Abstract
Human epidemiologic and genetic evidence using the Mendelian randomization approach in large-scale studies now strongly supports that elevated lipoprotein (a) [Lp(a)] is a causal risk factor for cardiovascular disease, that is, for myocardial infarction, atherosclerotic stenosis, and aortic valve stenosis. The Mendelian randomization approach used to infer causality is generally not affected by confounding and reverse causation, the major problems of observational epidemiology. This approach is particularly valuable to study causality of Lp(a), as single genetic variants exist that explain 27–28% of all variation in plasma Lp(a). The most important genetic variant likely is the kringle IV type 2 (KIV-2) copy number variant, as the apo(a) product of this variant influences fibrinolysis and thereby thrombosis, as opposed to the Lp(a) particle per se. We speculate that the physiological role of KIV-2 in Lp(a) could be through wound healing during childbirth, infections, and injury, a role that, in addition, could lead to more blood clots promoting stenosis of arteries and the aortic valve, and myocardial infarction. Randomized placebo-controlled trials of Lp(a) reduction in individuals with very high concentrations to reduce cardiovascular disease are awaited. Recent genetic evidence documents elevated Lp(a) as a cause of myocardial infarction, atherosclerotic stenosis, and aortic valve stenosis.
Keywords: apolipoproteins, atherosclerosis, cholesterol, dyslipidemias, inflammation, low density lipoprotein, lipids, plasminogen, vascular biology
The first articles on lipoprotein (a) [Lp(a)] were published in 1963 by Kåre Berg from Norway, describing Lp(a) in human plasma as a heritable trait (1–3). Over the next more than 20 years, the scientific interest in this lipoprotein was modest. Then in 1987, Richard Lawn, Angelo Scanu, and colleagues cloned and sequenced the LPA gene coding for apo(a) (4, 5), a protein with homology to plasminogen, which accounts for the difference between an Lp(a) particle and an LDL particle. These observations generated a huge scientific interest in Lp(a), leading to an exponential growth in the number of articles published, which then later declined again.
Renewed interested in Lp(a) came in 2009 from Pia Kamstrup et al. (6) with genetic evidence from Mendelian randomization that high Lp(a) is causally associated with cardiovascular disease, from the Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration led by John Danesh that Lp(a) epidemiologically is continuously and independently associated with cardiovascular disease risk (7), and from Robert Clarke et al. (8) that of 2,100 candidate genes for cardiovascular disease, genetic variation in the LPA gene was the strongest genetic cardiovascular risk factor. Following the publication of these studies, high concentrations of Lp(a) have been considered to be a direct cause of cardiovascular disease, just like high LDL cholesterol concentrations. Genetic evidence largely free of confounding and fully free of reverse causation, two major problems of observational epidemiology, is what has cemented the understanding of causality of Lp(a) for cardiovascular disease.
These novel and important findings led the European Atherosclerosis Society to publish a 2010 consensus panel statement recommending screening for elevated Lp(a) in individuals at intermediate, high, or very high cardiovascular risk, and suggested a desirable plasma concentration of less than 50 mg/dl (9). Of note, we naturally were fully aware that the risk of cardiovascular disease increases already at Lp(a) levels above 30 mg/dl, but to get the attention of the clinical community, we believed it was the best strategy to start focusing on individuals with the highest cardiovascular risk, that is, the 20% of individuals with concentrations above 50 mg/dl.
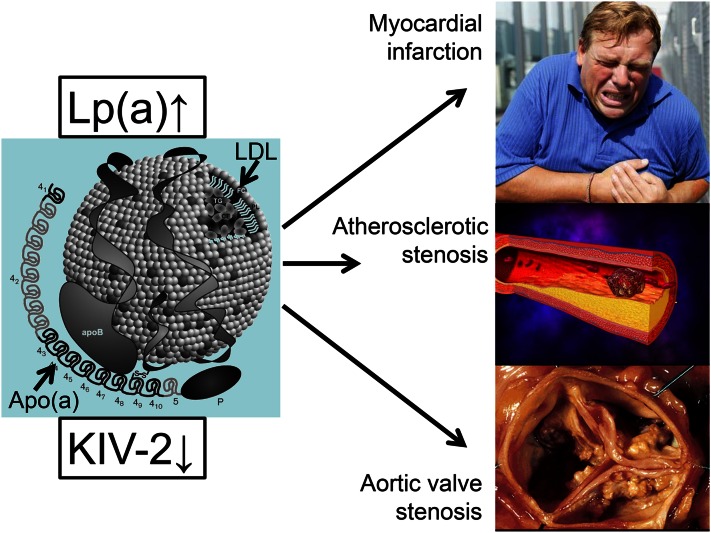
Although some cardiologists suspected for many years, as far back as the mid-1990s, that Lp(a) was a risk factor for aortic valve stenosis, a further novel development was the documentation by George Thanassoulis et al. (10) in 2013 that genetic variation in the LPA gene is strongly associated with aortic valve calcification and stenosis. It was later shown that high plasma Lp(a) concentrations are likewise causally associated with high risk of aortic valve stenosis (11). Taken together therefore, the genetic evidence now firmly demonstrates that high plasma Lp(a) concentration is a direct cause of cardiovascular disease, that is, myocardial infarction, atherosclerotic stenosis, and aortic valve stenosis (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
Summary of the strongest causal genetic evidence linking high Lp(a) concentrations with corresponding small apo(a) size due to low number of KIV-2 repeats to risk of disease.
Although mainly recent genetic research has firmly established the claim for causality for high Lp(a) concentrations to cardiovascular disease, these findings have only been possible due to the many other excellent scientific works on Lp(a) published from 1963 until today, produced by a large number of dedicated researchers within this field. In this review, it will not be possible to do justice to all the important scientific discoveries on Lp(a) in relation to cardiovascular disease published during the 50 years. That said, with our own personal touch to the story and with focus on evidence from human studies, we will try our best, in a historical perspective, to cover insights in epidemiology, genetics, and biology that led to the understanding of Lp(a) as a cause of cardiovascular disease. Many classic and more recent reviews, viewpoints, and meta-analyses cover related areas (5, 7, 9, 12–40), include even more references, and, together with the present review, provide a comprehensive coverage of Lp(a) as a cause of cardiovascular disease.
Lp(a) IN NORMAL, ATHEROSCLEROTIC, AND INJURED INTIMA
A necessary condition for Lp(a) to cause cardiovascular disease is its ability to enter into and accumulate in the intima of arteries and aortic valve leaflets. Lp(a) or apo(a) is indeed found within the lesioned intima of human arteries and coronary artery bypass vein grafts removed at reoperation (41–46), as well as within the lesioned intima of monkey arteries (47) and arteries in rabbits and mice after intravenous injection of human Lp(a) (48, 49) or after transgenic modification with human Lp(a) (50). Likewise, apo(a) is found within early to end-stage lesions of human aortic valve stenosis (51).
In vivo kinetic studies show that radiolabeled human Lp(a) enters the intima at similar rates to LDL in normal and atherosclerotic arteries in humans and rabbits (49, 52, 53), which appears to be like other lipoproteins, through a simple molecular sieving not involving any receptors, but dependent on lipoprotein plasma concentrations and on lipoprotein particle size, blood pressure, and on arterial wall permeability (54). Importantly, however, as the plasma concentration of LDL is much higher than that of Lp(a) in most individuals, the mass intimal influx of LDL was 15-fold that of Lp(a) in humans (52). Again using kinetic studies in vivo, the rates of relative removal of Lp(a) and LDL from the arterial intima were similar, while the trapping of both lipoproteins was higher in lesioned compared with normal intima (53); it cannot entirely be excluded that there may be preferential trapping of Lp(a) in settings where lesion formation is ongoing and/or more advanced. Also, degradation in vivo of human Lp(a) was higher in atherosclerotic compared with nonlesioned rabbit intima (55).
Surprisingly, when the arterial intima in a rabbit model was subjected to a balloon injury, radiolabeled human Lp(a) accumulated in vivo 2- to 3-fold greater than that of radiolabeled human LDL in the balloon-injured aortic intima, but not in the adjacent uninjured arterial intima (56). As removal of intact endothelial cells would not explain why Lp(a) preferentially accumulates, because entry into the intima would be enhanced for LDL and Lp(a) equally, this can most likely occur because of prolonged residence time, e.g., enhanced binding of Lp(a) selectively to the matrix in the intima. A simple explanation for this observation could be that the balloon-injury removes the endothelial cells and thus exposes the intima directly to flowing blood, favoring deposition of fibrin. Thereby Lp(a), unlike LDL, can bind to small blood clots rapidly forming at the injured sites, or to exposed glycosaminoglycans (21, 56, 57). Preferential accumulation of Lp(a) compared with LDL at injured sites could thus be related to the greater capacity of Lp(a) than LDL to bind to fibrin (58) or glycosaminoglycans (59). Indeed, Lp(a) compared with LDL appeared to be preferentially immobilized via fibrin binding in human arterial tissue (44).
Taken together, these data suggest that Lp(a) accumulation at sites of injury could be a primary mechanism by which elevated Lp(a) causes cardiovascular disease. That said, there is also evidence that Lp(a) can be taken up by macrophages to produce foam cells (60–62), a mechanism by which LDL and triglyceride-rich lipoproteins are believed to cause the development of atherosclerosis (63–65). Interestingly, in coronary artery bypass vein grafts and relative to plasma concentrations, Lp(a) accumulated 2.4-fold more than all apoB-containing lipoproteins combined, that is, LDL, Lp(a), and triglyceride-rich lipoproteins, and unlike apoB that was found mainly at atherosclerotic core regions, this was not the case for Lp(a) (43). The latter suggests that the intimal accumulation of Lp(a) is by a different mechanism than that of other apoB-containing lipoproteins, and that Lp(a) accumulation is throughout the intima, while other apoB-containing lipoproteins mainly are found at atherosclerotic lesions.
PLASMA CONCENTRATIONS AND GENETICS
The fact that plasma concentrations of Lp(a) are mainly genetically determined (14, 39) has been instrumental in the study of causality of Lp(a) for cardiovascular disease. Because of this, the genetic evidence for causality in cardiovascular disease is much stronger for Lp(a) than for most other cardiovascular risk factors (8, 30, 66). It is also of huge importance for Mendelian randomization studies that single genetic variants exist that explain 27–28% of all variation in plasma Lp(a), and that these variants can be genotyped in large-scale studies (6, 8, 10, 11, 67). Therefore, a brief discussion of plasma Lp(a) concentrations and the genetic principles used in Mendelian randomization studies is given below. An in depth review of this topic is presented elsewhere in this Thematic Review Series (39, 68).
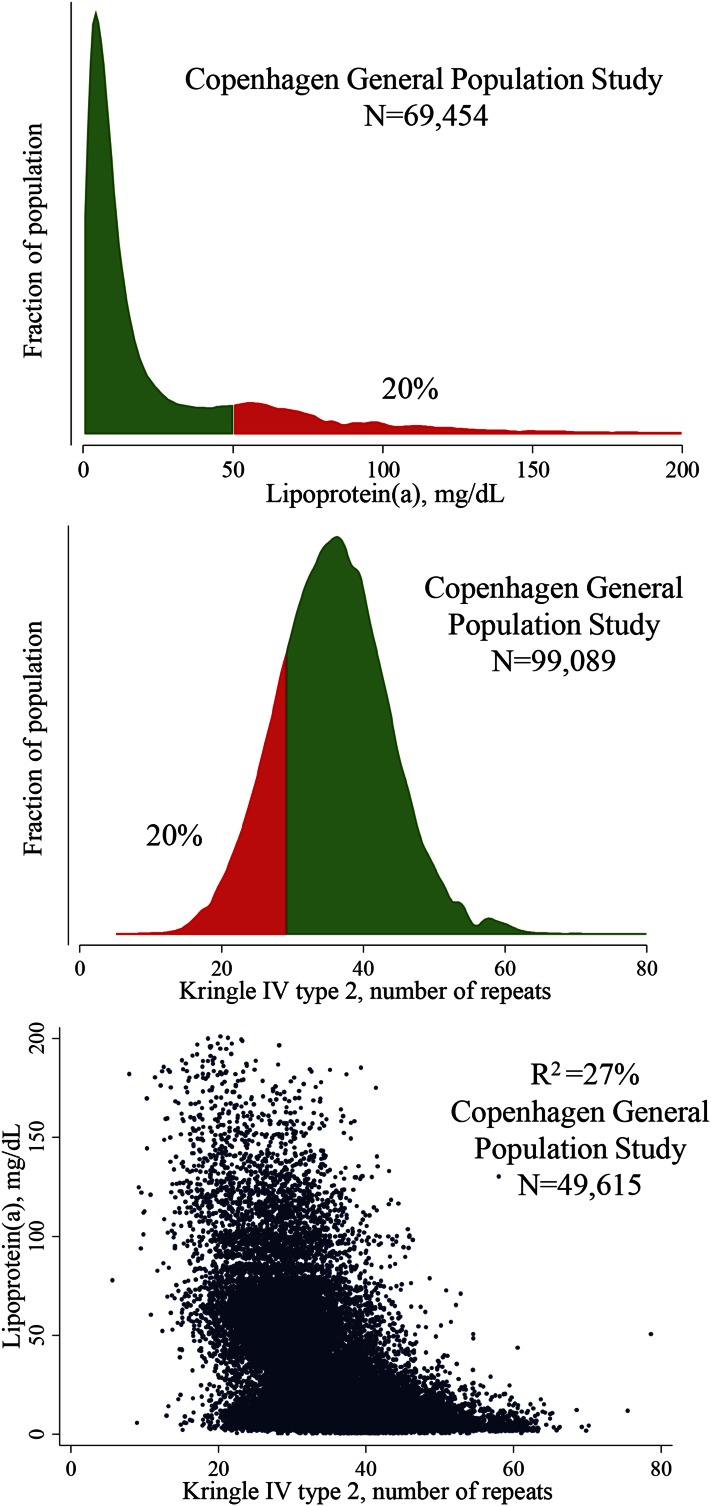
In the general population, plasma concentrations of Lp(a) vary to a great extent among individuals (14). Concentrations also differ between different ethnicities, with higher concentrations in individuals of African compared with European and Asian descent (14, 68–74). In Europeans and Asians, Lp(a) concentrations are highly skewed with a tail toward higher concentrations (Fig. 2, top panel), and in the Copenhagen General Population Study, we observed concentrations as high as 387 mg/dl. Concentrations of other lipoproteins are often affected by life-style and physiological factors, whereas Lp(a) concentrations remain stable inter-individually throughout life, indirectly suggesting that Lp(a) concentrations are mostly genetically determined.
Fig. 2.
Distribution of and correlation between plasma Lp(a) concentrations and KIV-2 number of repeats in the Danish general population.
In very early studies, Lp(a) was suggested to be an inherited trait with autosomal dominant inheritance (2, 3, 75–77) and a major gene and polygenic factors were proposed as contributors to the variation in Lp(a) concentrations (78–80). Hasstedt et al. (78) found that the major gene and the polygenic factors accounted for 95% of the variation in plasma Lp(a) concentrations. Following this, a number of studies primarily led by Gerd Utermann and colleagues revealed that apo(a) varied in size due to kringle IV type 2 (KIV-2) copy number variation, and that the number of KIV-2 copies were inversely correlated to plasma Lp(a) concentrations (81–87) (Fig. 2, middle and lower panel). However, the correlation between the apo(a) size polymorphism and Lp(a) plasma concentrations was found to vary greatly among individuals of different ethnicity, as do plasma Lp(a) concentrations (69, 70, 73, 74, 88). One study found that the apo(a) allele frequencies were different among different populations (69). In that study, the size variation of apo(a) explained from 19% in Sudanese to 77% in Malays of the variability in plasma Lp(a) concentrations.
In 49,615 individuals from the Copenhagen General Population Study, the KIV-2 number of repeats in the LPA gene coding for the apo(a) size polymorphism explained 27% of the variation in plasma Lp(a) concentrations (Fig. 2, lower panel); however, the KIV-2 number of repeats was measured as both alleles combined and does not take different expression of alleles into account, suggesting that the 27% should be viewed as a minimal estimate for Danes. Therefore, the measurements of KIV-2 in these studies do not necessarily reflect the dominant isoform that is associated with the highest Lp(a) concentrations. For Mendelian randomization studies, the most important genetic variant is likely the KIV-2 copy number variation, or corresponding apo(a) size polymorphism, as this causal variant possibly is the direct cause of cardiovascular disease (39). However, although genotyping of this variant can be done in large-scale-studies, it requires, at present, quantitative polymerase chain reaction (6) or even more complicated techniques (39). Importantly, for now, it is not possible to determine for sure whether it is the KIV-2 copy number variation or the associated plasma Lp(a) concentration that is causally associated with cardiovascular disease.
In 2009, Robert Clarke et al. (8) published an article using a gene chip with 48,742 SNPs in 2,100 candidate genes examining individuals with coronary disease and controls. They found that the rs10455872 and rs3798220 SNPs in the LPA gene explained 25% and 8% of the variation in plasma Lp(a) concentrations, and each was associated with high risk of coronary heart disease. Importantly, in numerous other studies, including genome-wide linkage and association studies, multiple genetic variants in or around LPA on chromosome 6q27 were also found to be major determinants of plasma Lp(a) concentrations (39, 89–93). For Mendelian randomization studies, however, the most important SNP is LPA rs10455872, as this variant explains up to 28% of variation in plasma Lp(a) concentrations in the general population of Whites (11, 67), and this variant, unlike the KIV-2 copy number variation, is very easy to genotype in large-scale studies. Even though this SNP is not causal for high Lp(a) (39), it can still be an excellent instrument to examine causality of high Lp(a) concentrations per se.
Taken together, the LPA KIV-2 copy number variation and the LPA rs10455872 SNP have so far been the best genetic instruments in large-scale Mendelian randomization studies, each explaining 27–28% variation in plasma Lp(a) concentrations. Because KIV-2 copy number variation directly measures apo(a) size differences as opposed to rs10455872, which marks both apo(a) size differences and Lp(a) concentrations unrelated to this genetic variation (67), the combined use of both has the potential to explore whether it is the KIV-2 copy number variation or the Lp(a) particle, per se, that is the direct cause of cardiovascular disease.
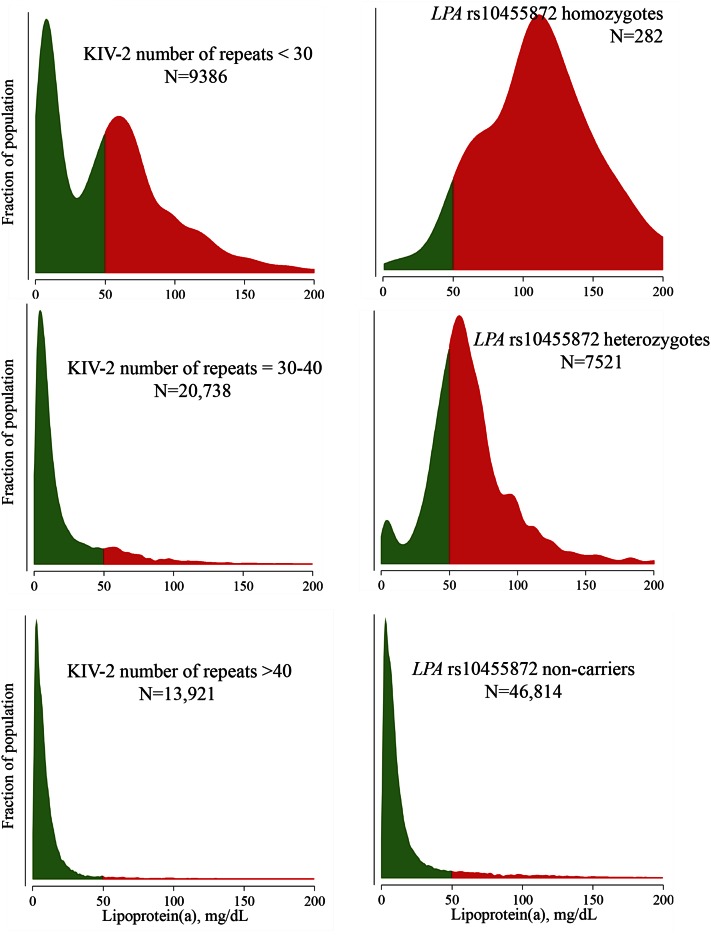
While KIV-2 number of repeats above 40 and rs10455872 noncarrier state both mark very low Lp(a) concentrations, heterozygosity and homozygosity for rs10455872 mark very different plasma Lp(a) concentration profiles than intermediate or low number of KIV-2 number of repeats (Fig. 3). Using these two genetic variants simultaneously has previously been used by us to suggest that the well-documented slightly higher risk of type 2 diabetes in those with the lowest Lp(a) concentration (67, 94–96) is possibly explained by the KIV-2 copy number variation rather than the Lp(a) particle per se (67). In other words, these data indirectly suggest that lowering of Lp(a) pharmacologically is unlikely to lead to increased risk of diabetes. Importantly however, more evidence using even better genetic instruments is needed before this can be concluded definitively (67, 97).
Fig. 3.
Distribution of plasma Lp(a) concentrations as a function of LPA KIV-2 number of repeats and of LPA rs10455872 in the Copenhagen General Population Study. Green and red parts correspond to the bottom 80% and top 20% of the entire population distribution of plasma Lp(a) concentrations (see Fig. 3).
GENETIC STUDIES TO INFER CAUSALITY: THE MENDELIAN RANDOMIZATION APPROACH
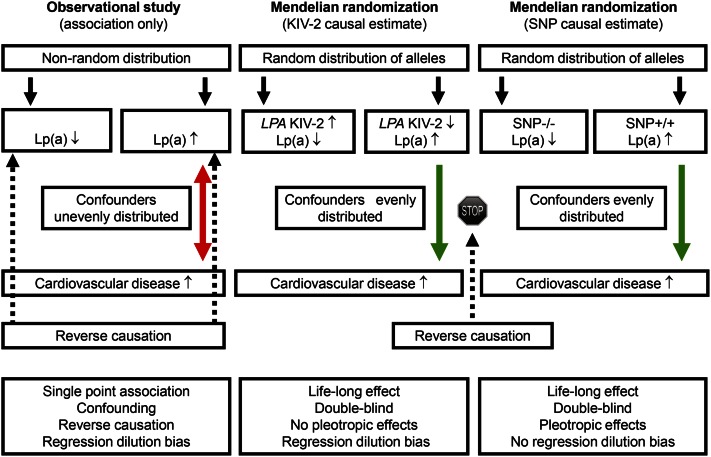
Genetic studies, like randomized intervention trials, are completely free of reverse causation and largely free of confounding. Therefore, if a genetic variant or a drug leads to higher or lower concentrations of a lipoprotein and this further leads to higher or lower risk of cardiovascular disease, then it is quite likely that it is the lipoprotein that causes the effect on cardiovascular disease. In essence, this is the principle of the Mendelian randomization approach. In contrast, results from observational epidemiology can mislead through confounding and reverse causation. Confounding is when a third factor influences both lipoprotein concentrations and cardiovascular disease risk, while reverse causation implies that cardiovascular disease leads to changes in lipoprotein concentrations, rather than vice versa.
There are several early examples of studies that suggest the idea that if a risk factor is elevated or reduced due to genetic variation, and if such genetic variation is or is not associated with a disease of interest, then it would be possible to infer or exclude causality of the risk factor (98–100). This idea involving the causal genetic influence of high Lp(a) concentrations on risk of coronary heart disease was already presented in 1992 by Gerd Utermann and colleagues (101, 102). However, the concept of the Mendelian randomization approach, including in-depth discussion of strengths and limitations, mainly crystallized due to many insightful publications from George Davey Smith and colleagues (103–108), publications that can be used as a “starter’s kit” to understand the Mendelian randomization approach. Growing out of the awareness of the limitations of observational epidemiology, it was suggested that Mendelian randomization, that is, the random assortment of genes from parents to offspring that occurs during gamete formation and conception, would provide a method for assessing the causal nature of risk factors on disease. The clear formulation of these ideas has substantially influenced thinking on how to understand disease causality, especially in cardiovascular medicine and most importantly for the role of Lp(a) as a cause of cardiovascular disease.
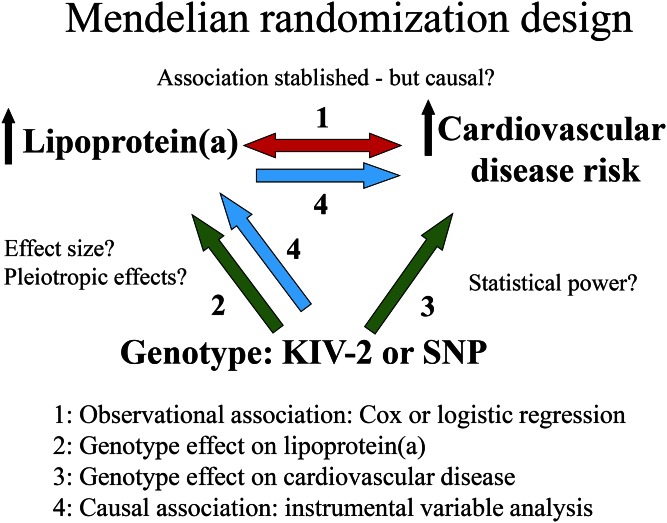
Epidemiology alone cannot determine causality due to potential problems with confounding and reverse causation (Fig. 4, double-pointed arrow #1). Thus, potential confounders, including life-style factors, may be unevenly distributed between those with high and low Lp(a) concentrations, and such confounders may be the real explanation for the high risk of cardiovascular disease in those with high Lp(a) (Fig. 5, left panel). In contrast, in the Mendelian randomization study design, such confounders are always evenly distributed between those with high and low Lp(a), and therefore, cannot explain the high cardiovascular risk in those with genetically high Lp(a) concentrations (Fig. 5, middle and right panels). The other major potential limitation of observational studies is reverse causation, that is, the possibility that cardiovascular disease leads to high Lp(a) concentrations, rather than vice versa (Fig. 5, left panel). In the Mendelian randomization study design, reverse causation is simply not possible, as cardiovascular disease cannot change your genes (Fig. 5, middle and right panels). In other words, the Mendelian randomization study design can be used to infer causality just like a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled Lp(a)-reducing trial and these two types of studies share many advantages and have similar limitations [see Fig. 5 in (65)]. Unfortunately however, so far no randomized double-blind placebo-controlled Lp(a)-reducing trials to prevent cardiovascular disease have been published or even initiated. Therefore, for now, the human evidence to suggest that high Lp(a) causes cardiovascular disease has to depend on genetics and the Mendelian randomization approach. While these approaches are powerful, it is naturally the totality of evidence that counts in understanding causality.
Fig. 4.
The four different statistical parts of a complete Mendelian randomization study design to examine causality from high plasma Lp(a) concentrations to high risk of cardiovascular disease. Potential limitations are shown with question marks.
Fig. 5.
Comparison of observational studies and Mendelian randomization studies to help understand causality from high plasma Lp(a) concentrations to high risk of cardiovascular disease.
Another limitation of observational studies is the problem of regression dilution bias (109, 110) because risk factors typically are only measured once, and therefore the association observed will only represent a single point estimate (Fig. 5, left panel). Regression dilution bias means that the effect size of the risk estimate is underestimated, although this bias does not influence statistical significance. In contrast, SNPs used in the Mendelian randomization design generally are measured precisely and have less of a problem with regression dilution bias (Fig. 5, right panel). The exception here is KIV-2 number of repeats measured using quantitative polymerase chain reaction, as this measurement will vary due to measurement error just like plasma Lp(a) concentrations and likewise is affected by regression dilution bias (Fig. 5, middle panel), suggesting that the effect sizes for KIV-2 number of repeats for causal associations with cardiovascular disease should be viewed as minimal estimates (6, 11, 67, 111–113).
Mendelian randomization studies using human genetics have many similarities with randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trials and, thus, advantages over traditional observational studies (Fig. 5). Like in randomized trials, Mendelian randomization studies are double-blind and confounding and reserve causation are circumvented due to nature’s own randomization method during distribution of alleles at meiosis. Mendelian randomization studies have the additional advantage over conventional epidemiology that genetics typically capture a life-long effect (Fig. 5, middle and right panels), while observational studies only include the time between risk factor assessment and end of follow-up. Like a drug in randomized trials, genetics can have the problem of pleiotropic effects; however, while this can be a problem with SNPs as markers of high Lp(a) concentrations, direct measurement of KIV-2 number of repeats or corresponding apo(a) size polymorphism will not have this problem (Fig. 5, right and middle panels).
Another potential problem of Mendelian randomization studies includes linkage disequilibrium with other causative genetic variants in other genes; however, this is not a problem for KIV-2, although it can be a problem for SNPs associated with high Lp(a) concentrations. Also, population admixture can be a major problem if both genotype and the disease studied are found preferentially in certain subpopulations; however, this potential problem can be largely circumvented by studying ethnically homogeneous populations or by adjusting for different ethnicity using genetic information. Finally, it is essential to use genetic variation with sufficiently large effect sizes, which has been done in Lp(a) causality research more than for any other cardiovascular risk factor: the LPA KIV-2 copy number variation and the LPA rs10455872 SNP, which can be used for genotyping large-scale studies, each explain 27–28% of the variation in plasma Lp(a) concentrations.
Technically, what is done in a complete Mendelian randomization study is depicted in Fig. 4. Published examples of this complete design that are easy to follow for the nonspecialist include that low concentrations of vitamin D are causally associated with high all-cause mortality (114), and that low concentrations of nonfasting triglycerides are causally associated with low all-cause mortality (115).
First, the well-known observational association is shown in the study population (Fig. 4, double-pointed arrow #1). Second, the causal association between LPA genotype (KIV-2 or a SNP) on Lp(a) concentration is documented and the extent of variation on plasma concentrations determined by genotype is quantified. This allows assessment of the value of the genotype as an instrument in the Mendelian randomization study design (Fig. 4, single-pointed arrow #2). At this stage, it is also important to exclude pleiotropic effects, that is, genotype should not be associated with any other factor that might cause cardiovascular disease (Table 1). Third, genotype is then directly associated with cardiovascular disease, using a study with sufficient statistical power to document or reject the causal association (Fig. 4, single-pointed arrow #3). Fourth, the formal test of causality involves running an instrumental variable analysis (Fig. 4, single-pointed arrows #4) that integrates the effect of genotype on Lp(a) concentrations (arrow #2) with the effect of genotype on cardiovascular disease risk (arrow #3). Observational and genetic causal risk estimates can then be compared directly, as arrows #1 and #4 will be on the same scale, that is, for Lp(a) per, for example, a 30 mg/dl higher concentration either observationally or genetically.
TABLE 1.
Baseline characteristic in individuals from the Copenhagen General Population and the Copenhagen City Heart Study combined
| Characteristic | Observational (N = 58,232), Plasma Lp(a) | Genetic (N = 98,941), LPA KIV-2 Number of Repeats | Genetic (N = 104,366), LPA rs10455872 SNP | |||
| High 80% | Low 20% | Low 20% | High 80% | Non-carrier 86% | Carrier 14% | |
| Age, years | 58 (49–68) | 59 (50–68) | 58 (48–67) | 58 (48–67) | 58 (48–67) | 58 (48–67) |
| Women, % | 54 | 57 | 55 | 55 | 55 | 55 |
| Hypertension, % | 67 | 68 | 66 | 66 | 66 | 66 |
| Diabetes, % | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Smoking, % | 17 | 17 | 17 | 19 | 17 | 17 |
| Cholesterol-lowering therapy, % | 11 | 17 | 13 | 11 | 11 | 14 |
| Body Mass Index, kg/m2 | 26 (23–28) | 26 (23–28) | 26 (23–28) | 26 (23–29) | 26 (23–28) | 26 (23–28) |
| Total cholesterol, mmol/l | 5.5 (4.8–6.2) | 5.7 (5.0–6.4) | 5.6 (4.9–6.3) | 5.5 (4.8–6.3) | 5.5 (4.8–6.3) | 5.6 (4.9–6.4) |
| Triglycerides, mmol/l | 1.4 (1.0–2.0) | 1.4 (1.0–2.1) | 1.4 (1.0–2.1) | 1.4 (1.0–2.1) | 1.4 (1.0–2.1) | 1.4 (1.0–2.1) |
Values are median (interquartile range).
For research on Lp(a) as a cause of cardiovascular disease, it can be argued that even conventional epidemiology will suffice in understanding causality of Lp(a), as the concentrations of this lipoprotein are largely genetically determined (14, 39) and minimally confounded by environmental variables (Table 1). Although this seems to be a valid statement, experience has shown that it was mainly the large-scale genetic Mendelian randomization studies published from 2009 and onwards that paved the path for a general understanding that high concentrations of Lp(a) are a direct cause of myocardial infarction, atherosclerotic stenosis, and aortic valve stenosis (Fig. 1).
MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION AND ISCHEMIC HEART DISEASE
Early retrospective case-control studies found that Lp(a) concentrations were higher in patients with myocardial infarction and ischemic heart disease (coronary heart disease), than in individuals without these diseases (116–118). Later on, many similar studies followed (102, 119–130), the majority with the same conclusion that Lp(a) was higher in those with than in those without myocardial infarction and ischemic heart disease. On hindsight, with the current understanding of the Mendelian randomization approach, this is an impressive set of studies; however, at the time of publication of these studies evidence from prospective population-based studies was needed.
Early population-based prospective cohort and nested case-control studies (131–140) were summarized in a meta-analysis by Wendy Craig et al. (141) in 1998. In these studies dominated by White participants, 12 of 14 prospective studies found that Lp(a) concentrations were higher in subjects who later developed ischemic heart disease than in those who did not. After addition of six more prospective population-based studies (142–147), John Danesh and colleagues updated the meta-analysis in 2000 to show that after including 4,044 deaths from coronary heart disease or nonfatal myocardial infarction during a mean follow-up of 10 years in 18 studies, individuals in the top versus bottom third of the Lp(a) concentration distribution had a combined risk ratio of 1.7 [95% confidence interval (CI): 1.4–1.9] (23).
Different results in some of the early studies could be because measurement of Lp(a) is complicated by the varying isoform sizes of apo(a), that is, assays that are not isoform independent might overestimate Lp(a) plasma concentrations when large isoforms are present and underestimate concentrations when small isoforms are present (148–150). Further, many of these early studies used Lp(a) samples that had been frozen for several years, which might affect the structure of Lp(a) and thereby lead to incorrect measurement of plasma Lp(a) concentrations (151). Also, most previous studies did not estimate risk in individuals with extremely high Lp(a) concentrations, the concentrations that would seem most relevant clinically. Finally, many early studies did not correct for regression dilution bias (109, 110) and, therefore, effect sizes for risk of myocardial infarction and ischemic heart disease likely were underestimated.
After publication of yet another six prospective population-based studies (152–157), we published in 2008 the results of the Copenhagen City Heart Study with 9,330 individuals followed for 10 years during which time 498 developed a myocardial infarction (158). We measured Lp(a) concentrations in 1991–1994 shortly after sampling using an apo(a) isoform-insensitive assay. Risk estimates were corrected for regression dilution bias, and we focused on the risk of myocardial infarction in those with the extremely high concentrations. Specifically, we chose myocardial infarction as the endpoint, as this disease is registered correctly 99.5% of the time in the Danish registries and the follow-up in this population is 100% complete (6). In women, multifactorially adjusted hazard ratios for myocardial infarction for high Lp(a) concentrations were 1.1 (95% CI: 0.6–1.9) for 5–29 mg/dl, 1.7 (95% CI: 1.0–3.1) for 30–84 mg/dl, 2.6 (95% CI: 1.2–5.9) for 85–119 mg/dl, and 3.6 (95% CI: 1.7–7.7) for above 120 mg/dl versus concentrations below 5 mg/dl (158). Corresponding hazard ratios in men were 1.5 (95% CI: 0.9–2.3), 1.6 (95% CI: 1.0–2.6), 2.6 (95% CI: 1.2–5.5), and 3.7 (95% CI: 1.7–8.0), respectively. Also, absolute 10 year risks of myocardial infarction were 10 and 20% in smoking hypertensive women aged above 60 years with Lp(a) concentrations of below 5 mg/dl and above 120 mg/dl, respectively, with corresponding values in men of 19 and 35%.
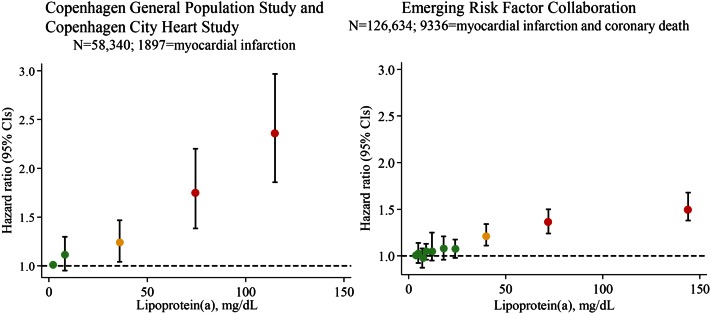
The Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration included individual records for 126,634 participants from 36 prospective studies, recorded 9,318 myocardial infarctions and coronary deaths, corrected for regression dilution bias, and also focused on the risk of myocardial infarction and coronary death in those with the extremely high Lp(a) concentrations (7) (Fig. 6, right panel). In that study, risk was higher after approximately 30 mg/dl and the age- and sex-adjusted risk ratio was 1.5-fold in those with Lp(a) above 100 mg/dl versus below 4 mg/dl. There were continuous, independent, and modest associations of Lp(a) concentration with risk of coronary heart disease that appeared exclusive to vascular outcomes. Importantly however, this meta-analysis included many former studies using frozen samples and nonoptimal Lp(a) assays, likely partly explaining the relatively modest overall effect sizes observed. Also, this may partly be explained by nondifferential misclassification of events from study to study, as myocardial infarction and coronary death events were classified according to the International Classification of Diseases or, where this was not available, on study-specific classification systems.
Fig. 6.
Observational associations between high plasma Lp(a) concentrations and risk of cardiovascular disease in the Copenhagen City Heart Study and Copenhagen General Population Study combined (left panel) and in the Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration (right panel). Hazard ratios in the left panel were estimated by Cox proportional hazard regression models and were adjusted for age and sex and corrected for regression dilution bias. Right panel was adapted from (7).
For use specifically in this review, we updated our former epidemiological studies (6, 112, 158) based on the Copenhagen City Heart Study and the Copenhagen General Population Study combined to achieve maximal statistical power (Fig. 6, left panel). We included 58,340 individuals, measured Lp(a) concentrations in fresh samples using apo(a)-insensitive assays, corrected for regression dilution bias, recorded 1,897 validated myocardial infarctions, and also focused on the risk in those with the extremely high Lp(a) concentrations. In this new analysis, the risk was again higher after approximately 30 mg/dl and the age- and sex-adjusted hazard ratio for myocardial infarction was 2.4-fold in those with Lp(a) above 100 mg/dl versus below 5 mg/dl, and thus more pronounced than in the Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration (compare Fig. 6, left and right panels).
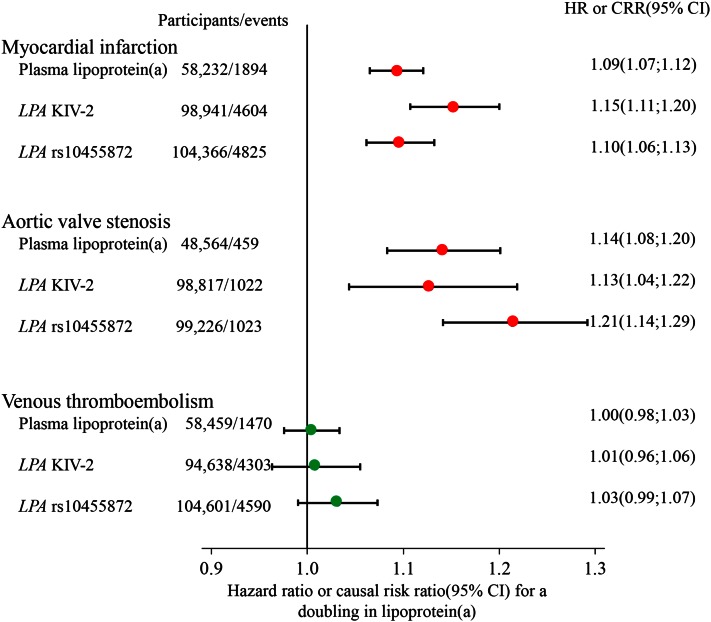
A complete large-scale Mendelian randomization study was first published by us in 2009 (6), although the basic idea had been suggested previously (101, 102). For use specifically in this review, we updated our former Mendelian randomization studies (6, 67, 112) based on the Copenhagen City Heart Study and the Copenhagen General Population Study combined to achieve maximal statistical power (Fig. 7, top panel). In instrumental variable analyses, a doubling in plasma Lp(a) concentrations caused a 15% (95% CI: 11–20%) higher risk ratio for myocardial infarction using LPA KIV-2 number of repeats and a 10% (95% CI: 6–13%) higher risk ratio using LPA rs10455872 SNP. This should be compared with the corresponding observational estimate of 9% (95% CI: 7–12%). Importantly, as Lp(a) concentrations vary up to a 1,000-fold between individuals (14), then Lp(a) can double many times. LPA genotypes were largely unconfounded by conventional cardiovascular risk factors (Table 1), which was also close to being the case for plasma Lp(a) concentrations.
Fig. 7.
Observational and causal genetic associations between high plasma Lp(a) concentrations and risk of cardiovascular disease in the Copenhagen City Heart Study and Copenhagen General Population Study combined. Hazard ratios for observational analyses of plasma Lp(a) concentrations were estimated by Cox proportional hazard regression models and were adjusted for age and sex. Causal risk ratios for analyses of genetically determined plasma Lp(a) concentrations were estimated by instrumental variable analyses and were adjusted for age and sex.
Many recent large-scale genetic studies also strongly supported high Lp(a) concentrations as a cause of myocardial infarction and ischemic heart disease (8, 66, 159, 160); however, these publications did not include a complete Mendelian randomization approach, but mainly provided data for the direct association between genotypes and risk of disease (Fig. 4, arrow #3). Most importantly, Robert Clarke et al. (8) identified two common LPA variants, rs10455872 with a per allele odds ratio for coronary heart disease of 1.70 (95% CI: 1.49–1.95; allele frequency 0.07) and rs3798220 with a per allele odds ratio of 1.92 (1.48–2.49; allele frequency 0.02).
Also important was a 2010 meta-analysis on apo(a) isoforms and risk of coronary heart disease (24). The 34 included studies of mainly White and Asian individuals used either phenotyping (69, 70, 102, 127, 139, 156, 161–182), that is, gel migration speed of plasma Lp(a) and molecular weight determination of apo(a), or genotyping of KIV-2 number of repeats (6, 183). For the 30 studies using phenotyping and including 7,382 cases and 8,514 controls, relative risk of coronary heart disease for smaller versus larger apo(a) isoforms was 2.08 (95% CI: 1.67–2.58). The genotyping studies were dominated by our own study mentioned above in the complete Mendelian randomization study design (6). It is also important to note that individuals carrying LPA loss-of-function alleles with low Lp(a) concentrations have low risk of cardiovascular disease (184, 185). Although relatively few Blacks have been studied in the past, a study in 2012 documented that risk of coronary heart disease is also higher in Black individuals with high plasma Lp(a) concentrations (186).
Taken together, there is now overwhelming evidence from epidemiology and genetics that high Lp(a) concentrations cause high risk of myocardial infarction. It could be argued that the same is true for ischemic and coronary heart disease, but the findings for these disease endpoints could be driven largely by that for myocardial infarction and for atherosclerotic stenosis as described below.
ATHEROSCLEROTIC STENOSIS
When high Lp(a) concentrations lead to high risk of myocardial infarction and ischemic heart disease, then automatically almost everybody will think that this must be because Lp(a) is atherogenic. However, there are other possible explanations and one could be that high Lp(a) leads to thrombosis causing myocardial infarction and to atherosclerotic stenosis causing angina pectoris, rather than Lp(a) causing atherosclerosis per se (111, 187, 188). To us, the latter idea became more plausible when it was suddenly documented that high Lp(a) concentrations also cause aortic valve stenosis (10, 11). However, it can be argued that this is a poor analogy. Indeed, the pathophysiology of “stenosis” in a coronary artery is complex and due to atherosclerotic mediated narrowing of the arterial lumen, some smooth muscle cell proliferation, and likely some element of thrombosis. Thus, the process of atherosclerotic stenosis is very complex and possibly very different than what goes on in aortic valve stenosis. Nevertheless, let us review the human evidence for this idea.
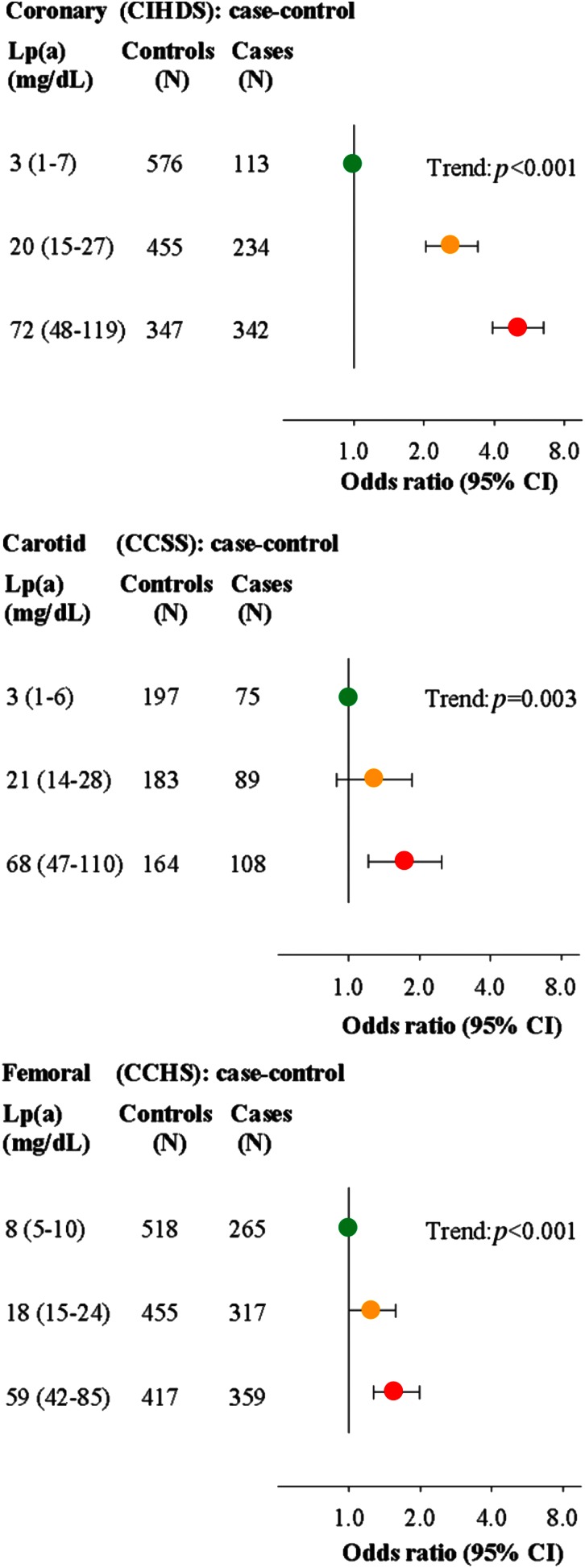
In a study by Kamstrup, Tybjærg-Hansen, and Nordestgaard (111) in the Copenhagen Ischemic Heart Disease Study, the Copenhagen Carotid Stroke Study, and the Copenhagen City Heart Study, the highest versus lowest tertile of Lp(a) was associated with high risk of coronary, carotid, and femoral atherosclerotic stenosis; that the findings were similar for the lowest versus highest tertile of KIV-2 number of repeats supports that these findings represent causal relationships. For risk of coronary atherosclerotic stenosis, the age- and sex-adjusted odds ratio for highest versus lowest tertile of Lp(a) was 5.0 (95% CI: 3.9–6.5) (Fig. 8, top panel). Corresponding odd ratios were 1.7 (95% CI: 1.2–2.5) for carotid atherosclerotic stenosis (Fig. 8, middle panel) and 1.6 (95% CI: 1.3–2.0) for femoral atherosclerotic stenosis (Fig. 8, bottom panel).
Fig. 8.
Observational associations between high plasma Lp(a) concentrations and risk of coronary, carotid, and femoral atherosclerotic stenosis in the Copenhagen Ischemic Heart Disease Study, Copenhagen Carotid Stroke Study, and Copenhagen City Heart Study, respectively. Odds ratios were estimated by logistic regression models and were adjusted for age and sex. CIHDS, Copenhagen Ischemic Heart Disease Study; CCSS, Copenhagen Carotid Stroke Study; CCHS, Copenhagen City Heart Study. Adapted from (111).
Many other studies have also found an association between high concentrations of Lp(a) or LPA risk genotypes and high risk of coronary, carotid, and femoral atherosclerotic stenosis (101, 102, 121, 160, 189–207). For example, in a cohort of 504 patients, Sam Tsimikas, Joe Witztum, and colleagues showed a strong association between high oxidized phospholipids and high Lp(a) concentrations with the presence and extent of coronary artery disease, detected by coronary angiography as the number of vessels with a stenosis of more than 50% of the luminal diameter (190). Also, in the InCHIANTI Study, 1,002 individuals aged above 60 years had their ankle-brachial index assessed over a 6 year period, and the authors found that high Lp(a) was an independent risk factor for peripheral arterial disease of the lower limbs (192). Finally, in a large case-control study, the odds ratio per LPA rs10455872 or rs3798220 risk alleles was 1.47 (95% CI: 1.33–1.62) for peripheral arterial disease (N = 5,215 cases) (160).
In contrast, high Lp(a) concentrations or LPA risk alleles have not been associated with early atherosclerosis measured as modest intima-media thickening in carotid or femoral arteries (160, 208–213); however, there is controversy as to whether such intima-media thickness represents atherosclerosis per se. For example, in the Young Finns Study, including 939 men and 1,141 women, data from observational and Mendelian randomization analyses provided no support for early atherogenic effects of high Lp(a) concentrations (211). Also, after pooling two studies and including 3,714 individuals, LPA rs10455872 or rs3798220 risk alleles were not associated with carotid intima-media thickness (160).
Taken together, a large number of studies unanimously show that high plasma Lp(a) concentrations are associated with high risk of coronary, carotid, and femoral atherosclerotic stenosis, with concordance between observational and causal genetic risk estimates. In contrast, there is no human evidence to support that high Lp(a) concentrations should cause early atherosclerosis in the form of increased intima-media thickness. That said, many researchers likely disagree with us on this topic, and many view aortic stenosis and carotid, femoral, or coronary stenosis as separate pathological entities.
AORTIC VALVE STENOSIS
In a 1995 study from Japan, it was observed in 347 men and 437 women that high age and high plasma Lp(a) concentrations were the best risk factors for aortic valve stenosis (sclerosis) (214). Likewise, in 1997, it was observed in 5,201 US individuals aged 65 and above, that age, male sex, and high plasma Lp(a) concentrations were the most important factors to discriminate between individuals with and without calcific aortic valve stenosis (disease) (215). High Lp(a) concentration as an important risk factor for aortic valve stenosis was later confirmed (216, 217), and interestingly, in individuals with both high Lp(a) and high Chlamydia pneumoniae IgG antibodies the risk was particularly high (216). Probably not too many noticed these early findings, and after all, this was observational evidence believed to be prone to confounding and reverse causation.
Then in 2013, Thanassoulis et al. (10) discovered that the LPA rs10455872 SNP, well-known as a high risk factor for myocardial infarction and coronary heart disease, was also found to be the best genetic causal risk factor for aortic valve calcification and stenosis: the per allele odds ratio for aortic valve calcification was 2.05 (95% CI: 1.63–2.57). This finding was replicated in additional White European, African-American, and Hispanic-American cohorts. In prospective analyses, this LPA SNP had a per allele hazard ratio for incident aortic valve stenosis of 1.68 (95% CI: 1.32–2.15) and 1.60 (95% CI: 1.12–2.28) in Swedish and Danish cohorts of the general population.
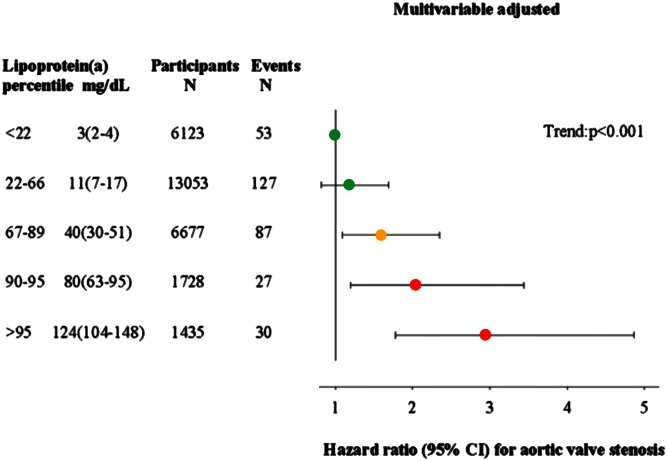
In a subsequent study in 2014 based on the Copenhagen City Heart Study and the Copenhagen General Population Study combined, we showed a stepwise higher risk of aortic valve stenosis with stepwise higher extreme concentrations of Lp(a) (Fig. 9) (11). Multivariable adjusted hazard ratios for aortic valve stenosis were 1.2 (95% CI: 0.8–1.7) for 5–19 mg/dl, 1.6 (95% CI: 1.1–2.4) for 20–64 mg/dl, 2.0 (95% CI: 1.2–3.4) for 65–90 mg/dl, and 2.9 (95% CI: 1.8–4.9) for above 90 mg/dl, versus Lp(a) concentrations below 5 mg/dl. Also, combining LPA rs10455872, rs3798220, and KIV-2 number of repeats, instrumental variable analysis yielded a genetic causal risk ratio for aortic valve stenosis of 1.6 (95% CI: 1.2–2.1) for a 10-fold higher Lp(a) concentration, comparable to the observational hazard ratio of 1.4 (95% CI: 1.2–1.7) for a 10-fold higher plasma Lp(a) concentration. Interestingly, as observed in the same individuals from Copenhagen and for a comparable doubling in Lp(a) concentrations, the risk estimated for aortic valve stenosis appeared slightly higher than for myocardial infarction, with concordance between observational and causal genetic risk estimates (Fig. 7, compare middle and upper panels).
Fig. 9.
Observational associations between high plasma Lp(a) concentrations and risk of aortic valve stenosis in the Copenhagen City Heart Study and Copenhagen General Population Study combined. Hazard ratios were estimated by Cox proportional hazard regression models and were multivariable adjusted for age, sex, total cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, systolic blood pressure, smoking, and diabetes. Lp(a) in milligrams per deciliter is shown as median (interquartile range). Adapted from (11).
Even more studies have now confirmed that high Lp(a) concentrations observationally and genetically represent strong causal risk factors for aortic valve calcification, stenosis, and stenosis progression (218–223). This is true for Whites and Asians alike.
Together, these studies document high Lp(a) concentrations as one of the strongest causal risk factors for aortic valve stenosis, with risk estimates slightly higher than for myocardial infarction. As both these diseases are among the main causes of heart failure, high Lp(a) concentrations may also be a strong causal risk factor for this condition.
HEART FAILURE
Given the role of high Lp(a) concentrations in myocardial infarction and aortic valve stenosis, it seemed natural to explore the impact of Lp(a) on the end product of these two diseases in the form of heart failure. We combined the Copenhagen City Heart Study and the Copenhagen General Population Study with 98,097 Danish individuals, of whom 4,122 were diagnosed with heart failure from 1976 through 2013. High Lp(a) concentrations were associated with multivariable adjusted hazard ratios for heart failure of 1.10 (95% CI: 0.97–1.25) for 8–19 mg/dl, 1.24 (95% CI: 1.08–1.42) for 20–67 mg/dl, 1.57 (95% CI: 1.32–1.87) for 68–153 mg/dl, and of 1.79 (95% CI: 1.18–2.73) for concentrations above153 mg/dl, versus Lp(a) concentrations below 8 mg/dl. Of all heart failure in the population, high Lp(a) had a population-attributable fraction of 9%. This means that if high Lp(a) was not present in the Danish population, then heart failure prevalence would be 9% lower than current levels.
By combining all LPA risk genotypes, instrumental variable analysis yielded a genetic causal risk ratio for heart failure of 1.18 (95% CI: 1.04–1.34) per 10-fold higher Lp(a) concentrations, which was comparable to the corresponding observational hazard ratio of 1.22 (95% CI: 1.11–1.35). Finally, in mediation analysis, 63% (95% CI: 45–99%) of heart failure risk due to high Lp(a) was mediated via myocardial infarction and aortic valve stenosis combined. Although 63% is a very high number in a mediation analysis, we naturally cannot exclude that high Lp(a) could lead to heart failure via yet another mechanism, e.g., through occlusion of small blood vessels in the myocardium.
VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM
Because high Lp(a) is a causal factor for myocardial infarction, and as there is ample evidence that Lp(a) interferes with fibrinolysis and likely promotes thrombosis (34), it seems logical that high Lp(a) should also be a strong causal risk factor for venous thromboembolism, that is, deep venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Interestingly however, this is probably not the case except at extremely high Lp(a) concentrations (111). Importantly, Lp(a) likely does not have inherent pro-thrombotic properties, but it may be anti-fibrinolytic, i.e., a clot has to be forming for Lp(a) to potentially affect growth. This implies a first hit of some other pro-thrombotic risk factor that is worsened by Lp(a), which might explain why different results on venous thromboembolism have been reported.
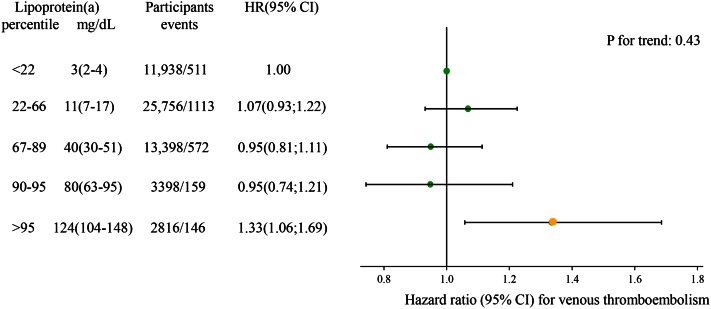
Kamstrup, Tybjærg-Hansen, and Nordestgaard (111) found that highest versus lowest tertile of Lp(a) did not associate with high risk of venous thrombosis; however, the extreme top 5% versus the lowest 22% of the concentration distribution of Lp(a) yielded an odds ratio of 1.7 (95% CI: 1.2–2.3) for risk of venous thrombosis. For the purpose of the present review, we updated this analysis and now included 53,908 individuals from the Copenhagen General Population Study and the Copenhagen City Heart Study with a total of 2,501 events of venous thromboembolism, and correspondingly found at extremely high Lp(a) concentrations above 100 mg/dl compared with concentrations below 5 mg/dl, a hazard ratio of 1.33 (95% CI: 1.06–1.69) for risk of venous thromboembolism (Fig. 10).
Fig. 10.
Observational associations between high plasma Lp(a) concentrations and risk of venous thromboembolism in the Copenhagen City Heart Study and Copenhagen General Population Study combined. Hazard ratios were estimated by Cox proportional hazard regression models and were adjusted for age and sex. Lp(a) in milligrams per deciliter is shown as median (interquartile range). HR, hazard ratio.
A meta-analysis from 2007, including six case-control studies with 1,826 patients with venous thromboembolism and 1,074 controls, found an odds ratio for venous thromboembolism of 1.8 (95% CI: 1.1–2.8) for Lp(a) concentrations above versus below 30 mg/dl (224). Three of the studies in the meta-analysis found individually higher risk of venous thromboembolism (225–227), whereas three studies had insignificant results (228–230). Further, the Longitudinal Investigation of Thromboembolism Etiology (LITE) study, including 19,921 participants with no venous thromboembolism at baseline, observed 327 venous thromboembolic events in Whites and 83 in African Americans during follow-up: the hazard ratio for risk of venous thromboembolism at Lp(a) above versus below 30 mg/dl was 1.12 (95% CI: 0.55–2.27) for Whites and 1.31 (95% CI: 0.69–2.47) for African Americans (231). In addition, several studies have been carried out in children with respect to high Lp(a) concentrations and risk of venous thromboembolism, with conflicting results (232–242).
As for genetic association of high Lp(a) with venous thromboembolism, one study found that after combining the LPA rs10455872 and rs3798220 SNPs, both of which are associated with high Lp(a) concentrations, there was no association of the LPA risk score with venous thromboembolism (N = 4,607 cases) (160). Also, another study among 21,483 women found similar results (243).
Calculated for the present review, among 104,601 individuals in the Copenhagen General Population Study and the Copenhagen City Heart Study combined, we find, using instrumental variable analyses, that the LPA rs10455872 SNP has a causal risk ratio of 1.03 (95% CI: 0.99–1.07) per doubling in Lp(a) for risk of venous thromboembolism (Fig. 7, bottom panel). A recently published study, including 516 patients with venous thromboembolism and 1,117 healthy controls, found that LPA KIV-2 number of repeats was independently associated with venous thromboembolism and that KIV-2 number of repeats was lower in patients than in controls (244). This is in contrast to what we find in 94,638 individuals in the Copenhagen General Population Study and the Copenhagen City Heart Study combined, where the LPA KIV-2 in instrumental variable analysis had a causal risk ratio of 1.01 (95% CI: 0.96–1.06) per doubling in Lp(a) concentrations for risk of venous thromboembolism (Fig. 7, bottom panel), also in accordance with previously published data on our studies (111).
Taken together, it seems likely that extremely high Lp(a) concentrations lead to modestly higher risk of venous thromboembolism. However, over the major part of the concentration range of Lp(a), risk of venous thromboembolism does not seem to be higher. Certainly, when compared directly using the same roughly 100,000 individuals from Copenhagen, then high Lp(a) is a much stronger causal factor for risk of myocardial infarction and aortic valve stenosis than for risk of venous thromboembolism, with concordance between observational and causal genetic risk estimates (Fig. 7).
SPECULATIONS ON POSSIBLE MECHANISMS IN PHYSIOLOGY AND PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Given the evidence presented above, it is worth considering what human epidemiologic and genetic evidence can teach us about mechanisms, that is, how high Lp(a) concentrations can cause disease and, conversely, whether that will tell us something about the physiological role of Lp(a). Certainly, as Lp(a) has developed twice in evolution in two different forms, around 140 million years ago in the hedgehog and around 40 million years ago in Old World monkeys, apes, and humans (14), Lp(a) likely must have had an important function on survival.
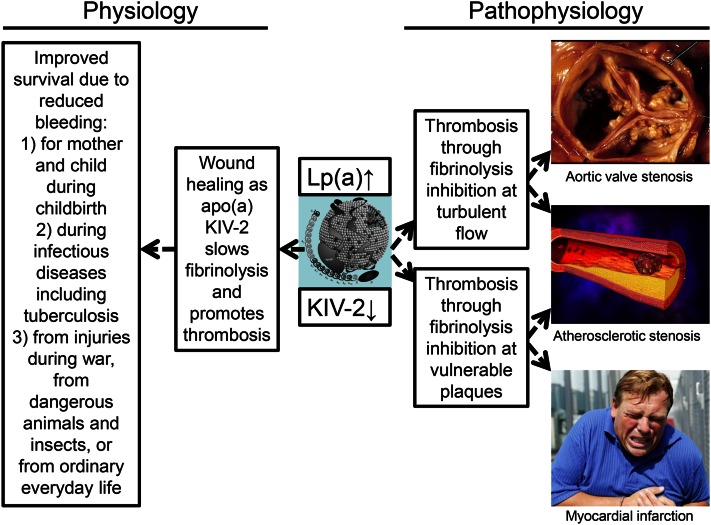
Physiologically, it was proposed by Michael Brown and Joe Goldstein (12) in 1987 that Lp(a) may play a role in wound healing, an idea that has been elaborated on (14, 27, 245–247). The physiological mechanism suggested is that Lp(a) binds to fibrin by its kringle structures and thereby specifically is transported to sites of injury, to facilitate wound healing via fibrinolysis inhibition and perhaps providing cholesterol for cell proliferation during tissue repair. If the latter hypothesis is true, it would seem natural that high Lp(a) concentrations should lead to low risk of bleeding.
From an evolutionary perspective in a context without modern medicine, it is easy to envision how protection from major fatal bleeds at a young age facilitated by high plasma Lp(a) concentration could have had a positive influence on survival (Fig. 11, left part). Improved survival due to reduced bleeding would seem highly likely for mother and child during childbirth, during infectious diseases, including tuberculosis, and from injuries during war or from dangerous animals and insects, or just in ordinary everyday life.
Fig. 11.
Speculations on physiological role and pathophysiology of high plasma Lp(a) concentrations, with corresponding small apo(a) size due to low number of KIV-2 repeats.
Until now, no convincing large-scale human data have been presented to support the hypothesis of improved wound healing at high Lp(a) concentrations. However, in a study including 109,169 individuals from the Copenhagen City Heart Study and the Copenhagen General Population study combined, we found that high Lp(a) concentrations were associated with low risk of major bleeding observationally and causal, genetically (A. Langsted, P.R. Kamstrup, B.G. Nordestgaard, unpublished observations). To us, this supports that Lp(a) physiologically may play a role in wound healing, although the hypothesis, at present, is mainly speculative.
In support of our findings, a prospective cohort study of the Japanese general population, including 10,494 individuals, found that the highest versus the lowest tertile of Lp(a) was associated with a hazard ratio for risk of cerebral hemorrhage of 0.34 (95% CI: 0.15–0.76) for men and of 0.44 (95% CI: 0.21–0.96) for women (249). Also, a previous study showed that Lp(a) particles with small apo(a) isoforms [and thus high Lp(a) concentrations] may inhibit fibrinolysis (250), and another study showed that high Lp(a) concentrations or small apo(a) sizes were associated with the formation of dense fibrin clots of reduced clot permeability and prolonged clot lysis time (251).
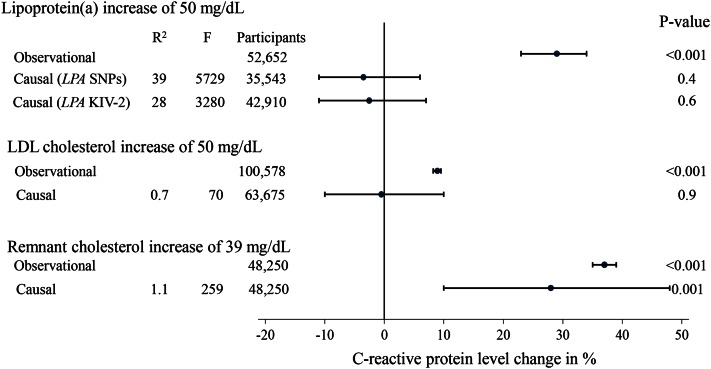
Further, a proteomic study identified Lp(a)-associated proteins to be assigned to wound healing, including the processes of coagulation, complement activation, and inflammatory response, implying that Lp(a) might have a role in the wound healing process (252). Interestingly though, although high Lp(a) concentrations may be involved in inflammation locally at sites of injury, e.g., locally in the arterial wall (253), genetically high Lp(a) concentrations (like genetically high LDL cholesterol concentrations) were not associated with high concentrations of C-reactive protein in individuals in the general population (Fig. 12) (112); in contrast, high triglyceride-rich lipoproteins measured as high remnant cholesterol led to low-grade inflammation on a whole body level (254).
Fig. 12.
Observational and causal genetic associations between high Lp(a) cholesterol, high LDL cholesterol, and high remnant cholesterol with C-reactive protein concentrations. Observational changes were by linear regression and causal genetic estimates were by instrumental variable analyses. Adapted from (112, 254).
The exact molecular mechanism by which high Lp(a) concentrations and small apo(a) size inhibit fibrinolysis and thereby possibly may promote thrombosis and facilitate wound healing, is discussed in another article in this Thematic Review series (34). If wound healing is indeed promoted by high Lp(a) concentrations, then it could even be speculated that the higher Lp(a) concentrations in individuals of African descent compared with individuals of European or Asian descent (14), could specifically, in an African context, present a survival advantage, e.g., through less bleeding during childbirth, infectious diseases, and injury, as speculated in Fig. 11.
An evolutionary advantage at a young age, like wound healing, could at an old age lead to more thrombosis and related diseases (Fig. 11, right part). As apo(a) has homology with plasminogen (4, 39), Lp(a) may promote thrombosis by competing with plasminogen and thereby inhibiting the role of plasmin in dissolving fibrin clots (34, 255–257). This could then, through fibrin deposition, lead to progressive aortic valve and atherosclerotic stenosis. We speculate that Lp(a) could bind to fibrin and be transported to and accumulate at sites of vulnerable plaques, and thereby deliver cholesterol via its LDL-component to sites of tissue healing, and as such is part of a wound healing process leading to progressive narrowing at atherosclerotic stenoses in coronary, carotid, and femoral arteries. If Lp(a) accumulates at sites of wound healing during rupture of vulnerable plaques, then it can further be speculated that Lp(a) might also accumulate at sites of minor injury during turbulent blood flow with beginning aortic valve and atherosclerotic stenosis, enhancing the deposition of cholesterol and possibly thrombi (12, 258), each of which may lead to further stenosis.
In support of this idea, Lp(a), compared with LDL, preferentially accumulates at sites of arterial injury, but not in adjacent uninjured arteries (56). Also, high Lp(a) concentration was a strong predictor of vein graft stenosis after coronary artery bypass surgery (259), although this was not the case after percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (260). The exact molecular mechanism by which high Lp(a) concentrations and small apo(a) size may cause aortic valve and atherosclerotic stenosis, e.g., by oxidized phospholipids through pro-inflammatory and pro-calcifying effects, is discussed in other articles in this Thematic Review series (34, 261). Importantly, a recent study suggests that Lp(a) induces monocyte trafficking to the arterial wall and mediates pro-inflammatory responses through its oxidized phospholipid content, pointing at a possible novel mechanism by which Lp(a) mediates cardiovascular disease (253).
As Lp(a) consists of a LDL cholesterol-rich particle covalently bound to an apo(a) glycoprotein, another possible mechanism involves that Lp(a), after transfer from the blood stream into the wall of aortic valve leaflets and the arterial intima (49, 52, 53), leads to cholesterol deposition in the manner similar to LDL and remnant cholesterol (63, 65). This would then cause a thickening of aortic valve leaflets and the arterial intima. However, as mentioned above, there is no human evidence to support that high Lp(a) concentrations promote early atherosclerosis (160, 208–213), at least in the form of increased intima-media thickness.
We speculate that the physiological role of KIV-2 in Lp(a) could be through wound healing during childbirth, infections, and injury, a role that at an old age could lead to more blood clots promoting stenosis of arteries and the aortic valve, and to myocardial infarction at sites of vulnerable plaques. Although many speculations are involved in this chain of events, this scenario seems to us to be the most straightforward explanation for the human data available today. We recognize that many experts in the field of Lp(a) research will find the proposed function of Lp(a) to promote wound healing as overemphasized here; nevertheless, we feel this subject should be presented in this Thematic Review so that the full range of ideas may be presented. The many other possible functions that might be equally or even more important are discussed in other articles in this Thematic Review series.
FAMILIAL HYPERCHOLESTEROLEMIA
Many early studies have demonstrated that Lp(a) concentrations are particularly high in those with clinically diagnosed heterozygous or homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) (122, 262–267), while others have not been able to document this (268, 269). FH with genetically very high LDL cholesterol is an autosomal dominant condition found in almost 1 in 200 individuals (270–274). Kinetic studies in subjects with homozygous FH found that Lp(a) is not catabolized via the LDL-receptor (275), demonstrating that the mechanism for high Lp(a) concentrations in FH is not the same as that for high LDL concentrations. In fact, plasma Lp(a) concentrations are mainly determined by production rates (276). Studies of genetic variation in both the LDLR and LPA genes have nevertheless supported that the observed high Lp(a) in those with clinically diagnosed FH is biologically based (268, 277).
Individuals diagnosed clinically with FH are prone to ascertainment bias (278), that is, individuals with the most extreme risk factors are most likely to be referred to hospital clinics. It is therefore possible that the high Lp(a) concentrations in individuals with clinically defined FH simply is the additional risk factor making the person attend a lipid clinic. In accordance with this idea, nonaffected family members of clinically diagnosed FH patients had higher Lp(a) concentrations than individuals in a reference population (267).
As reviewed above, it is now well demonstrated that high Lp(a) concentration is a causal risk factor for cardiovascular disease in the average person (6, 8, 9), irrespective of the concentration of LDL cholesterol (7, 158), and studies in FH patients demonstrate that high Lp(a) is also an important cardiovascular risk factor in this population (125, 279). In other words, high Lp(a) concentrations make risk of cardiovascular disease even worse in those already at extremely high risk due to the high LDL associated with FH. In accordance with this, European Atherosclerosis Society consensus panel statements made it a priority to screen all FH patients for high Lp(a) concentrations (9, 271, 280, 281).
On this background, we recently tested the hypotheses that high Lp(a) cholesterol and LPA risk genotypes are a cause of clinical FH, and that individuals with both high Lp(a) and clinical FH have the highest risk of myocardial infarction (113). In 46,200 individuals from the Copenhagen General Population Study, we used the Dutch Lipid Clinic Network criteria to diagnose FH clinically.
It should be recognized that the conventional measurement of “LDL cholesterol” contains the cholesterol content of both LDL as well as that found in the LDL component of Lp(a). Using routine LDL cholesterol measurements, e.g., unadjusted LDL cholesterol, mean Lp(a) concentrations were 23 mg/dl in individuals unlikely to have FH, 32 mg/dl in those with possible FH, and 35 mg/dl in those with probable or definite FH (P < 0.0001 for trend) (113). However, when adjusting LDL cholesterol for Lp(a) cholesterol content by subtracting 30% of the total Lp(a) mass from LDL cholesterol, the corresponding values were 24, 22, and 21 mg/dl, respectively (P = 0.46 for trend). Thus, the contribution of high Lp(a) cholesterol to the unadjusted LDL cholesterol measurement accounted for a quarter of all individuals diagnosed with clinical FH. Further, LPA risk genotypes were more frequent in clinical FH, whereas Lp(a) concentrations were similar in those with and without FH mutations in LDLR and APOB genes.
The hazard ratios for myocardial infarction compared with individuals unlikely to have FH and Lp(a) concentration below 50 mg/dl were 1.4 (95% CI: 1.1–1.7) in those unlikely to have FH and Lp(a) concentrations above 50 mg/dl, 3.2 (95% CI: 2.5–4.1) in those with possible, probable, or definite FH and Lp(a) concentration below 50 mg/dl, and 5.3 (95% CI: 3.6–7.6) in those with possible, probable, or definite FH and Lp(a) concentration above 50 mg/dl (113). In analyses using Simon Broome or MEDPED criteria, results were similar to those using Dutch Lipid Clinic Network criteria to diagnose clinical FH.
Taken together, plasma Lp(a) concentrations are higher in individuals with clinically diagnosed FH, but this is not due to FH mutations in LDLR and APOB genes. Rather, because Lp(a) cholesterol contributed to LDL cholesterol in the clinical diagnosis of FH, 25% of all clinically defined FH is due to high Lp(a) concentrations. The combined evidence strongly supports that all individuals with FH should have their Lp(a) measured in order to identify those with the highest concentrations, and as a result, the highest risk of myocardial infarction.
CONCLUSION AND PERSPECTIVES
Research and clinical interest in Lp(a) has had its ups and downs since its initial discovery in 1963 (1). The first golden age in Lp(a) research started in 1987 with the cloning and sequencing of the LPA gene coding for apo(a) in Lp(a) (4), leading to a huge increase in scientific interest in Lp(a). Then 22 years later in 2009, new genetic evidence that Lp(a) was a direct cause of cardiovascular disease just like LDL, started the second golden age in research and clinical interest in Lp(a) (6, 8), an interest that is only unraveling right now. We hope to experience a third golden age, a period in which, hopefully, randomized trials of Lp(a) reduction in individuals with very high concentrations can document reduction in cardiovascular disease. Only then will the clinical interest in Lp(a) become widespread. Certainly, for LDL cholesterol this is what happened after the 4S trial of statin therapy documented that reduction in LDL cholesterol lead to reduced cardiovascular disease and reduced all-cause mortality (282).
Footnotes
Abbreviations:
- CI
- confidence interval
- FH
- familial hypercholesterolemia
- KIV-2
- kringle IV type 2
- Lp(a)
- lipoprotein (a)
B.G.N. has received lecture and/or consultancy honoraria from Sanofi, Regeneron, Ionis, Dezima, Fresenius, B Braun, Kaneka, Amgen, and Denka Seiken. A.L. has nothing to declare.
REFERENCES
- 1.Berg, K. 1963. A new serum type system in man–the LP system. Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Scand. 59: 369–382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Berg, K., and J. Mohr. 1963. Genetics of the LP system. Acta Genet. Stat. Med. 13: 349–360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Mohr, J., and K. Berg. 1963. Genetics of the LP serum types: associations and linkage relations. Acta Genet. Stat. Med. 13: 343–348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.McLean J. W., Tomlinson J. E., Kuang W. J., Eaton D. L., Chen E. Y., Fless G. M., Scanu A. M., and Lawn R. M.. 1987. cDNA sequence of human apolipoprotein(a) is homologous to plasminogen. Nature. 330: 132–137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lawn R. M. 1992. Lipoprotein(a) in heart disease. Sci. Am. 266: 54–60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kamstrup P. R., Tybjaerg-Hansen A., Steffensen R., and Nordestgaard B. G.. 2009. Genetically elevated lipoprotein(a) and increased risk of myocardial infarction. JAMA. 301: 2331–2339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Erqou S., Kaptoge S., Perry P. L., Di A. E., Thompson A., White I. R., Marcovina S. M., Collins R., Thompson S. G., and Danesh J.. 2009. Lipoprotein(a) concentration and the risk of coronary heart disease, stroke, and nonvascular mortality. JAMA. 302: 412–423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Clarke R., Peden J. F., Hopewell J. C., Kyriakou T., Goel A., Heath S. C., Parish S., Barlera S., Franzosi M. G., Rust S. , et al. 2009. Genetic variants associated with Lp(a) lipoprotein level and coronary disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 361: 2518–2528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Nordestgaard B. G., Chapman M. J., Ray K., Boren J., Andreotti F., Watts G. F., Ginsberg H., Amarenco P., Catapano A., Descamps O. S., et al. 2010. Lipoprotein(a) as a cardiovascular risk factor: current status. Eur. Heart J. 31: 2844–2853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Thanassoulis G., Campbell C. Y., Owens D. S., Smith J. G., Smith A. V., Peloso G. M., Kerr K. F., Pechlivanis S., Budoff M. J., Harris T. B., et al. 2013. Genetic associations with valvular calcification and aortic stenosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 368: 503–512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kamstrup P. R., Tybjaerg-Hansen A., and Nordestgaard B. G.. 2014. Elevated lipoprotein(a) and risk of aortic valve stenosis in the general population. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 63: 470–477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Brown M. S., and Goldstein J. L.. 1987. Plasma lipoproteins: teaching old dogmas new tricks. Nature. 330: 113–114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Utermann G. 1989. The mysteries of lipoprotein(a). Science. 246: 904–910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Utermann G. 2001. Lipoprotein(a). In The Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease. 8th edition. C. R. Scriver, A. L. Beaudet, W. S. Sly, et al., editors. McGraw-Hill, New York. 2753–2787. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Scanu A. M., and Fless G. M.. 1990. Lipoprotein (a). Heterogeneity and biological relevance. J. Clin. Invest. 85: 1709–1715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Scanu A. M. 1990. Lipoprotein(a). Academic Press, Inc., San Diego. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Dahlén G. H. 1994. Lp(a) lipoprotein in cardiovascular disease. Atherosclerosis. 108: 111–126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Rader D. J., Hoeg J. M., and Brewer H. B. Jr. 1994. Quantitation of plasma apolipoproteins in the primary and secondary prevention of coronary artery disease. Ann. Intern. Med. 120: 1012–1025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Howard G. C., and Pizzo S. V.. 1993. Lipoprotein(a) and its role in atherothrombotic disease. Lab. Invest. 69: 373–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.MBewu A. D., and Durrington P. N.. 1990. Lipoprotein (a): structure, properties and possible involvement in thrombogenesis and atherogenesis. Atherosclerosis. 85: 1–14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Nielsen L. B. 1999. Atherogenecity of lipoprotein(a) and oxidized low density lipoprotein: insight from in vivo studies of arterial wall influx, degradation and efflux. Atherosclerosis. 143: 229–243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kamstrup P. R. 2010. Lipoprotein(a) and ischemic heart disease-A causal association? A review. Atherosclerosis. 211: 15–23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Danesh J., Collins R., and Peto R.. 2000. Lipoprotein(a) and coronary heart disease. Meta-analysis of prospective studies. Circulation. 102: 1082–1085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Erqou S., Thompson A., Di A. E., Saleheen D., Kaptoge S., Marcovina S., and Danesh J.. 2010. Apolipoprotein(a) isoforms and the risk of vascular disease: systematic review of 40 studies involving 58,000 participants. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 55: 2160–2167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Nordestgaard B. G., and Tybjaerg-Hansen A.. 2011. Genetic determinants of LDL, lipoprotein(a), triglyceride-rich lipoproteins and HDL: concordance and discordance with cardiovascular disease risk. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 22: 113–122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Dubé J. B., Boffa M. B., Hegele R. A., and Koschinsky M. L.. 2012. Lipoprotein(a): more interesting than ever after 50 years. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 23: 133–140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kronenberg F., and Utermann G.. 2013. Lipoprotein(a): resurrected by genetics. J. Intern. Med. 273: 6–30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kostner K. M., Marz W., and Kostner G. M.. 2013. When should we measure lipoprotein (a)? Eur. Heart J. 34: 3268–3276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Jacobson T. A. 2013. Lipoprotein(a), cardiovascular disease, and contemporary management. Mayo Clin. Proc. 88: 1294–1311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Jansen H., Samani N. J., and Schunkert H.. 2014. Mendelian randomization studies in coronary artery disease. Eur. Heart J. 35: 1917–1924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Nave A. H., Lange K. S., Leonards C. O., Siegerink B., Doehner W., Landmesser U., Steinhagen-Thiessen E., Endres M., and Ebinger M.. 2015. Lipoprotein (a) as a risk factor for ischemic stroke: a meta-analysis. Atherosclerosis. 242: 496–503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Orho-Melander M. 2015. Genetics of coronary heart disease: towards causal mechanisms, novel drug targets and more personalized prevention. J. Intern. Med. 278: 433–446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Witztum J. L., and Ginsberg H. N.. 2016. Lipoprotein (a): coming of age at last. J. Lipid Res. 57: 336–339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Boffa M. B., and Koschinsky M. L.. 2016. Lipoprotein (a): truly a direct prothrombotic factor in cardiovascular disease? J. Lipid Res. 57: 745–757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Thanassoulis G. 2016. Lipoprotein (a) in calcific aortic valve disease: from genomics to novel drug target for aortic stenosis. J. Lipid Res. 57: 917–924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Tsimikas S. 2016. Lipoprotein(a): novel target and emergence of novel therapies to lower cardiovascular disease risk. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 23: 157–164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Stender S., and Tybjaerg-Hansen A.. 2016. Using human genetics to predict the effects and side-effects of drugs. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 27: 105–111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Musunuru K., and Kathiresan S.. 2016. Surprises from genetic analyses of lipid risk factors for atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 118: 579–585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Schmidt K., Noureen A., Kronenberg F., and Utermann G.. 2016. Structure, function, and genetics of lipoprotein(a). J. Lipid Res. 57: 1339–1359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Kronenberg F. 2016. Human genetics and the causal role of lipoprotein(a) for various diseases. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 30: 87–100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Rath M., Niendorf A., Reblin T., Dietel M., Krebber H. J., and Beisiegel U.. 1989. Detection and quantification of lipoprotein(a) in the arterial wall of 107 coronary bypass patients. Arteriosclerosis. 9: 579–592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Niendorf A., Rath M., Wolf K., Peters S., Arps H., Beisiegel U., and Dietel M.. 1990. Morphological detection and quantification of lipoprotein(a) deposition in atheromatous lesions of human aorta and coronary arteries. Virchows Arch. A Pathol. Anat. Histopathol. 417: 105–111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Cushing G. L., Gaubatz J. W., Nava M. L., Burdick B. J., Bocan T. M., Guyton J. R., Weilbaecher D., DeBakey M. E., Lawrie G. M., and Morrisett J. D.. 1989. Quantitation and localization of apolipoproteins [a] and B in coronary artery bypass vein grafts resected at re-operation. Arteriosclerosis. 9: 593–603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Smith E. B., and Cochran S.. 1990. Factors influencing the accumulation in fibrous plaques of lipid derived from low density lipoprotein. II. Preferential immobilization of lipoprotein (a) (Lp(a)). Atherosclerosis. 84: 173–181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Hoff H. F., O’Neil J., and Yashiro A.. 1993. Partial characterization of lipoproteins containing apo[a] in human atherosclerotic lesions. J. Lipid Res. 34: 789–798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Reblin T., Meyer N., Labeur C., Henne-Bruns D., and Beisiegel U.. 1995. Extraction of lipoprotein(a), apo B, and apo E from fresh human arterial wall and atherosclerotic plaques. Atherosclerosis. 113: 179–188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Nachman R. L., Gavish D., Azrolan N., and Clarkson T. B.. 1991. Lipoprotein(a) in diet-induced atherosclerosis in nonhuman primates. Arterioscler. Thromb. 11: 32–38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Kreuzer J., Lloyd M. B., Bok D., Fless G. M., Scanu A. M., Lusis A. J., and Haberland M. E.. 1994. Lipoprotein (a) displays increased accumulation compared with low-density lipoprotein in the murine arterial wall. Chem. Phys. Lipids. 67–68: 175–190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Nielsen L. B., Nordestgaard B. G., Stender S., Niendorf A., and Kjeldsen K.. 1995. Transfer of lipoprotein(a) and LDL into aortic intima in normal and in cholesterol-fed rabbits. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 15: 1492–1502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Yeang C., Cotter B., and Tsimikas S.. 2016. Experimental animal models evaluating the causal role of lipoprotein(a) in atherosclerosis and aortic stenosis. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 30: 75–85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.O’Brien K. D., Reichenbach D. D., Marcovina S. M., Kuusisto J., Alpers C. E., and Otto C. M.. 1996. Apolipoproteins B, (a), and E accumulate in the morphologically early lesion of ‘degenerative’ valvular aortic stenosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 16: 523–532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Nielsen L. B., Gronholdt M. L., Schroeder T. V., Stender S., and Nordestgaard B. G.. 1997. In vivo transfer of lipoprotein(a) into human atherosclerotic carotid arterial intima. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 17: 905–911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Nielsen L. B., Stender S., Jauhiainen M., and Nordestgaard B. G.. 1996. Preferential influx and decreased fractional loss of lipoprotein(a) in atherosclerotic compared with nonlesioned rabbit aorta. J. Clin. Invest. 98: 563–571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Nordestgaard B. G., and Nielsen L. B.. 1994. Atherosclerosis and arterial influx of lipoproteins. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 5: 252–257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Nielsen L. B., Juul K., and Nordestgaard B. G.. 1998. Increased degradation of lipoprotein(a) in atherosclerotic compared with nonlesioned aortic intima-inner media of rabbits: in vivo evidence that lipoprotein(a) may contribute to foam cell formation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 18: 641–649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Nielsen L. B., Stender S., Kjeldsen K., and Nordestgaard B. G.. 1996. Specific accumulation of lipoprotein(a) in balloon-injured rabbit aorta in vivo. Circ. Res. 78: 615–626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Nordestgaard B. G. 1996. The vascular endothelial barrier–selective retention of lipoproteins. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 7: 269–273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Fless G. M., and Snyder M. L.. 1994. Polymorphic forms of Lp(a) with different structural and functional properties: cold-induced self-association and binding to fibrin and lysine-Sepharose. Chem. Phys. Lipids. 67–68: 69–79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Bihari-Varga M., Gruber E., Rotheneder M., Zechner R., and Kostner G. M.. 1988. Interaction of lipoprotein Lp(a) and low density lipoprotein with glycosaminoglycans from human aorta. Arteriosclerosis. 8: 851–857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Bottalico L. A., Keesler G. A., Fless G. M., and Tabas I.. 1993. Cholesterol loading of macrophages leads to marked enhancement of native lipoprotein(a) and apoprotein(a) internalization and degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 268: 8569–8573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Skiba P. J., Keesler G. A., and Tabas I.. 1994. Interferon-gamma down-regulates the lipoprotein(a)/apoprotein(a) receptor activity on macrophage foam cells. Evidence for disruption of ligand-induced receptor recycling by interferon-gamma. J. Biol. Chem. 269: 23059–23067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Keesler G. A., Li Y., Skiba P. J., Fless G. M., and Tabas I.. 1994. Macrophage foam cell lipoprotein(a)/apoprotein(a) receptor. Cell-surface localization, dependence of induction on new protein synthesis, and ligand specificity. Arterioscler. Thromb. 14: 1337–1345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Stary H. C., Chandler A. B., Glagov S., Guyton J. R., Insull W. Jr., Rosenfeld M. E., Schaffer S. A., Schwartz C. J., Wagner W. D., and Wissler R. W.. 1994. A definition of initial, fatty streak, and intermediate lesions of atherosclerosis. A report from the Committee on Vascular Lesions of the Council on Arteriosclerosis, American Heart Association. Arterioscler. Thromb. 14: 840–856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Nordestgaard B. G., and Varbo A.. 2014. Triglycerides and cardiovascular disease. Lancet. 384: 626–635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Nordestgaard B. G. 2016. Triglyceride-rich lipoproteins and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: new insights from epidemiology, genetics, and biology. Circ. Res. 118: 547–563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Schunkert H., Konig I. R., Kathiresan S., Reilly M. P., Assimes T. L., Holm H., Preuss M., Stewart A. F., Barbalic M., Gieger C. , et al. 2011. Large-scale association analysis identifies 13 new susceptibility loci for coronary artery disease. Nat. Genet. 43: 333–338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Kamstrup P. R., and Nordestgaard B. G.. 2013. Lipoprotein(a) concentrations, isoform size, and risk of type 2 diabetes: a Mendelian randomisation study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 1: 220–227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Enkhmaa B., Anuurad E., and Berglund L.. 2016. Lipoprotein (a): impact by ethnicity and environmental and medical conditions. J. Lipid Res. 57: 1111–1125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Sandholzer C., Hallman D. M., Saha N., Sigurdsson G., Lackner C., Csaszar A., Boerwinkle E., and Utermann G.. 1991. Effects of the apolipoprotein(a) size polymorphism on the lipoprotein(a) concentration in 7 ethnic groups. Hum. Genet. 86: 607–614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Kraft H. G., Lingenhel A., Pang R. W., Delport R., Trommsdorff M., Vermaak H., Janus E. D., and Utermann G.. 1996. Frequency distributions of apolipoprotein(a) kringle IV repeat alleles and their effects on lipoprotein(a) levels in Caucasian, Asian, and African populations: the distribution of null alleles is non-random. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 4: 74–87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Gaw A., Boerwinkle E., Cohen J. C., and Hobbs H. H.. 1994. Comparative analysis of the apo(a) gene, apo(a) glycoprotein, and plasma concentrations of Lp(a) in three ethnic groups. Evidence for no common “null” allele at the apo(a) locus. J. Clin. Invest. 93: 2526–2534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Matthews K. A., Sowers M. F., Derby C. A., Stein E., Miracle-McMahill H., Crawford S. L., and Pasternak R. C.. 2005. Ethnic differences in cardiovascular risk factor burden among middle-aged women: Study of Women’s Health Across the Nation (SWAN). Am. Heart J. 149: 1066–1073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Marcovina S. M., Albers J. J., Wijsman E., Zhang Z., Chapman N. H., and Kennedy H.. 1996. Differences in Lp[a] concentrations and apo[a] polymorphs between black and white Americans. J. Lipid Res. 37: 2569–2585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Helmhold M., Bigge J., Muche R., Mainoo J., Thiery J., Seidel D., and Armstrong V. W.. 1991. Contribution of the apo[a] phenotype to plasma Lp[a] concentrations shows considerable ethnic variation. J. Lipid Res. 32: 1919–1928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Schultz J. S., Schreffler D. C., Sing C. F., and Harvie N. R.. 1974. The genetics of the Lp antigen. I. Its quantitation and distribution in a sample population. Ann. Hum. Genet. 38: 39–46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Sing C. F., Schultz J. S., and Shreffler D. C.. 1974. The genetics of the Lp antigen. II. A family study and proposed models of genetic control. Ann. Hum. Genet. 38: 47–56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Iselius L., Dahlen G. , U. de Faire, and T. Lundman. 1981. Complex segregation analysis of the Lp(a)/pre-beta 1-lipoprotein trait. Clin. Genet. 20: 147–151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Hasstedt S. J., Wilson D. E., Edwards C. Q., Cannon W. N., Carmelli D., and Williams R. R.. 1983. The genetics of quantitative plasma Lp(a): analysis of a large pedigree. Am. J. Med. Genet. 16: 179–188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Morton N. E., K. Berg, G. Dahlen, R. E. Ferrell, and G. G. Rhoads. 1985. Genetics of the Lp lipoprotein in Japanese-Americans. Genet. Epidemiol. 2: 113–121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Hasstedt S. J., and Williams R. R.. 1986. Three alleles for quantitative Lp(a). Genet. Epidemiol. 3: 53–55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Fless G. M., ZumMallen M. E., and Scanu A. M.. 1986. Physicochemical properties of apolipoprotein(a) and lipoprotein(a-) derived from the dissociation of human plasma lipoprotein (a). J. Biol. Chem. 261: 8712–8718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Utermann G., Menzel H. J., Kraft H. G., Duba H. C., Kemmler H. G., and Seitz C.. 1987. Lp(a) glycoprotein phenotypes. Inheritance and relation to Lp(a)-lipoprotein concentrations in plasma. J. Clin. Invest. 80: 458–465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Grinstead G. F., and Ellefson R. D.. 1988. Heterogeneity of lipoprotein Lp(a) and apolipoprotein(a). Clin. Chem. 34: 1036–1040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Utermann G., Duba C., and Menzel H. J.. 1988. Genetics of the quantitative Lp(a) lipoprotein trait. II. Inheritance of Lp(a) glycoprotein phenotypes. Hum. Genet. 78: 47–50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Utermann G., Kraft H. G., Menzel H. J., Hopferwieser T., and Seitz C.. 1988. Genetics of the quantitative Lp(a) lipoprotein trait. I. Relation of LP(a) glycoprotein phenotypes to Lp(a) lipoprotein concentrations in plasma. Hum. Genet. 78: 41–46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Boerwinkle E., Menzel H. J., Kraft H. G., and Utermann G.. 1989. Genetics of the quantitative Lp(a) lipoprotein trait. III. Contribution of Lp(a) glycoprotein phenotypes to normal lipid variation. Hum. Genet. 82: 73–78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Kraft H. G., Sandholzer C., Menzel H. J., and Utermann G.. 1992. Apolipoprotein (a) alleles determine lipoprotein (a) particle density and concentration in plasma. Arterioscler. Thromb. 12: 302–306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Hallman D. M., Boerwinkle E., Saha N., Sandholzer C., Menzel H. J., Csazar A., and Utermann G.. 1991. The apolipoprotein E polymorphism: a comparison of allele frequencies and effects in nine populations. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 49: 338–349. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Barlera S., Specchia C., Farrall M., Chiodini B. D., Franzosi M. G., Rust S., Green F., Nicolis E. B., Peden J., Assmann G., et al. 2007. Multiple QTL influence the serum Lp(a) concentration: a genome-wide linkage screen in the PROCARDIS study. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 15: 221–227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.López S., Buil A., Ordoñez J., Souto J. C., Almasy L., Lathrop M., Blangero J., Blanco-Vaca F., Fontcuberta J., and Soria J. M.. 2008. Genome-wide linkage analysis for identifying quantitative trait loci involved in the regulation of lipoprotein a (Lpa) levels. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 16: 1372–1379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Ober C., Nord A. S., Thompson E. E., Pan L., Tan Z., Cusanovich D., Sun Y., Nicolae R., Edelstein C., Schneider D. H., et al. 2009. Genome-wide association study of plasma lipoprotein(a) levels identifies multiple genes on chromosome 6q. J. Lipid Res. 50: 798–806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Zabaneh D., Kumari M., Sandhu M., Wareham N., Wainwright N., Papamarkou T., Hopewell J., Clarke R., Li K., Palmen J., et al. 2011. Meta analysis of candidate gene variants outside the LPA locus with Lp(a) plasma levels in 14,500 participants of six White European cohorts. Atherosclerosis. 217: 447–451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Qi Q., Workalemahu T., Zhang C., Hu F. B., and Qi L.. 2012. Genetic variants, plasma lipoprotein(a) levels, and risk of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality among two prospective cohorts of type 2 diabetes. Eur. Heart J. 33: 325–334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Mora S., Kamstrup P. R., Rifai N., Nordestgaard B. G., Buring J. E., and Ridker P. M.. 2010. Lipoprotein(a) and risk of type 2 diabetes. Clin. Chem. 56: 1252–1260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Ye Z., Haycock P. C., Gurdasani D., Pomilla C., Boekholdt S. M., Tsimikas S., Khaw K. T., Wareham N. J., Sandhu M. S., and Forouhi N. G.. 2014. The association between circulating lipoprotein(a) and type 2 diabetes: is it causal? Diabetes. 63: 332–342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Ding L., Song A., Dai M., Xu M., Sun W., Xu B., Sun J., Wang T., Xu Y., Lu J., et al. 2015. Serum lipoprotein (a) concentrations are inversely associated with T2D, prediabetes, and insulin resistance in a middle-aged and elderly Chinese population. J. Lipid Res. 56: 920–926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Lamina C., and Kronenberg F.. 2013. The mysterious lipoprotein(a) is still good for a surprise. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 1: 170–172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Katan M. B. 1986. Apolipoprotein E isoforms, serum cholesterol, and cancer. Lancet. 1: 507–508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Gray R., and Wheatley K.. 1991. How to avoid bias when comparing bone marrow transplantation with chemotherapy. Bone Marrow Transplant. 7(Suppl 3): 9–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Tybjaerg-Hansen A., Agerholm-Larsen B., Humphries S. E., Abildgaard S., Schnohr P., and Nordestgaard B. G.. 1997. A common mutation (G-455→ A) in the beta-fibrinogen promoter is an independent predictor of plasma fibrinogen, but not of ischemic heart disease. A study of 9,127 individuals based on the Copenhagen City Heart Study. J. Clin. Invest. 99: 3034–3039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Sandholzer C., Boerwinkle E., Saha N., Tong M. C., and Utermann G.. 1992. Apolipoprotein(a) phenotypes, Lp(a) concentration and plasma lipid levels in relation to coronary heart disease in a Chinese population: evidence for the role of the apo(a) gene in coronary heart disease. J. Clin. Invest. 89: 1040–1046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Sandholzer C., Saha N., Kark J. D., Rees A., Jaross W., Dieplinger H., Hoppichler F., Boerwinkle E., and Utermann G.. 1992. Apo(a) isoforms predict risk for coronary heart disease. A study in six populations. Arterioscler. Thromb. 12: 1214–1226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Smith G. D., and Ebrahim S.. 2003. ‘Mendelian randomization’: can genetic epidemiology contribute to understanding environmental determinants of disease? Int. J. Epidemiol. 32: 1–22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Smith G. D., and Ebrahim S.. 2004. Mendelian randomization: prospects, potentials, and limitations. Int. J. Epidemiol. 33: 30–42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Davey Smith G., Ebrahim S., Lewis S., Hansell A. L., Palmer L. J., and Burton P. R.. 2005. Genetic epidemiology and public health: hope, hype, and future prospects. Lancet. 366: 1484–1498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Lawlor D. A., Harbord R. M., Sterne J. A., Timpson N., and Davey Smith G.. 2008. Mendelian randomization: using genes as instruments for making causal inferences in epidemiology. Stat. Med. 27: 1133–1163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Palmer T. M., Sterne J. A., Harbord R. M., Lawlor D. A., Sheehan N. A., Meng S., Granell R., Davey Smith G., and Didelez V.. 2011. Instrumental variable estimation of causal risk ratios and causal odds ratios in Mendelian randomization analyses. Am. J. Epidemiol. 173: 1392–1403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Davey Smith G., and Hemani G.. 2014. Mendelian randomization: genetic anchors for causal inference in epidemiological studies. Hum. Mol. Genet. 23: R89–R98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Clarke R., Shipley M., Lewington S., Youngman L., Collins R., Marmot M., and Peto R.. 1999. Underestimation of risk associations due to regression dilution in long-term follow-up of prospective studies. Am. J. Epidemiol. 150: 341–353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.MacMahon S., Peto R., Cutler J., Collins R., Sorlie P., Neaton J., Abbott R., Godwin J., Dyer A., and Stamler J.. 1990. Blood pressure, stroke, and coronary heart disease. Part 1, Prolonged differences in blood pressure: prospective observational studies corrected for the regression dilution bias. Lancet. 335: 765–774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Kamstrup P. R., Tybjaerg-Hansen A., and Nordestgaard B. G.. 2012. Genetic evidence that lipoprotein(a) associates with atherosclerotic stenosis rather than venous thrombosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 32: 1732–1741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Langsted A., Varbo A., Kamstrup P. R., and Nordestgaard B. G.. 2015. Elevated lipoprotein(a) does not cause low-grade inflammation despite causal association with aortic valve stenosis and myocardial infarction: a study of 100,578 individuals from the general population. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 100: 2690–2699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Langsted A., Kamstrup P. R., Benn M., Tybjaerg-Hansen A., and Nordestgaard B. G.. 2016. High lipoprotein(a) as a possible cause of clinical familial hypercholesterolaemia: a prospective cohort study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 4: 577–587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Afzal S., Brondum-Jacobsen P., Bojesen S. E., and Nordestgaard B. G.. 2014. Genetically low vitamin D concentrations and increased mortality: Mendelian randomisation analysis in three large cohorts. BMJ. 349: g6330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Thomsen M., Varbo A., Tybjaerg-Hansen A., and Nordestgaard B. G.. 2014. Low nonfasting triglycerides and reduced all-cause mortality: a Mendelian randomization study. Clin. Chem. 60: 737–746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Dahlén G., Ericson C., Furberg C., Lundkvist L., and Svardsudd K.. 1972. Studies on an extra pre-beta lipoprotein fraction. Acta Med. Scand. Suppl. 531: 1–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Berg, K., G. Dahlén, and M. H. Frick. 1974. Lp(a) lipoprotein and pre-beta1-lipoprotein in patients with coronary heart disease. Clin. Genet. 6: 230–235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Dahlén G., K. Berg, T. Gillnas, and C. Ericson. 1975. Lp(a) lipoprotein/pre-beta1-lipoprotein in Swedish middle-aged males and in patients with coronary heart disease. Clin. Genet. 7: 334–341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Rhoads G. G., Morton N. E., Gulbrandsen C. L., and Kagan A.. 1978. Sinking pre-beta lipoprotein and coronary heart disease in Japanese-American men in Hawaii. Am. J. Epidemiol. 108: 350–356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Kostner G. M., Avogaro P., Cazzolato G., Marth E., Bittolo-Bon G., and Qunici G. B.. 1981. Lipoprotein Lp(a) and the risk for myocardial infarction. Atherosclerosis. 38: 51–61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Dahlen G. H., Guyton J. R., Attar M., Farmer J. A., Kautz J. A., and Gotto A. M. Jr. 1986. Association of levels of lipoprotein Lp(a), plasma lipids, and other lipoproteins with coronary artery disease documented by angiography. Circulation. 74: 758–765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Wiklund O., Angelin B., Olofsson S. O., Eriksson M., Fager G., Berglund L., and Bondjers G.. 1990. Apolipoprotein(a) and ischaemic heart disease in familial hypercholesterolaemia. Lancet. 335: 1360–1363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Rhoads G. G., Dahlén G. , K. Berg, N. E. Morton, and A. L. Dannenberg. 1986. Lp(a) lipoprotein as a risk factor for myocardial infarction. JAMA. 256: 2540–2544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Durrington P. N., Ishola M., Hunt L., Arrol S., and Bhatnagar D.. 1988. Apolipoproteins (a), AI, and B and parental history in men with early onset ischaemic heart disease. Lancet. 1: 1070–1073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Seed M., Hoppichler F., Reaveley D., McCarthy S., Thompson G. R., Boerwinkle E., and Utermann G.. 1990. Relation of serum lipoprotein(a) concentration and apolipoprotein(a) phenotype to coronary heart disease in patients with familial hypercholesterolemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 322: 1494–1499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Sandkamp M., Funke H., Schulte H., Kohler E., and Assmann G.. 1990. Lipoprotein(a) is an independent risk factor for myocardial infarction at a young age. Clin. Chem. 36: 20–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Kark J. D., Sandholzer C., Friedlander Y., and Utermann G.. 1993. Plasma Lp(a), apolipoprotein(a) isoforms and acute myocardial infarction in men and women: a case-control study in the Jerusalem population. Atherosclerosis. 98: 139–151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Simons L., Friedlander Y., Simons J., and McCallum J.. 1993. Lipoprotein(a) is not associated with coronary heart disease in the elderly: cross-sectional data from the Dubbo study. Atherosclerosis. 99: 87–95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Zhuang Y. Y., Wang J. J., and Xu P.. 1993. Increased lipoprotein (a) as an independent risk factor for cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. Chin. Med. J. (Engl.). 106: 597–600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Orth-Gomér K., Mittleman M. A., Schenck-Gustafsson K., Wamala S. P., Eriksson M., Belkic K., Kirkeeide R., Svane B., and Rydén L.. 1997. Lipoprotein(a) as a determinant of coronary heart disease in young women. Circulation. 95: 329–334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Rosengren A., Wilhelmsen L., Eriksson E., Risberg B., and Wedel H.. 1990. Lipoprotein (a) and coronary heart disease: a prospective case-control study in a general population sample of middle aged men. BMJ. 301: 1248–1251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Jauhiainen M., Koskinen P., Ehnholm C., Frick M. H., Manttari M., Manninen V., and Huttunen J. K.. 1991. Lipoprotein (a) and coronary heart disease risk: a nested case-control study of the Helsinki Heart Study participants. Atherosclerosis. 89: 59–67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Coleman M. P., Key T. J., Wang D. Y., Hermon C., Fentiman I. S., Allen D. S., Jarvis M., Pike M. C., and Sanders T. A.. 1992. A prospective study of obesity, lipids, apolipoproteins and ischaemic heart disease in women. Atherosclerosis. 92: 177–185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Ridker P. M., Hennekens C. H., and Stampfer M. J.. 1993. A prospective study of lipoprotein(a) and the risk of myocardial infarction. JAMA. 270: 2195–2199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Cremer P., Nagel D., Labrot B., Mann H., Muche R., Elster H., and Seidel D.. 1994. Lipoprotein Lp(a) as predictor of myocardial infarction in comparison to fibrinogen, LDL cholesterol and other risk factors: results from the prospective Gottingen Risk Incidence and Prevalence Study (GRIPS). Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 24: 444–453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Alfthan G., Pekkanen J., Jauhiainen M., Pitkaniemi J., Karvonen M., Tuomilehto J., Salonen J. T., and Ehnholm C.. 1994. Relation of serum homocysteine and lipoprotein(a) concentrations to atherosclerotic disease in a prospective Finnish population based study. Atherosclerosis. 106: 9–19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Wald N. J., Law M., Watt H. C., Wu T., Bailey A., Johnson A. M., Craig W. Y., Ledue T. B., and Haddow J. E.. 1994. Apolipoproteins and ischaemic heart disease: implications for screening. Lancet. 343: 75–79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Assmann G., Schulte H. , and A. von Eckardstein. 1996. Hypertriglyceridemia and elevated lipoprotein(a) are risk factors for major coronary events in middle-aged men. Am. J. Cardiol. 77: 1179–1184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Klausen I. C., Sjol A., Hansen P. S., Gerdes L. U., Moller L., Lemming L., Schroll M., and Faergeman O.. 1997. Apolipoprotein(a) isoforms and coronary heart disease in men: a nested case-control study. Atherosclerosis. 132: 77–84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Wild S. H., Fortmann S. P., and Marcovina S. M.. 1997. A prospective case-control study of lipoprotein(a) levels and apo(a) size and risk of coronary heart disease in Stanford Five-City Project participants. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 17: 239–245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Craig W. Y., Neveux L. M., Palomaki G. E., Cleveland M. M., and Haddow J. E.. 1998. Lipoprotein(a) as a risk factor for ischemic heart disease: metaanalysis of prospective studies. Clin. Chem. 44: 2301–2306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Dahlén G. 1988. Lipoprotein (a) as a risk factor for atherosclerotic diseases. Arctic Med. Res. 47(Suppl 1): 458–461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Dahlén G. H., Weinehall L., Stenlund H., Jansson J. H., Hallmans G., Huhtasaari F., and Wall S.. 1998. Lipoprotein(a) and cholesterol levels act synergistically and apolipoprotein A-I is protective for the incidence of primary acute myocardial infarction in middle-aged males. An incident case-control study from Sweden. J. Intern. Med. 244: 425–430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Cantin B., Gagnon F., Moorjani S., Despres J. P., Lamarche B., Lupien P. J., and Dagenais G. R.. 1998. Is lipoprotein(a) an independent risk factor for ischemic heart disease in men? The Quebec Cardiovascular Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 31: 519–525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Bostom A. G., Cupples L. A., Jenner J. L., Ordovas J. M., Seman L. J., Wilson P. W., Schaefer E. J., and Castelli W. P.. 1996. Elevated plasma lipoprotein(a) and coronary heart disease in men aged 55 years and younger. A prospective study. JAMA. 276: 544–548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Bostom A. G., Gagnon D. R., Cupples L. A., Wilson P. W., Jenner J. L., Ordovas J. M., Schaefer E. J., and Castelli W. P.. 1994. A prospective investigation of elevated lipoprotein (a) detected by electrophoresis and cardiovascular disease in women. The Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. 90: 1688–1695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Nguyen T. T., Ellefson R. D., Hodge D. O., Bailey K. R., Kottke T. E., and Abu-Lebdeh H. S.. 1997. Predictive value of electrophoretically detected lipoprotein(a) for coronary heart disease and cerebrovascular disease in a community-based cohort of 9936 men and women. Circulation. 96: 1390–1397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Marcovina S. M., Albers J. J., Gabel B., Koschinsky M. L., and Gaur V. P.. 1995. Effect of the number of apolipoprotein(a) kringle 4 domains on immunochemical measurements of lipoprotein(a). Clin. Chem. 41: 246–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Tate J. R., Rifai N. , K. Berg, R. Couderc, F. Dati, G. M. Kostner, I. Sakurabayashi, and A. Steinmetz. 1998. International Federation of Clinical Chemistry standardization project for the measurement of lipoprotein(a). Phase I. Evaluation of the analytical performance of lipoprotein(a) assay systems and commercial calibrators. Clin. Chem. 44: 1629–1640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Marcovina S. M., Koschinsky M. L., Albers J. J., and Skarlatos S.. 2003. Report of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Workshop on Lipoprotein(a) and Cardiovascular Disease: recent advances and future directions. Clin. Chem. 49: 1785–1796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Kronenberg F., Trenkwalder E., Dieplinger H., and Utermann G.. 1996. Lipoprotein(a) in stored plasma samples and the ravages of time. Why epidemiological studies might fail. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 16: 1568–1572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.von Eckardstein A., Schulte H., Cullen P., and Assmann G.. 2001. Lipoprotein(a) further increases the risk of coronary events in men with high global cardiovascular risk. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 37: 434–439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Sharrett A. R., Ballantyne C. M., Coady S. A., Heiss G., Sorlie P. D., Catellier D., and Patsch W.. 2001. Coronary heart disease prediction from lipoprotein cholesterol levels, triglycerides, lipoprotein(a), apolipoproteins A-I and B, and HDL density subfractions: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study. Circulation. 104: 1108–1113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Luc G., Bard J. M., Arveiler D., Ferrieres J., Evans A., Amouyel P., Fruchart J. C., and Ducimetiere P.. 2002. Lipoprotein (a) as a predictor of coronary heart disease: the PRIME Study. Atherosclerosis. 163: 377–384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Ariyo A. A., Thach C., and Tracy R.. 2003. Lp(a) lipoprotein, vascular disease, and mortality in the elderly. N. Engl. J. Med. 349: 2108–2115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Rifai N., Ma J., Sacks F. M., Ridker P. M., Hernandez W. J., Stampfer M. J., and Marcovina S. M.. 2004. Apolipoprotein(a) size and lipoprotein(a) concentration and future risk of angina pectoris with evidence of severe coronary atherosclerosis in men: The Physicians’ Health Study. Clin. Chem. 50: 1364–1371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Suk Danik J., Rifai N., Buring J. E., and Ridker P. M.. 2006. Lipoprotein(a), measured with an assay independent of apolipoprotein(a) isoform size, and risk of future cardiovascular events among initially healthy women. JAMA. 296: 1363–1370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Kamstrup P. R., Benn M., Tybjaerg-Hansen A., and Nordestgaard B. G.. 2008. Extreme lipoprotein(a) levels and risk of myocardial infarction in the general population: the Copenhagen City Heart Study. Circulation. 117: 176–184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Trégouët D. A., König I. R., Erdmann J., Munteanu A., Braund P. S., Hall A. S., Grosshennig A., Linsel-Nitschke P., Perret C., DeSuremain M., et al. 2009. Genome-wide haplotype association study identifies the SLC22A3-LPAL2-LPA gene cluster as a risk locus for coronary artery disease. Nat. Genet. 41: 283–285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Helgadottir A., Gretarsdottir S., Thorleifsson G., Holm H., Patel R. S., Gudnason T., Jones G. T., van Rij A. M., Eapen D. J., Baas A. F. , et al. 2012. Apolipoprotein(a) genetic sequence variants associated with systemic atherosclerosis and coronary atherosclerotic burden but not with venous thromboembolism. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 60: 722–729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Gazzaruso C., Garzaniti A., Buscaglia P., Bonetti G., Falcone C., Fratino P., Finardi G., and Geroldi D.. 1998. Apolipoprotein(a) phenotypes and their predictive value for coronary heart disease: identification of an operative cut-off of apolipoprotein(a) polymorphism. J. Cardiovasc. Risk. 5: 37–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Qin S., Wang S., and Li C.. 1995. Apolipoprotein (a) polymorphism in relation to coronary heart disease in Chinese Han nationality [article in Chinese]. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 75: 588–591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Emanuele E., Peros E., Minoretti P., D’Angelo A., Piccinni M. N., Montagna L., and Geroldi D.. 2004. Apolipoprotein(a) size polymorphism is associated with coronary heart disease in polygenic hypercholesterolemia. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 14: 193–199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Emanuele E., Peros E., Minoretti P., D’Angelo A., Montagna L., Falcone C., and Geroldi D.. 2004. Significance of apolipoprotein(a) phenotypes in acute coronary syndromes: relation with clinical presentation. Clin. Chim. Acta. 350: 159–165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Emanuele E., Peros E., Minoretti P., Falcone C., D’Angelo A., Montagna L., and Geroldi D.. 2003. Relationship between apolipoprotein(a) size polymorphism and coronary heart disease in overweight subjects. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 3: 12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Parlavecchia M., Pancaldi A., Taramelli R., Valsania P., Galli L., Pozza G., Chierchia S., and Ruotolo G.. 1994. Evidence that apolipoprotein(a) phenotype is a risk factor for coronary artery disease in men < 55 years of age. Am. J. Cardiol. 74: 346–351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Martín S., Pedro-Botet J., Joven J., Simó J. M., Ladona M. G., Pavesi M., and Rubiés-Prat J.. 2002. Heterozygous apolipoprotein (a) status and protein expression as a risk factor for premature coronary heart disease. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 139: 181–187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Simó J. M., Joven J., Vilella E., Ribas M., Pujana M. A., Sundaram I. M., Hammel J. P., and Hoover-Plow J. L.. 2001. Impact of apolipoprotein(a) isoform size heterogeneity on the lysine binding function of lipoprotein(a) in early onset coronary artery disease. Thromb. Haemost. 85: 412–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Geethanjali F. S., Jose V. J., and Kanagasabapathy A. S.. 2002. Lipoprotein (a) phenotypes in south Indian patients with coronary artery disease. Indian Heart J. 54: 50–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Zeljkovic A., Bogavac-Stanojevic N., Jelic-Ivanovic Z., Spasojevic-Kalimanovska V., Vekic J., and Spasic S.. 2009. Combined effects of small apolipoprotein (a) isoforms and small, dense LDL on coronary artery disease risk. Arch. Med. Res. 40: 29–35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Calmarza P., Cordero J., Santos V., and Vella J. C.. 2004. Apolipoprotein(a) isoforms in infarcted men under 60 years old. Clin. Biochem. 37: 911–918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Akanji A. O. 2000. Apo(a) isoforms do not predict risk for coronary heart disease in a Gulf Arab population. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 37: 360–366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Katsouras C. S., Karabina S. A., Tambaki A. P., Goudevenos J. A., Michalis L. K., Tsironis L. D., Stroumbis C. S., Elisaf M. S., Sideris D. A., and Tselepis A. D.. 2001. Serum lipoprotein(a) concentrations and apolipoprotein(a) isoforms: association with the severity of clinical presentation in patients with coronary heart disease. J. Cardiovasc. Risk. 8: 311–317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Gazzaruso C., Garzaniti A., Falcone C., Geroldi D., Finardi G., and Fratino P.. 2001. Association of lipoprotein(a) levels and apolipoprotein(a) phenotypes with coronary artery disease in type 2 diabetic patients and in non-diabetic subjects. Diabet. Med. 18: 589–594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Gambhir J. K., Kaur H., Prabhu K. M., Morrisett J. D., and Gambhir D. S.. 2008. Association between lipoprotein(a) levels, apo(a) isoforms and family history of premature CAD in young Asian Indians. Clin. Biochem. 41: 453–458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Zorio E., Falco C., Arnau M. A., Espana F., Osa A., Ramon L. A., Castello R., Almenar L., Palencia M. A., and Estelles A.. 2006. Lipoprotein (a) in young individuals as a marker of the presence of ischemic heart disease and the severity of coronary lesions. Haematologica. 91: 562–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Kalina A., Csaszar A., Fust G., Nagy B., Szalai C., Karadi I., Duba J., Prohaszka Z., Horvath L., and Dieplinger H.. 2001. The association of serum lipoprotein(a) levels, apolipoprotein(a) size and (TTTTA)(n) polymorphism with coronary heart disease. Clin. Chim. Acta. 309: 45–51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Bigot E., Robert B., Bard J. M., and Mainard F.. 1997. Lipoprotein (a) phenotype distribution in a population of bypass patients and its influence on lipoprotein (a) concentration. Clin. Chim. Acta. 265: 99–111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Paultre F., Pearson T. A., Weil H. F., Tuck C. H., Myerson M., Rubin J., Francis C. K., Marx H. F., Philbin E. F., Reed R. G., et al. 2000. High levels of Lp(a) with a small apo(a) isoform are associated with coronary artery disease in African American and white men. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 20: 2619–2624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Abe A., Noma A., Lee Y. J., and Yamaguchi H.. 1992. Studies on apolipoprotein(a) phenotypes. Part 2. Phenotype frequencies and Lp(a) concentrations in different phenotypes in patients with angiographically defined coronary artery diseases. Atherosclerosis. 96: 9–15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181.Brazier L., Tiret L., Luc G., Arveiler D., Ruidavets J. B., Evans A., Chapman J., Cambien F., and Thillet J.. 1999. Sequence polymorphisms in the apolipoprotein(a) gene and their association with lipoprotein(a) levels and myocardial infarction. The ECTIM Study. Atherosclerosis. 144: 323–333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182.Holmer S. R., Hengstenberg C., Kraft H. G., Mayer B., Poll M., Kurzinger S., Fischer M., Lowel H., Klein G., Riegger G. A., et al. 2003. Association of polymorphisms of the apolipoprotein(a) gene with lipoprotein(a) levels and myocardial infarction. Circulation. 107: 696–701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183.Geethanjali F. S., Luthra K., Lingenhel A., Kanagasaba-Pathy A. S., Jacob J., Srivastava L. M., Vasisht S., Kraft H. G., and Utermann G.. 2003. Analysis of the apo(a) size polymorphism in Asian Indian populations: association with Lp(a) concentration and coronary heart disease. Atherosclerosis. 169: 121–130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184.Lim E. T., Wurtz P., Havulinna A. S., Palta P., Tukiainen T., Rehnstrom K., Esko T., Magi R., Inouye M., Lappalainen T., et al. 2014. Distribution and medical impact of loss-of-function variants in the Finnish founder population. PLoS Genet. 10: e1004494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185.Kyriakou T., Seedorf U., Goel A., Hopewell J. C., Clarke R., Watkins H., and Farrall M.. 2014. A common LPA null allele associates with lower lipoprotein(a) levels and coronary artery disease risk. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 34: 2095–2099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 186.Virani S. S., Brautbar A., Davis B. C., Nambi V., Hoogeveen R. C., Sharrett A. R., Coresh J., Mosley T. H., Morrisett J. D., Catellier D. J., et al. 2012. Associations between lipoprotein(a) levels and cardiovascular outcomes in black and white subjects: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study. Circulation. 125: 241–249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 187.Spence J. D. 2006. Lipoprotein(a): involved in events, but not burden of atherosclerotic disease? Stroke. 37: 1350–1351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 188.Spence J. D., and Koschinsky M.. 2012. Mechanisms of lipoprotein(a) pathogenicity: prothrombotic, proatherosclerotic, or both? Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 32: 1550–1551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 189.Frick M. H., Dahlen G. , K. Berg, M. Valle, and P. Hekali. 1978. Serum lipids in angiographically assessed coronary atherosclerosis. Chest. 73: 62–65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 190.Tsimikas S., Brilakis E. S., Miller E. R., McConnell J. P., Lennon R. J., Kornman K. S., Witztum J. L., and Berger P. B.. 2005. Oxidized phospholipids, Lp(a) lipoprotein, and coronary artery disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 353: 46–57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 191.Klein J. H., Hegele R. A., Hackam D. G., Koschinsky M. L., Huff M. W., and Spence J. D.. 2008. Lipoprotein(a) is associated differentially with carotid stenosis, occlusion, and total plaque area. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 28: 1851–1856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 192.Volpato S., Vigna G. B., McDermott M. M., Cavalieri M., Maraldi C., Lauretani F., Bandinelli S., Zuliani G., Guralnik J. M., Fellin R., et al. 2010. Lipoprotein(a), inflammation, and peripheral arterial disease in a community-based sample of older men and women (the InCHIANTI study). Am. J. Cardiol. 105: 1825–1830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 193.Ronald J., Rajagopalan R., Cerrato F., Nord A. S., Hatsukami T., Kohler T., Marcovina S., Heagerty P., and Jarvik G. P.. 2011. Genetic variation in LPAL2, LPA, and PLG predicts plasma lipoprotein(a) level and carotid artery disease risk. Stroke. 42: 2–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 194.Armstrong V. W., Cremer P., Eberle E., Manke A., Schulze F., Wieland H., Kreuzer H., and Seidel D.. 1986. The association between serum Lp(a) concentrations and angiographically assessed coronary atherosclerosis. Dependence on serum LDL levels. Atherosclerosis. 62: 249–257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 195.Groves P., Rees A., Bishop A., Morgan R., Ruttley M., Lewis N., Lane I., and Hall R.. 1993. Apolipoprotein (a) concentrations and susceptibility to coronary artery disease in patients with peripheral vascular disease. Br. Heart J. 69: 26–30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 196.Budde T., Fechtrup C., Bosenberg E., Vielhauer C., Enbergs A., Schulte H., Assmann G., and Breithardt G.. 1994. Plasma Lp(a) levels correlate with number, severity, and length-extension of coronary lesions in male patients undergoing coronary arteriography for clinically suspected coronary atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. 14: 1730–1736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 197.Wang X. L., Tam C., McCredie R. M., and Wilcken D. E.. 1994. Determinants of severity of coronary artery disease in Australian men and women. Circulation. 89: 1974–1981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 198.Zenker G., Koltringer P., Bone G., Niederkorn K., Pfeiffer K., and Jurgens G.. 1986. Lipoprotein(a) as a strong indicator for cerebrovascular disease. Stroke. 17: 942–945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 199.Cambillau M., Simon A., Amar J., Giral P., Atger V., Segond P., Levenson J., Merli I., Megnien J. L., and Plainfosse M. C.. 1992. Serum Lp(a) as a discriminant marker of early atherosclerotic plaque at three extracoronary sites in hypercholesterolemic men. The PCVMETRA Group. Arterioscler. Thromb. 12: 1346–1352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 200.Brown S. A., Morrisett J. D., Boerwinkle E., Hutchinson R., and Patsch W.. 1993. The relation of lipoprotein[a] concentrations and apolipoprotein[a] phenotypes with asymptomatic atherosclerosis in subjects of the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study. Arterioscler. Thromb. 13: 1558–1566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 201.Baldassarre D., Tremoli E., Franceschini G., Michelagnoli S., and Sirtori C. R.. 1996. Plasma lipoprotein(a) is an independent factor associated with carotid wall thickening in severely but not moderately hypercholesterolemic patients. Stroke. 27: 1044–1049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 202.Norrgård O., Angquist K. A., and Dahlen G.. 1991. Lp(a) lipoprotein in patients with arterial insufficiency of the lower extremities. Eur. J. Vasc. Surg. 5: 277–282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 203.Mölgaard J., Klausen I. C., Lassvik C., Faergeman O., Gerdes L. U., and Olsson A. G.. 1992. Significant association between low-molecular-weight apolipoprotein(a) isoforms and intermittent claudication. Arterioscler. Thromb. 12: 895–901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 204.Widmann M. D., and Sumpio B. E.. 1993. Lipoprotein (a): a risk factor for peripheral vascular disease. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 7: 446–451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 205.Pedro-Botet J., Senti M., Auguet T., Nogues X., Rubies-Prat J., Aubo C., and Vidal-Barraquer F.. 1993. Apolipoprotein(a) genetic polymorphism and serum lipoprotein(a) concentration in patients with peripheral vascular disease. Atherosclerosis. 104: 87–94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 206.Valentine R. J., Grayburn P. A., Vega G. L., and Grundy S. M.. 1994. Lp(a) lipoprotein is an independent, discriminating risk factor for premature peripheral atherosclerosis among white men. Arch. Intern. Med. 154: 801–806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 207.Schreiner P. J., Morrisett J. D., Sharrett A. R., Patsch W., Tyroler H. A., Wu K., and Heiss G.. 1993. Lipoprotein[a] as a risk factor for preclinical atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. 13: 826–833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 208.Denti L., Marchini L., Pasolini G., Baffoni M. T., Ablondi F., and Valenti G.. 1995. Lipoprotein Lp(a) and cerebrovascular disease in the elderly: correlations with the severity of extracranial carotid atherosclerosis assessed by ultrasonography. Acta Biomed. Ateneo Parmense. 66: 175–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 209.Srámek A., Reiber J. H., Baak-Pablo R., Sturk A., and Rosendaal F. R.. 2003. Lipoprotein(a) and ultrasonographically determined early atherosclerotic changes in the carotid and femoral artery. J. Thromb. Haemost. 1: 374–379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 210.Grebe M. T., Schoene E., Schaefer C. A., Boedeker R. H., Kemkes-Matthes B., Voss R., and Tillmanns H. H.. 2007. Elevated lipoprotein(a) does not promote early atherosclerotic changes of the carotid arteries in young, healthy adults. Atherosclerosis. 190: 194–198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 211.Kivimäki M., Magnussen C. G., Juonala M., Kähönen M., Kettunen J., Loo B. M., Lehtimäki T., Viikari J., and Raitakari O. T.. 2011. Conventional and Mendelian randomization analyses suggest no association between lipoprotein(a) and early atherosclerosis: the Young Finns Study. Int. J. Epidemiol. 40: 470–478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 212.Calmarza P., Trejo J. M., Lapresta C., and Lopez P.. 2012. Relationship between lipoprotein(a) concentrations and intima-media thickness: a healthy population study. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 19: 1290–1295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 213.Bos S., Duvekot M. H., Touw-Blommesteijn A. C., Verhoeven A. J., Mulder M. T., Watts G. F., Sijbrands E. J., and Roeters van Lennep J. E.. 2015. Lipoprotein (a) levels are not associated with carotid plaques and carotid intima media thickness in statin-treated patients with familial hypercholesterolemia. Atherosclerosis. 242: 226–229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 214.Gotoh T., Kuroda T., Yamasawa M., Nishinaga M., Mitsuhashi T., Seino Y., Nagoh N., Kayaba K., Yamada S., and Matsuo H.. 1995. Correlation between lipoprotein(a) and aortic valve sclerosis assessed by echocardiography (the JMS Cardiac Echo and Cohort Study). Am. J. Cardiol. 76: 928–932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 215.Stewart B. F., Siscovick D., Lind B. K., Gardin J. M., Gottdiener J. S., Smith V. E., Kitzman D. W., and Otto C. M.. 1997. Clinical factors associated with calcific aortic valve disease. Cardiovascular Health Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 29: 630–634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 216.Glader C. A., Birgander L. S., Soderberg S., Ildgruben H. P., Saikku P., Waldenstrom A., and Dahlen G. H.. 2003. Lipoprotein(a), Chlamydia pneumoniae, leptin and tissue plasminogen activator as risk markers for valvular aortic stenosis. Eur. Heart J. 24: 198–208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 217.Bozbas H., Yildirir A., Atar I., Pirat B., Eroglu S., Aydinalp A., Ozin B., and Muderrisoglu H.. 2007. Effects of serum levels of novel atherosclerotic risk factors on aortic valve calcification. J. Heart Valve Dis. 16: 387–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 218.Arsenault B. J., Boekholdt S. M., Dube M. P., Rheaume E., Wareham N. J., Khaw K. T., Sandhu M. S., and Tardif J. C.. 2014. Lipoprotein(a) levels, genotype, and incident aortic valve stenosis: a prospective Mendelian randomization study and replication in a case-control cohort. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 7: 304–310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 219.Capoulade R., Chan K. L., Yeang C., Mathieu P., Bosse Y., Dumesnil J. G., Tam J. W., Teo K. K., Mahmut A., Yang X., et al. 2015. Oxidized phospholipids, lipoprotein(a), and progression of calcific aortic valve stenosis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 66: 1236–1246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 220.Vongpromek R., Bos S., Ten Kate G. J., Yahya R., Verhoeven A. J., de Feyter P. J., Kronenberg F., Roeters van Lennep J. E., Sijbrands E. J., and Mulder M. T.. 2015. Lipoprotein(a) levels are associated with aortic valve calcification in asymptomatic patients with familial hypercholesterolaemia. J. Intern. Med. 278: 166–173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 221.Yang N., Zhang G., Li X., and Zhou L.. 2015. Correlation analysis between serum lipoprotein (a) and the incidence of aortic valve sclerosis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 8: 19318–19324. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 222.Hojo Y., Kumakura H., Kanai H., Iwasaki T., Ichikawa S., and Kurabayashi M.. 2016. Lipoprotein(a) is a risk factor for aortic and mitral valvular stenosis in peripheral arterial disease. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging. 17: 492–497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 223.Nsaibia M. J., Mahmut A., Boulanger M. C., Arsenault B. J., Bouchareb R., Simard S., Witztum J. L., Clavel M. A., Pibarot P., Bosse Y., et al. Autotaxin interacts with lipoprotein(a) and oxidized phospholipids in predicting the risk of calcific aortic valve stenosis in patients with coronary artery disease. J. Intern. Med. Epub ahead of print. May 30, 2016; doi:10.1111/joim.12519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 224.Sofi F., Marcucci R., Abbate R., Gensini G. F., and Prisco D.. 2007. Lipoprotein (a) and venous thromboembolism in adults: a meta-analysis. Am. J. Med. 120: 728–733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 225.Atsumi T., Khamashta M. A., Andujar C., Leandro M. J., Amengual O., Ames P. R., and Hughes G. R.. 1998. Elevated plasma lipoprotein(a) level and its association with impaired fibrinolysis in patients with antiphospholipid syndrome. J. Rheumatol. 25: 69–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 226.von Depka M., Nowak-Gottl U., Eisert R., Dieterich C., Barthels M., Scharrer I., Ganser A., and Ehrenforth S.. 2000. Increased lipoprotein (a) levels as an independent risk factor for venous thromboembolism. Blood. 96: 3364–3368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 227.Marcucci R., Liotta A. A., Cellai A. P., Rogolino A., Gori A. M., Giusti B., Poli D., Fedi S., Abbate R., and Prisco D.. 2003. Increased plasma levels of lipoprotein(a) and the risk of idiopathic and recurrent venous thromboembolism. Am. J. Med. 115: 601–605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 228.März W., Aygören E., Trommlitz M., Scharrer I., and Gross W.. 1990. Lipoprotein(a): an indicator of risk in thromboembolic disease? [article in German]. Klin. Wochenschr. 68(Suppl 22): 111–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 229.Van Wersch J. W. 1994. The behaviour of lipoprotein(a) in patients with various diseases. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest. 54: 559–562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 230.Vormittag R., Vukovich T., Stain M., Lehr S., Minar E., and Pabinger I.. 2007. Lipoprotein (a) in patients with spontaneous venous thromboembolism. Thromb. Res. 120: 15–20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 231.Tsai A. W., Cushman M., Rosamond W. D., Heckbert S. R., Polak J. F., and Folsom A. R.. 2002. Cardiovascular risk factors and venous thromboembolism incidence: the longitudinal investigation of thromboembolism etiology. Arch. Intern. Med. 162: 1182–1189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 232.Nowak-Göttl U., Debus O., Findeisen M., Kassenbohmer R., Koch H. G., Pollmann H., Postler C., Weber P., and Vielhaber H.. 1997. Lipoprotein (a): its role in childhood thromboembolism. Pediatrics. 99: E11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 233.Münchow N., Kosch A., Schobess R., Junker R., Auberger K., and Nowak-Göttl U.. 1999. Role of genetic prothrombotic risk factors in childhood caval vein thrombosis. Eur. J. Pediatr. 158(Suppl 3): S109–S112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 234.Nowak-Göttl U., Junker R., Hartmeier M., Koch H. G., Münchow N., Assmann G. , and A. von Eckardstein. 1999. Increased lipoprotein(a) is an important risk factor for venous thromboembolism in childhood. Circulation. 100: 743–748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 235.Nowak-Göttl U., Wermes C., Junker R., Koch H. G., Schobess R., Fleischhack G., Schwabe D., and Ehrenforth S.. 1999. Prospective evaluation of the thrombotic risk in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia carrying the MTHFR TT 677 genotype, the prothrombin G20210A variant, and further prothrombotic risk factors. Blood. 93: 1595–1599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 236.Heller C., Schobess R., Kurnik K., Junker R., Gunther G., Kreuz W., and Nowak-Gottl U.. 2000. Abdominal venous thrombosis in neonates and infants: role of prothrombotic risk factors - a multicentre case-control study. For the Childhood Thrombophilia Study Group. Br. J. Haematol. 111: 534–539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 237.Kosch A., Junker R., Kurnik K., Schobess R., Gunther G., Koch H., and Nowak-Gottl U.. 2000. Prothrombotic risk factors in children with spontaneous venous thrombosis and their asymptomatic parents: a family study. Thromb. Res. 99: 531–537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 238.Korte W., Greiner J., Feldges A., and Riesen W. F.. 2001. Increased lipoprotein(a) levels are not a steady prothrombotic defect. Blood. 98: 1993–1994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 239.Nowak-Göttl U., Junker R., Kreuz W. , A. von Eckardstein, A. Kosch, N. Nohe, R. Schobess, and S. Ehrenforth. 2001. Risk of recurrent venous thrombosis in children with combined prothrombotic risk factors. Blood. 97: 858–862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 240.Gözdaşoğlu S., Uysal Z., Ertem M., and Akar N.. 2002. Three risk factors–high lipoprotein (a), elevated FVIII, and FV Leiden–in a pediatric Behcet’s disease patient with deep vein thrombosis. Thromb. Res. 106: 263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 241.Revel-Vilk S., Chan A., Bauman M., and Massicotte P.. 2003. Prothrombotic conditions in an unselected cohort of children with venous thromboembolic disease. J. Thromb. Haemost. 1: 915–921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 242.Kosch A., Kuwertz-Broking E., Heller C., Kurnik K., Schobess R., and Nowak-Gottl U.. 2004. Renal venous thrombosis in neonates: prothrombotic risk factors and long-term follow-up. Blood. 104: 1356–1360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 243.Danik J. S., Buring J. E., Chasman D. I., Zee R. Y., Ridker P. M., and Glynn R. J.. 2013. Lipoprotein(a), polymorphisms in the LPA gene, and incident venous thromboembolism among 21483 women. J. Thromb. Haemost. 11: 205–208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 244.Sticchi E., Magi A., Kamstrup P. R., Marcucci R., Prisco D., Martinelli I., Mannucci P. M., Abbate R., and Giusti B.. 2016. Apolipoprotein(a) kringle-IV type 2 copy number variation is associated with venous thromboembolism. PLoS One. 11: e0149427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 245.Nordestgaard B. G., and Langsted A.. 2015. How does elevated lipoprotein(a) cause aortic valve stenosis? J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 66: 1247–1249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 246.Caplice N. M., Panetta C., Peterson T. E., Kleppe L. S., Mueske C. S., Kostner G. M., Broze G. J. Jr., and Simari R. D.. 2001. Lipoprotein (a) binds and inactivates tissue factor pathway inhibitor: a novel link between lipoproteins and thrombosis. Blood. 98: 2980–2987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 247.Boffa M. B., Marcovina S. M., and Koschinsky M. L.. 2004. Lipoprotein(a) as a risk factor for atherosclerosis and thrombosis: mechanistic insights from animal models. Clin. Biochem. 37: 333–343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 248.Deleted in proof.
- 249.Ishikawa S., Kotani K., Kario K., Kayaba K., Gotoh T., Nakamura Y., and Kajii E.. 2013. Inverse association between serum lipoprotein(a) and cerebral hemorrhage in the Japanese population. Thromb. Res. 131: e54–e58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 250.Anglés-Cano E., de la Peña D. A., and Loyau S.. 2001. Inhibition of fibrinolysis by lipoprotein(a). Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 936: 261–275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 251.Undas A., Stepien E., Tracz W., and Szczeklik A.. 2006. Lipoprotein(a) as a modifier of fibrin clot permeability and susceptibility to lysis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 4: 973–975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 252.von Zychlinski A., Kleffmann T., Williams M. J., and McCormick S. P.. 2011. Proteomics of lipoprotein(a) identifies a protein complement associated with response to wounding. J. Proteomics. 74: 2881–2891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 253.van der Valk F. M., Bekkering S., Kroon J., Yeang C., Van den Bossche J., van Buul J. D., Ravandi A., Nederveen A. J., Verberne H. J., Scipione C., et al. 2016. Oxidized phospholipids on lipoprotein(a) elicit arterial wall inflammation and an inflammatory monocyte response in humans. Circulation. 134: 611–624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 254.Varbo A., Benn M., Tybjaerg-Hansen A., and Nordestgaard B. G.. 2013. Elevated remnant cholesterol causes both low-grade inflammation and ischemic heart disease, whereas elevated low-density lipoprotein cholesterol causes ischemic heart disease without inflammation. Circulation. 128: 1298–1309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 255.Loscalzo J., Weinfeld M., Fless G. M., and Scanu A. M.. 1990. Lipoprotein(a), fibrin binding, and plasminogen activation. Arteriosclerosis. 10: 240–245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 256.Simon D. I., Fless G. M., Scanu A. M., and Loscalzo J.. 1991. Tissue-type plasminogen activator binds to and is inhibited by surface-bound lipoprotein(a) and low-density lipoprotein. Biochemistry. 30: 6671–6677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 257.Rouy D., Grailhe P., Nigon F., Chapman J., and Angles-Cano E.. 1991. Lipoprotein(a) impairs generation of plasmin by fibrin-bound tissue-type plasminogen activator. In vitro studies in a plasma milieu. Arterioscler. Thromb. 11: 629–638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 258.Yano Y., Shimokawa K., Okada Y., and Noma A.. 1997. Immunolocalization of lipoprotein(a) in wounded tissues. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 45: 559–568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 259.Hoff H. F., Beck G. J., Skibinski C. I., Jurgens G., O’Neil J., Kramer J., and Lytle B.. 1988. Serum Lp(a) level as a predictor of vein graft stenosis after coronary artery bypass surgery in patients. Circulation. 77: 1238–1244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 260.Cooke T., Sheahan R., Foley D., Reilly M., D’Arcy G., Jauch W., Gibney M., Gearty G., Crean P., and Walsh M.. 1994. Lipoprotein(a) in restenosis after percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty and coronary artery disease. Circulation. 89: 1593–1598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 261.Graham M. J., Viney N., Crooke R. M., and Tsimikas S.. 2016. Antisense inhibition of apolipoprotein (a) to lower plasma lipoprotein (a) levels in humans. J. Lipid Res. 57: 340–351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 262.Guo H. C., Chapman M. J., Bruckert E., Farriaux J. P., and De Gennes J. L.. 1991. Lipoprotein Lp(a) in homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia: density profile, particle heterogeneity and apolipoprotein(a) phenotype. Atherosclerosis. 86: 69–83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 263.Leitersdorf E., Friedlander Y., Bard J. M., Fruchart J. C., Eisenberg S., and Stein Y.. 1991. Diverse effect of ethnicity on plasma lipoprotein[a] levels in heterozygote patients with familial hypercholesterolemia. J. Lipid Res. 32: 1513–1519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 264.Mbewu A. D., Bhatnagar D., Durrington P. N., Hunt L., Ishola M., Arrol S., Mackness M., Lockley P., and Miller J. P.. 1991. Serum lipoprotein(a) in patients heterozygous for familial hypercholesterolemia, their relatives, and unrelated control populations. Arterioscler. Thromb. 11: 940–946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 265.Soutar A. K., McCarthy S. N., Seed M., and Knight B. L.. 1991. Relationship between apolipoprotein(a) phenotype, lipoprotein(a) concentration in plasma, and low density lipoprotein receptor function in a large kindred with familial hypercholesterolemia due to the pro664—leu mutation in the LDL receptor gene. J. Clin. Invest. 88: 483–492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 266.Bowden J. F., Pritchard P. H., Hill J. S., and Frohlich J. J.. 1994. Lp(a) concentration and apo(a) isoform size. Relation to the presence of coronary artery disease in familial hypercholesterolemia. Arterioscler. Thromb. 14: 1561–1568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 267.Lingenhel A., Kraft H. G., Kotze M., Peeters A. V., Kronenberg F., Kruse R., and Utermann G.. 1998. Concentrations of the atherogenic Lp(a) are elevated in FH. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 6: 50–60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 268.Ghiselli G., Gaddi A., Barozzi G., Ciarrocchi A., and Descovich G.. 1992. Plasma lipoprotein(a) concentration in familial hypercholesterolemic patients without coronary artery disease. Metabolism. 41: 833–838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 269.Carmena R., Lussier-Cacan S., Roy M., Minnich A., Lingenhel A., Kronenberg F., and Davignon J.. 1996. Lp(a) levels and atherosclerotic vascular disease in a sample of patients with familial hypercholesterolemia sharing the same gene defect. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 16: 129–136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 270.Benn M., Watts G. F., Tybjaerg-Hansen A., and Nordestgaard B. G.. 2012. Familial hypercholesterolemia in the Danish general population: prevalence, coronary artery disease and cholesterol-lowering medication. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 97: 3956–3964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 271.Nordestgaard B. G., Chapman M. J., Humphries S. E., Ginsberg H. N., Masana L., Descamps O. S., Wiklund O., Hegele R. A., Raal F. J., Defesche J. C., et al. 2013. Familial hypercholesterolaemia is underdiagnosed and undertreated in the general population: guidance for clinicians to prevent coronary heart disease: consensus statement of the European Atherosclerosis Society. Eur. Heart J. 34: 3478–3490a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 272.Benn M., Watts G. F., Tybjaerg-Hansen A., and Nordestgaard B. G.. 2016. Mutations causative of familial hypercholesterolaemia: screening of 98 098 individuals from the Copenhagen General Population Study estimated a prevalence of 1 in 217. Eur. Heart J. 37: 1384–1394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 273.Sjouke B., Kusters D. M., Kindt I., Besseling J., Defesche J. C., Sijbrands E. J., Roeters van Lennep J. E., Stalenhoef A. F., Wiegman A. , J. de Graaf, et al. 2015. Homozygous autosomal dominant hypercholesterolaemia in the Netherlands: prevalence, genotype-phenotype relationship, and clinical outcome. Eur. Heart J. 36: 560–565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 274.Do R., Stitziel N. O., Won H. H., Jorgensen A. B., Duga S., Angelica M. P., Kiezun A., Farrall M., Goel A., Zuk O., et al. 2015. Exome sequencing identifies rare LDLR and APOA5 alleles conferring risk for myocardial infarction. Nature. 518: 102–106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 275.Rader D. J., Mann W. A., Cain W., Kraft H. G., Usher D., Zech L. A., Hoeg J. M., Davignon J., Lupien P., and Grossman M.. 1995. The low density lipoprotein receptor is not required for normal catabolism of Lp(a) in humans. J. Clin. Invest. 95: 1403–1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 276.Rader D. J., Cain W., Ikewaki K., Talley G., Zech L. A., Usher D., and Brewer H. B. Jr. 1994. The inverse association of plasma lipoprotein(a) concentrations with apolipoprotein(a) isoform size is not due to differences in Lp(a) catabolism but to differences in production rate. J. Clin. Invest. 93: 2758–2763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 277.Kraft H. G., Lingenhel A., Raal F. J., Hohenegger M., and Utermann G.. 2000. Lipoprotein(a) in homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 20: 522–528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 278.Tybjaerg-Hansen A., Jensen H. K., Benn M., Steffensen R., Jensen G., and Nordestgaard B. G.. 2005. Phenotype of heterozygotes for low-density lipoprotein receptor mutations identified in different background populations. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 25: 211–215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 279.Jansen A. C., van Aalst-Cohen E. S., Tanck M. W., Trip M. D., Lansberg P. J., Liem A. H., van Lennep H. W., Sijbrands E. J., and Kastelein J. J.. 2004. The contribution of classical risk factors to cardiovascular disease in familial hypercholesterolaemia: data in 2400 patients. J. Intern. Med. 256: 482–490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 280.Cuchel M., Bruckert E., Ginsberg H. N., Raal F. J., Santos R. D., Hegele R. A., Kuivenhoven J. A., Nordestgaard B. G., Descamps O. S., Steinhagen-Thiessen E., et al. 2014. Homozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia: new insights and guidance for clinicians to improve detection and clinical management. A position paper from the Consensus Panel on Familial Hypercholesterolaemia of the European Atherosclerosis Society. Eur. Heart J. 35: 2146–2157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 281.Wiegman A., Gidding S. S., Watts G. F., Chapman M. J., Ginsberg H. N., Cuchel M., Ose L., Averna M., Boileau C., Boren J., et al. 2015. Familial hypercholesterolaemia in children and adolescents: gaining decades of life by optimizing detection and treatment. Eur. Heart J. 36: 2425–2437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 282.Randomised trial of cholesterol lowering in 4444 patients with coronary heart disease: the Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study (4S). Lancet 1994. 344: 1383–1389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]