Abstract
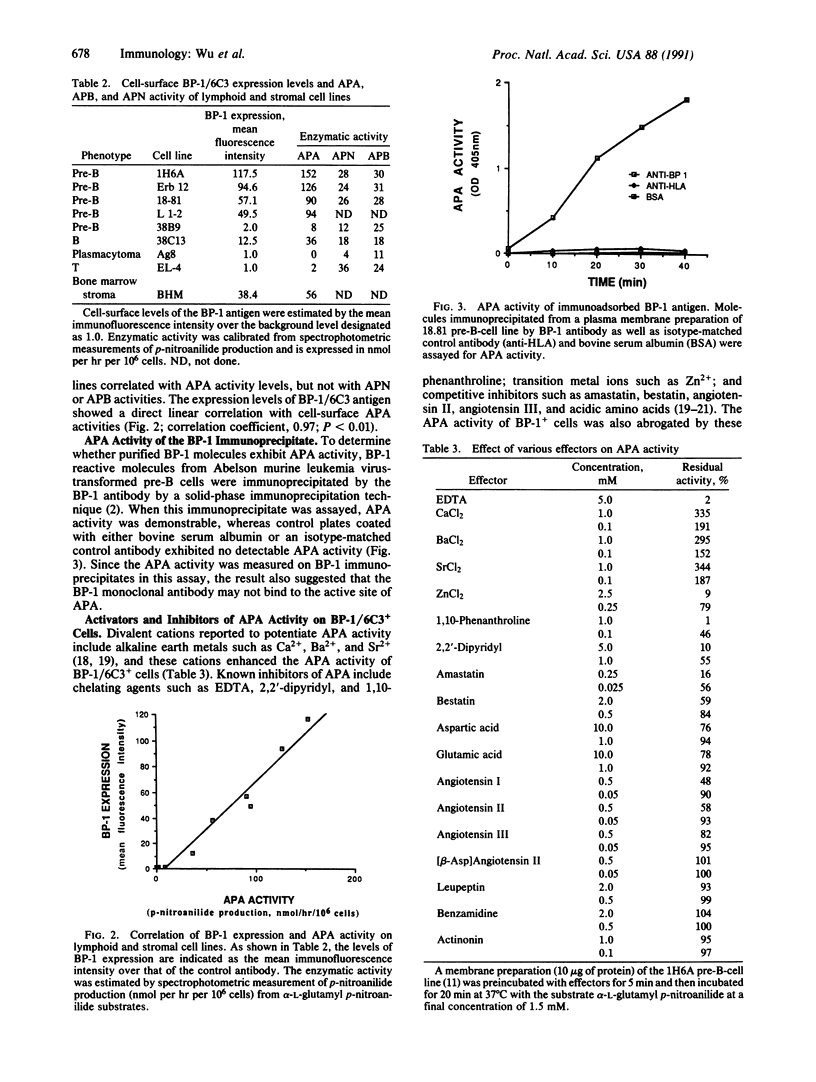
The predicted amino acid sequence of the cDNA encoding the murine B-lymphocyte differentiation antigen BP-1/6C3 suggested that it is a member of the zinc-dependent metalloprotease family, possibly an aminopeptidase related to aminopeptidase N [microsomal aminopeptidase; alpha-aminoacyl-peptide hydrolase (microsomal), EC 3.4.11.2]. In the present studies, we examined the enzymatic activity of this antigen. From brush border preparations of the small intestine, a rich source of many endopeptidases and exopeptidases, the BP-1 antibody selectively removed aminopeptidase A [APA; L-alpha-aspartyl(L-alpha-glutamyl)-peptide hydrolase, EC 3.4.11.7] activity. The APA activity of a panel of cell lines correlated in linear fashion with cell-surface levels of the BP-1/6C3 antigen. APA activity was demonstrated for the BP-1/6C3 antigen immunopurified from the pre-B-cell membrane. This activity was enhanced by alkaline earth metals such as Ca2+ and was abrogated by amastatin and angiotensin, which are known competitive inhibitors of APA. The data indicate that the murine BP-1/6C3 antigen is active APA, an enzyme that catalyzes specifically the removal of unsubstituted, N-terminal glutamic acid and aspartic acid residues from peptides.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adkins B., Tidmarsh G. F., Weissman I. L. Normal thymic cortical epithelial cells developmentally regulate the expression of a B-lineage transformation-associated antigen. Immunogenetics. 1988;27(3):180–186. doi: 10.1007/BF00346584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bausback H. H., Churchill L., Ward P. E. Angiotensin metabolism by cerebral microvascular aminopeptidase A. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Jan 15;37(2):155–160. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90712-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benajiba A., Maroux S. Purification and characterization of an aminopeptidase A from hog intestinal brush-border membrane. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):381–388. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06040.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper M. D., Mulvaney D., Coutinho A., Cazenave P. A. A novel cell surface molecule on early B-lineage cells. Nature. 1986 Jun 5;321(6070):616–618. doi: 10.1038/321616a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Vecchio P. J., Ryan J. W., Chung A., Ryan U. S. Capillaries of the adrenal cortex possess aminopeptidase A and angiotensin-converting-enzyme activities. Biochem J. 1980 Feb 15;186(2):605–608. doi: 10.1042/bj1860605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feracci H., Benajiba A., Gorvel J. P., Doumeng C., Maroux S. Enzymatic and immunological properties of the protease form of aminopeptidase N and A from pig and rabbit intestinal brush border. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Mar 13;658(1):148–157. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(81)90258-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorvel J. P., Benajiba A., Maroux S. Purification and characterization of the rabbit intestinal brush-border aminopeptidase A. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Sep 9;615(1):271–274. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(80)90030-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorvel J. P., Rigal A., Olive D., Mawas C., Maroux S. Identification of an early expressed marker of the luminal membrane of rabbit small intestinal columnar cells. Presence of a homologous antigen in kidney proximal tubules and glomeruli. Biol Cell. 1986;56(2):121–126. doi: 10.1111/j.1768-322x.1986.tb00449.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jongeneel C. V., Bouvier J., Bairoch A. A unique signature identifies a family of zinc-dependent metallopeptidases. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jan 2;242(2):211–214. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80471-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny A. J., Maroux S. Topology of microvillar membrance hydrolases of kidney and intestine. Physiol Rev. 1982 Jan;62(1):91–128. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1982.62.1.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kugler P. Localization of aminopeptidase A (angiotensinase A) in the rat and mouse kidney. Histochemistry. 1981;72(2):269–278. doi: 10.1007/BF00517140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalu K., Lampelo S., Nummelin-Kortelainen M., Vanha-Perttula T. Purification and partial characterization of aminopeptidase A from the serum of pregnant and non-pregnant women. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Sep 25;789(3):324–333. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(84)90188-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lojda Z., Gossrau R. Study on aminopeptidase A. Histochemistry. 1980;67(3):267–290. doi: 10.1007/BF00692761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louvard D., Maroux S., Vannier C., Desnuelle P. Topological studies on the hydrolases bound to the intestinal brush border membrane. I. Solubilization by papain and Triton X-100. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jan 28;375(2):235–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massoulié J., Bon S. The molecular forms of cholinesterase and acetylcholinesterase in vertebrates. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1982;5:57–106. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.05.030182.000421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizutani S., Okano K., Hasegawa E., Sakura H., Yamada M. Aminopeptidase A in human placenta. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Nov 13;662(1):168–178. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(81)90240-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moktari S., Feracci H., Gorvel J. P., Mishal Z., Rigal A., Maroux S. Subcellular fractionation and subcellular localization of aminopeptidase N in the rabbit enterocytes. J Membr Biol. 1986;89(1):53–63. doi: 10.1007/BF01870895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Márquez C., De la Hera A., Leonardo E., Pezzi L., Strasser A., Martínez-A C. Identity of PB76 differentiation antigen and lymphocyte alkaline phosphatase. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Apr;20(4):947–950. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagatsu I., Nagatsu T., Yamamoto T., Glenner G. G., Mehl J. W. Purification of aminopeptidase A in human serum and degradation of angiotensin II by the purified enzyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Feb 11;198(2):255–270. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(70)90058-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pillemer E., Whitlock C., Weissman I. L. Transformation-associated proteins in murine B-cell lymphomas that are distinct from Abelson virus gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4434–4438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raftery M. A., Hunkapiller M. W., Strader C. D., Hood L. E. Acetylcholine receptor: complex of homologous subunits. Science. 1980 Jun 27;208(4451):1454–1456. doi: 10.1126/science.7384786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishnan L., Wu Q., Yue A., Cooper M. D., Rosenberg N. BP-1/6C3 expression defines a differentiation stage of transformed pre-B cells and is not related to malignant potential. J Immunol. 1990 Sep 1;145(5):1603–1608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakura H., Kobayashi H., Mizutani S., Sakura N., Hashimoto T., Kawashima Y. Kinetic properties of placental aminopeptidase A: N-terminal degradation of angiotensin II. Biochem Int. 1983 May;6(5):609–615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semenza G. Anchoring and biosynthesis of stalked brush border membrane proteins: glycosidases and peptidases of enterocytes and renal tubuli. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:255–313. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.001351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwood P. J., Weissman I. L. The growth factor IL-7 induces expression of a transformation-associated antigen in normal pre-B cells. Int Immunol. 1990;2(5):399–406. doi: 10.1093/intimm/2.5.399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipp M. A., Stefano G. B., D'Adamio L., Switzer S. N., Howard F. D., Sinisterra J., Scharrer B., Reinherz E. L. Downregulation of enkephalin-mediated inflammatory responses by CD10/neutral endopeptidase 24.11. Nature. 1990 Sep 27;347(6291):394–396. doi: 10.1038/347394a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipp M. A., Vijayaraghavan J., Schmidt E. V., Masteller E. L., D'Adamio L., Hersh L. B., Reinherz E. L. Common acute lymphoblastic leukemia antigen (CALLA) is active neutral endopeptidase 24.11 ("enkephalinase"): direct evidence by cDNA transfection analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):297–301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tidmarsh G. F., Dailey M. O., Weissman I. L. Expression of a monoclonal antibody-defined, B-lineage transformation antigen specifically identifies Abelson-diseased animals. Genetically determined resistance to Abelson murine leukemia virus acts before induction of gp160(6C3). J Exp Med. 1986 Oct 1;164(4):1356–1361. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.4.1356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tidmarsh G. F., Dailey M. O., Whitlock C. A., Pillemer E., Weissman I. L. Transformed lymphocytes from Abelson-diseased mice express levels of a B lineage transformation-associated antigen elevated from that found on normal lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1985 Nov 1;162(5):1421–1434. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.5.1421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobe H., Kojima F., Aoyagi T., Umezawa H. Purification by affinity chromatography using amastatin and properties of aminopeptidase A from pig kidney. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jun 13;613(2):459–468. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(80)90100-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch P. A., Burrows P. D., Namen A., Gillis S., Cooper M. D. Bone marrow stromal cells and interleukin-7 induce coordinate expression of the BP-1/6C3 antigen and pre-B cell growth. Int Immunol. 1990;2(8):697–705. doi: 10.1093/intimm/2.8.697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitlock C. A., Tidmarsh G. F., Muller-Sieburg C., Weissman I. L. Bone marrow stromal cell lines with lymphopoietic activity express high levels of a pre-B neoplasia-associated molecule. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):1009–1021. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90709-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Q., Lahti J. M., Air G. M., Burrows P. D., Cooper M. D. Molecular cloning of the murine BP-1/6C3 antigen: a member of the zinc-dependent metallopeptidase family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):993–997. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Q., Tidmarsh G. F., Welch P. A., Pierce J. H., Weissman I. L., Cooper M. D. The early B lineage antigen BP-1 and the transformation-associated antigen 6C3 are on the same molecule. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 15;143(10):3303–3308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada R., Mizutani S., Kurauchi O., Okano K., Imaizumi H., Narita O., Tomoda Y. Purification and characterization of human placental aminopeptidase A. Enzyme. 1988;40(4):223–230. doi: 10.1159/000469167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]