Abstract
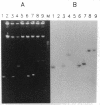
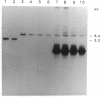
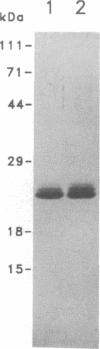
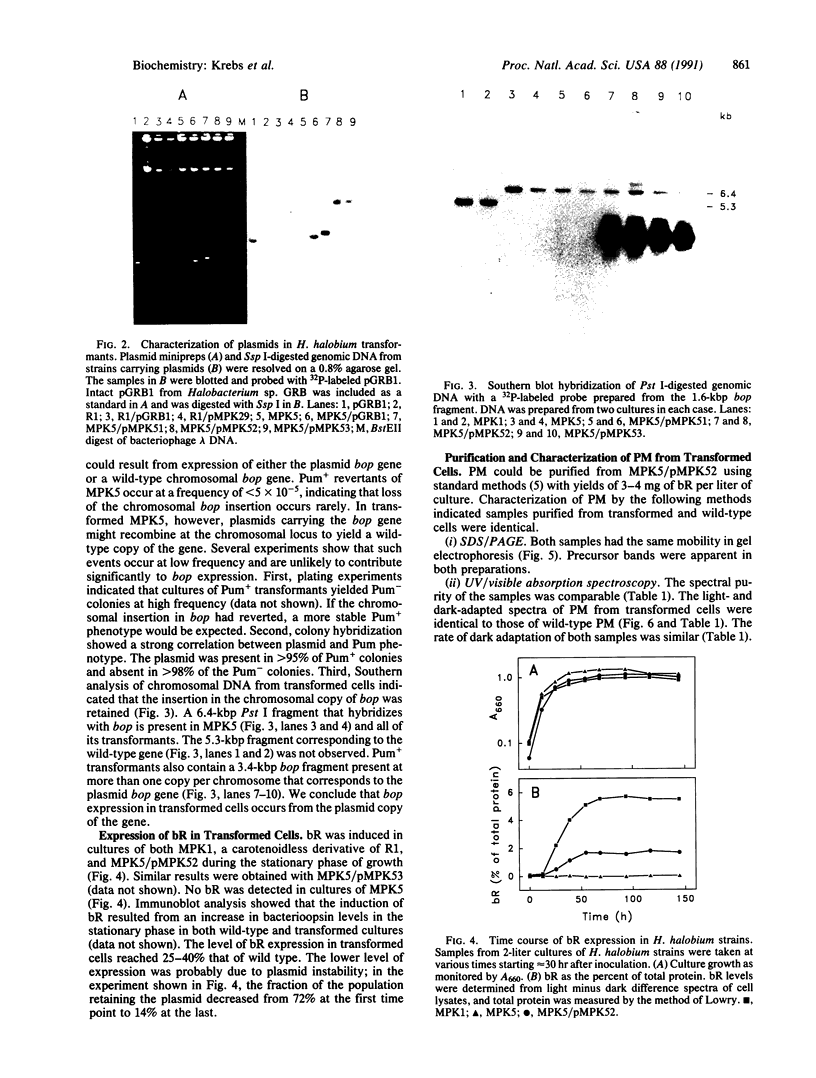
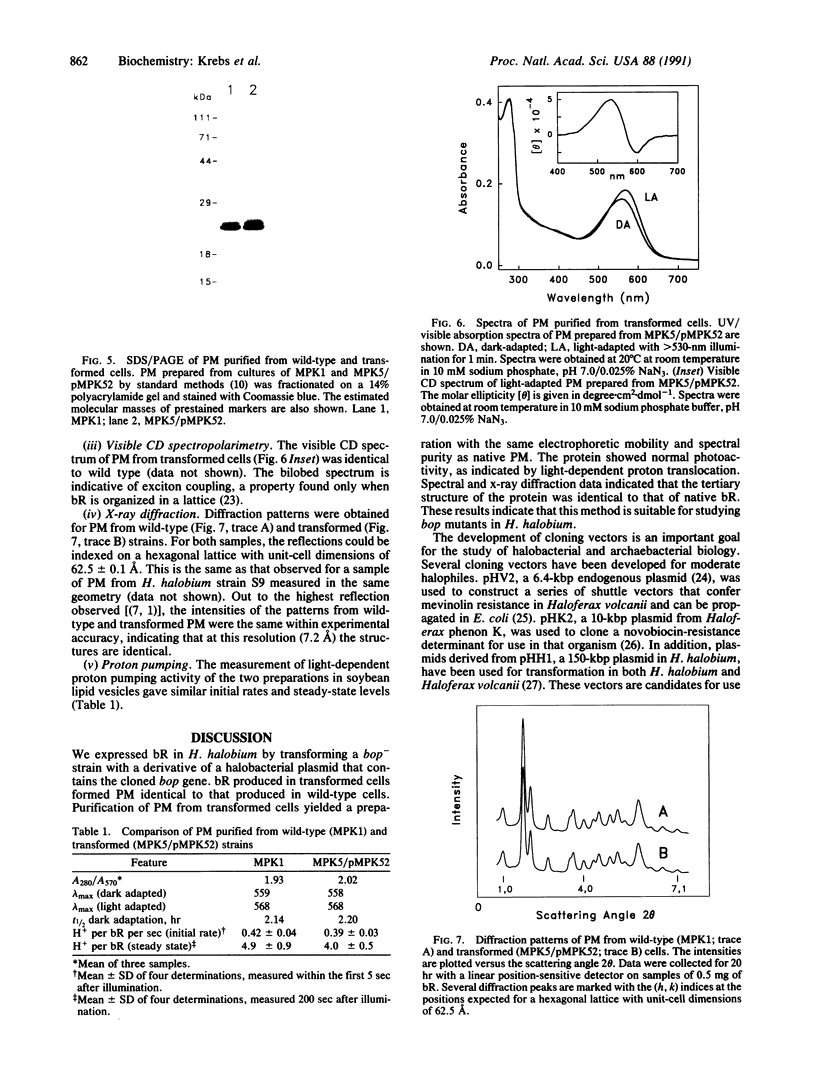
Bacteriorhodopsin (bR) was expressed in Halobacterium halobium by using a multicopy plasmid containing the bop gene. The plasmid contains pGRB1, a 1.8-kilobase-pair plasmid; a 70-base-pair fragment from ISH11, a recently characterized insertion sequence; and a 1.6-kilobase-pair fragment carrying the bop gene from H. halobium S9. When transformed with this plasmid, a bop- insertion mutant of H. halobium yielded purple (Pum+) colonies. The insertion at the chromosomal bop locus remained intact in transformed cells, indicating that the plasmid bop gene was responsible for the Pum+ phenotype. bR was induced in early stationary phase in both wild-type and transformed cells. The final level of bR in transformed cells was 25-40% of that in wild type. The lower level of expression was presumably due to plasmid instability. Purple membrane purified from transformed strains had absorption and visible CD properties similar to wild type and contained bR in a hexagonal lattice with the same unit-cell dimension as wild type. The structure of bR from wild-type and transformed strains was identical at a resolution of 7.2 A. When reconstituted into vesicles, the purple membrane from wild-type and transformed strains showed similar light-dependent proton-pumping activity.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayley H., Radhakrishnan R., Huang K. S., Khorana H. G. Light-driven proton translocation by bacteriorhodopsin reconstituted with the phenyl analog of retinal. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3797–3801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaseio U., Pfeifer F. Transformation of Halobacterium halobium: development of vectors and investigation of gas vesicle synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6772–6776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlebois R. L., Lam W. L., Cline S. W., Doolittle W. F. Characterization of pHV2 from Halobacterium volcanii and its use in demonstrating transformation of an archaebacterium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8530–8534. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline S. W., Doolittle W. F. Efficient transfection of the archaebacterium Halobacterium halobium. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1341–1344. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1341-1344.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dassarma S., Rajbhandary U. L., Khorana H. G. Bacterio-opsin mRNA in wild-type and bacterio-opsin-deficient Halobacterium halobium strains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):125–129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn R. J., Hackett N. R., McCoy J. M., Chao B. H., Kimura K., Khorana H. G. Structure-function studies on bacteriorhodopsin. I. Expression of the bacterio-opsin gene in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):9246–9254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferretti L., Karnik S. S., Khorana H. G., Nassal M., Oprian D. D. Total synthesis of a gene for bovine rhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):599–603. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gropp F., Palm P., Zillig W. Expression and regulation of Halobacterium halobium phage phi H genes. Can J Microbiol. 1989 Jan;35(1):182–188. doi: 10.1139/m89-028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackett N. R., DasSarma S. Characterization of the small endogenous plasmid of Halobacterium strain SB3 and its use in transformation of H. halobium. Can J Microbiol. 1989 Jan;35(1):86–91. doi: 10.1139/m89-013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackett N. R., Krebs M. P., DasSarma S., Goebel W., RajBhandary U. L., Khorana H. G. Nucleotide sequence of a high copy number plasmid from Halobacterium strain GRB. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 11;18(11):3408–3408. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.11.3408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackett N. R., Stern L. J., Chao B. H., Kronis K. A., Khorana H. G. Structure-function studies on bacteriorhodopsin. V. Effects of amino acid substitutions in the putative helix F. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):9277–9284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall M. J., Hackett N. R. DNA sequence of a small plasmid from Halobacterium strain GN101. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 25;17(24):10501–10501. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.24.10501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyn M. P., Bauer P. J., Dencher N. A. A natural CD label to probe the structure of the purple membrane from Halobacterium halobium by means of exciton coupling effects. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Dec 1;67(3):897–903. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90761-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyn M. P., Dudda C., Otto H., Seiff F., Wallat I. The purple to blue transition of bacteriorhodopsin is accompanied by a loss of the hexagonal lattice and a conformational change. Biochemistry. 1989 Nov 14;28(23):9166–9172. doi: 10.1021/bi00449a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes M. L., Dyall-Smith M. L. A plasmid vector with a selectable marker for halophilic archaebacteria. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):756–761. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.756-761.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagramanova V. K., Derckacheva N. I., Mankin A. S. The complete nucleotide sequence of the arcaebacterial plasmid pHSB from Halobacterium, strain SB3. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 11;16(9):4158–4158. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.9.4158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khorana H. G. Bacteriorhodopsin, a membrane protein that uses light to translocate protons. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7439–7442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs M. P., RajBhandary U. L., Khorana H. G. Nucleotide sequence of ISH11, a new Halobacterium halobium insertion element isolated from the plasmid pGRB1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6699–6699. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam W. L., Doolittle W. F. Shuttle vectors for the archaebacterium Halobacterium volcanii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5478–5482. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ni B. F., Chang M., Duschl A., Lanyi J., Needleman R. An efficient system for the synthesis of bacteriorhodopsin in Halobacterium halobium. Gene. 1990 May 31;90(1):169–172. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90456-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Stoeckenius W. Functions of a new photoreceptor membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2853–2857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Stoeckenius W. Isolation of the cell membrane of Halobacterium halobium and its fractionation into red and purple membrane. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:667–678. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31072-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Stoeckenius W. Rhodopsin-like protein from the purple membrane of Halobacterium halobium. Nat New Biol. 1971 Sep 29;233(39):149–152. doi: 10.1038/newbio233149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson N. H., Pauling C. Evidence for two restriction-modification systems in Halobacterium cutirubrum. J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):783–784. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.783-784.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter W. D., Palm P., Zillig W. Analysis of transcription in the archaebacterium Sulfolobus indicates that archaebacterial promoters are homologous to eukaryotic pol II promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 11;16(1):1–19. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnabel H., Zillig W., Pfäffle M., Schnabel R., Michel H., Delius H. Halobacterium halobium phage øH. EMBO J. 1982;1(1):87–92. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01129.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simsek M., DasSarma S., RajBhandary U. L., Khorana H. G. A transposable element from Halobacterium halobium which inactivates the bacteriorhodopsin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7268–7272. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sioud M., Baldacci G., de Recondo A. M., Forterre P. Novobiocin induces positive supercoiling of small plasmids from halophilic archaebacteria in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 25;16(4):1379–1391. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.4.1379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soppa J., Oesterhelt D. Bacteriorhodopsin mutants of Halobacterium sp. GRB. I. The 5-bromo-2'-deoxyuridine selection as a method to isolate point mutants in halobacteria. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):13043–13048. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckenius W., Lozier R. H., Bogomolni R. A. Bacteriorhodopsin and the purple membrane of halobacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Mar 14;505(3-4):215–278. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(79)90006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumper M., Reitmeier H., Oesterhelt D. Biosynthesis of the purple membrane of halobacteria. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 1976 Apr;15(4):187–194. doi: 10.1002/anie.197601871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomm M., Wich G. An archaebacterial promoter element for stable RNA genes with homology to the TATA box of higher eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 11;16(1):151–163. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.1.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang C. F., DasSarma S. Transcriptional induction of purple membrane and gas vesicle synthesis in the archaebacterium Halobacterium halobium is blocked by a DNA gyrase inhibitor. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):4118–4121. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.4118-4121.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]