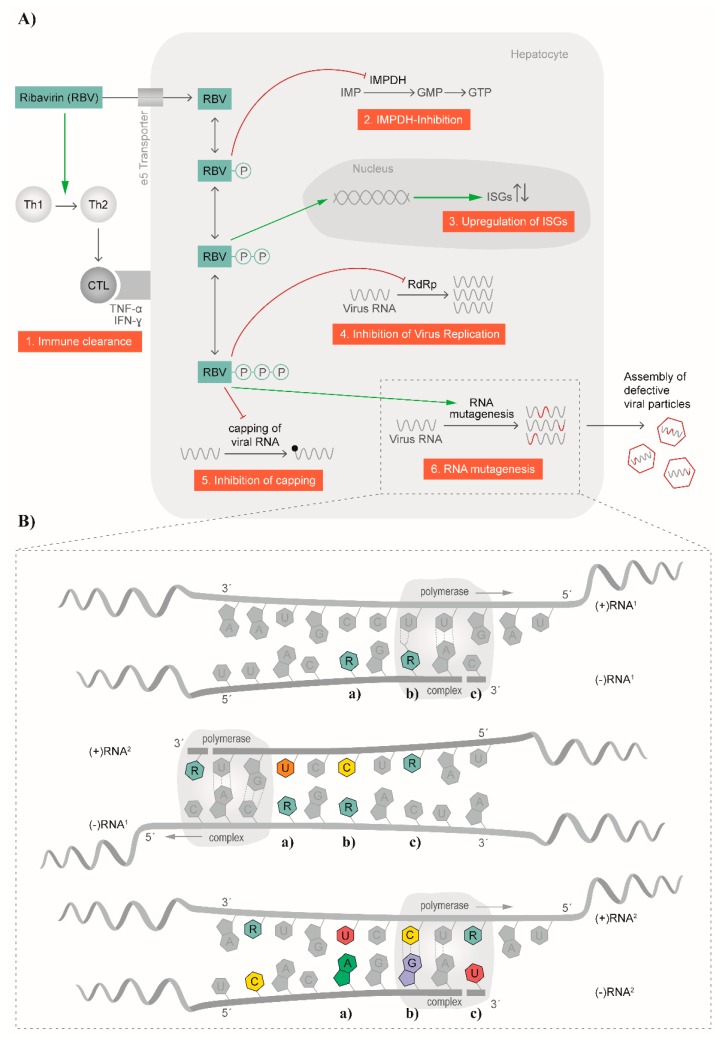
Figure 2.
Mode of action of ribavirin. (A) Several antiviral mechanisms for ribavirin have been proposed and are depicted schematically. Among these are effects on the immune clearance, inhibition of inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPDH), influence on interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs), inhibition of viral replication, inhibition of capping, and RNA mutagenesis; (B) The mutagenic effect on RNA is visualized in more detail. In altering the synthesis of (−)RNA and (+)RNA, RBV is randomly incorporated in the nascent strands and subsequently leads to transition events causing C–U (a), U–C (b) and G–A (c) or A–G substitutions. CTL: cytotoxic T lymphocyte; Th1: T helper cell, type 1; Th2: T helper cell, type 2; TNFα: Tumor necrosis factor alpha; INFγ: interferon gamma; IMP: inosine monophosphate; GMP: guanosine monophosphate; GTP: guanosine triphosphate.