Figure 5. ISX enhances E2F1-mediated cell proliferation and oncogenic activity.
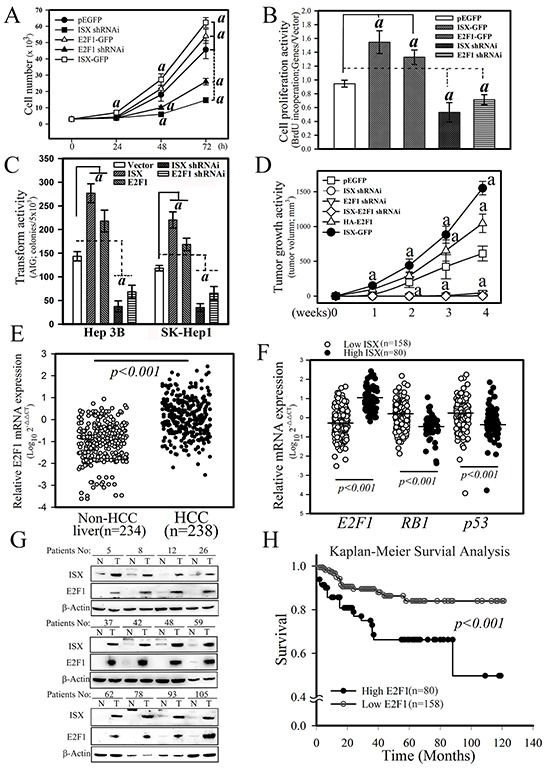
A. Effect of ISX and E2F1 on the cell growth of SK-Hep1 cells transfected with forced expression vectors of ISX-GFP and/or E2F1-GFP and knockdown vector of ISX and E2F1. SK-Hep1 cells expressed endogenous ISX. a, p < 0.001. B. BrdU incorporation of SK-Hep1 cells transfected with ISX-GFP and/or E2F1-GFP and knockdown vector of ISX and E2F1. a, p < 0.0001. C. Cell anchorage-dependent transformation activity detected by soft agar colony formation. Hep 3B and SK-Hep 1 cells were transfected with forced expression vector of ISX and E2F1 and knockdown vector shRNAi against E2F1 and ISX. a, p < 0.001. D. Tumor growth activity of SK-Hep1 cells transfected with forced expression vector of ISX and E2F1 and knockdown vector shRNAi against E2F1 and ISX. a, p < 0.001. E. Comparison of the mRNA expression of E2F1 between HCC tumor and non-tumor tissues as described in the Materials and Methods. F. The mRNA level of E2F1 in HCC patients with high ISX expression was significantly higher than that with the low ISX-expressing HCC patients. Both RB1 and p53 mRNA expressions in the high ISX expression HCC group were significantly downregulated relative to those in the low ISX expression HCC group. G. Western blot of ISX and E2F1 proteins in HCC patient tissues. A high protein level of E2F1 was observed in HCC patients with higher ISX. H. The Kaplan–Meier survival curve analysis between HCC patients with low and high expression of E2F1. All results are shown as means ± S.D. a, p < 0.001. Each experiment was repeated three times.
