Full text
PDF
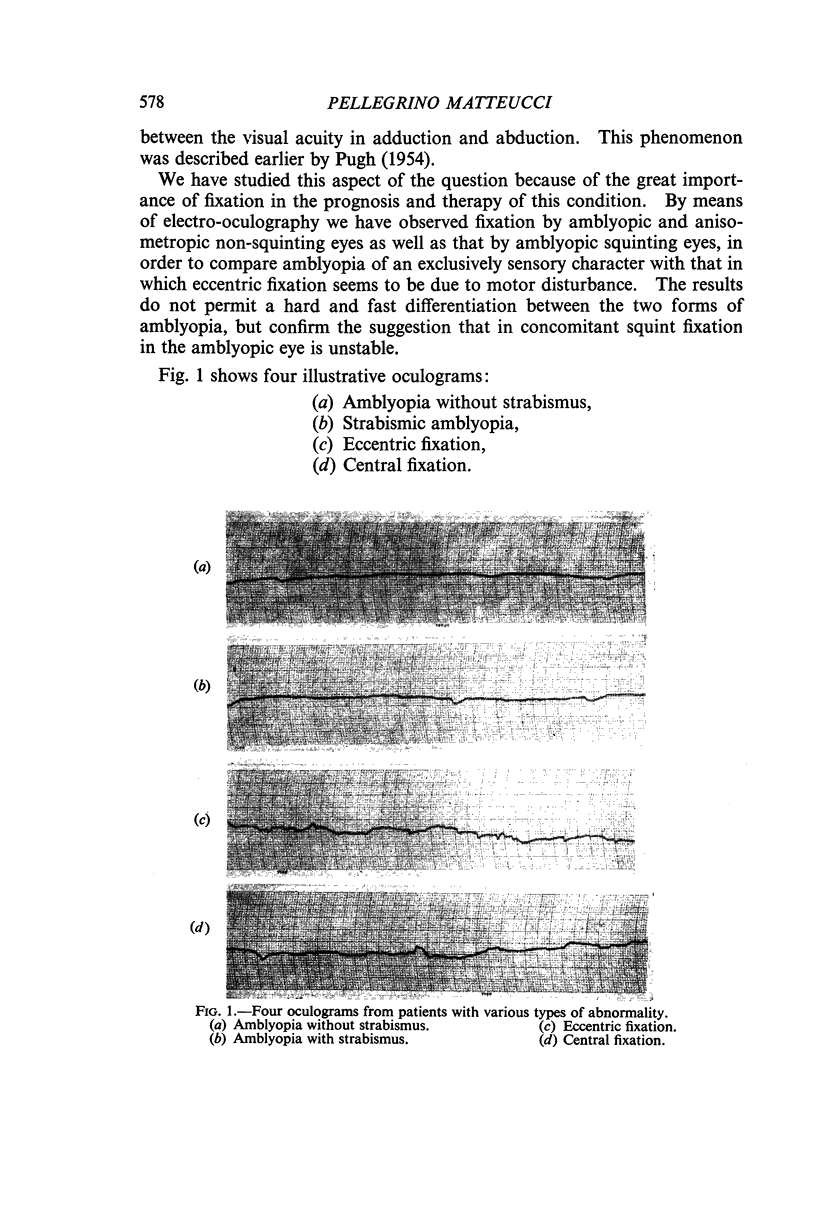




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOHME G. Uber die motorische Komponente der exzentrischen Fixation und ihre operative Korrektur. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd Augenarztl Fortbild. 1957;130(5):628–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROCK F. W., GIVNER I. Fixation anomalies in amblyopia. AMA Arch Ophthalmol. 1952 Jun;47(6):775–786. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1952.01700030794008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EHRICH W. Die Diagnose der Trennschwierigkeit bei der Amblyopie und ihre Behandlungsmethodik mit einem neuen Trennungstrainer. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd Augenarztl Fortbild. 1955;127(2):221–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUIBOR G. P. Some eye defects seen in cerebral palsy, with some statistics. Am J Phys Med. 1953 Dec;32(6):342–347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKENSEN G. Das Fixationsverhalten amblyopischer Augen; Elektrooculographische Untersuchungen. Albrecht Von Graefes Arch Ophthalmol. 1957;159(2):200–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PUGH M. Foveal vision in amblyopia. Br J Ophthalmol. 1954 Jun;38(6):321–331. doi: 10.1136/bjo.38.6.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- URIST M. J. Eccentric fixation in amblyopia ex anopsia. AMA Arch Ophthalmol. 1955 Sep;54(3):345–350. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1955.00930020351003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]