Abstract
Although in vitro experiments have established that extrinsic pathway inhibitor (EPI) is the only known plasma inhibitor of factor VIIa-tissue factor (TF) catalytic activity of potential physiologic significance, evidence of its function in vivo has been lacking. TF-induced intravascular coagulation may occur in patients despite normal plasma levels of EPI and, in our earlier studies, normal plasma EPI levels did not protect rabbits from intravascular coagulation induced by an infusion of purified TF (1 microgram/kg). Studies have now been carried out in which plasma EPI levels were reduced in rabbits to below 20% of the initial level by injection of anti-rabbit EPI IgG. Infusion into such animals of purified rabbit TF apoprotein (0.25 microgram/kg) reconstituted into phospholipid vesicles induced substantial disseminated intravascular coagulation. Infusion of control saline or phospholipid vesicles not containing TF was without significant effect as was infusion of TF (0.25 microgram/kg) into animals injected with nonimmune goat IgG. These data establish that EPI can dampen TF-induced intravascular coagulation in rabbits. They support the hypothesis that EPI plays a significant role in regulating coagulation resulting from the exposure of blood to trace concentrations of TF during the illnesses and minor injuries of normal existence.
Full text
PDF
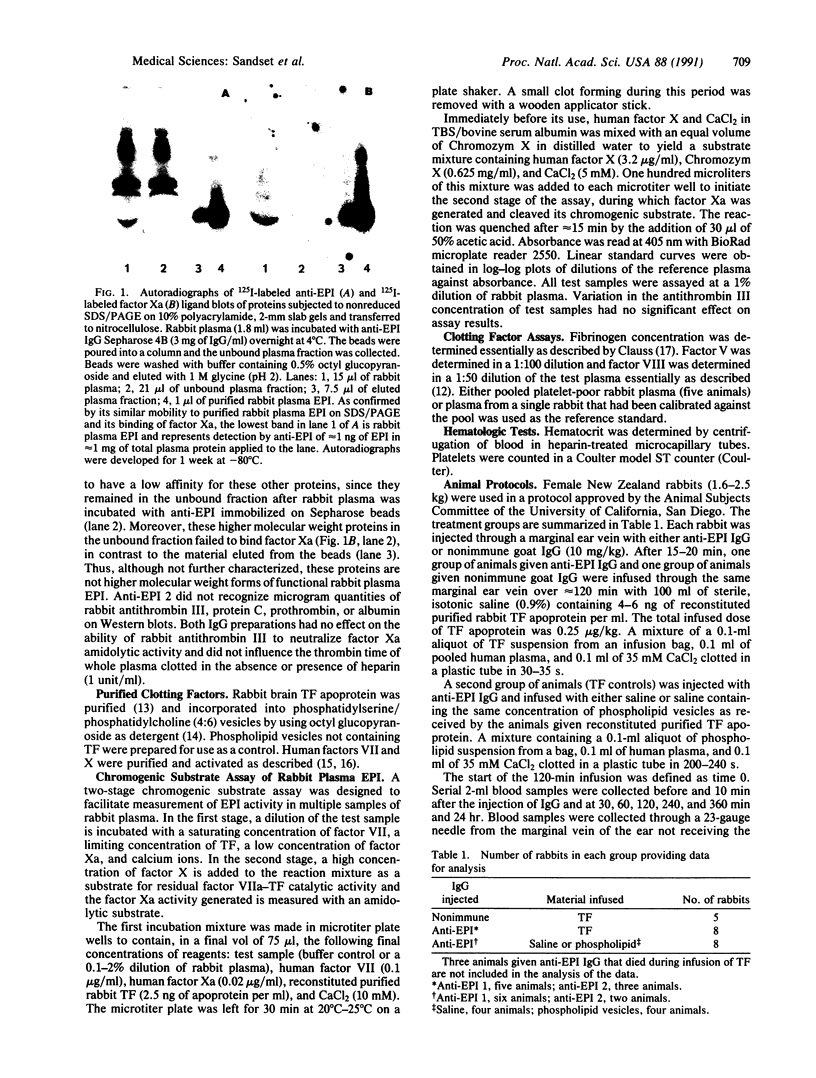

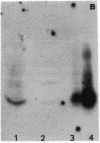
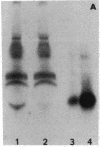
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almus F. E., Rao L. V., Fleck R. A., Rapaport S. I. Properties of factor VIIa/tissue factor complexes in an umbilical vein model. Blood. 1990 Jul 15;76(2):354–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almus F. E., Rao L. V., Rapaport S. I. Functional properties of factor VIIa/tissue factor formed with purified tissue factor and with tissue factor expressed on cultured endothelial cells. Thromb Haemost. 1989 Dec 29;62(4):1067–1073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bajaj S. P., Rapaport S. I., Prodanos C. A simplified procedure for purification of human prothrombin, factor IX and factor X. Prep Biochem. 1981;11(4):397–412. doi: 10.1080/00327488108065531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P., Sandset P. M., Joø G. B., Ovstebø R., Abildgaard U., Kierulf P. The quantitative association of plasma endotoxin, antithrombin, protein C, extrinsic pathway inhibitor and fibrinopeptide A in systemic meningococcal disease. Thromb Res. 1989 Aug 15;55(4):459–470. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(89)90054-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broze G. J., Jr, Girard T. J., Novotny W. F. Regulation of coagulation by a multivalent Kunitz-type inhibitor. Biochemistry. 1990 Aug 21;29(33):7539–7546. doi: 10.1021/bi00485a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broze G. J., Jr, Warren L. A., Novotny W. F., Higuchi D. A., Girard J. J., Miletich J. P. The lipoprotein-associated coagulation inhibitor that inhibits the factor VII-tissue factor complex also inhibits factor Xa: insight into its possible mechanism of action. Blood. 1988 Feb;71(2):335–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLAUSS A. Gerinnungsphysiologische Schnellmethode zur Bestimmung des Fibrinogens. Acta Haematol. 1957 Apr;17(4):237–246. doi: 10.1159/000205234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson S. D., Ross S. E. Effects of lipid-binding proteins apo A-I, apo A-IL, beta 2-glycoprotein I, and C-reactive protein on activation of factor X by tissue factor--factor VIIa. Thromb Res. 1988 Jun 1;50(5):669–678. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(88)90325-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colucci M., Balconi G., Lorenzet R., Pietra A., Locati D., Donati M. B., Semeraro N. Cultured human endothelial cells generate tissue factor in response to endotoxin. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jun;71(6):1893–1896. doi: 10.1172/JCI110945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conkling P. R., Patton K. L., Hannun Y. A., Greenberg C. S., Weinberg J. B. Sphingosine inhibits monocyte tissue factor-initiated coagulation by altering factor VII binding. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18440–18444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flaherty M. J., West S., Heimark R. L., Fujikawa K., Tait J. F. Placental anticoagulant protein-I: measurement in extracellular fluids and cells of the hemostatic system. J Lab Clin Med. 1990 Feb;115(2):174–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gramzinski R. A., Broze G. J., Jr, Carson S. D. Human fibroblast tissue factor is inhibited by lipoprotein-associated coagulation inhibitor and placental anticoagulant protein but not by apolipoprotein A-II. Blood. 1989 Mar;73(4):983–989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo S., Noguchi M., Funakoshi T., Fujikawa K., Kisiel W. Inhibition of human factor VIIa-tissue factor activity by placental anticoagulant protein. Thromb Res. 1987 Nov 15;48(4):449–459. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(87)90402-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl A. K., Sandset P. M., Abildgaard U., Andersson T. R., Harbitz T. B. High plasma levels of extrinsic pathway inhibitor and low levels of other coagulation inhibitors in advanced cancer. Acta Chir Scand. 1989 Aug;155(8):389–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mimms L. T., Zampighi G., Nozaki Y., Tanford C., Reynolds J. A. Phospholipid vesicle formation and transmembrane protein incorporation using octyl glucoside. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 17;20(4):833–840. doi: 10.1021/bi00507a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawroth P. P., Handley D. A., Esmon C. T., Stern D. M. Interleukin 1 induces endothelial cell procoagulant while suppressing cell-surface anticoagulant activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3460–3464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemerson Y. Tissue factor and hemostasis. Blood. 1988 Jan;71(1):1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotny W. F., Girard T. J., Miletich J. P., Broze G. J., Jr Purification and characterization of the lipoprotein-associated coagulation inhibitor from human plasma. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18832–18837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao L. V., Bajaj S. P. Purification of human factor VII utilizing O-(diethylaminoethyl)-Sephadex and Sulfopropyl-Sephadex chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;136(2):357–361. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90230-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao L. V., Hoang A. D. Purification and characterization of rabbit tissue factor. Thromb Res. 1989 Oct 1;56(1):109–118. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(89)90013-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao L. V., Rapaport S. I., Bajaj S. P. Activation of human factor VII in the initiation of tissue factor-dependent coagulation. Blood. 1986 Sep;68(3):685–691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao L. V., Rapaport S. I. Studies of a mechanism inhibiting the initiation of the extrinsic pathway of coagulation. Blood. 1987 Feb;69(2):645–651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapaport S. I. Inhibition of factor VIIa/tissue factor-induced blood coagulation: with particular emphasis upon a factor Xa-dependent inhibitory mechanism. Blood. 1989 Feb;73(2):359–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivers R. P., Hathaway W. E., Weston W. L. The endotoxin-induced coagulant activity of human monocytes. Br J Haematol. 1975 Jul;30(3):311–316. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1975.tb00547.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders N. L., Bajaj S. P., Zivelin A., Rapaport S. I. Inhibition of tissue factor/factor VIIa activity in plasma requires factor X and an additional plasma component. Blood. 1985 Jul;66(1):204–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandset P. M., Abildgaard U., Larsen M. L. Heparin induces release of extrinsic coagulation pathway inhibitor (EPI). Thromb Res. 1988 Jun 15;50(6):803–813. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(88)90340-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandset P. M., Abildgaard U., Pettersen M. A sensitive assay of extrinsic coagulation pathway inhibitor (EPI) in plasma and plasma fractions. Thromb Res. 1987 Aug 15;47(4):389–400. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(87)90454-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandset P. M., Røise O., Aasen A. O., Abildgaard U. Extrinsic pathway inhibitor in postoperative/posttraumatic septicemia: increased levels in fatal cases. Haemostasis. 1989;19(4):189–195. doi: 10.1159/000215916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligsohn U., Rapaport S. I., Kuefler P. R. Extra-adrenal effect of ACTH on fibrinogen synthesis. Am J Physiol. 1973 May;224(5):1172–1179. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.224.5.1172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warn-Cramer B. J., Rao L. V., Maki S. L., Rapaport S. I. Modifications of extrinsic pathway inhibitor (EPI) and factor Xa that affect their ability to interact and to inhibit factor VIIa/tissue factor: evidence for a two-step model of inhibition. Thromb Haemost. 1988 Dec 22;60(3):453–456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warr T. A., Rao L. V., Rapaport S. I. A sensitive, accurate assay for extrinsic pathway inhibitor (EPI) activity in rabbit plasma: paradoxical effect of excess exogenous factor X. Thromb Res. 1990 Aug 15;59(4):773–782. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(90)90058-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warr T. A., Rao L. V., Rapaport S. I. Disseminated intravascular coagulation in rabbits induced by administration of endotoxin or tissue factor: effect of anti-tissue factor antibodies and measurement of plasma extrinsic pathway inhibitor activity. Blood. 1990 Apr 1;75(7):1481–1489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warr T. A., Rao L. V., Rapaport S. I. Human plasma extrinsic pathway inhibitor activity: II. Plasma levels in disseminated intravascular coagulation and hepatocellular disease. Blood. 1989 Aug 15;74(3):994–998. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wun T. C., Kretzmer K. K., Girard T. J., Miletich J. P., Broze G. J., Jr Cloning and characterization of a cDNA coding for the lipoprotein-associated coagulation inhibitor shows that it consists of three tandem Kunitz-type inhibitory domains. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6001–6004. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]