Abstract
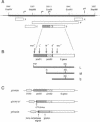
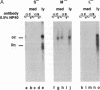
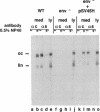
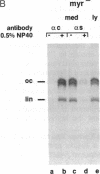
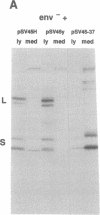
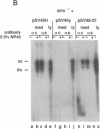
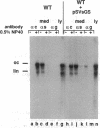
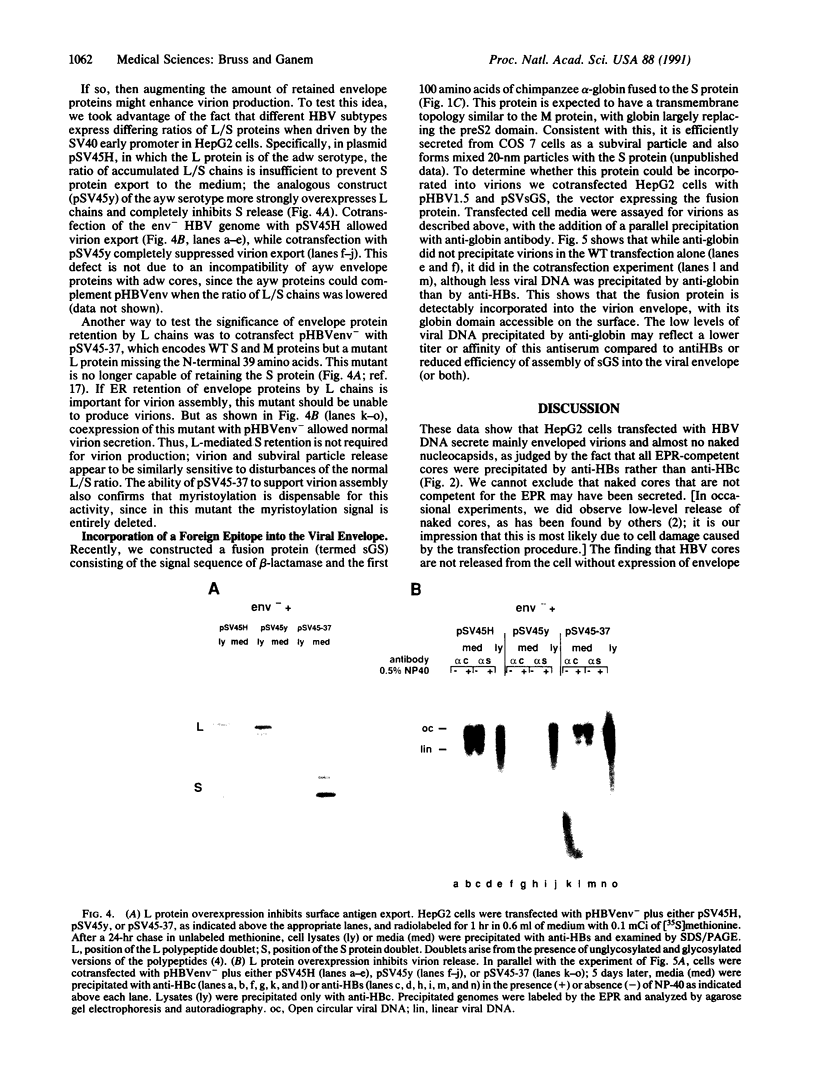
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) particles are generated by budding of preformed cytoplasmic nucleocapsids into endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membranes containing the three viral envelope proteins (L, M, and S). We have examined the contributions of the envelope proteins to virion assembly by using cultured hepatoma cells transfected with mutant HBV genomes bearing lesions in the envelope coding regions. We show here that HBV nucleocapsids are not released from cells without expression of envelope proteins, implying an active role for these proteins in viral morphogenesis. S and L but not M proteins are necessary for virion production. L protein over-expression inhibits virion release, just as it inhibits the release of subviral hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) particles. Mutant L proteins that are no longer capable of retaining HBsAg particles in the ER still allow virion formation, indicating that this ER retention reaction is not required for viral budding. Myristoylation of L protein is also dispensable for virion formation. A chimeric protein bearing foreign epitopes fused to the S protein can be incorporated into virions when coexpressed with the wild-type envelope proteins. Models for the dependence of virion formation on both L and S proteins are discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chisari F. V., Filippi P., McLachlan A., Milich D. R., Riggs M., Lee S., Palmiter R. D., Pinkert C. A., Brinster R. L. Expression of hepatitis B virus large envelope polypeptide inhibits hepatitis B surface antigen secretion in transgenic mice. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):880–887. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.880-887.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dane D. S., Cameron C. H., Briggs M. Virus-like particles in serum of patients with Australia-antigen-associated hepatitis. Lancet. 1970 Apr 4;1(7649):695–698. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)90926-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois M. F., Pourcel C., Rousset S., Chany C., Tiollais P. Excretion of hepatitis B surface antigen particles from mouse cells transformed with cloned viral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4549–4553. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eble B. E., Lingappa V. R., Ganem D. Hepatitis B surface antigen: an unusual secreted protein initially synthesized as a transmembrane polypeptide. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1454–1463. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eble B. E., Lingappa V. R., Ganem D. The N-terminal (pre-S2) domain of a hepatitis B virus surface glycoprotein is translocated across membranes by downstream signal sequences. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1414–1419. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1414-1419.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eble B. E., MacRae D. R., Lingappa V. R., Ganem D. Multiple topogenic sequences determine the transmembrane orientation of the hepatitis B surface antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3591–3601. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller S. D. The T=4 envelope of Sindbis virus is organized by interactions with a complementary T=3 capsid. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):923–934. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90701-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganem D., Varmus H. E. The molecular biology of the hepatitis B viruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:651–693. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber M. A., Hadziyannis S., Vissoulis C., Schaffner F., Paronetto F., Popper H. Electron microscopy and immunoelectronmicroscopy of cytoplasmic hepatitis B antigen in hepatocytes. Am J Pathol. 1974 Jun;75(3):489–502. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heermann K. H., Goldmann U., Schwartz W., Seyffarth T., Baumgarten H., Gerlich W. H. Large surface proteins of hepatitis B virus containing the pre-s sequence. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):396–402. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.396-402.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R. B. Pathways of protein secretion in eukaryotes. Science. 1985 Oct 4;230(4721):25–32. doi: 10.1126/science.2994224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroki K., Floreani M., Mimms L. T., Ganem D. Epitope mapping of the PreS1 domain of the hepatitis B virus large surface protein. Virology. 1990 Jun;176(2):620–624. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90032-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroki K., Russnak R., Ganem D. Novel N-terminal amino acid sequence required for retention of a hepatitis B virus glycoprotein in the endoplasmic reticulum. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4459–4466. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patzer E. J., Nakamura G. R., Simonsen C. C., Levinson A. D., Brands R. Intracellular assembly and packaging of hepatitis B surface antigen particles occur in the endoplasmic reticulum. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):884–892. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.884-892.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persing D. H., Varmus H. E., Ganem D. Inhibition of secretion of hepatitis B surface antigen by a related presurface polypeptide. Science. 1986 Dec 12;234(4782):1388–1391. doi: 10.1126/science.3787251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persing D. H., Varmus H. E., Ganem D. The preS1 protein of hepatitis B virus is acylated at its amino terminus with myristic acid. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1672–1677. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1672-1677.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson D. L. The structure of hepatitis B surface antigen and its antigenic sites. Bioessays. 1987 Jun;6(6):258–262. doi: 10.1002/bies.950060604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson H. L. Isolation of noninfectious particles containing Rous sarcoma virus RNA from the medium of Rous sarcoma virus-transformed nonproducer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jun;57(6):1655–1662. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.6.1655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roingeard P., Lu S. L., Sureau C., Freschlin M., Arbeille B., Essex M., Romet-Lemonne J. L. Immunocytochemical and electron microscopic study of hepatitis B virus antigen and complete particle production in hepatitis B virus DNA transfected HepG2 cells. Hepatology. 1990 Feb;11(2):277–285. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840110219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon K., Lingappa V. R., Ganem D. Secreted hepatitis B surface antigen polypeptides are derived from a transmembrane precursor. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 1):2163–2168. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standring D. N., Ou J. H., Rutter W. J. Assembly of viral particles in Xenopus oocytes: pre-surface-antigens regulate secretion of the hepatitis B viral surface envelope particle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9338–9342. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers J., Smith P. M., Horwich A. L. Hepadnavirus envelope proteins regulate covalently closed circular DNA amplification. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2819–2824. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2819-2824.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sureau C., Romet-Lemonne J. L., Mullins J. I., Essex M. Production of hepatitis B virus by a differentiated human hepatoma cell line after transfection with cloned circular HBV DNA. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):37–47. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90364-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]