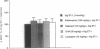Abstract
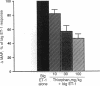
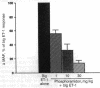
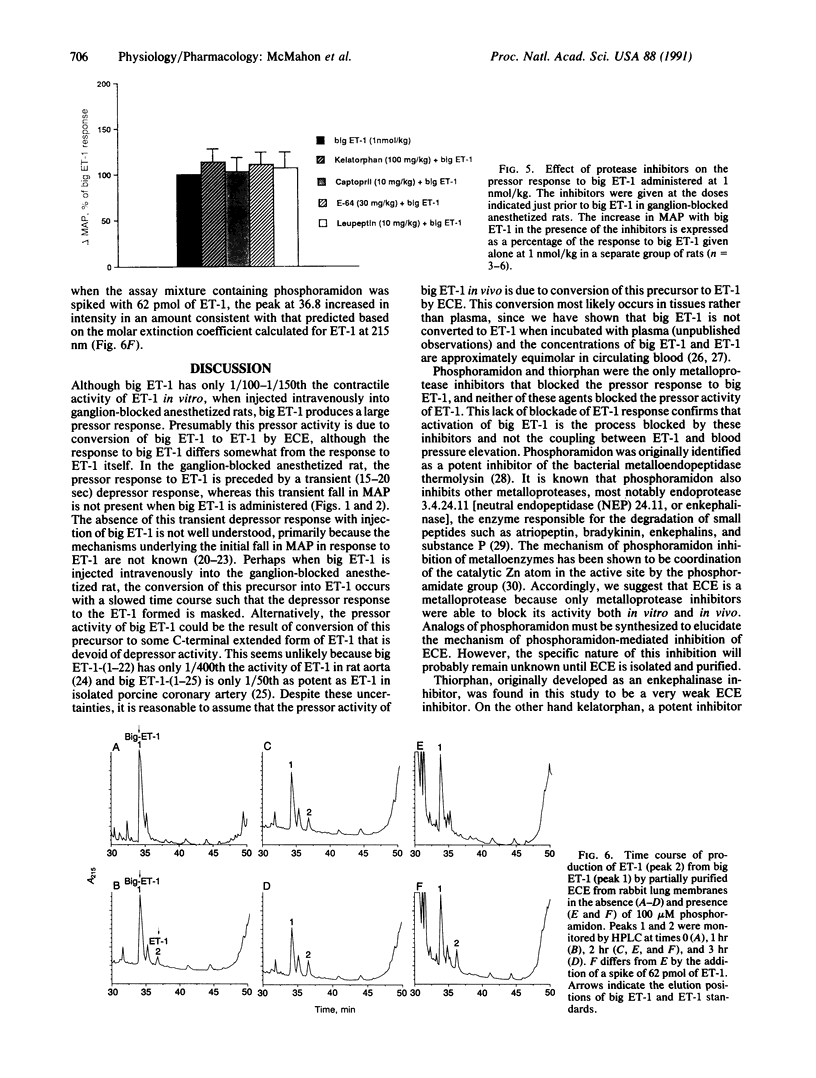
In porcine aortic endothelial cells, the 21-amino acid peptide endothelin-1 (ET-1) is formed from a 39-amino acid intermediate called "big endothelin-1" (big ET-1) by a putative ET-converting enzyme (ECE) that cleaves the 39-mer at the bond between Trp-21 and Val-22. Since big ET-1 has only 1/100-1/150th the contractile activity of ET-1, inhibition of ECE should effectively block the biological effects of ET-1. Big ET-1 injected intravenously into anesthetized rats produces a sustained pressor response that presumably is due to conversion of big ET-1 into ET-1 by ECE. We determined the type of protease activity responsible for this conversion by evaluating the effectiveness of protease inhibitors in blocking the pressor response to big ET-1 in ganglion-blocked anesthetized rats. The serine protease inhibitor leupeptin, the cysteinyl protease inhibitor E-64, and the metalloprotease inhibitors captopril and kelatorphan were all ineffective at blocking the pressor response to big ET-1. However, the metalloprotease inhibitors phosphoramidon and thiorphan dose-dependently inhibited the pressor response to big ET-1, although phosphoramidon was substantially more potent than thiorphan. None of the inhibitors blocked the pressor response to ET-1 and none had any effect on mean arterial pressure when administered alone. In a rabbit lung membrane preparation, ECE activity was identified that was blocked by the metalloprotease inhibitors phosphoramidon and 1,10-phenanthroline in a concentration-dependent manner. This enzyme converted big ET-1 to a species of ET that comigrated on HPLC with ET-1 and produced an ET-like contraction in isolated rat aortic rings. Our results suggest that the physiologically relevant ECE is a metalloprotease.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fournie-Zaluski M. C., Lucas E., Waksman G., Roques B. P. Differences in the structural requirements for selective interaction with neutral metalloendopeptidase (enkephalinase) or angiotensin-converting enzyme. Molecular investigation by use of new thiol inhibitors. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Mar 1;139(2):267–274. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08003.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda N., Izumi Y., Soma M., Watanabe Y., Watanabe M., Hatano M., Sakuma I., Yasuda H. L-NG-monomethyl arginine inhibits the vasodilating effects of low dose of endothelin-3 on rat mesenteric arteries. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Mar 16;167(2):739–745. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)92087-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gafford J. T., Skidgel R. A., Erdös E. G., Hersh L. B. Human kidney "enkephalinase", a neutral metalloendopeptidase that cleaves active peptides. Biochemistry. 1983 Jun 21;22(13):3265–3271. doi: 10.1021/bi00282a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner S. M., Compton A. M., Bennett T., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. NG-monomethyl-L-arginine does not inhibit the hindquarters vasodilator action of endothelin-1 in conscious rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Nov 21;171(2-3):237–240. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90113-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R. B. Processing of pro-hormone precursor proteins. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Dec;275(2):315–333. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90379-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikegawa R., Matsumura Y., Tsukahara Y., Takaoka M., Morimoto S. Phosphoramidon, a metalloproteinase inhibitor, suppresses the secretion of endothelin-1 from cultured endothelial cells by inhibiting a big endothelin-1 converting enzyme. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Sep 14;171(2):669–675. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91198-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashiwabara T., Inagaki Y., Ohta H., Iwamatsu A., Nomizu M., Morita A., Nishikori K. Putative precursors of endothelin have less vasoconstrictor activity in vitro but a potent pressor effect in vivo. FEBS Lett. 1989 Apr 10;247(1):73–76. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81243-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kon V., Yoshioka T., Fogo A., Ichikawa I. Glomerular actions of endothelin in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1989 May;83(5):1762–1767. doi: 10.1172/JCI114079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurihara H., Yamaoki K., Nagai R., Yoshizumi M., Takaku F., Satoh H., Inui J., Yazaki Y. Endothelin: a potent vasoconstrictor associated with coronary vasospasm. Life Sci. 1989;44(25):1937–1943. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(89)90406-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masaoka H., Suzuki R., Hirata Y., Emori T., Marumo F., Hirakawa K. Raised plasma endothelin in aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage. Lancet. 1989 Dec 9;2(8676):1402–1402. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)92019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura Y., Hisaki K., Takaoka M., Morimoto S. Phosphoramidon, a metalloproteinase inhibitor, suppresses the hypertensive effect of big endothelin-1. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Aug 21;185(1):103–106. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90216-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura Y., Ikegawa R., Takaoka M., Morimoto S. Conversion of porcine big endothelin to endothelin by an extract from the porcine aortic endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Feb 28;167(1):203–210. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91751-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon E. G., Fok K. F., Moore W. M., Smith C. E., Siegel N. R., Trapani A. J. In vitro and in vivo activity of chymotrypsin-activated big endothelin (porcine 1-40). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jun 15;161(2):406–413. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92613-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyauchi T., Yanagisawa M., Tomizawa T., Sugishita Y., Suzuki N., Fujino M., Ajisaka R., Goto K., Masaki T. Increased plasma concentrations of endothelin-1 and big endothelin-1 in acute myocardial infarction. Lancet. 1989 Jul 1;2(8653):53–54. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90303-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumford R. A., Pierzchala P. A., Strauss A. W., Zimmerman M. Purification of a membrane-bound metalloendopeptidase from porcine kidney that degrades peptide hormones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6623–6627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlstein E. H., Arleth A., Ezekiel M., Horohonich S., Ator M. A., Caltabiano M. M., Sung C. P. Biosynthesis and modulation of endothelin from bovine pulmonary arterial endothelial cells. Life Sci. 1990;46(3):181–188. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(90)90103-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohnaka K., Takayanagi R., Yamauchi T., Okazaki H., Ohashi M., Umeda F., Nawata H. Identification and characterization of endothelin converting activity in cultured bovine endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 May 16;168(3):1128–1136. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91146-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olins G. M., Krieter P. A., Trapani A. J., Spear K. L., Bovy P. R. Specific inhibitors of endopeptidase 24.11 inhibit the metabolism of atrial natriuretic peptides in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1989 Feb;61(2):201–208. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(89)90131-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito Y., Nakao K., Mukoyama M., Imura H. Increased plasma endothelin level in patients with essential hypertension. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jan 18;322(3):205–205. doi: 10.1056/nejm199001183220315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawamura T., Kimura S., Shinmi O., Sugita Y., Yanagisawa M., Masaki T. Analysis of endothelin related peptides in culture supernatant of porcine aortic endothelial cells: evidence for biosynthetic pathway of endothelin-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Aug 15;162(3):1287–1294. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90813-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolovsky M., Galron R., Kloog Y., Bdolah A., Indig F. E., Blumberg S., Fleminger G. Endothelins are more sensitive than sarafotoxins to neutral endopeptidase: possible physiological significance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4702–4706. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suda H., Aoyagi T., Takeuchi T., Umezawa H. Letter: A thermolysin inhibitor produced by Actinomycetes: phospholamidon. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1973 Oct;26(10):621–623. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.26.621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki N., Miyauchi T., Tomobe Y., Matsumoto H., Goto K., Masaki T., Fujino M. Plasma concentrations of endothelin-1 in spontaneously hypertensive rats and DOCA-salt hypertensive rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Mar 30;167(3):941–947. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90614-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takaoka M., Takenobu Y., Miyata Y., Ikegawa R., Matsumura Y., Morimoto S. Pepsin, an aspartic protease, converts porcine big endothelin to 21-residue endothelin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jan 15;166(1):436–442. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91964-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijayaraghavan J., Scicli A. G., Carretero O. A., Slaughter C., Moomaw C., Hersh L. B. The hydrolysis of endothelins by neutral endopeptidase 24.11 (enkephalinase). J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14150–14155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe T., Suzuki N., Shimamoto N., Fujino M., Imada A. Endothelin in myocardial infarction. Nature. 1990 Mar 8;344(6262):114–114. doi: 10.1038/344114a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver L. H., Kester W. R., Matthews B. W. A crystallographic study of the complex of phosphoramidon with thermolysin. A model for the presumed catalytic transition state and for the binding of extended substances. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jul;114(1):119–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90286-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winquist R. J., Scott A. L., Vlasuk G. P. Enhanced release of atrial natriuretic factor by endothelin in atria from hypertensive rats. Hypertension. 1989 Jul;14(1):111–114. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.14.1.111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa M., Kurihara H., Kimura S., Tomobe Y., Kobayashi M., Mitsui Y., Yazaki Y., Goto K., Masaki T. A novel potent vasoconstrictor peptide produced by vascular endothelial cells. Nature. 1988 Mar 31;332(6163):411–415. doi: 10.1038/332411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Nucci G., Thomas R., D'Orleans-Juste P., Antunes E., Walder C., Warner T. D., Vane J. R. Pressor effects of circulating endothelin are limited by its removal in the pulmonary circulation and by the release of prostacyclin and endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9797–9800. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]