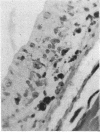
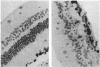
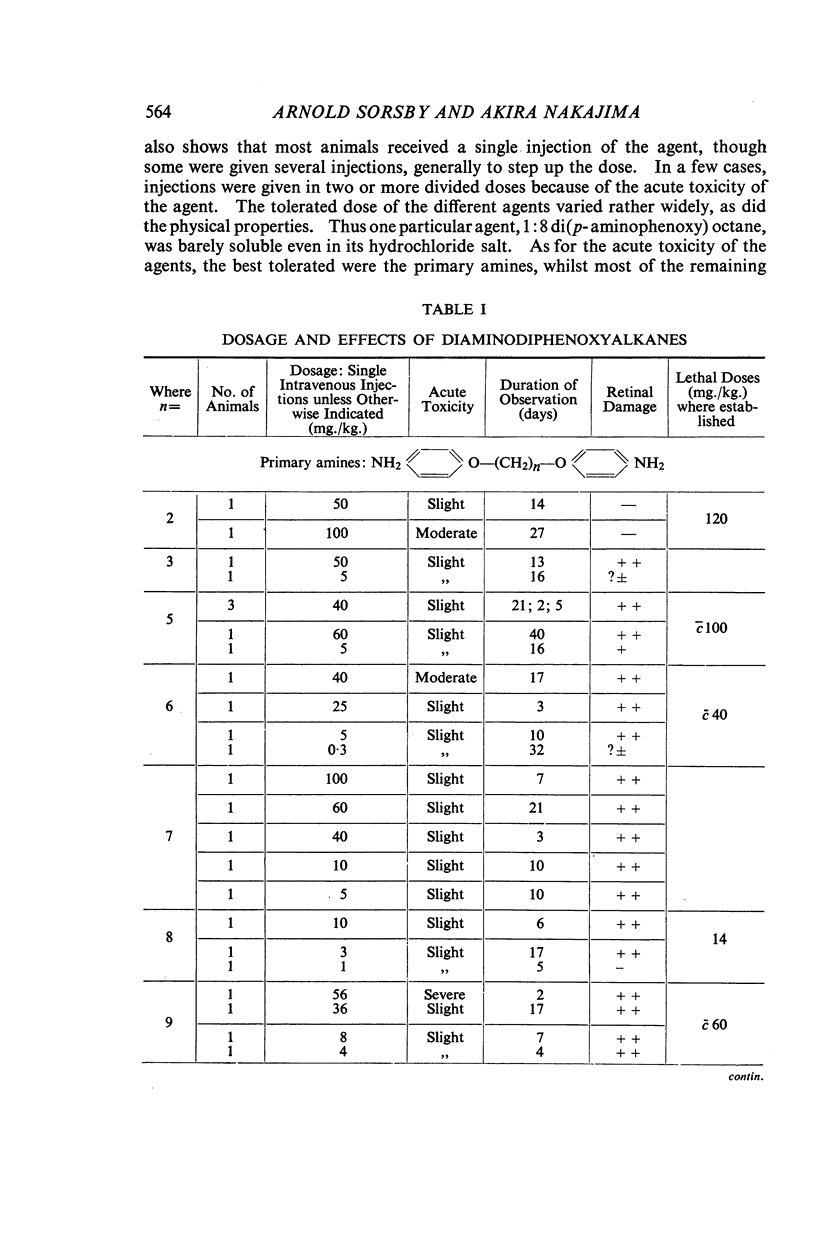
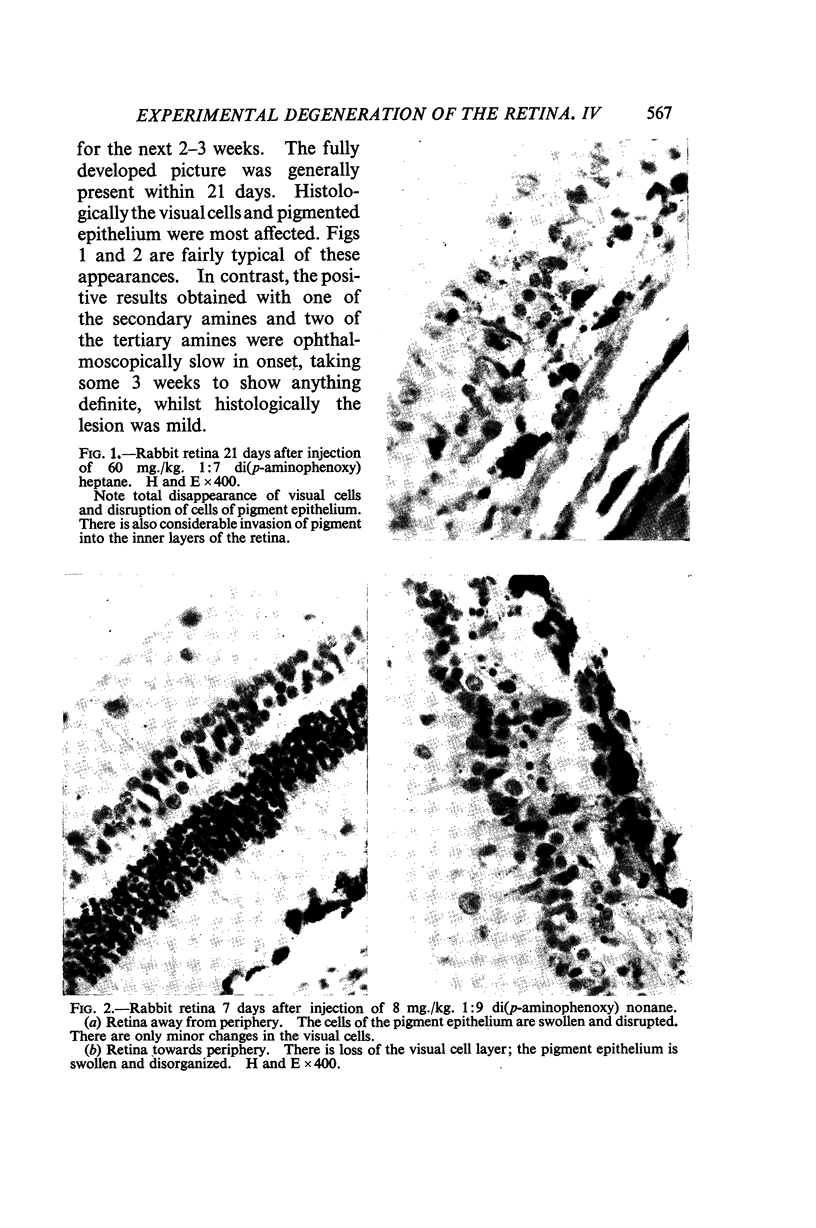
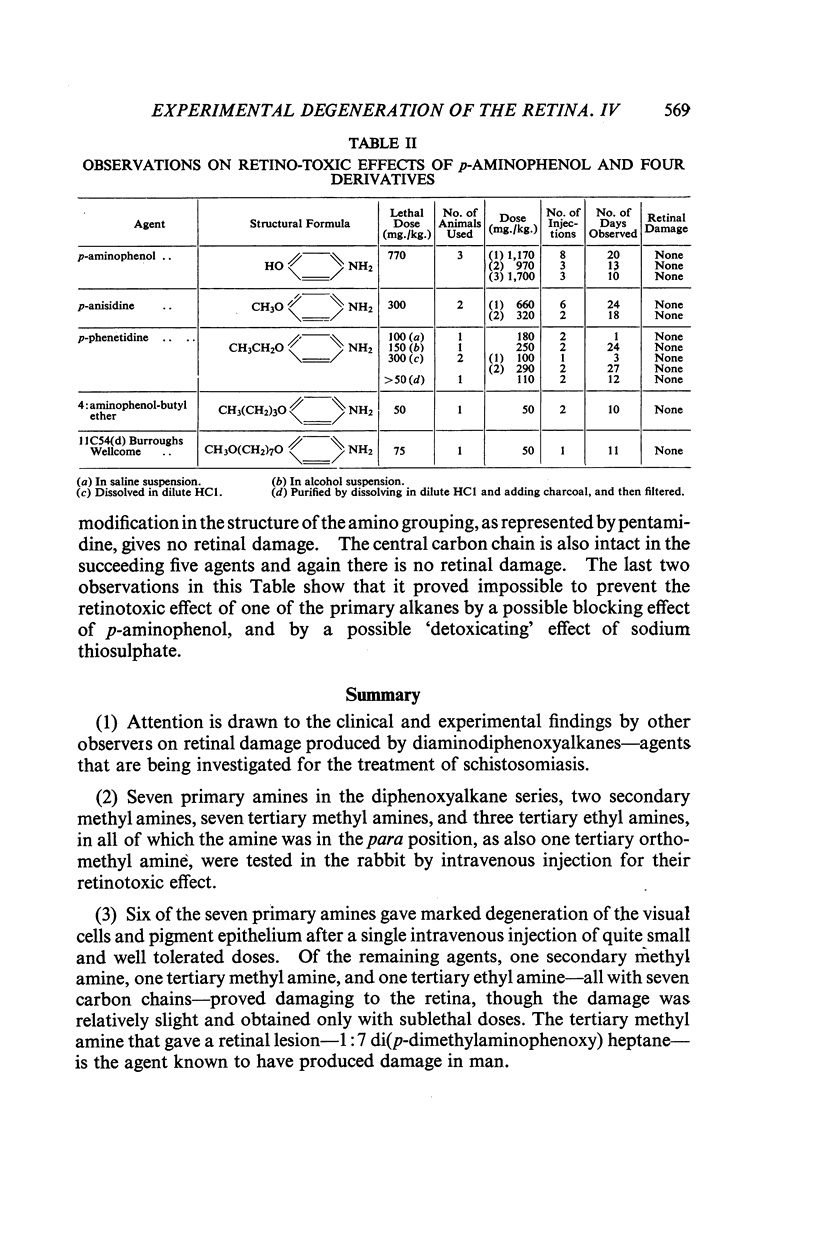
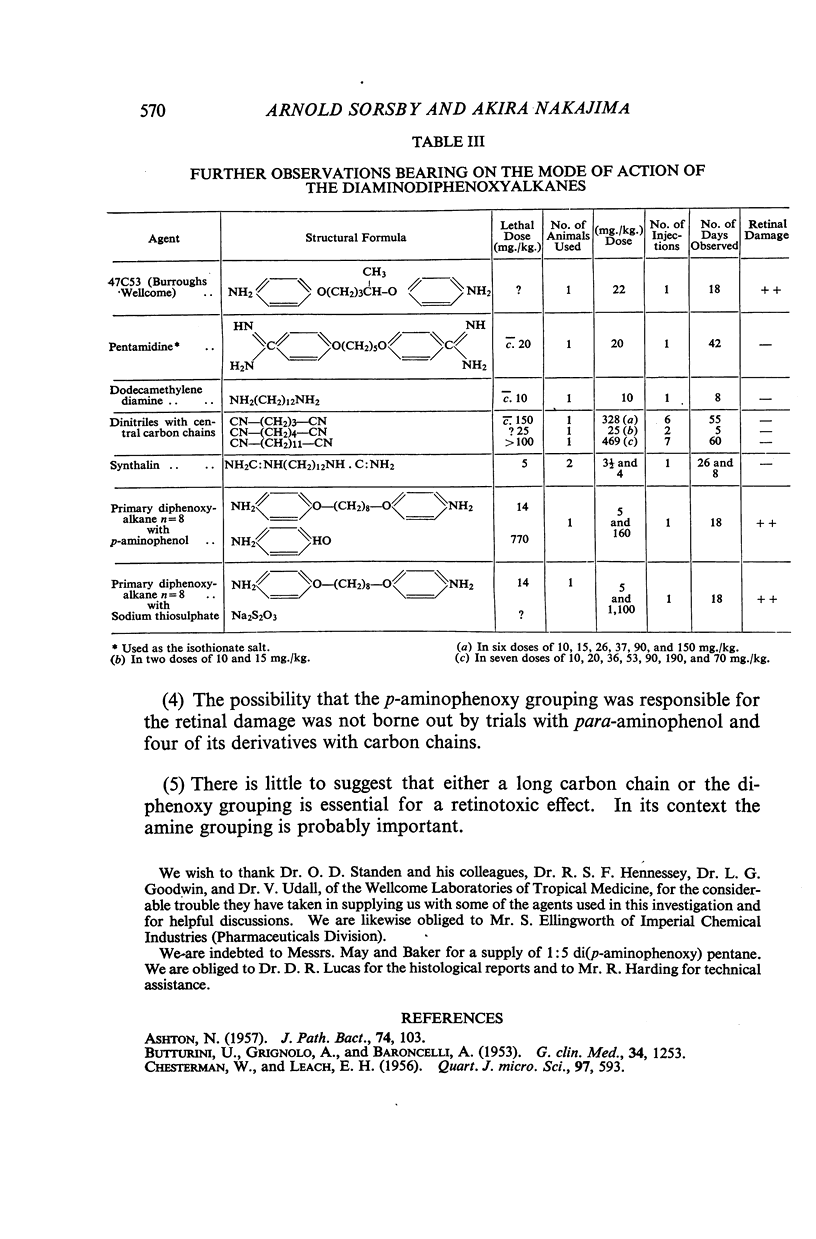
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BUTTURINI U., GRIGNOLO A., BARONCHELLI A. Diabete da ditizone: aspetti metabolici, oculari ed istologici. G Clin Med. 1953 Nov;34(11):1253–1347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDGE N. D., MASON D. F., WIEN R. Pharmacological effects of certain diaminodiphenoxy alkanes. Nature. 1956 Oct 13;178(4537):806–807. doi: 10.1038/178806a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODWIN L. G., RICHARDS W. H., UDALL V. The toxicity of diaminodiphenoxyalkanes. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1957 Dec;12(4):468–474. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1957.tb00167.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUCAS D. R., NEWHOUSE J. P., DAVEY J. B. Experimental degeneration of the retina. II. The lesion produced by bromoacetate: ophthalmoscopic and histological features. Br J Ophthalmol. 1957 May;41(5):313–316. doi: 10.1136/bjo.41.5.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOELL W. K. The effect of iodoacetate on the vertebrate retina. J Cell Physiol. 1951 Apr;37(2):283–307. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030370209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHUBERT G., BORNSCHEIN H. Spezifische Schädigung von Netzhautelementen durch Jodazetat. Experientia. 1951 Dec;7(12):461–462. doi: 10.1007/BF02168694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SORSBY A., NEWHOUSE J. P., LUCAS D. R. Experimental degeneration of the retina. I. Thiol reactors as inducing agents. Br J Ophthalmol. 1957 May;41(5):309–312. doi: 10.1136/bjo.41.5.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]