Abstract
Background:
It is believed that most of thrombi form in the left atrial appendage (LAA)before they emboli. Different surgical and percutaneouse approaches were suggested to manage the LAA. In this study we are evaluating the safety of clipping the LAA via minithoractotomy approach.
Method:
All consecutive patients who had minimally invasive mitral valve surgery with concomitant LAA clipping between December 2012 and February 2014 were included in the study. LAA exclusion was performed using AtriClip® LAA Exclusion System (Cincinnati, Ohio, AtriCure®). The patient s’ clinical characteristics, intraoperative complications, and in-hospital coarse were obtained by reviewing the medical records.
Result:
Total of 22 patients(50% males) were included in the study. The median ages was 66.0 years (IQR: 50.8 to 81.3). Eight(36%) had mitral valve replacement and the rest had mitral repair surgery. Five(23%) patients needed blood product transfusion during the surgery. No clip related bleeding was observed and no perioperative mortality was recorded.
Conclusion:
During minimally invasive mitral valve surgery, Concomitant exclusion of the left atrial appendage using AtriClip® can be performed rapidly and safely.
Keywords: Left Atrial Appendage, Mitral Valve Surgery, Transesophageal Echocardiogram
Introduction
Although the left atrial appendage (LAA) is not the only site of intracardiac thrombus formation, it is the main site where most thrombi form prior to embolization.[1] Several approaches to this problem have been suggested, either by excising or excluding the left atrial appendage (LAA) in patients who are at high risk of stroke. This is particularly relevant for , patients whom chronic anticoagulation is contraindicated. Furthermore, management of the LAA is recommended by American College of Cardiology in patients who are undergoing mitral valve surgery.[2,3]
LAA clipping is a new US FDA- approved technique which has been increasingly used to exclude the LAA from the circulation during cardiac surgery in patients who have atrial fibrillation or have high CHADS2 risk score. [2-4] The atrial clip has usually been deployed via median sternotomy incision.[4-7] Herein we examine the safety and feasibility of epicardial clipping of the LAA via a mini-thoracotomy approach during minimally invasive mitral valve surgery.
Methods
Setting
This study was conducted in a 700 bed, tertiary care teaching hospital in the northeastern US. Because the study used only pre-existing post-operative records, the study was declared exempt by the St. Joseph’s Healthcare System Institutional Review Board.
Patients And Protocol
All consecutive patients who had no previous history of cardiac surgery and had minimally invasive mitral valve surgery with concomitant LAA exclusion using The AtriClip® LAA Exclusion System (Cincinnati, Ohio, AtriCure®) were included. The AtriClip® is composed of two rods, which are made from titanium and interconnected with nitinol hinges. The clip is covered in a braided polyester lining.[4-6]
Patient demographics, clinical characteristics, intra-operative complications, and in-hospital course were collected by reviewing the medical records. Transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE) was used intraoperatively to exclude left atrial thrombus.
Technique Of Laa Clip Placement Via Right Minithoracotmy
First, the femoral artery and vein are exposed and unroofed. The anterior portion of each vessel is exposed only with minimal dissection. This provides more support during cannulation and reduces potential risk of seroma formation. A five to six centimeter right minithoracotomy incision is then made in the fourth intercostal space in the midaxillary line. An Alexis soft tissue retractor is placed, and a small chest tube incision is made in the ninth intercostal space. A stay stitch is then placed in the tendonious portion of the diaphragm and pulled out through the chest tube incision. This retracts the diaphragm down and provides better exposure to the entire heart and pericardium. The pericardium is then opened and the cardiac structures are examined.
Carbon dioxide(CO2) is then introduced into the chest. Intravenous heparin is given to achieve an activated clotting time (ACT) greater than 450. Then, femoral artery and vein cannulas are placed and positioned under TEE guidance. Cardiopulmonary bypass is initiated. The aorta is cross clamped using a Chitwood clamp and the heart is arrested using antegrade and retrograde cardioplegia. The transverse sinus is exposed and examined in order to visualize the left atrial appendage (LAA). This is done to assess the location and size of the LAA and its base. The base of the LAA is measured with the AtriClip sizer (AtriCure®). The mitral valve is then exposed through the right superior and inferior pulmonary veins. Watersons groove is not dissected. The interatrial septum is left undisturbed so it can be retracted and allow for better exposure of the mitral valve and left atrium. The left atrium is retracted with a Cardiovation left atrial retractor (Edwards Life Sciences). The mitral valve portion of the operation is then completed and the atrium is closed. The LAA is not addressed until after the LA is closed. This is because it is difficult to safely expose the LAA with the atrial retractor in place. The LAA is again exposed through the transverse sinus. The AtriClip® is then slid through the transverse sinus until the pericardium on the opposite (left) side is seen. The Atriclip® is placed over the LAA with the help of endoforceps ([Fig-1]). The LAA is eased into the transverse sinus and pulled towards the right chest. The clip is then released and assessed to assure it is at the base of the LAA ([Fig-2]). The clip is deployed just before opening the aortic cross-clamp and while the heart is still immobilized.
Figure 1. By mobilizing the ascending aorta, the base of the LAA can be visualized posterior to the aorta in the coronal junction of the transverse sinus. The atrial clip is advanced through the coronal junction of transverse sinus and placed over the base of the LAA .
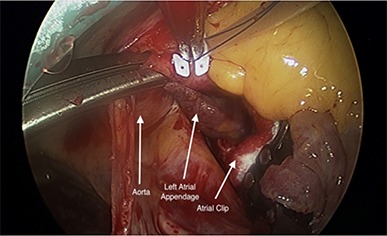
Figure 2. Once the clip is secured at the base and judged satisfactory by the primary surgeon, the LAA is clipped using appropriately sized clip.
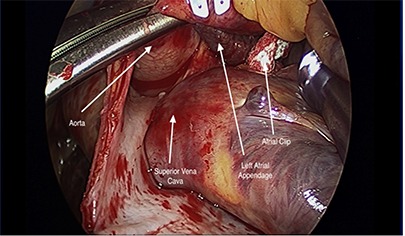
The heart is then de-aired and the CO2 is stopped. The cross-clamp is then removed, the patient is ventilated and weaned off cardiopulmonary bypass. The mitral valve and LAA are evaluated by TEE. Particular attention is paid to determine flow into the LAA and that the clip is at the base of the LAA. The patient is then de-cannulated.
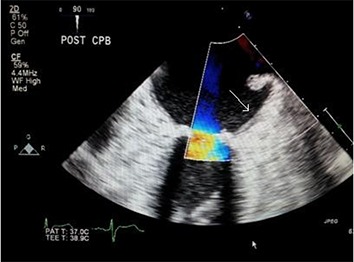
One pericardial and one right pleural drain are placed through the original ninth intercostal space chest tube incision. The mini thoracotomy and groin incisions are then closed. The coronary sinus catheter is removed. TEE is performed to assess the success of the LAA([Fig-3A]) with no color flow. ([Fig-3B])
Figure 3A. TEE image shows complete obliteration of the LAA post clipping ( Arrow).
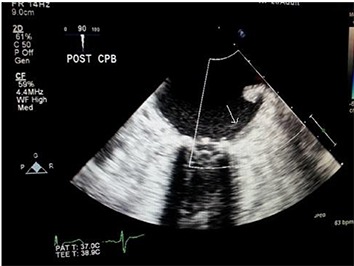
Figure 3B. TEE image shows no color flow across the LAA orifice post clipping (Arrow).
Statistical Analysis
Baseline characteristics are presented as a median (interquartile range (IQR)). The thromboembolic risk after surgery for mitral regurgitation is estimated to be 1.9 ± 0.4% at 30 days.[7] The minimum event rate that a 22 patient might be expected would be 0.42. This study was not powered to evaluate stroke prevention.
Results
Total of 22 patients were included in our study. The median age was 66.0 years (IQR: 50.8 to 81.3). Eight (36%) patients had mitral valve replacement (tThree patients had severe mitral stenosis, 1 patient had infective endocarditis, and 4 with severe mitral regurgitation, which were un-repairable due to severe annular calcification). The rest of the patients had mitral valve repair surgery to treat severe degenerative mitral regurgitation. The ACC guidelines recommend management of the LAA during mitral valve surgery. All patients had concomitant LAA clipping as recommended by the ACC guidelines. [Table-1] shows the different clinical characteristics of the cohort.
Table 1. Clinical characteristics .
| Clinical characteristics | |
|---|---|
| Age Median(IQR) | 66.0 yrs (50.8 to 81.3) |
| Male | 11(50%) |
| BMI | 26.4(23.0 to 32.0) |
| White ethnicity | 15(68%) |
| HTN | 15(68%) |
| DM | 4(18%) |
| CHF(NYHA>2) | 13(59%) |
| Renal Failure | 2(11%) |
| Ever smoked | 3(14%) |
| On aspirin | 8(37%) |
| History of PCI | 2(9%) |
| Urgent surgery | 11(50%) |
| Dyslipidemia | 9(41%) |
Intra-Operative And Postoperative Course
All patients had transesophageal echocardiogram(TEE), confirming the absence of left atrial thrombus before the surgery. All patients had minimally invasive mitral valve surgery through right mini-thoracotomy incision. All patients were operated on by the same surgeon. All patients were on-pump during the surgery. Bioprosthetic mitral valve was used in all patients who required valve replacement.
Intraoperatively, 5 patients required blood product transfusion. All patients had successful clipping of the LAA from the first time and no repositioning was needed. Two patients had re-operation to evacuate chest wall hematoma. Both patients were males, have hypertension, and underwent annuloplasty surgery; however, there was no in-hospital mortality.
IQR:interqurtile range;BMI: body mass index; HTN: hypertension; DM: diabetes mellitus; CHF: congestive heart failure; PCI percutaneous coronary intervention.
Discussion
LAA surgical excision or exclusion (by stapling or suturing) are frequently performed as a concomitant procedure during atrial fibrillation cardiac surgery or mitral valve surgery. However, those procedures have been associated with high failure rates and increased risk of bleeding.[8-11]
LAA clipping is one of the interesting recent technologiesused to epicardially exclude the left atrial appendage from the circulatory system during cardiac surgery. This has been suggested to decrease the cardioembolic stroke rates, especially in patients who have atrial fibrillation or high CHADS2 score.[4-6] Moreover, recent reports have postulated that epicardial clippings will electrically isolate the LAA and decrease the recurrence rate of atrial fibrillation.[12]
Preclinical studies had shown that the epicardial exclusion of the LAA is safe and can be achieved without inserting foreign body into the left atrium.[4] The first human application of the LAA clip was reported by Salzberg et. al in 2010 in patients who underwent cardiac surgery via median sternotomy approach.[5] Ailawadi and coworkers also reported successful clipping of the LAA in 70 patients using the AtriClip in patients undergoing elective cardiac surgery via median sternotomy.[6]
Table 2. Intra-operative data.
| Intra-operative data | |
|---|---|
| Valve replacement | 8(37%) |
| Aortic Cross clamp time (min) | 71.0(IQR 62.3 to 80.0 ) |
| Cardiopulmonary bypass time(min) | 92.5 (IQR 81.0 to 105.0) |
| Blood product needed during the surgery | 5(23%) |
We are reporting the first human application of the atrial clip through sternal-sparing, direct vision, right-sided minithoracotomy as a concomitant procedure in patients who are undergoing mitral valve surgery. The clipping was achieved rapidly and safely with no intraoperative complications. And no inhospital mortality.
Clipping the LAA appendage during minimally invasive mitral valve surgery can be achieved with relative ease and without significant increase in the time of the surgery. This approach may change the surgeons management approach and could expand the practice of clipping the LAA in this subset of patients. In addition, it could offer a less invasive management option to those patients with atrial fibrillation who have contraindication for chronic anticoagulation.
Limitation
This is a small retrospective study, which should be replicated using a prospective design of a larger number. It is not powered to evaluate stroke prevention and no outpatient follow up was done. There was also no subsequent follow-up of the success of the procedure by either TEE or CT post-operatively. IQR:interqurtile range
Conclusions
Occluding the LAA using AtriClip device during minimally invasive mitral surgery can be achieved safely and rapidly. Applying the LAA clip via min-thoracotomy approach offers a new and safe approach for patients who are at high risk of cardio-embolic stroke and undergoing cardiac surgery.
Disclosures
None.
References
- 1.Frost L, Engholm G, Johnsen S, Møller H, Husted S. Incident stroke after discharge from the hospital with a diagnosis of atrial fibrillation. Am. J. Med. 2000 Jan;108 (1):36–40. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(99)00415-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Gillinov A Marc. Advances in surgical treatment of atrial fibrillation. Stroke. 2007 Feb;38 (2 Suppl):618–23. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000247934.04848.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Fuster Valentin, Rydén Lars E, Cannom Davis S, Crijns Harry J, Curtis Anne B, Ellenbogen Kenneth A, Halperin Jonathan L, Kay G Neal, Le Huezey Jean-Yves, Lowe James E, Olsson S Bertil, Prystowsky Eric N, Tamargo Juan Luis, Wann L Samuel. 2011 ACCF/AHA/HRS focused updates incorporated into the ACC/AHA/ESC 2006 Guidelines for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines developed in partnership with the European Society of Cardiology and in collaboration with the European Heart Rhythm Association and the Heart Rhythm Society. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011 Mar 15;57 (11):e101–98. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2010.09.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Fumoto Hideyuki, Gillinov A Marc, Ootaki Yoshio, Akiyama Masatoshi, Saeed Diyar, Horai Tetsuya, Ootaki Chiyo, Vince D Geoffrey, Popović Zoran B, Dessoffy Raymond, Massiello Alex, Catanese Jacquelyn, Fukamachi Kiyotaka. A novel device for left atrial appendage exclusion: the third-generation atrial exclusion device. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2008 Oct;136 (4):1019–27. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2008.06.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Salzberg Sacha P, Plass Andre, Emmert Maximillian Y, Desbiolles Lotus, Alkadhi Hatem, Grünenfelder Jurg, Genoni Michele. Left atrial appendage clip occlusion: early clinical results. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2010 May;139 (5):1269–74. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2009.06.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ailawadi Gorav, Gerdisch Marc W, Harvey Richard L, Hooker Robert L, Damiano Ralph J, Salamon Thomas, Mack Michael J. Exclusion of the left atrial appendage with a novel device: early results of a multicenter trial. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2011 Nov;142 (5):1002–9, 1009.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2011.07.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Russo Antonio, Grigioni Francesco, Avierinos Jean-François, Freeman William K, Suri Rakesh, Michelena Hector, Brown Robert, Sundt Thoralf M, Enriquez-Sarano Maurice. Thromboembolic complications after surgical correction of mitral regurgitation incidence, predictors, and clinical implications. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008 Mar 25;51 (12):1203–11. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2007.10.058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Emmert Maximilian Y, Puippe Gilbert, Baumüller Stephan, Alkadhi Hatem, Landmesser Ulf, Plass Andre, Bettex Dominique, Scherman Jacques, Grünenfelder Jürg, Genoni Michele, Falk Volkmar, Salzberg Sacha P. Safe, effective and durable epicardial left atrial appendage clip occlusion in patients with atrial fibrillation undergoing cardiac surgery: first long-term results from a prospective device trial. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2014 Jan;45 (1):126–31. doi: 10.1093/ejcts/ezt204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Moss Joshua D. Left atrial appendage exclusion for prevention of stroke in atrial fibrillation: review of minimally invasive approaches. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2014 Feb;16 (2) doi: 10.1007/s11886-013-0448-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Blackshear Joseph L, Johnson W Dudley, Odell John A, Baker Vickie S, Howard Mary, Pearce Lesly, Stone Christopher, Packer Douglas L, Schaff Hartzell V. Thoracoscopic extracardiac obliteration of the left atrial appendage for stroke risk reduction in atrial fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2003 Oct 1;42 (7):1249–52. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(03)00953-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ostermayer Stefan H, Reisman Mark, Kramer Paul H, Matthews Ray V, Gray William A, Block Peter C, Omran Heyder, Bartorelli Antonio L, Della Bella Paolo, Di Mario Carlo, Pappone Carlo, Casale Paul N, Moses Jeffrey W, Poppas Athena, Williams David O, Meier Bernhard, Skanes Allan, Teirstein Paul S, Lesh Michael D, Nakai Toshiko, Bayard Yves, Billinger Kai, Trepels Thomas, Krumsdorf Ulrike, Sievert Horst. Percutaneous left atrial appendage transcatheter occlusion (PLAATO system) to prevent stroke in high-risk patients with non-rheumatic atrial fibrillation: results from the international multi-center feasibility trials. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2005 Jul 5;46 (1):9–14. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2005.03.042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Slater A David, Tatooles Antone J, Coffey Arthur, Pappas Patroklos S, Bresticker Michael, Greason Kevin, Slaughter Mark S. Prospective clinical study of a novel left atrial appendage occlusion device. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2012 Jun;93 (6):2035–8. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2011.12.077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Starck Christoph T, Steffel Jan, Emmert Maximilian Y, Plass Andre, Mahapatra Srijoy, Falk Volkmar, Salzberg Sacha P. Epicardial left atrial appendage clip occlusion also provides the electrical isolation of the left atrial appendage. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2012 Sep;15 (3):416–8. doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivs136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


