Abstract
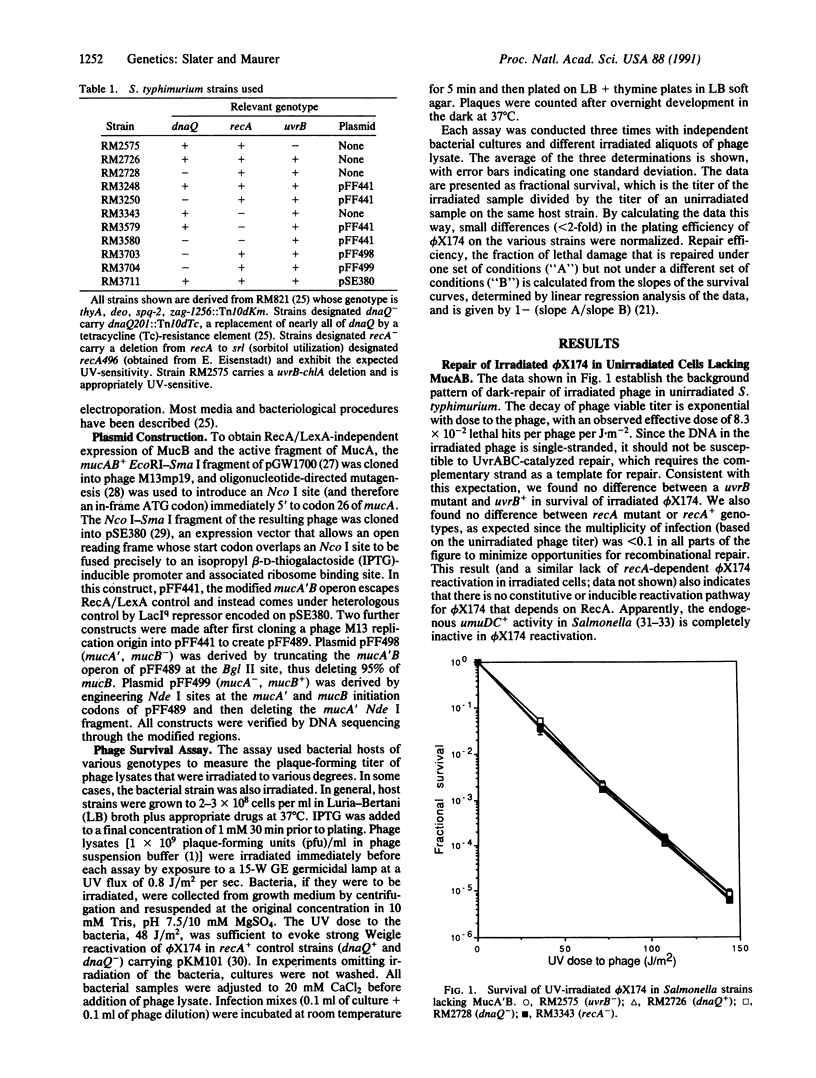
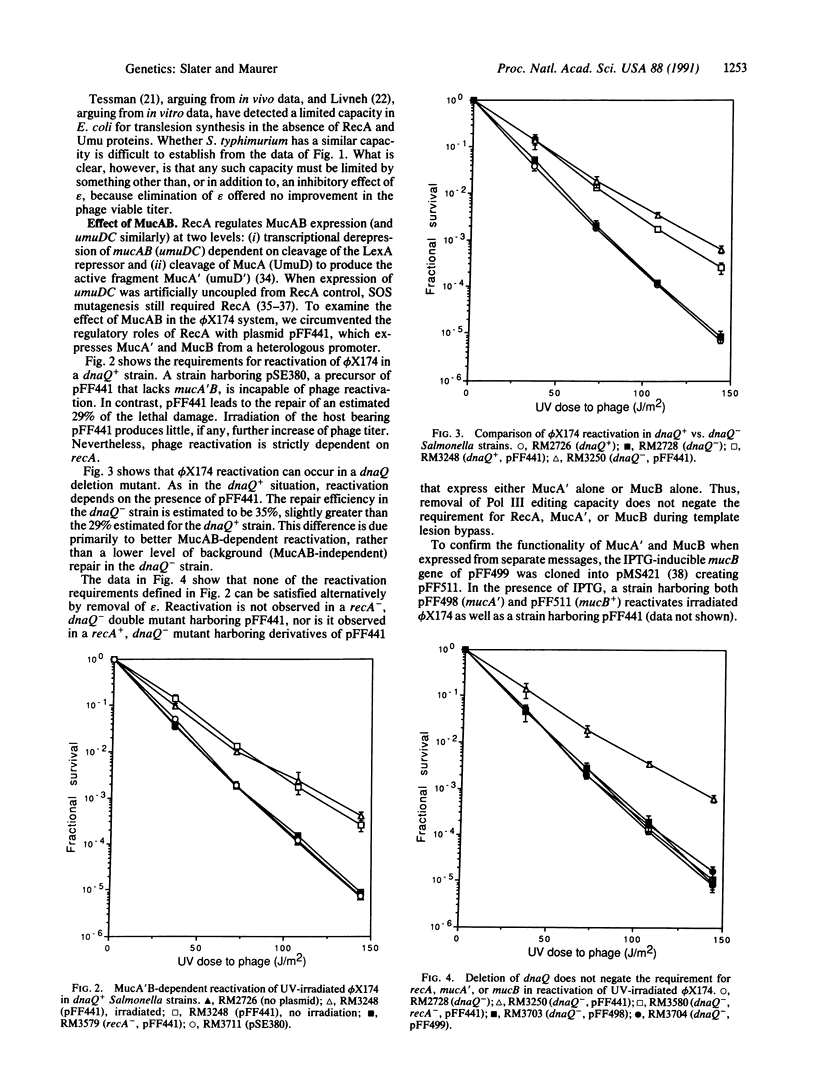
According to the current model for mutagenic bypass of UV-induced lesions, efficient bypass requires three proteins: activated RecA (RecA*) and either activated UmuD (UmuD') and UmuC or their plasmid-encoded analogues, MucA' and MucB. RecA* aids synthesis of UmuD' and UmuC (and MucA'/MucB) at two levels: by inactivation of the LexA transcriptional repressor of these genes and by cleavage of UmuD (and MucA) to produce the active fragments, UmuD' (MucA'). A third role for RecA is revealed when these two roles are otherwise satisfied in a suitably engineered strain. An often-suggested possible role for RecA in bypass is inhibition of editing by the epsilon subunit of DNA polymerase III. Here, by demonstrating that elimination of epsilon by deletion of its gene, dnaQ, does not relieve the requirement for the third function of RecA, we show that RecA must perform some function other than, or in addition to, inhibition of epsilon. We also show that elimination of epsilon does not relieve the requirement for either Muc protein. Moreover, we observed reactivation of irradiated phi X174 in unirradiated cells expressing MucA' and MucB. This finding makes it unlikely that the additional role of recA involves derepression of an unidentified gene or cleavage of an unidentified protein and makes it more likely that RecA participates directly in bypass.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bridges B. A., Woodgate R., Ruiz-Rubio M., Sharif F., Sedgwick S. G., Hübscher U. Current understanding of UV-induced base pair substitution mutation in E. coli with particular reference to the DNA polymerase III complex. Mutat Res. 1987 Dec;181(2):219–226. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(87)90099-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J. Superpolylinkers in cloning and expression vectors. DNA. 1989 Dec;8(10):759–777. doi: 10.1089/dna.1989.8.759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caillet-Fauquet P., Defais M., Radman M. Molecular mechanisms of induced mutagenesis. Replication in vivo of bacteriophage phiX174 single-stranded, ultraviolet light-irradiated DNA in intact and irradiated host cells. J Mol Biol. 1977 Nov 25;117(1):95–110. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90025-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen J. R., LeClerc J. E., Tata P. V., Christensen R. B., Lawrence C. W. UmuC function is not essential for the production of all targeted lacI mutations induced by ultraviolet light. J Mol Biol. 1988 Oct 5;203(3):635–641. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90198-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciesla Z., Jonczyk P., Fijalkowska I. Effect of enhanced synthesis of the epsilon subunit of DNA polymerase III on spontaneous and UV-induced mutagenesis of the Escherichia coli glyU gene. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Apr;221(2):251–255. doi: 10.1007/BF00261728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Ari R., Huisman O. DNA replication and indirect induction of the SOS response in Escherichia coli. Biochimie. 1982 Aug-Sep;64(8-9):623–627. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(82)80100-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutreix M., Moreau P. L., Bailone A., Galibert F., Battista J. R., Walker G. C., Devoret R. New recA mutations that dissociate the various RecA protein activities in Escherichia coli provide evidence for an additional role for RecA protein in UV mutagenesis. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2415–2423. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2415-2423.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S., Griffith J., Kornberg A. phiX174 cistron A protein is a multifunctional enzyme in DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3198–3202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ennis D. G., Ossanna N., Mount D. W. Genetic separation of Escherichia coli recA functions for SOS mutagenesis and repressor cleavage. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2533–2541. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2533-2541.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fersht A. R., Knill-Jones J. W. Contribution of 3' leads to 5' exonuclease activity of DNA polymerase III holoenzyme from Escherichia coli to specificity. J Mol Biol. 1983 Apr 25;165(4):669–682. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80273-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster P. L., Sullivan A. D., Franklin S. B. Presence of the dnaQ-rnh divergent transcriptional unit on a multicopy plasmid inhibits induced mutagenesis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3144–3151. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3144-3151.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster P. L., Sullivan A. D. Interactions between epsilon, the proofreading subunit of DNA polymerase III, and proteins involved in the SOS response of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Nov;214(3):467–473. doi: 10.1007/BF00330482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freitag N., McEntee K. "Activated"-RecA protein affinity chromatography of LexA repressor and other SOS-regulated proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8363–8367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigliani F., Sporeno E., Perri S., Battaglia P. A. The uvp1 gene of plasmid pR cooperates with mucAB genes in the DNA repair process. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Jul;218(1):18–24. doi: 10.1007/BF00330560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graña D., Gardella T., Susskind M. M. The effects of mutations in the ant promoter of phage P22 depend on context. Genetics. 1988 Oct;120(2):319–327. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.2.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera G., Urios A., Aleixandre V., Blanco M. UV-light-induced mutability in Salmonella strains containing the umuDC or the mucAB operon: evidence for a umuC function. Mutat Res. 1988 Mar;198(1):9–13. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(88)90034-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard-Flanders P., Boyce R. P. DNA repair and genetic recombination: studies on mutants of Escherichia coli defective in these processes. Radiat Res. 1966;(Suppl):156+–156+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda J. E., Yudelevich A., Hurwitz J. Isolation and characterization of the protein coded by gene A of bacteriophage phiX174 DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2669–2673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonczyk P., Fijalkowska I., Ciesla Z. Overproduction of the epsilon subunit of DNA polymerase III counteracts the SOS mutagenic response of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9124–9127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancy E. D., Lifsics M. R., Kehres D. G., Maurer R. Isolation and characterization of mutants with deletions in dnaQ, the gene for the editing subunit of DNA polymerase III in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5572–5580. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5572-5580.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancy E. D., Lifsics M. R., Munson P., Maurer R. Nucleotide sequences of dnaE, the gene for the polymerase subunit of DNA polymerase III in Salmonella typhimurium, and a variant that facilitates growth in the absence of another polymerase subunit. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5581–5586. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5581-5586.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livneh Z. Mechanism of replication of ultraviolet-irradiated single-stranded DNA by DNA polymerase III holoenzyme of Escherichia coli. Implications for SOS mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9526–9533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livneh Z. Replication of UV-irradiated single-stranded DNA by DNA polymerase III holoenzyme of Escherichia coli: evidence for bypass of pyrimidine photodimers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4599–4603. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu C., Echols H. RecA protein and SOS. Correlation of mutagenesis phenotype with binding of mutant RecA proteins to duplex DNA and LexA cleavage. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 5;196(3):497–504. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90027-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu C., Scheuermann R. H., Echols H. Capacity of RecA protein to bind preferentially to UV lesions and inhibit the editing subunit (epsilon) of DNA polymerase III: a possible mechanism for SOS-induced targeted mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):619–623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh L., Walker G. C. New phenotypes associated with mucAB: alteration of a MucA sequence homologous to the LexA cleavage site. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):1818–1823. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.1818-1823.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. D., Bose K. K., Rabkin S. D., Strauss B. S. Sites of termination of in vitro DNA synthesis on ultraviolet- and N-acetylaminofluorene-treated phi X174 templates by prokaryotic and eukaryotic DNA polymerases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):110–114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P., Strauss B. S. Sites of inhibition of in vitro DNA synthesis in carcinogen- and UV-treated phi X174 DNA. Nature. 1979 Apr 12;278(5705):664–666. doi: 10.1038/278664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortelmans K. E., Stocker B. A. Ultraviolet light protection, enhancement of ultraviolet light mutagenesis, and mutator effect of plasmid R46 in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1976 Oct;128(1):271–282. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.1.271-282.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nohmi T., Battista J. R., Dodson L. A., Walker G. C. RecA-mediated cleavage activates UmuD for mutagenesis: mechanistic relationship between transcriptional derepression and posttranslational activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1816–1820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry K. L., Walker G. C. Identification of plasmid (pKM101)-coded proteins involved in mutagenesis and UV resistance. Nature. 1982 Nov 18;300(5889):278–281. doi: 10.1038/300278a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rupp W. D., Wilde C. E., 3rd, Reno D. L., Howard-Flanders P. Exchanges between DNA strands in ultraviolet-irradiated Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1971 Oct 14;61(1):25–44. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90204-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassanfar M., Roberts J. W. Nature of the SOS-inducing signal in Escherichia coli. The involvement of DNA replication. J Mol Biol. 1990 Mar 5;212(1):79–96. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90306-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shavitt O., Livneh Z. Rolling-circle replication of UV-irradiated duplex DNA in the phi X174 replicative-form----single-strand replication system in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3530–3538. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3530-3538.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shwartz H., Livneh Z. Dynamics of termination during in vitro replication of ultraviolet-irradiated DNA with DNA polymerase III holoenzyme of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10518–10523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shwartz H., Shavitt O., Livneh Z. The role of exonucleolytic processing and polymerase-DNA association in bypass of lesions during replication in vitro. Significance for SOS-targeted mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18277–18285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. M., Eisenstadt E. Identification of a umuDC locus in Salmonella typhimurium LT2. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):3860–3865. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.3860-3865.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweasy J. B., Witkin E. M., Sinha N., Roegner-Maniscalco V. RecA protein of Escherichia coli has a third essential role in SOS mutator activity. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):3030–3036. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.3030-3036.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tessman I. UV-induced mutagenesis of phage S13 can occur in the absence of the RecA and UmuC proteins of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6614–6618. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas S. M., Sedgwick S. G. Cloning of Salmonella typhimurium DNA encoding mutagenic DNA repair. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):5776–5782. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.5776-5782.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villani G., Boiteux S., Radman M. Mechanism of ultraviolet-induced mutagenesis: extent and fidelity of in vitro DNA synthesis on irradiated templates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3037–3041. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigle J. J. Induction of Mutations in a Bacterial Virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1953 Jul;39(7):628–636. doi: 10.1073/pnas.39.7.628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson R. G., Gemski P., Jr, Stocker B. A. Non-smooth mutants of Salmonella typhimurium: differentiation by phage sensitivity and genetic mapping. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 May;70(3):527–554. doi: 10.1099/00221287-70-3-527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodgate R., Bridges B. A., Herrera G., Blanco M. Mutagenic DNA repair in Escherichia coli. XIII. Proofreading exonuclease of DNA polymerase III holoenzyme is not operational during UV mutagenesis. Mutat Res. 1987 Jan;183(1):31–37. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(87)90042-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodgate R., Rajagopalan M., Lu C., Echols H. UmuC mutagenesis protein of Escherichia coli: purification and interaction with UmuD and UmuD'. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7301–7305. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



