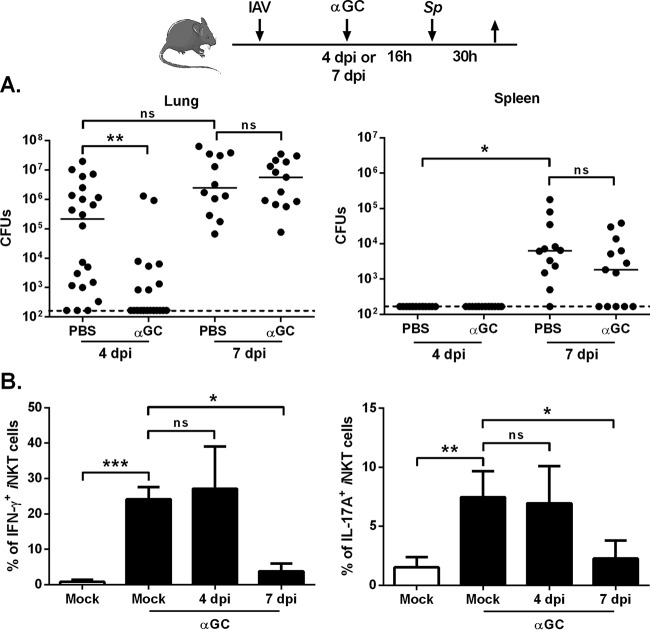
FIG 2 .
Effect of α-GalCer treatment during early influenza on secondary bacterial infection. (A) Overview of the procedure. Age-matched male mice were i.n. infected with IAV (30 PFU). Four or 7 days later, the mice were challenged with S. pneumoniae (Sp [103 CFU]). Mice were i.n. treated with PBS or α-GalCer (2 µg/mouse) 16 h before the pneumococcal challenge. The number of CFU was determined in lungs and spleen 30 h after S. pneumoniae infection. The solid lines correspond to the median values. Results from a pool of three experiments are shown. (B) Mock-infected mice or IAV-infected mice (4 or 7 dpi) were i.n. treated with α-GalCer. Gated iNKT cells (TCR-β+ PBS57-loaded CD1d tetramer+) were analyzed for intracellular IFN-γ and IL-17Aproduction (16 h after α-GalCer inoculation). The y axis refers to the mean percentages of pulmonary iNKT cells positive for IFN-γ and IL-17A ± SD (n = 6 to 12, two pooled experiments). Of note, the absolute numbers of iNKT cells in the lungs of mock-infected and IAV-infected mice were similar (data not shown). ns, not significant. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001 (one-way ANOVA Kruskal-Wallis test in panel B).