Abstract
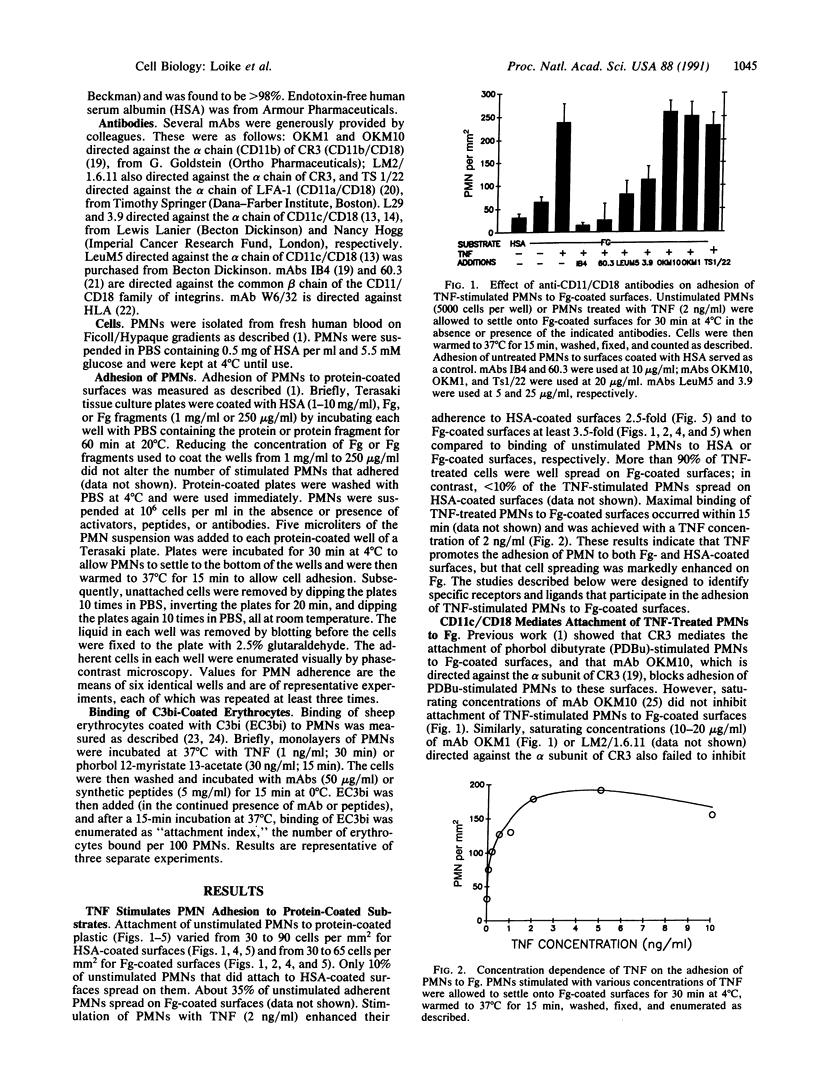
Fibrinogen and fibrin serve as adhesive substrates for a variety of cells including platelets, endothelial cells, and leukocytes. Previously, we identified the C terminus of the gamma chain of fibrinogen as the region of the fibrinogen molecule that contains a ligand for CD11b/CD18 (complement receptor 3) on phorbol ester-stimulated polymorphonuclear leukocytes. In contrast, we report here that neutrophils stimulated with tumor necrosis factor adhere to fibrinogen-coated surfaces, but not to human serum albumin-coated surfaces, via the integrin CD11c/CD18 (p150/95). Monoclonal antibodies LeuM5 and 3.9, which are directed against the alpha subunit of CD11c/CD18, but not monoclonal antibodies OKM10 and OKM1, which are directed against the alpha subunit of CD11b/CD18, inhibit the adhesion of tumor necrosis factor-stimulated neutrophils to fibrinogen-coated surfaces. To identify the site on fibrinogen recognized by CD11c/CD18, we have examined the adhesion of tumor necrosis factor-stimulated neutrophils to surfaces coated with various fibrinogen fragments. Stimulated neutrophils adhere to surfaces coated with the N-terminal disulfide knot fragment of fibrinogen or fibrinogen fragment E. Moreover, peptides containing the sequence Gly-Pro-Arg (which corresponds to amino acids 17-19 of the N-terminal region of the A alpha chain of fibrinogen), and monoclonal antibody LeuM5, block tumor necrosis factor-stimulated neutrophil adhesion to fibrinogen and to the N-terminal disulfide knot fragment of fibrinogen. Thus, CD11c/CD18 on tumor necrosis factor-stimulated neutrophils functions as a fibrinogen receptor that recognizes the sequence Gly-Pro-Arg in the N-terminal domain of the A alpha chain of fibrinogen.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altieri D. C., Agbanyo F. R., Plescia J., Ginsberg M. H., Edgington T. S., Plow E. F. A unique recognition site mediates the interaction of fibrinogen with the leukocyte integrin Mac-1 (CD11b/CD18). J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12119–12122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altieri D. C., Bader R., Mannucci P. M., Edgington T. S. Oligospecificity of the cellular adhesion receptor Mac-1 encompasses an inducible recognition specificity for fibrinogen. J Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;107(5):1893–1900. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.5.1893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altieri D. C., Edgington T. S. The saturable high affinity association of factor X to ADP-stimulated monocytes defines a novel function of the Mac-1 receptor. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 25;263(15):7007–7015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altieri D. C., Morrissey J. H., Edgington T. S. Adhesive receptor Mac-1 coordinates the activation of factor X on stimulated cells of monocytic and myeloid differentiation: an alternative initiation of the coagulation protease cascade. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7462–7466. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. C., Miller L. J., Schmalstieg F. C., Rothlein R., Springer T. A. Contributions of the Mac-1 glycoprotein family to adherence-dependent granulocyte functions: structure-function assessments employing subunit-specific monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1986 Jul 1;137(1):15–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnaout M. A., Lanier L. L., Faller D. V. Relative contribution of the leukocyte molecules Mo1, LFA-1, and p150,95 (LeuM5) in adhesion of granulocytes and monocytes to vascular endothelium is tissue- and stimulus-specific. J Cell Physiol. 1988 Nov;137(2):305–309. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041370214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnhart M. I. Importance of neutrophilic leukocytes in the resolution of fibrin. Fed Proc. 1965 Jul-Aug;24(4):846–853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnstable C. J., Bodmer W. F., Brown G., Galfre G., Milstein C., Williams A. F., Ziegler A. Production of monoclonal antibodies to group A erythrocytes, HLA and other human cell surface antigens-new tools for genetic analysis. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90296-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beatty P. G., Ledbetter J. A., Martin P. J., Price T. H., Hansen J. A. Definition of a common leukocyte cell-surface antigen (Lp95-150) associated with diverse cell-mediated immune functions. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):2913–2918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger M., Wetzler E. M., Wallis R. S. Tumor necrosis factor is the major monocyte product that increases complement receptor expression on mature human neutrophils. Blood. 1988 Jan;71(1):151–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blombäck B., Blombäck M., Henschen A., Hessel B., Iwanaga S., Woods K. R. N-terminal disulphide knot of human fibrinogen. Nature. 1968 Apr 13;218(5137):130–134. doi: 10.1038/218130a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullock W. E., Wright S. D. Role of the adherence-promoting receptors, CR3, LFA-1, and p150,95, in binding of Histoplasma capsulatum by human macrophages. J Exp Med. 1987 Jan 1;165(1):195–210. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.1.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Lo S. K., Malik A. B. Fibrin is a determinant of neutrophil sequestration in the lung. Circ Res. 1988 Oct;63(4):735–741. doi: 10.1161/01.res.63.4.735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detmers P. A., Lo S. K., Olsen-Egbert E., Walz A., Baggiolini M., Cohn Z. A. Neutrophil-activating protein 1/interleukin 8 stimulates the binding activity of the leukocyte adhesion receptor CD11b/CD18 on human neutrophils. J Exp Med. 1990 Apr 1;171(4):1155–1162. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.4.1155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonda S. R., Shainoff J. R. Adsorptive endocytosis of fibrin monomer by macrophages: evidence of a receptor for the amino terminus of the fibrin alpha chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4565–4569. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson E. J., Lukasiewicz H., Wachtfogel Y. T., Norton K. J., Schmaier A. H., Niewiarowski S., Colman R. W. High molecular weight kininogen inhibits fibrinogen binding to cytoadhesins of neutrophils and platelets. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):377–387. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermanowski-Vosatka A., Detmers P. A., Götze O., Silverstein S. C., Wright S. D. Clustering of ligand on the surface of a particle enhances adhesion to receptor-bearing cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 25;263(33):17822–17827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg N. The leukocyte integrins. Immunol Today. 1989 Apr;10(4):111–114. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90238-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaminski M., McDonagh J. Studies on the mechanism of thrombin. Interaction with fibrin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10530–10535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keizer G. D., Borst J., Visser W., Schwarting R., de Vries J. E., Figdor C. G. Membrane glycoprotein p150,95 of human cytotoxic T cell clone is involved in conjugate formation with target cells. J Immunol. 1987 May 15;138(10):3130–3136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Arnaout M. A., Schwarting R., Warner N. L., Ross G. D. p150/95, Third member of the LFA-1/CR3 polypeptide family identified by anti-Leu M5 monoclonal antibody. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Jul;15(7):713–718. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo S. K., Detmers P. A., Levin S. M., Wright S. D. Transient adhesion of neutrophils to endothelium. J Exp Med. 1989 May 1;169(5):1779–1793. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.5.1779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo S. K., Van Seventer G. A., Levin S. M., Wright S. D. Two leukocyte receptors (CD11a/CD18 and CD11b/CD18) mediate transient adhesion to endothelium by binding to different ligands. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 15;143(10):3325–3329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malhotra V., Hogg N., Sim R. B. Ligand binding by the p150,95 antigen of U937 monocytic cells: properties in common with complement receptor type 3 (CR3). Eur J Immunol. 1986 Sep;16(9):1117–1123. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marglin A., Merrifield R. B. Chemical synthesis of peptides and proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1970;39:841–866. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.39.070170.004205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myones B. L., Dalzell J. G., Hogg N., Ross G. D. Neutrophil and monocyte cell surface p150,95 has iC3b-receptor (CR4) activity resembling CR3. J Clin Invest. 1988 Aug;82(2):640–651. doi: 10.1172/JCI113643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F. The contribution of leukocyte proteases to fibrinolysis. Blut. 1986 Jul;53(1):1–9. doi: 10.1007/BF00320577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie D. G., Fuller G. M. Hepatocyte-stimulating factor: a monocyte-derived acute-phase regulatory protein. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1983 Jun 27;408:490–502. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1983.tb23268.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Madrid F., Nagy J. A., Robbins E., Simon P., Springer T. A. A human leukocyte differentiation antigen family with distinct alpha-subunits and a common beta-subunit: the lymphocyte function-associated antigen (LFA-1), the C3bi complement receptor (OKM1/Mac-1), and the p150,95 molecule. J Exp Med. 1983 Dec 1;158(6):1785–1803. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.6.1785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki T., Page I. H., Shainoff J. R. Stable complex of fibrinogen and fibrin. Science. 1966 May 20;152(3725):1069–1071. doi: 10.1126/science.152.3725.1069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman L. A., Lee J. Specific binding of soluble fibrin to macrophages. J Exp Med. 1977 Jan 1;145(1):76–85. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.1.76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitz J. I., Landman S. L., Crowley K. A., Birken S., Morgan F. J. Development of an assay for in vivo human neutrophil elastase activity. Increased elastase activity in patients with alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor deficiency. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jul;78(1):155–162. doi: 10.1172/JCI112545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Jong M. T. Adhesion-promoting receptors on human macrophages recognize Escherichia coli by binding to lipopolysaccharide. J Exp Med. 1986 Dec 1;164(6):1876–1888. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.6.1876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Levin S. M., Jong M. T., Chad Z., Kabbash L. G. CR3 (CD11b/CD18) expresses one binding site for Arg-Gly-Asp-containing peptides and a second site for bacterial lipopolysaccharide. J Exp Med. 1989 Jan 1;169(1):175–183. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.1.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Meyer B. C. Phorbol esters cause sequential activation and deactivation of complement receptors on polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 1;136(5):1759–1764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Rao P. E., Van Voorhis W. C., Craigmyle L. S., Iida K., Talle M. A., Westberg E. F., Goldstein G., Silverstein S. C. Identification of the C3bi receptor of human monocytes and macrophages by using monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5699–5703. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Tobias P. S., Ulevitch R. J., Ramos R. A. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) binding protein opsonizes LPS-bearing particles for recognition by a novel receptor on macrophages. J Exp Med. 1989 Oct 1;170(4):1231–1241. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.4.1231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Weitz J. I., Huang A. J., Levin S. M., Silverstein S. C., Loike J. D. Complement receptor type three (CD11b/CD18) of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes recognizes fibrinogen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7734–7738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



