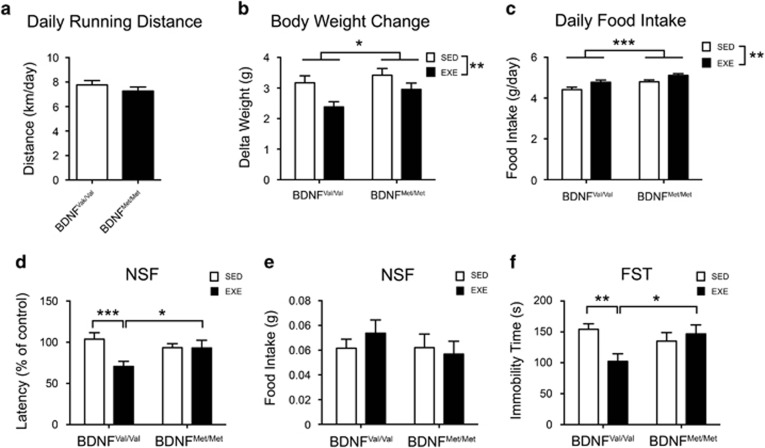
Figure 1.
BDNF Val66Met polymorphism impairs physical exercise-induced beneficial effect of physical exercise on anxious- and depressive-like phenotype in mice. (a) Total distance run daily by mice. Daily running distance was calculated by dividing for 2 the distance measured by a single electronic counter (two electronic counter per cage; four mice per cage). Data are expressed as means±SEM (n=35–39 number of electronic counters analyzed per group). Unpaired t-test. (b) Total body weight gain over 4 weeks of physical exercise treatment (n=45–52 mice per group). (c) Daily food consumption. Amount of daily food intake per mice was calculated by dividing for 4 the total amount of food consumed per cage (four mice per cage) (n=14–16 number of cage analyzed per group). (d, e) Novelty suppressed feeding (NSF) test. (d) Exercise reduces the latency to feed in NSF test only in BDNFVal/Val mice. (e) There is no difference in the amount of food consumed in the home cages among all the groups. (f) Forced swimming test (FST). Exercise decreases the immobility time only in BDNFVal/Val mice. Data are expressed as means±SEM (n=18–24 mice per group). Two-way ANOVA followed by Fischer's LSD post hoc analysis. *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001. EXE, exercise; SED, sedentary.