Abstract
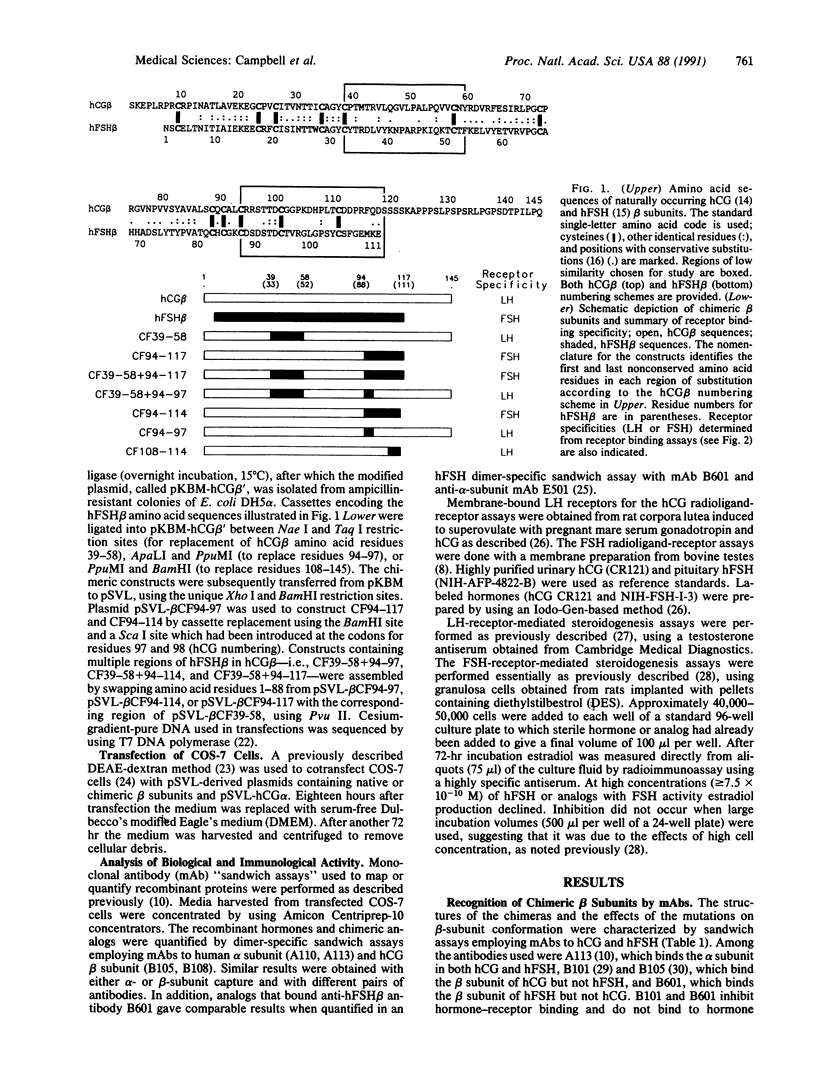
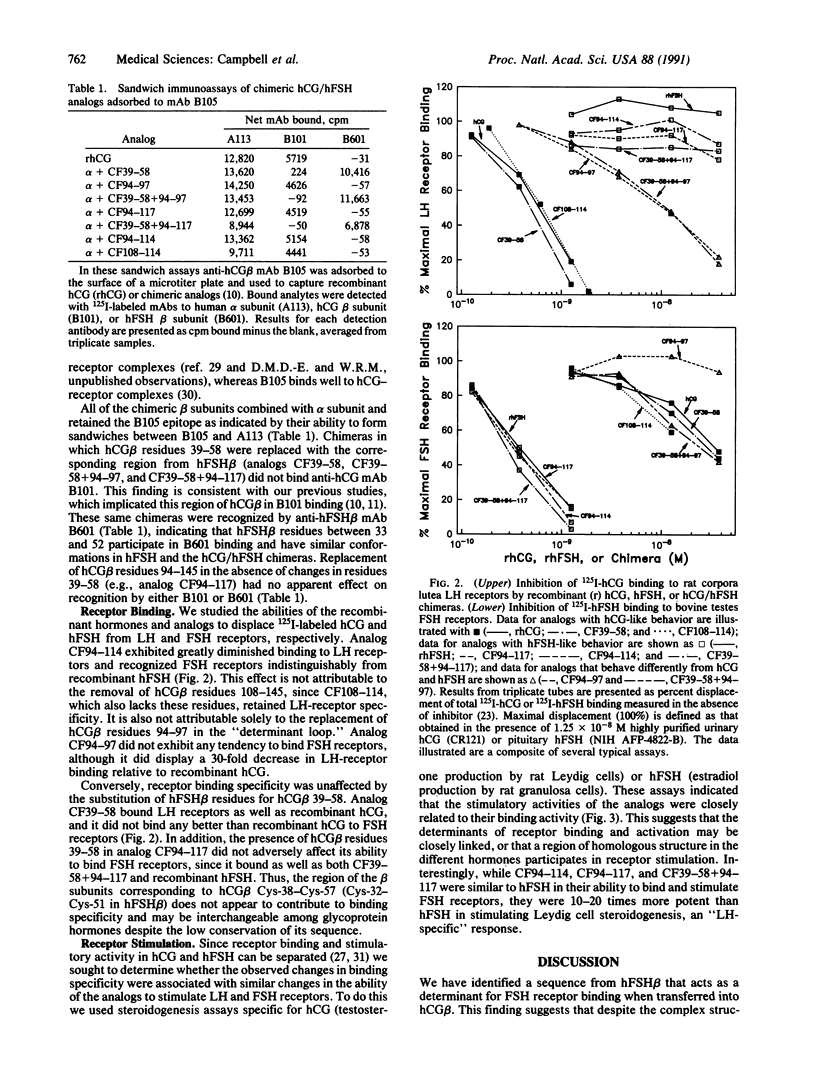
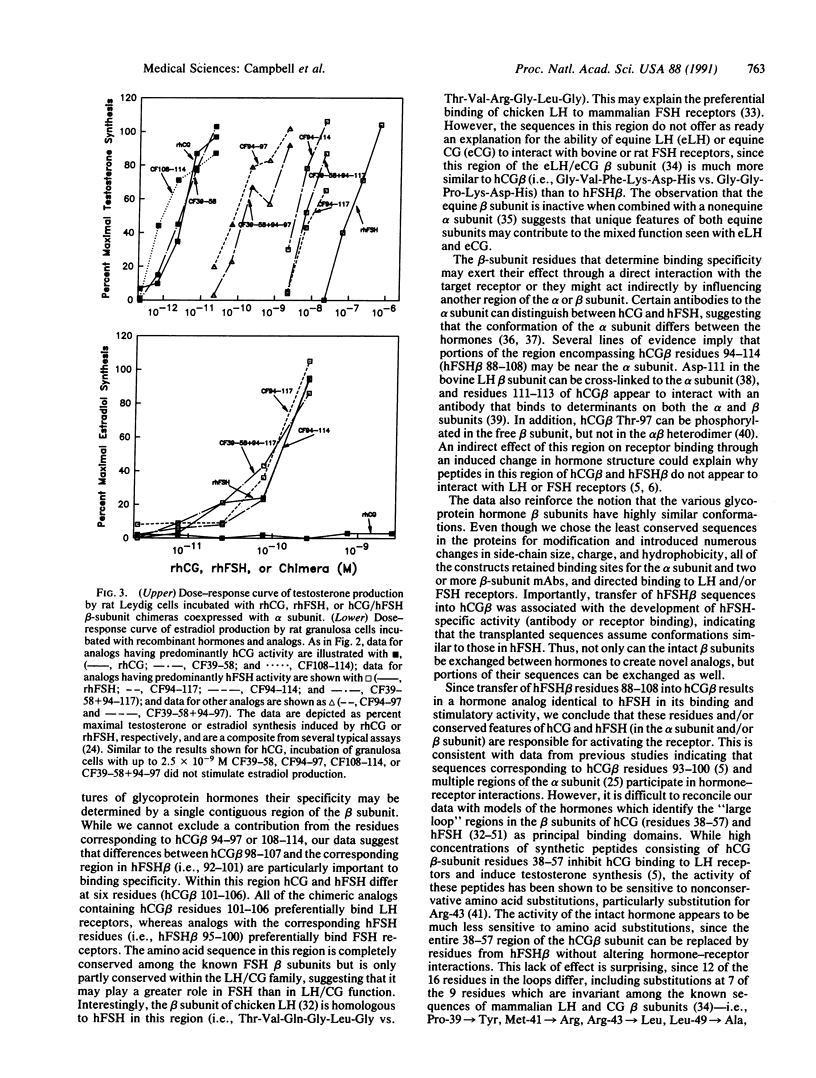
Human reproduction is dependent upon the actions of follicle-stimulating hormone (hFSH), luteinizing hormone (hLH), and chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). While the alpha subunits of these heterodimeric proteins can be interchanged without effect on receptor-binding specificity, their beta subunits differ and direct hormone binding to either LH/CG or FSH receptors. Previous studies employing chemical modifications of the hormones, monoclonal antibodies, or synthetic peptides have implicated hCG beta-subunit residues between Cys-38 and Cys-57 and corresponding regions of hLH beta and hFSH beta in receptor recognition and activation. Since the beta subunits of hCG or hLH and hFSH exhibit very little sequence similarity in this region, we postulated that these residues might contribute to hormone specificity. To test this hypothesis we constructed chimeric hCG/hFSH beta subunits, coexpressed them with the human alpha subunit, and examined their ability to interact with LH and FSH receptors and hormone-specific monoclonal antibodies. Surprisingly, substitution of hFSH beta residues 33-52 for hCG beta residues 39-58 had no effect on receptor binding or stimulation. However, substitution of hFSH beta residues 88-108 in place of the carboxyl terminus of hCG beta (residues 94-145) resulted in a hormone analog identical to hFSH in its ability to bind and stimulate FSH receptors. The altered binding specificity displayed by this analog is not attributable solely to the replacement of hCG beta residues 108-145 or substitution of residues in the "determinant loop" located between hCG beta residues 93 and 100.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bidart J. M., Troalen F., Bohuon C. J., Hennen G., Bellet D. H. Immunochemical mapping of a specific domain on human choriogonadotropin using anti-protein and anti-peptide monoclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15483–15489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bousfield G. R., Liu W. K., Sugino H., Ward D. N. Structural studies on equine glycoprotein hormones. Amino acid sequence of equine lutropin beta-subunit. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8610–8620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bousfield G. R., Liu W. K., Ward D. N. Hybrids from equine LH: alpha enhances, beta diminishes activity. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1985 Apr;40(1):69–77. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(85)90159-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bousfield G. R., Ward D. N. Selective proteolysis of ovine lutropin or its beta subunit by endoproteinase Arg-C. Properties of the Arg beta 43 cleaved hormone. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12602–12607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvo F. O., Keutmann H. T., Bergert E. R., Ryan R. J. Deglycosylated human follitropin: characterization and effects on adenosine cyclic 3',5'-phosphate production in porcine granulosa cells. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 1;25(13):3938–3943. doi: 10.1021/bi00361a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R. Use of eukaryotic expression technology in the functional analysis of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:684–704. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52074-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiddes J. C., Goodman H. M. Isolation, cloning and sequence analysis of the cDNA for the alpha-subunit of human chorionic gonadotropin. Nature. 1979 Oct 4;281(5730):351–356. doi: 10.1038/281351a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiddes J. C., Goodman H. M. The cDNA for the beta-subunit of human chorionic gonadotropin suggests evolution of a gene by readthrough into the 3'-untranslated region. Nature. 1980 Aug 14;286(5774):684–687. doi: 10.1038/286684a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiddes J. C., Talmadge K. Structure, expression, and evolution of the genes for the human glycoprotein hormones. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1984;40:43–78. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571140-1.50006-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris D. C., Machin K. J., Evin G. M., Morgan F. J., Isaacs N. W. Preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of human chorionic gonadotropin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):6705–6706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hojo H., Ryan R. J. Monoclonal antibodies against human follicle-stimulating hormone. Endocrinology. 1985 Dec;117(6):2428–2434. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-6-2428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keutmann H. T., Charlesworth M. C., Kitzmann K., Mason K. A., Johnson L., Ryan R. J. Primary and secondary structural determinants in the receptor binding sequence beta-(38-57) from human luteinizing hormone. Biochemistry. 1988 Dec 13;27(25):8939–8944. doi: 10.1021/bi00425a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keutmann H. T., Charlesworth M. C., Mason K. A., Ostrea T., Johnson L., Ryan R. J. A receptor-binding region in human choriogonadotropin/lutropin beta subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):2038–2042. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.2038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keutmann H. T., Ratanabanangkoon K., Pierce M. W., Kitzmann K., Ryan R. J. Phosphorylation of human choriogonadotropin. Stoichiometry and sites of phosphate incorporation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14521–14526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laver W. G., Air G. M., Webster R. G., Smith-Gill S. J. Epitopes on protein antigens: misconceptions and realities. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):553–556. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90464-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. Y., Ryan R. J. Luteinizing hormone receptors: specific binding of human luteinizing hormone to homogenates of luteinized rat ovaries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3520–3523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao T. H., Pierce J. G. The presence of a common type of subunit in bovine thyroid-stimulating and luteinizing hormones. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jul 10;245(13):3275–3281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lustbader J. W., Birken S., Pileggi N. F., Kolks M. A., Pollak S., Cuff M. E., Yang W., Hendrickson W. A., Canfield R. E. Crystallization and characterization of human chorionic gonadotropin in chemically deglycosylated and enzymatically desialylated states. Biochemistry. 1989 Nov 28;28(24):9239–9243. doi: 10.1021/bi00450a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarland K. C., Sprengel R., Phillips H. S., Köhler M., Rosemblit N., Nikolics K., Segaloff D. L., Seeburg P. H. Lutropin-choriogonadotropin receptor: an unusual member of the G protein-coupled receptor family. Science. 1989 Aug 4;245(4917):494–499. doi: 10.1126/science.2502842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyle W. R., Anderson D. M., Macdonald G. J., Armstrong E. G. Bioimmunoassay (BIA): a sandwich immunoassay scheme employing monoclonal antibodies and hormone receptors to quantify analytes. J Recept Res. 1988;8(1-4):419–436. doi: 10.3109/10799898809049002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyle W. R., Bahl O. P., März L. Role of carbohydrate of human chorionic gonadotropin in the mechanism of hormone action. J Biol Chem. 1975 Dec 10;250(23):9163–9169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyle W. R., Ehrlich P. H., Canfield R. E. Use of monoclonal antibodies to subunits of human chorionic gonadotropin to examine the orientation of the hormone in its complex with receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2245–2249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyle W. R., Matzuk M. M., Campbell R. K., Cogliani E., Dean-Emig D. M., Krichevsky A., Barnett R. W., Boime I. Localization of residues that confer antibody binding specificity using human chorionic gonadotropin/luteinizing hormone beta subunit chimeras and mutants. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 25;265(15):8511–8518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyle W. R., Pressey A., Dean-Emig D., Anderson D. M., Demeter M., Lustbader J., Ehrlich P. Detection of conformational changes in human chorionic gonadotropin upon binding to rat gonadal receptors. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 15;262(35):16920–16926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noce T., Ando H., Ueda T., Kubokawa K., Higashinakagawa T., Ishii S. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence analysis of the putative cDNA for the precursor molecule of the chicken LH-beta subunit. J Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Sep;3(2):129–137. doi: 10.1677/jme.0.0030129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce J. G., Parsons T. F. Glycoprotein hormones: structure and function. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:465–495. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratanabanangkoon K., Keutmann H. T., Kitzmann K., Ryan R. J. Properties of the phosphorylated beta subunit of human choriogonadotropin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14527–14531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan R. J., Keutmann H. T., Charlesworth M. C., McCormick D. J., Milius R. P., Calvo F. O., Vutyavanich T. Structure-function relationships of gonadotropins. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1987;43:383–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santa Coloma T. A., Dattatreyamurty B., Reichert L. E., Jr A synthetic peptide corresponding to human FSH beta-subunit 33-53 binds to FSH receptor, stimulates basal estradiol biosynthesis, and is a partial antagonist of FSH. Biochemistry. 1990 Feb 6;29(5):1194–1200. doi: 10.1021/bi00457a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santa Coloma T. A., Reichert L. E., Jr Identification of a follicle-stimulating hormone receptor-binding region in hFSH-beta-(81-95) using synthetic peptides. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 25;265(9):5037–5042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneyer A. L., Sluss P. M., Huston J. S., Ridge R. J., Reichert L. E., Jr Identification of a receptor binding region on the beta subunit of human follicle-stimulating hormone. Biochemistry. 1988 Jan 26;27(2):666–671. doi: 10.1021/bi00402a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skaf R. A., Macdonald G. J., Shelden R. M., Moyle W. R. Use of antisera to follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) to detect non-FSH factors in human serum which modulate rat granulosa cell steroidogenesis. Endocrinology. 1985 Jul;117(1):106–113. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-1-106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sluss P. M., Krystek S. R., Jr, Andersen T. T., Melson B. E., Huston J. S., Ridge R., Reichert L. E., Jr Inhibition of iodine-125-labeled human follitropin binding to testicular receptor by epidermal growth factor and synthetic peptides. Biochemistry. 1986 May 6;25(9):2644–2649. doi: 10.1021/bi00357a053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprengel R., Braun T., Nikolics K., Segaloff D. L., Seeburg P. H. The testicular receptor for follicle stimulating hormone: structure and functional expression of cloned cDNA. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Apr;4(4):525–530. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-4-525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland T. W., Puett D. Alpha-subunit conformation in glycoprotein hormones and recombinants as assessed by specific antisera. Endocrinology. 1982 Jul;111(1):95–100. doi: 10.1210/endo-111-1-95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins P. C., Eddy R., Beck A. K., Vellucci V., Leverone B., Tanzi R. E., Gusella J. F., Shows T. B. DNA sequence and regional assignment of the human follicle-stimulating hormone beta-subunit gene to the short arm of human chromosome 11. DNA. 1987 Jun;6(3):205–212. doi: 10.1089/dna.1987.6.205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weare J. A., Reichert L. E., Jr Studies with carbodiimide-cross-linked derivatives of bovine lutropin. II. Location of the cross-link and implication for interaction with the receptors in testes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):6972–6979. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



