer J Perinatal. 2010;27:285–292. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1241737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Jänisch W, Schreiber D, Martin H, et al. Primary intracranial tumors as cause of death in the fetus and infant. Zentralbl Allg Pathol. 1985;129:75–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Jellinger K, Sunder-Plassmann M. Connatal intracranial tumours. Neuropadiatr. 1973;4:46–63. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1091727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Jooma R, Kendall BE, Hayward RD. Intracranial tumors in neonates: a report of seventeen cases. Surg Neurol. 1984;21:165–170. doi: 10.1016/0090-3019(84)90336-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kamitomo M, Sameshima H, Uetsuhara K, et al. Fetal glioblastoma: rapid growth during the third trimester. Fetal Diagn Ther. 1998;13:339–342. doi: 10.1159/000020865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Kleihues P, Cavenee WK. Pathology and Genetics of Tumors of the Nervous System. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer, WHO; 1997. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Kotulska K, Borkowska J, Mandera M, et al. Congenital subependymal giant cell astrocytomas in patients with tuberous sclerosis. Childs Nerv syst. 2014;30:2037–2042. doi: 10.1007/s00381-014-2555-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Krouwer HG, Davis RL, Silver P, Prados M. Gemistocytic astrocytomas: a reappraisal. J neurosurg. 1991;74:399–406. doi: 10.3171/jns.1991.74.3.0399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Lee DY, Kim YM, Yoo SJ, et al. Congenital glioblastoma diagnosed by fetal sonography. Childs NS. 1999;15:197–201. doi: 10.1007/s003810050369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Leins AM, Kainer F, Weis S. Sonography and neuropathology of a congenital brain tumor: report of a rare incident. Ultrastr Obstet Gynecol. 2001;17:245–247. doi: 10.1046/j.1469-0705.2001.00350.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Lertchavanakul A, Baimai C, Siwanuwatn R, et al. (2001) Optic nerve glioma in infancy: a case report of the youngest patient in Thailand. 84(Suppl 1):S137–141 [PubMed]
- 45.Louis DN, von Deimling A, Dickersin GR, et al. Desmoplastic cerebral astrocytomas of infancy: a histopathologic, immunohistochemical, ultrastructural, and molecular genetic study. Human Pathol. 1992;23:1402–1409. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(92)90061-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Macy ME, Birk DK, Barton VN, et al. Clinical and molecular characteristics of congenital glioblastoma. Neuro-oncol. 2012;14:931–941. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nos125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Mallucci C, Lellouch Tubiana A, Salazar C. The management of desmoplastic neuroepithelial tumours in childhood. Child’s Nervous System. 2000;16:8–14. doi: 10.1007/PL00007280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Manoranjan B, Provias JP. Congenital brain tumors: diagnostic pitfalls and therapeutic interventions. J Child Neurol. 2011;26:599–614. doi: 10.1177/0883073810394848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.McConachie NS, Twining P, Lamb MP. Case report: antenatal diagnosis of congenital glioblastoma. Clin Radiol. 1991;44:121–122. doi: 10.1016/S0009-9260(05)80511-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Milano GM, Cerri C, Ferruzzi V, et al. Congenital glioblastoma. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2009;53:124–126. doi: 10.1002/pbc.22008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Mirkin LD, Ey EH, Chaparro M. Congenital subependymal giant-cell astrocytoma: case report with prenatal ultrasonogram. Pediatr Radiol. 1999;29:776–780. doi: 10.1007/s002470050693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Navarro R, Reitman AJ, de León GA, et al. Astroblastoma in childhood: pathological and clinical analysis. Child’s Nervous System. 2005;21:211–220. doi: 10.1007/s00381-004-1055-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Ng A, Pizer B, May P. Congenital spinal astrocytoma: how favourable is the long-term outcome? Br J Neurosurg. 2000;14:366–370. doi: 10.1080/026886900417423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Nozaki M, Ohnishi A, Fujimaki T, et al. Congenital gemistocytic astrocytoma in a fetus. Child’s Nerv Syst. 2006;22:168–171. doi: 10.1007/s00381-004-1109-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Oi S, Kokunai T, Matsumoto S. Congenital brain tumors in Japan (ISPN Cooperative Study): specific clinical features in neonates. Child’s Nervous System. 1990;6:86–91. doi: 10.1007/BF00307927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Oikawa S, Sakamoto K, Kobayashi N. A neonatal huge subependymal giant cell astrocytoma: case report. Neurosurg. 1994;35:748–750. doi: 10.1227/00006123-199410000-00025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Ortega Aznar A, Romero Vidal FJ, de la Torre J. Neonatal tumors of the CNS: a report of 9 cases and a review. Clinical Neuropathol. 2001;20:181–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Ostör AG, Fortune DW. Tuberous sclerosis initially seen as hydrops fetalis: report of a case and review of the literature. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1978;102:34–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Painter MJ, Pang D, Ahdab Barmada M, Bergman I. Connatal brain tumors in patients with tuberous sclerosis. Neurosurg. 1984;14:570–573. doi: 10.1227/00006123-198405000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Phi JH, Park S, Chae JH, et al. Congenital subependymal giant cell astrocytoma: clinical considerations and expression of radial glial cell markers in giant cells. Child’s Nerv Syst. 2008;24:1499–1503. doi: 10.1007/s00381-008-0681-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Pizer BL, Moss T, Oakhill A, et al. Congenital astroblastoma: an immunohisto-chemical study. Case report. J Neurosurg. 1995;83:550–555. doi: 10.3171/jns.1995.83.3.0550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Prakash V, Batanian JR, Guzman MA, et al. Malignant transformation of a desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma in an infant carrier of a nonsynonymous TP53 mutation. Pediatr Neurol. 2014;51:138–143. doi: 10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2014.02.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Raju GP, Urion DK, Sahin M. Neonatal subependymal giant cell astrocytoma: new case and review of literature. Pediatr Neurol. 2007;36:128–131. doi: 10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2006.08.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Ramenghi LA, Verrotti A, Domizio S, et al. Neonatal diagnosis of tuberous sclerosis. Child’s Nerv Syst. 1996;12:121–123. doi: 10.1007/BF00819512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Reddy AT, Packer RJ. Chemotherapy for low-grade gliomas. Child’s Nerv Syst. 1999;15:506–513. doi: 10.1007/s003810050539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Riboni G, De Simoni M, Leopardi O, Molla R. Ultrasound appearance of a glioblastoma in a 33-week fetus in utero. J Clin Ultrasound. 1985;13:345–346. doi: 10.1002/jcu.1870130510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Riccardi VM. Type 1 neurofibromatosis and the pediatric patient. Curr Probl Pediatr. 1992;22:66–106. doi: 10.1016/0045-9380(92)90053-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Rickert CH. Neuropathology and prognosis of foetal brain tumours. Acta Neuropathol. 1999;98:567–576. doi: 10.1007/s004010051120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Roosen N, Deckert M, Nicola N, et al. Congenital anaplastic astrocytoma with favorable prognosis. Case report. J Neurosurg. 1988;69:604–609. doi: 10.3171/jns.1988.69.4.0604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Rothman SM, Nelson JS, DeVivo DC, Coxe WS. Congenital astrocytoma presenting with intracerebral hematoma. Case report. J Neurosurg. 1979;51:237–239. doi: 10.3171/jns.1979.51.2.0237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Rout P, Santosh V, Mahadevan A, et al. Desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma—clinicopathological and immunohistochemical study of four cases. Child’s Nerv Syst. 2002;18:463–467. doi: 10.1007/s00381-002-0610-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Sabet LM. Congenital glioblastoma multiforme associated with congestive heart failure. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1982;106:31–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Scheithauer BW. The neuropathology of tuberous sclerosis. J Dermatol. 1992;19:897–903. doi: 10.1111/j.1346-8138.1992.tb03802.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Seker A, Ozek MM. Congenital glioblastoma multiforme. Case report and review of the literature. J Neurosurg. 2006;105(6 Suppl):473–479. doi: 10.3171/ped.2006.105.6.473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Setty SN, Miller DC, Camras L. Desmoplastic infantile astrocytoma with metastases at presentation. Modern Pathology. 1997;10:945–951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Severino M, Schwartz ES, Thurnher M, et al. Congenital tumors of the central nervous system. Neuroradiol. 2010;52:531–548. doi: 10.1007/s00234-010-0699-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Shafrir Y, Kaufman BA. Quadriplegia after chiropractic manipulation in an infant with congenital torticollis caused by a spinal cord astrocytoma. J Pediatr. 1992;120:266–269. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3476(05)80440-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Shin HJ, Kwon YJ, Park HJ, et al. An infant with prenatally diagnosed congenital anaplastic astrocytoma who remains disease-free after proton therapy. J Korean Med Sci. 2013;28:1394–1398. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2013.28.9.1394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Sievert AJ, Jackson EM, Gai X, et al. Duplication of 7q34 in pediatric low-grade astrocytomas detected by high-density single-nucleotide polymorphism-based genotype arrays results in a novel BRAF fusion gene. Brain Pathol. 2009;19:449–458. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2008.00225.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Stark AM, Modlich S, Claviez A, et al. Congenital diffuse anaplastic astrocytoma with ependymal and leptomeningeal spread: case report. J Neuro-Oncol. 2007;84:325–328. doi: 10.1007/s11060-007-9381-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Sugiyama K, Arita K, Shima T, et al. Good clinical course in infants with desmoplastic cerebral neuroepithelial tumor treated by surgery alone. J Neuro-oncol. 2002;59:63–69. doi: 10.1023/A:1016309813752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Takaku A, Kodama N, Ohara H, Hori S. Brain tumor in newborn babies. Child’s Brain. 1978;4:365–375. doi: 10.1159/000119793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Tekkök IH, Ventureyra EC. Spontaneous intracranial hemorrhage of structural origin during the first year of life. Child’s Nerv Syst. 1997;13:154–165. doi: 10.1007/s003810050061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Thankamony A, Harlow FH, Ponnampalam J, Clark P. Congenital brain tumour mimicking fetal intracranial haemorrhage. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2007;27:314–317. doi: 10.1080/01443610701241217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Thiessen B, Finlay J, Kulkarni R, Rosenblum MK. Astroblastoma: does histology predict biologic behavior? J Neuro-Oncol. 1998;40:59–65. doi: 10.1023/A:1006025000409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Trehan G, Bruge H, Vinchon M, et al. MR imaging in the diagnosis of desmoplastic infantile tumor: retrospective study of six cases. AJNR, Amer J Neuroradiol. 2004;25:1028–1033. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Turkmen E, Raisanen J, Dogan M, et al. A newborn with massive congenital astroblastoma. Fetal Pediatr Pathol. 2011;30:325–328. doi: 10.3109/15513815.2011.564718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Vanden Berg SR. Desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma and desmoplastic cerebral astrocytoma of infancy. Brain Pathol. 1993;3:275–281. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.1993.tb00754.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Volpe JJ. Brain tumors and vein malformations. In: Volpe JJ, editor. Neurology of the newborn. 5th. Philadelphia: WB Saunders Co; 2008. pp. 989–1005. [Google Scholar]
- 90.Wakai S, Arai T, Nagai M. Congenital brain tumors. Surg Neurol. 1984;21:597–609. doi: 10.1016/0090-3019(84)90277-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Watanabe K, Tachibana O, Yonekawa Y, et al. Role of gemistocytes in astrocytoma progression. Lab Invest. 1997;76:277–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Wheless JW, Klimo P. Subependymal giant cell astrocytomas in patients with tuberous sclerosis complex: considerations for surgical or pharmacotherapeutic intervention. J Child Neurol. 2014;29:1562–1571. doi: 10.1177/0883073813501870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Winters JL, Wilson D, Davis DG. Congenital glioblastoma multiforme: a report of three cases and a review of the literature. J Neurol Sci. 2001;188:13–19. doi: 10.1016/S0022-510X(01)00538-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Yamashita S, Ryu S, Miyata S, et al. A huge intraventricular congenital anaplastic astrocytoma: case report with histopathological and genetic consideration. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2012;29:107–112. doi: 10.1007/s10014-011-0071-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]