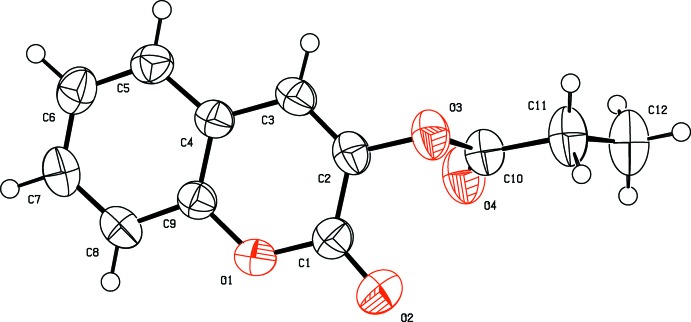
In the title compound, C12H9O4, the dihedral angle between the coumarin ring system and the propionate side chain is 78.48 (8)°.
Keywords: crystal structure, π–π interactions, C—H⋯π interactions, chromane, quantum-chemical calculations
Abstract
In the title compound, C12H10O4, the dihedral angle between the coumarin ring system [maximum deviation = 0.033 (8) Å] and the propionate side chain is 78.48 (8)°. In the crystal, weak C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds generate inversion dimers and and C—H⋯π and π–π interactions link the dimers into a three-dimensional network. A quantum chemical calculation is in good agreement with the observed structure.
Chemical context
Coumarin and its derivatives are widely recognized for their multiple biological activities, including anticancer (Lacy et al., 2004 ▸; Kostova, 2005 ▸), anti-inflammatory (Todeschini et al., 1998 ▸), antiviral (Borges et al., 2005 ▸), antimalarial (Agarwal et al., 2005 ▸) and anticoagulant (Maurer et al., 1998 ▸) properties. As part of our studies in this area, we now describe the synthesis and crystal structure of the title compound, (I).
Structural commentary
In compound (I) (Fig. 1 ▸), the coumarin ring system is almost planar [maximum deviation = 0.033 (1)Å] and is oriented at an angle of 70.84 (8)° with respect to the plane formed by the propanoate group. An inspection of the bond lengths shows that there is a slight asymmetry of the electronic distribution around the coumarin ring: the C2—C3 [1.329 (2) Å] and C2—C1 [1.460 (2) Å] bond lengths are shorter and longer, respectively, than those expected for a Car—Car bond. This suggests that the electron density is preferentially located in the C2—C3 bond at the pyrone ring, as seen in other coumarin-3-carboxamide derivatives (Gomes et al., 2016 ▸).
Figure 1.
The molecular structure of compound (I), with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level.
Supramolecular features
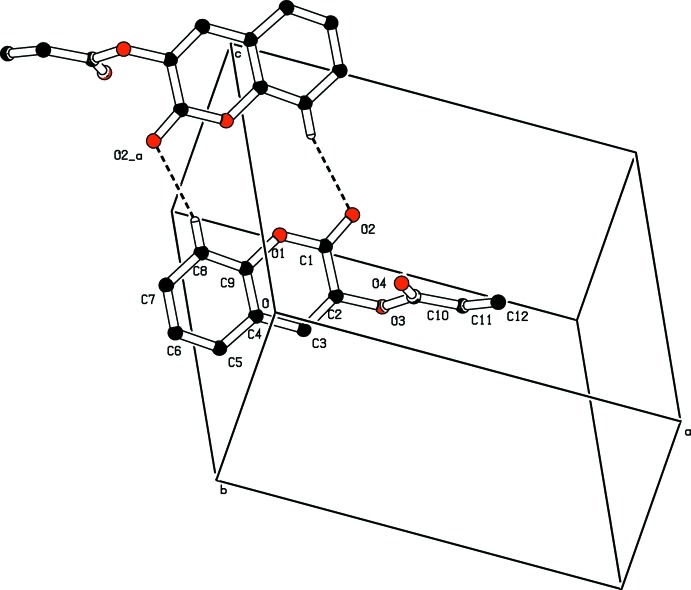
In the crystal, the molecules are linked by pairs of C8—H8⋯O2(x, −y, 1 − z) weak hydrogen bonds to form 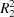 (12) loops, which lie in a chain running along the c axis direction (Fig. 2 ▸). Weak aromatic π–π stacking interactions of 3.7956 (8) Å (Janiak, 2000 ▸) are present between the coumarin pyran ring (centroid Cg1) and benzene ring (centroid Cg2) of symmetry-related (−x, 1 − y, 1 − z) molecules, thus forming a three-dimensional supramolecular network. A weak C—H⋯Cg (π–ring) interaction is also present (Figs. 3 ▸ and 4 ▸, and Table 1 ▸).
(12) loops, which lie in a chain running along the c axis direction (Fig. 2 ▸). Weak aromatic π–π stacking interactions of 3.7956 (8) Å (Janiak, 2000 ▸) are present between the coumarin pyran ring (centroid Cg1) and benzene ring (centroid Cg2) of symmetry-related (−x, 1 − y, 1 − z) molecules, thus forming a three-dimensional supramolecular network. A weak C—H⋯Cg (π–ring) interaction is also present (Figs. 3 ▸ and 4 ▸, and Table 1 ▸).
Figure 2.
View of an inversion dimer linked by a pair of C8—H8⋯O2 (−x, −y, −z + 1) interactions, generating an 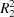 (12) loop. This dimers stack by unit translation along the c axis. H atoms not involved in hydrogen bonding have been omitted.
(12) loop. This dimers stack by unit translation along the c axis. H atoms not involved in hydrogen bonding have been omitted.
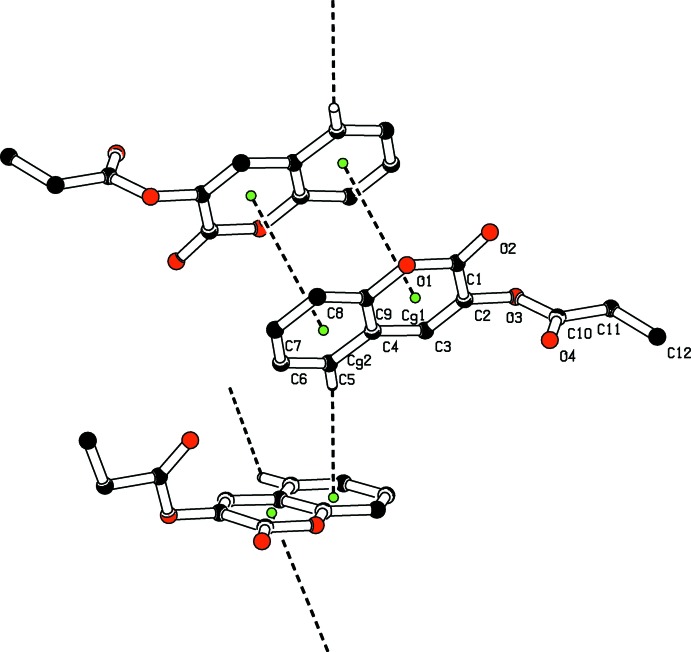
Figure 3.
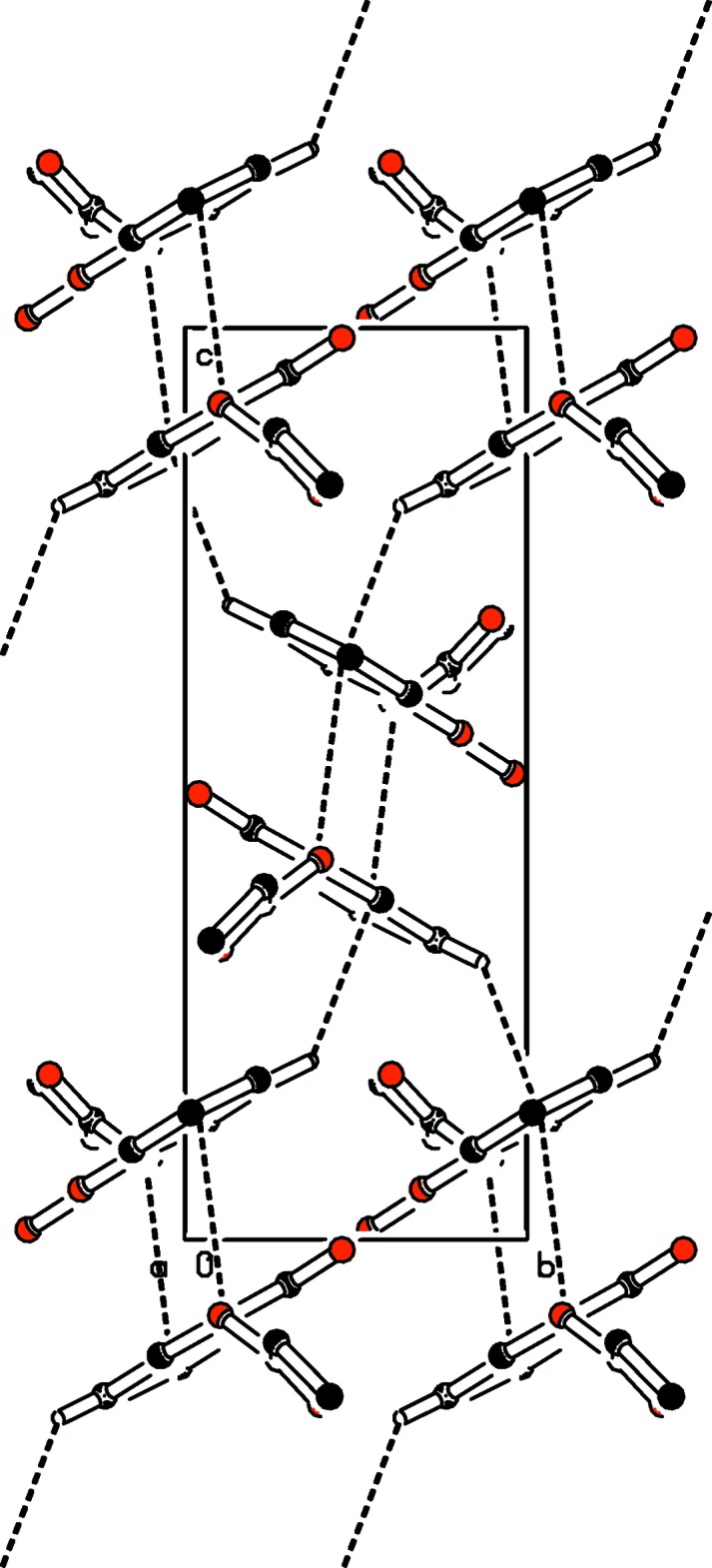
A view of the crystal packing, showing the π–π stacking and C—H⋯π interactions (dashed lines). The green dots are ring centroids. H atoms not involved in the C—H⋯π interactions have been omitted for clarity.
Figure 4.
Part of the crystal structure of (I), showing C—H⋯π and π–π interactions as dashed lines. H atoms have been omitted for clarity.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg2 is the centroid of the C4–C9 ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C8—H8⋯O2i | 0.93 | 2.59 | 3.4783 (19) | 161 |
| C5—H5⋯Cg2ii | 0.93 | 2.78 | 3.4959 (16) | 134 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 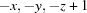 ; (ii)
; (ii) 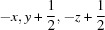 .
.
Theoretical calculations
Quantum-chemical calculations were performed to compare with the experimental analysis. An ab-initio Hartree–Fock (HF) method was used with the standard basis set of 6-31G using the GAUSSIAN03 software package (Frisch et al., 2004 ▸; Dennington et al., 2007 ▸) to obtain the optimized molecular structure. The computational results are in good agreement with the experimental crystallographic data (Table 2 ▸).
Table 2. Experimental and calculated bond lengths (Å).
| Bond | X-ray | HF(6–31G) |
|---|---|---|
| O1—C1 | 1.3628 (17) | 1.371 |
| O1—C9 | 1.3769 (17) | 1.378 |
| O2—C1 | 1.2004 (18) | 1.227 |
| O3—C10 | 1.3713 (18) | 1.359 |
| O3—C2 | 1.3893 (17) | 1.381 |
| O4—C10 | 1.1932 (19) | 1.21 |
| C1—C2 | 1.460 (2) | 1.468 |
| C2—C3 | 1.329 (2) | 1.355 |
| C3—C4 | 1.4403 (19) | 1.441 |
| C4—C5 | 1.401 (2) | 1.406 |
| C4—C9 | 1.3928 (18) | 1.407 |
| C5—C6 | 1.370 (2) | 1.387 |
| C6—C7 | 1.386 (2) | 1.395 |
| C7—C8 | 1.379 (2) | 1.383 |
| C8—C9 | 1.3842 (19) | 1.408 |
| C10—C11 | 1.495 (2) | 1.497 |
| C11—C12 | 1.491 (3) | 1.525 |
Synthesis and crystallization
In a 100 ml round-necked flask topped with a water condenser were introduced successively 25 ml of dried diethyl ether, 6.17 × 10 −3 mol (≃ 0.8 ml) of propionic anhydride and 2.35 ml (4.7 molar equivalents) of dried pyridine. While stirring strongly, 6.17 × 10−3 mol (1 g) of 3-hydroxycoumarin was added in small portions over 30 min. The reaction mixture was left under agitation at room temperature for 3 h. The mixture was then poured in a separating funnel containing 40 ml of chloroform and washed with diluted hydrochloric acid solution until the pH was 2–3. The organic layer was extracted, washed with water to neutrality, dried over MgSO4 and the solvent removed. The resulting precipitate (crude product) was filtered off with petroleum ether and recrystallized from a solvent mixture of chloroform–hexane (1/3, v/v). Colourless prisms of the title compound were obtained in a yield of 65%, m. p. = 351–353 K.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 3 ▸. H atoms were placed in calculated positions [C—H = 0.93 (aromatic), 0.96 (methyl) or 0.97 Å (methylene)] and refined using a riding-model approximation with U iso(H) constrained to 1.2 (aromatic and methylene group) or 1.5 (methyl group) times U eq of the respective parent atom.
Table 3. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C12H10O4 |
| M r | 218.20 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/c |
| Temperature (K) | 293 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 12.1179 (4), 5.7243 (2), 15.3275 (5) |
| β (°) | 94.881 (3) |
| V (Å3) | 1059.36 (6) |
| Z | 4 |
| Radiation type | Cu Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.87 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.46 × 0.16 × 0.08 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Agilent SuperNova Dual (Cu at zero) Source diffractometer with an AtlasS2 detector |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2014 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.778, 1.000 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 6028, 1930, 1655 |
| R int | 0.020 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.605 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.038, 0.117, 1.06 |
| No. of reflections | 1930 |
| No. of parameters | 145 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.16, −0.16 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, New_Global_Publ_Block. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016015279/hb7613sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016015279/hb7613Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016015279/hb7613Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1507161
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Spectropole Service of the faculty of Sciences (Aix-Marseille, France) for the use of the diffractometer and the NMR and MS spectrometers.
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| C12H10O4 | F(000) = 456 |
| Mr = 218.20 | Dx = 1.368 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Melting point: 351 K |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54184 Å |
| a = 12.1179 (4) Å | Cell parameters from 3028 reflections |
| b = 5.7243 (2) Å | θ = 5.8–68.6° |
| c = 15.3275 (5) Å | µ = 0.87 mm−1 |
| β = 94.881 (3)° | T = 293 K |
| V = 1059.36 (6) Å3 | Prism, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.46 × 0.16 × 0.08 mm |
Data collection
| Agilent SuperNova Dual (Cu at zero) Source diffractometer with an AtlasS2 detector | 1930 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: sealed X-ray tube | 1655 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Mirror monochromator | Rint = 0.020 |
| Detector resolution: 5.3048 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 68.9°, θmin = 3.7° |
| ω scan | h = −14→14 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2014) | k = −6→6 |
| Tmin = 0.778, Tmax = 1.000 | l = −15→18 |
| 6028 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.038 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.117 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.06 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0631P)2 + 0.1085P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 1930 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 145 parameters | Δρmax = 0.16 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.16 e Å−3 |
| 40 constraints |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.08845 (8) | 0.19504 (17) | 0.44462 (6) | 0.0505 (3) | |
| O3 | 0.36752 (8) | 0.39585 (19) | 0.41680 (7) | 0.0567 (3) | |
| C9 | 0.02550 (11) | 0.3708 (2) | 0.40435 (8) | 0.0426 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.25245 (11) | 0.3964 (2) | 0.40998 (9) | 0.0466 (3) | |
| C3 | 0.19407 (11) | 0.5719 (2) | 0.37284 (8) | 0.0455 (3) | |
| H3 | 0.2298 | 0.6985 | 0.3497 | 0.055* | |
| C4 | 0.07494 (11) | 0.5644 (2) | 0.36879 (8) | 0.0420 (3) | |
| C8 | −0.08834 (12) | 0.3450 (3) | 0.40123 (9) | 0.0521 (3) | |
| H8 | −0.1198 | 0.2150 | 0.4258 | 0.063* | |
| C1 | 0.20130 (12) | 0.1982 (2) | 0.45088 (9) | 0.0492 (3) | |
| O4 | 0.36176 (9) | 0.1032 (2) | 0.31915 (8) | 0.0683 (3) | |
| O2 | 0.24985 (10) | 0.0406 (2) | 0.48893 (8) | 0.0695 (3) | |
| C5 | 0.00553 (12) | 0.7361 (2) | 0.32863 (9) | 0.0497 (3) | |
| H5 | 0.0362 | 0.8676 | 0.3045 | 0.060* | |
| C6 | −0.10727 (13) | 0.7114 (3) | 0.32463 (10) | 0.0566 (4) | |
| H6 | −0.1527 | 0.8257 | 0.2975 | 0.068* | |
| C7 | −0.15398 (12) | 0.5169 (3) | 0.36080 (10) | 0.0567 (4) | |
| H7 | −0.2306 | 0.5022 | 0.3578 | 0.068* | |
| C10 | 0.41542 (12) | 0.2272 (3) | 0.36892 (10) | 0.0530 (3) | |
| C11 | 0.53858 (13) | 0.2315 (4) | 0.38698 (13) | 0.0728 (5) | |
| H11A | 0.5644 | 0.3905 | 0.3808 | 0.087* | |
| H11B | 0.5576 | 0.1839 | 0.4471 | 0.087* | |
| C12 | 0.59736 (16) | 0.0768 (5) | 0.32791 (15) | 0.0858 (6) | |
| H12A | 0.6758 | 0.0871 | 0.3428 | 0.129* | |
| H12B | 0.5806 | 0.1252 | 0.2683 | 0.129* | |
| H12C | 0.5736 | −0.0817 | 0.3346 | 0.129* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0500 (5) | 0.0463 (5) | 0.0557 (5) | −0.0037 (4) | 0.0068 (4) | 0.0091 (4) |
| O3 | 0.0398 (5) | 0.0614 (6) | 0.0686 (6) | −0.0025 (4) | 0.0019 (4) | −0.0145 (5) |
| C9 | 0.0453 (7) | 0.0438 (6) | 0.0394 (6) | −0.0015 (5) | 0.0069 (5) | −0.0014 (5) |
| C2 | 0.0395 (7) | 0.0505 (7) | 0.0499 (7) | −0.0036 (5) | 0.0052 (5) | −0.0083 (5) |
| C3 | 0.0468 (7) | 0.0425 (7) | 0.0485 (7) | −0.0072 (5) | 0.0109 (5) | −0.0037 (5) |
| C4 | 0.0459 (7) | 0.0411 (6) | 0.0398 (6) | −0.0018 (5) | 0.0083 (5) | −0.0037 (5) |
| C8 | 0.0473 (7) | 0.0570 (8) | 0.0535 (7) | −0.0083 (6) | 0.0125 (6) | −0.0022 (6) |
| C1 | 0.0506 (7) | 0.0490 (7) | 0.0479 (7) | 0.0031 (6) | 0.0034 (5) | 0.0009 (6) |
| O4 | 0.0510 (6) | 0.0805 (8) | 0.0730 (7) | −0.0006 (5) | 0.0025 (5) | −0.0238 (6) |
| O2 | 0.0665 (7) | 0.0669 (7) | 0.0749 (7) | 0.0122 (6) | 0.0041 (6) | 0.0197 (6) |
| C5 | 0.0575 (8) | 0.0450 (7) | 0.0474 (7) | 0.0025 (6) | 0.0100 (6) | 0.0013 (5) |
| C6 | 0.0548 (8) | 0.0611 (9) | 0.0540 (7) | 0.0145 (7) | 0.0065 (6) | −0.0010 (6) |
| C7 | 0.0411 (7) | 0.0715 (9) | 0.0584 (8) | 0.0027 (6) | 0.0097 (6) | −0.0069 (7) |
| C10 | 0.0450 (8) | 0.0594 (8) | 0.0545 (7) | 0.0007 (6) | 0.0038 (6) | −0.0053 (6) |
| C11 | 0.0430 (8) | 0.0917 (13) | 0.0829 (11) | 0.0053 (8) | −0.0003 (7) | −0.0168 (10) |
| C12 | 0.0526 (10) | 0.1094 (16) | 0.0951 (13) | 0.0179 (10) | 0.0050 (9) | −0.0168 (12) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C1 | 1.3628 (17) | O4—C10 | 1.1932 (19) |
| O1—C9 | 1.3769 (17) | C5—C6 | 1.370 (2) |
| O3—C10 | 1.3713 (18) | C5—H5 | 0.9300 |
| O3—C2 | 1.3893 (17) | C6—C7 | 1.386 (2) |
| C9—C8 | 1.3842 (19) | C6—H6 | 0.9300 |
| C9—C4 | 1.3926 (18) | C7—H7 | 0.9300 |
| C2—C3 | 1.329 (2) | C10—C11 | 1.495 (2) |
| C2—C1 | 1.460 (2) | C11—C12 | 1.491 (3) |
| C3—C4 | 1.4403 (19) | C11—H11A | 0.9700 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C11—H11B | 0.9700 |
| C4—C5 | 1.401 (2) | C12—H12A | 0.9600 |
| C8—C7 | 1.379 (2) | C12—H12B | 0.9600 |
| C8—H8 | 0.9300 | C12—H12C | 0.9600 |
| C1—O2 | 1.2004 (18) | ||
| C1—O1—C9 | 122.43 (10) | C4—C5—H5 | 119.8 |
| C10—O3—C2 | 115.41 (11) | C5—C6—C7 | 120.31 (14) |
| O1—C9—C8 | 116.74 (12) | C5—C6—H6 | 119.8 |
| O1—C9—C4 | 121.11 (12) | C7—C6—H6 | 119.8 |
| C8—C9—C4 | 122.15 (13) | C8—C7—C6 | 120.90 (14) |
| C3—C2—O3 | 121.88 (12) | C8—C7—H7 | 119.6 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 122.80 (12) | C6—C7—H7 | 119.6 |
| O3—C2—C1 | 115.22 (12) | O4—C10—O3 | 121.89 (13) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 119.40 (12) | O4—C10—C11 | 127.56 (15) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.3 | O3—C10—C11 | 110.52 (13) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.3 | C12—C11—C10 | 113.50 (15) |
| C9—C4—C5 | 117.88 (12) | C12—C11—H11A | 108.9 |
| C9—C4—C3 | 118.03 (12) | C10—C11—H11A | 108.9 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 124.05 (12) | C12—C11—H11B | 108.9 |
| C7—C8—C9 | 118.32 (13) | C10—C11—H11B | 108.9 |
| C7—C8—H8 | 120.8 | H11A—C11—H11B | 107.7 |
| C9—C8—H8 | 120.8 | C11—C12—H12A | 109.5 |
| O2—C1—O1 | 118.14 (13) | C11—C12—H12B | 109.5 |
| O2—C1—C2 | 125.74 (14) | H12A—C12—H12B | 109.5 |
| O1—C1—C2 | 116.12 (12) | C11—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 120.43 (13) | H12A—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.8 | H12B—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| C1—O1—C9—C8 | 179.07 (12) | C9—O1—C1—C2 | −1.73 (18) |
| C1—O1—C9—C4 | −0.99 (18) | C3—C2—C1—O2 | −176.26 (14) |
| C10—O3—C2—C3 | −113.91 (15) | O3—C2—C1—O2 | 0.3 (2) |
| C10—O3—C2—C1 | 69.53 (17) | C3—C2—C1—O1 | 3.69 (19) |
| O3—C2—C3—C4 | −179.09 (11) | O3—C2—C1—O1 | −179.78 (10) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −2.8 (2) | C9—C4—C5—C6 | −0.27 (19) |
| O1—C9—C4—C5 | 179.85 (11) | C3—C4—C5—C6 | 177.46 (12) |
| C8—C9—C4—C5 | −0.21 (19) | C4—C5—C6—C7 | 0.4 (2) |
| O1—C9—C4—C3 | 1.98 (17) | C9—C8—C7—C6 | −0.4 (2) |
| C8—C9—C4—C3 | −178.08 (12) | C5—C6—C7—C8 | −0.1 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C9 | −0.08 (18) | C2—O3—C10—O4 | 6.2 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −177.81 (12) | C2—O3—C10—C11 | −175.47 (14) |
| O1—C9—C8—C7 | −179.53 (12) | O4—C10—C11—C12 | 6.5 (3) |
| C4—C9—C8—C7 | 0.5 (2) | O3—C10—C11—C12 | −171.65 (17) |
| C9—O1—C1—O2 | 178.23 (13) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg2 is the centroid of the C4–C9 ring.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C8—H8···O2i | 0.93 | 2.59 | 3.4783 (19) | 161 |
| C5—H5···Cg2ii | 0.93 | 2.78 | 3.4959 (16) | 134 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, −y, −z+1; (ii) −x, y+1/2, −z+1/2.
References
- Agarwal, A., Srivastava, K., Puri, S. K. & Chauhan, P. M. S. (2005). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 13, 4645–4650. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Agilent. (2014). CrysAlis PRO. Agilent Technologies Ltd, Yarnton, England.
- Borges, F., Roleira, F., Milhazes, N., Santana, L. & Uriarte, E. (2005). Curr. Med. Chem. 12, 887–916. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Dennington, R., Keith, T. & Millam, J. (2007). Gaussview4.1. Semichem Inc., Shawnee Mission, KS, USA.
- Frisch, M. J., et al. (2004). GAUSSIAN03. Gaussian Inc., Wallingford, CT, USA.
- Gomes, L. R., Low, J. N., Fonseca, A., Matos, M. J. & Borges, F. (2016). Acta Cryst. E72, 926–932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Janiak, C. (2000). J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. pp. 3885–3896.
- Kostova, I. (2005). Curr. Med. Chem. Anticancer Agents, 5, 29–46. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Lacy, A. & O’Kennedy, R. (2004). Curr. Pharm. Des. 10, 3797–3811. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Maurer, H. H. & Arlt, J. W. (1998). J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 714, 181–195. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Todeschini, A. R., de Miranda, A. L. P., da Silva, K. C. M., Parrini, S. C. & Barreiro, E. J. (1998). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 33, 189–199.
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst. 43, 920–925.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, New_Global_Publ_Block. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016015279/hb7613sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016015279/hb7613Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016015279/hb7613Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1507161
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report