Abstract
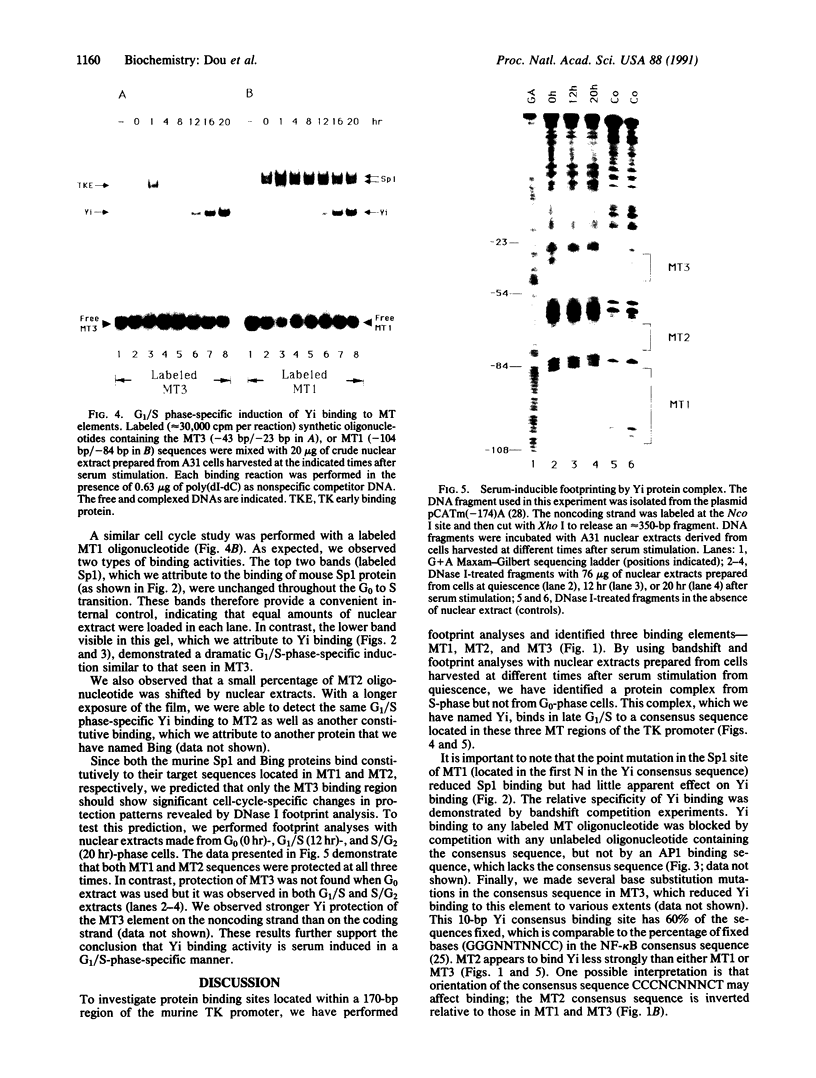
By performing DNase I footprint and band-shift analyses of a 170-base-pair region of the murine thymidine kinase promoter, we identified an inducible DNA binding activity that we named Yi. Yi binding activity was not detected in G0 and G1 extracts, but it was observed as cells crossed the G1/S boundary. Yi proteins bind specifically to a consensus sequence (CCCNCNNNCT) found at three distinct sites in this promoter region. We also observed a murine Sp1 binding activity that was constitutive throughout the cell cycle. We propose that the G1/S-specific Yi binding is important for murine thymidine kinase gene regulation and perhaps also for initiation of DNA synthesis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arcot S. S., Flemington E. K., Deininger P. L. The human thymidine kinase gene promoter. Deletion analysis and specific protein binding. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 5;264(4):2343–2349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. W., Dou Q. P., Fridovich-Keil J. L., Pardee A. B. Transformed and nontransformed cells differ in stability and cell cycle regulation of a binding activity to the murine thymidine kinase promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9310–9314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppock D. L., Pardee A. B. Regulation of thymidine kinase activity in the cell cycle by a labile protein. J Cell Physiol. 1985 Aug;124(2):269–274. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041240215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croy R. G., Pardee A. B. Enhanced synthesis and stabilization of Mr 68,000 protein in transformed BALB/c-3T3 cells: candidate for restriction point control of cell growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4699–4703. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flemington E., Bradshaw H. D., Jr, Traina-Dorge V., Slagel V., Deininger P. L. Sequence, structure and promoter characterization of the human thymidine kinase gene. Gene. 1987;52(2-3):267–277. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90053-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudas J. M., Knight G. B., Pardee A. B. Nuclear posttranscriptional processing of thymidine kinase mRNA at the onset of DNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4705–4709. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Carner K. R., Masiarz F. R., Tjian R. Isolation of cDNA encoding transcription factor Sp1 and functional analysis of the DNA binding domain. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1079–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90594-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Tjian R. Affinity purification of sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5889–5893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. K., Wells S., Lau Y. F., Lee A. S. Sequences contained within the promoter of the human thymidine kinase gene can direct cell-cycle regulation of heterologous fusion genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5894–5898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight G. B., Gudas J. M., Pardee A. B. Cell-cycle-specific interaction of nuclear DNA-binding proteins with a CCAAT sequence from the human thymidine kinase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8350–8354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W., Mitchell P., Tjian R. Purified transcription factor AP-1 interacts with TPA-inducible enhancer elements. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90612-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M. J., Baltimore D. NF-kappa B: a pleiotropic mediator of inducible and tissue-specific gene control. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):227–229. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90833-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letovsky J., Dynan W. S. Measurement of the binding of transcription factor Sp1 to a single GC box recognition sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 11;17(7):2639–2653. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.7.2639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman H. B., Lin P. F., Yeh D. B., Ruddle F. H. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional mechanisms regulate murine thymidine kinase gene expression in serum-stimulated cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5280–5291. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin P. F., Lieberman H. B., Yeh D. B., Xu T., Zhao S. Y., Ruddle F. H. Molecular cloning and structural analysis of murine thymidine kinase genomic and cDNA sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):3149–3156. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.3149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipson K. E., Chen S. T., Koniecki J., Ku D. H., Baserga R. S-phase-specific regulation by deletion mutants of the human thymidine kinase promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6848–6852. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscovitis G., Pardee A. B. Citric acid arrest and stabilization of nucleoside incorporation into cultured cells. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jan 1;101(1):221–224. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90064-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardee A. B. G1 events and regulation of cell proliferation. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):603–608. doi: 10.1126/science.2683075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roehl H. H., Conrad S. E. Identification of a G1-S-phase-regulated region in the human thymidine kinase gene promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3834–3837. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiser C., Knöfler M., Rudelstorfer I., Haas R., Wintersberger E. Mouse thymidine kinase: the promoter sequence and the gene and pseudogene structures in normal cells and in thymidine kinase deficient mutants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 11;17(1):185–195. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.1.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherley J. L., Kelly T. J. Regulation of human thymidine kinase during the cell cycle. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):8350–8358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travali S., Lipson K. E., Jaskulski D., Lauret E., Baserga R. Role of the promoter in the regulation of the thymidine kinase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1551–1557. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang H. C., Pardee A. B. Insulin-like growth factor I regulation of transcription and replicating enzyme induction necessary for DNA synthesis. J Cell Physiol. 1986 Jun;127(3):410–416. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041270309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]