Abstract
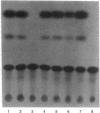
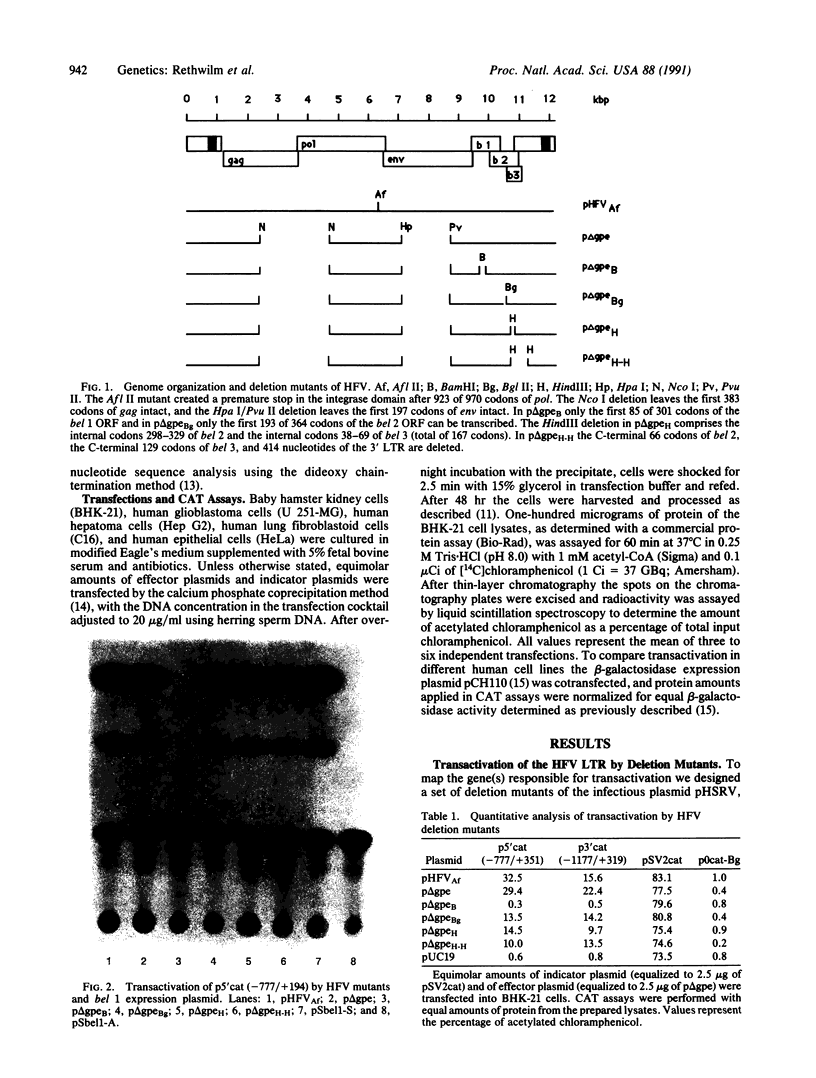
The human foamy virus (HFV) genome possesses three open reading frames (bel 1, 2, and 3) located between env and the 3' long terminal repeat. By analogy to other human retroviruses this region was selected as the most likely candidate to encode the viral transactivator. Results presented here confirmed this and showed further that a deletion introduced only into the bel 1 open reading frame of a plasmid derived from an infectious molecular clone of HFV abolished transactivation. In contrast, deletions in bel 2 and bel 3 had only minor effects on the ability to transactivate. The role of the bel 1 genomic region as a transactivator was further investigated by eukaryotic expression of a genome fragment of HFV spanning the bel 1 open reading frame. A construct expressing bel 1 under control of a heterologous promoter was found to transactivate the HFV long terminal repeat in a dose-dependent fashion. Furthermore, it is shown that the U3 region of the HFV long terminal repeat is sufficient to respond to the HFV transactivator.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achong B. G., Mansell P. W., Epstein M. A., Clifford P. An unusual virus in cultures from a human nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1971 Feb;46(2):299–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arya S. K. Human and simian immunodeficiency retroviruses: activation and differential transactivation of gene expression. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1988 Jun;4(3):175–186. doi: 10.1089/aid.1988.4.175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J., Jeang K. T., Duvall J., Khoury G. Identification of p40x-responsive regulatory sequences within the human T-cell leukemia virus type I long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2175–2181. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2175-2181.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Ernberg I., Gait M. J., Green S. M., Heaphy S., Karn J., Lowe A. D., Singh M., Skinner M. A., Valerio R. Human immunodeficiency virus 1 tat protein binds trans-activation-responsive region (TAR) RNA in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6925–6929. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flügel R. M., Rethwilm A., Maurer B., Darai G. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the env gene and its flanking regions of the human spumaretrovirus reveals two novel genes. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):2077–2084. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02473.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. V., Jacob P. E., Ringold G. M., Lee F. Expression and regulation of Escherichia coli lacZ gene fusions in mammalian cells. J Mol Appl Genet. 1983;2(1):101–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura A., Israël A., Le Bail O., Kourilsky P. Detailed analysis of the mouse H-2Kb promoter: enhancer-like sequences and their role in the regulation of class I gene expression. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):261–272. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90760-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer B., Bannert H., Darai G., Flügel R. M. Analysis of the primary structure of the long terminal repeat and the gag and pol genes of the human spumaretrovirus. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1590–1597. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1590-1597.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer B., Flügel R. M. Genomic organization of the human spumaretrovirus and its relatedness to AIDS and other retroviruses. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1988 Dec;4(6):467–473. doi: 10.1089/aid.1988.4.467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer B., Flügel R. M. The 3'-orf protein of human immunodeficiency virus 2 shows sequence homology with the bel3 gene of the human spumaretrovirus. FEBS Lett. 1987 Oct 5;222(2):286–288. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80387-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mergia A., Shaw K. E., Pratt-Lowe E., Barry P. A., Luciw P. A. Simian foamy virus type 1 is a retrovirus which encodes a transcriptional transactivator. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3598–3604. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3598-3604.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rethwilm A., Baunach G., Netzer K. O., Maurer B., Borisch B., ter Meulen V. Infectious DNA of the human spumaretrovirus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):733–738. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rethwilm A., Darai G., Rösen A., Maurer B., Flügel R. M. Molecular cloning of the genome of human spumaretrovirus. Gene. 1987;59(1):19–28. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90262-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rethwilm A., Mori K., Maurer B., ter Meulen V. Transacting transcriptional activation of human spumaretrovirus LTR in infected cells. Virology. 1990 Apr;175(2):568–571. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90442-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S., Felber B. K., Benko D. M., Fenyö E. M., Pavlakis G. N. Cloning and functional analysis of multiply spliced mRNA species of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2519–2529. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2519-2529.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seigel L. J., Ratner L., Josephs S. F., Derse D., Feinberg M. B., Reyes G. R., O'Brien S. J., Wong-Staal F. Transactivation induced by human T-lymphotropic virus type III (HTLV III) maps to a viral sequence encoding 58 amino acids and lacks tissue specificity. Virology. 1986 Jan 15;148(1):226–231. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90419-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiki M., Hikikoshi A., Taniguchi T., Yoshida M. Expression of the pX gene of HTLV-I: general splicing mechanism in the HTLV family. Science. 1985 Jun 28;228(4707):1532–1534. doi: 10.1126/science.2990031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodroski J., Patarca R., Rosen C., Wong-Staal F., Haseltine W. Location of the trans-activating region on the genome of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type III. Science. 1985 Jul 5;229(4708):74–77. doi: 10.1126/science.2990041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southgate C., Zapp M. L., Green M. R. Activation of transcription by HIV-1 Tat protein tethered to nascent RNA through another protein. Nature. 1990 Jun 14;345(6276):640–642. doi: 10.1038/345640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura T., Fujisawa J., Yoshida M. Multiple cDNA clones encoding nuclear proteins that bind to the tax-dependent enhancer of HTLV-1: all contain a leucine zipper structure and basic amino acid domain. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2537–2542. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07434.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]