Abstract
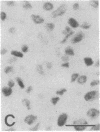
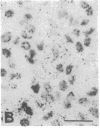
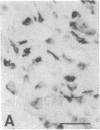
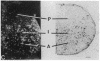
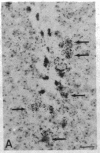
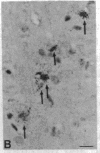
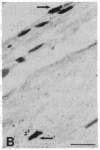
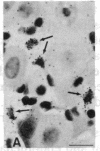
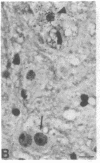
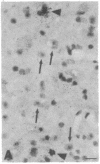
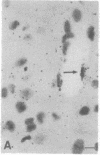
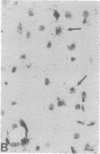
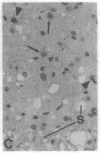
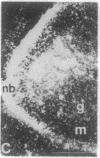
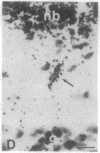
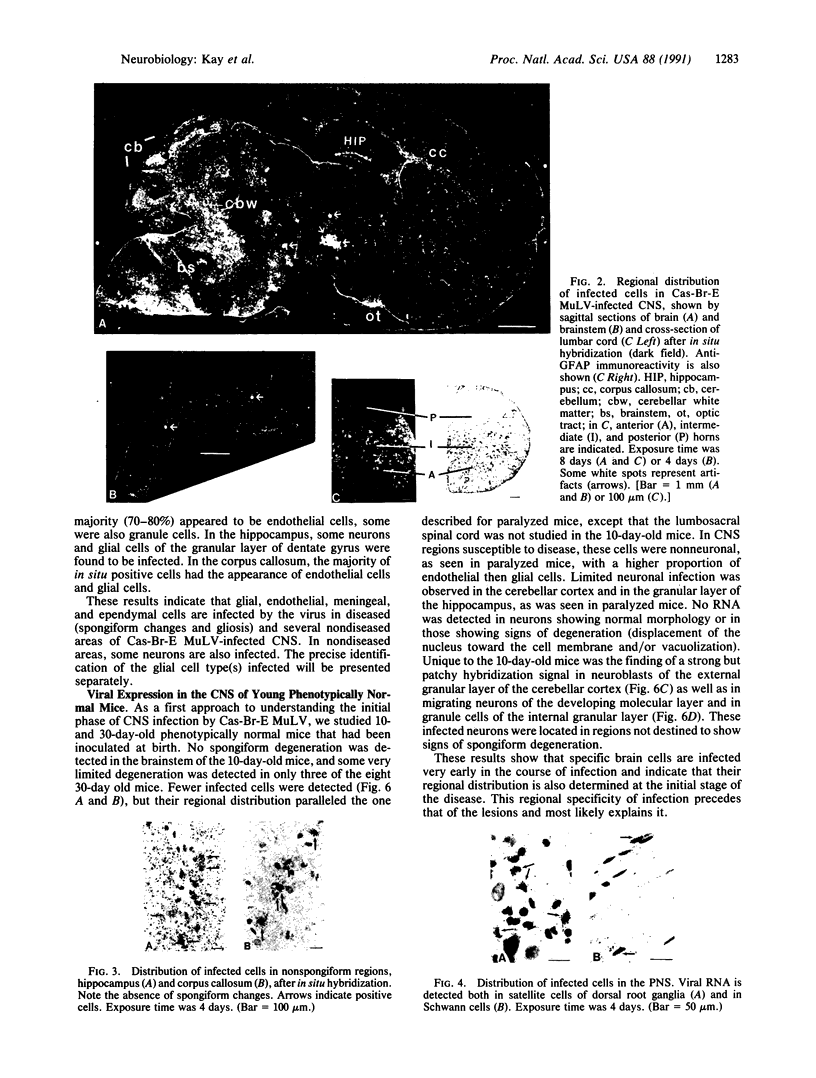
The Cas-Br-E murine leukemia virus (MuLV) induces a spongiform myeloencephalopathy resulting in a progressive hindlimb paralysis. We have used in situ hybridization with a Cas-Br-E MuLV-specific probe to study viral expression in the central nervous system. Infected cells were concentrated in regions where spongiform lesions and gliosis are detected (lumbosacral spinal cord, brainstem, deep cerebellar regions), suggesting a causative link between the level of virus expression and the degree of pathological changes in this disease. However, viral expression was not in itself sufficient to cause disease, since significant viral expression was observed in regions that did not exhibit pathological changes (cerebellar cortex, hippocampus, corpus callosum, peripheral nervous system). In both diseased and nondiseased regions, endothelial and glial cells were identified as the main target cells. Neurons in diseased regions did not show viral expression. The regional distribution of the spongiform changes appears to be laid down very early following infection, since expression could be detected at 10 days postinfection in regions that become diseased. These results indicate that nonneuronal cells have distinct properties in various regions of the central nervous system and suggest an indirect mechanism of neuronal loss consequent to viral expression in nonneuronal cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews J. M., Gardner M. B. Lower motor neuron degeneration associated with type C RNA virus infection in mice: neuropathological features. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1974 Apr;33(2):285–307. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197404000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilello J. A., Pitts O. M., Hoffman P. M. Characterization of a progressive neurodegenerative disease induced by a temperature-sensitive Moloney murine leukemia virus infection. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):234–241. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.234-241.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks B. R., Swarz J. R., Johnson R. T. Spongiform polioencephalomyelopathy caused by a murine retrovirus. I. Pathogenesis of infection in newborn mice. Lab Invest. 1980 Nov;43(5):480–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contag C. H., Plagemann P. G. Age-dependent poliomyelitis of mice: expression of endogenous retrovirus correlates with cytocidal replication of lactate dehydrogenase-elevating virus in motor neurons. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4362–4369. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4362-4369.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DesGroseillers L., Barrette M., Jolicoeur P. Physical mapping of the paralysis-inducing determinant of a wild mouse ecotropic neurotropic retrovirus. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):356–363. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.356-363.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DesGroseillers L., Rassart E., Robitaille Y., Jolicoeur P. Retrovirus-induced spongiform encephalopathy: the 3'-end long terminal repeat-containing viral sequences influence the incidence of the disease and the specificity of the neurological syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8818–8822. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner M. B., Henderson B. E., Officer J. E., Rongey R. W., Parker J. C., Oliver C., Estes J. D., Huebner R. J. A spontaneous lower motor neuron disease apparently caused by indigenous type-C RNA virus in wild mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Oct;51(4):1243–1254. doi: 10.1093/jnci/51.4.1243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner M. B. Type C viruses of wild mice: characterization and natural history of amphotropic, ecotropic, and xenotropic MuLv. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;79:215–259. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-66853-1_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickey W. F., Kimura H. Perivascular microglial cells of the CNS are bone marrow-derived and present antigen in vivo. Science. 1988 Jan 15;239(4837):290–292. doi: 10.1126/science.3276004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. M., Pitts O. M., Bilello J. A., Cimino E. F. Retrovirus induced motor neuron degeneration. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1988;144(11):676–679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolicoeur P., Nicolaiew N., DesGroseillers L., Rassart E. Molecular cloning of infectious viral DNA from ecotropic neurotropic wild mouse retrovirus. J Virol. 1983 Mar;45(3):1159–1163. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.3.1159-1163.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy G. F., Leblond C. P. Radioautographic evidence for slow astrocyte turnover and modest oligodendrocyte production in the corpus callosum of adult mice infused with 3H-thymidine. J Comp Neurol. 1988 May 22;271(4):589–603. doi: 10.1002/cne.902710409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Jensen F., Dixon F. J., Lampert P. W. Pathogenesis of the slow disease of the central nervous system associated with wild mouse virus. II. Role of virus and host gene products. Virology. 1980 Nov;107(1):180–193. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90283-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Jensen F., Elder J., Dixon F. J., Lampert P. W. Pathogenesis of the slow disease of the central nervous system associated with wild mouse virus. III. Role of input virus and MCF recombinants in disease. Virology. 1983 Jul 15;128(1):154–165. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90326-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Lampert P. W., Lee S., Dixon F. J. Pathogenesis of the slow disease of the central nervous system associated with WM 1504 E virus. I. Relationship of strain susceptibility and replication to disease. Am J Pathol. 1977 Jul;88(1):193–212. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paquette Y., Hanna Z., Savard P., Brousseau R., Robitaille Y., Jolicoeur P. Retrovirus-induced murine motor neuron disease: mapping the determinant of spongiform degeneration within the envelope gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3896–3900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paquette Y., Kay D. G., Rassart E., Robitaille Y., Jolicoeur P. Substitution of the U3 long terminal repeat region of the neurotropic Cas-Br-E retrovirus affects its disease-inducing potential. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3742–3752. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3742-3752.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry V. H., Hume D. A., Gordon S. Immunohistochemical localization of macrophages and microglia in the adult and developing mouse brain. Neuroscience. 1985 Jun;15(2):313–326. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90215-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitts O. M., Powers J. M., Bilello J. A., Hoffman P. M. Ultrastructural changes associated with retroviral replication in central nervous system capillary endothelial cells. Lab Invest. 1987 Apr;56(4):401–409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rassart E., Nelbach L., Jolicoeur P. Cas-Br-E murine leukemia virus: sequencing of the paralytogenic region of its genome and derivation of specific probes to study its origin and the structure of its recombinant genomes in leukemic tissues. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):910–919. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.910-919.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe A. H., Hunter J. J., Chassler P., Jaenisch R. Role of abortive retroviral infection of neurons in spongiform CNS degeneration. Nature. 1990 Jul 12;346(6280):181–183. doi: 10.1038/346181a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinoda H., Marini A. M., Cosi C., Schwartz J. P. Brain region and gene specificity of neuropeptide gene expression in cultured astrocytes. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):415–417. doi: 10.1126/science.2569236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swarz J. R., Brooks B. R., Johnson R. T. Spongiform polioencephalomyelopathy caused by a murine retrovirus. II. Ultrastructural localization of virus replication and spongiform changes in the central nervous system. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1981 Sep-Oct;7(5):365–380. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1981.tb00239.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]