Abstract
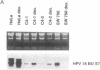
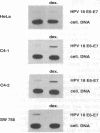
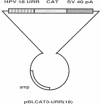
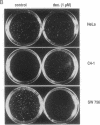
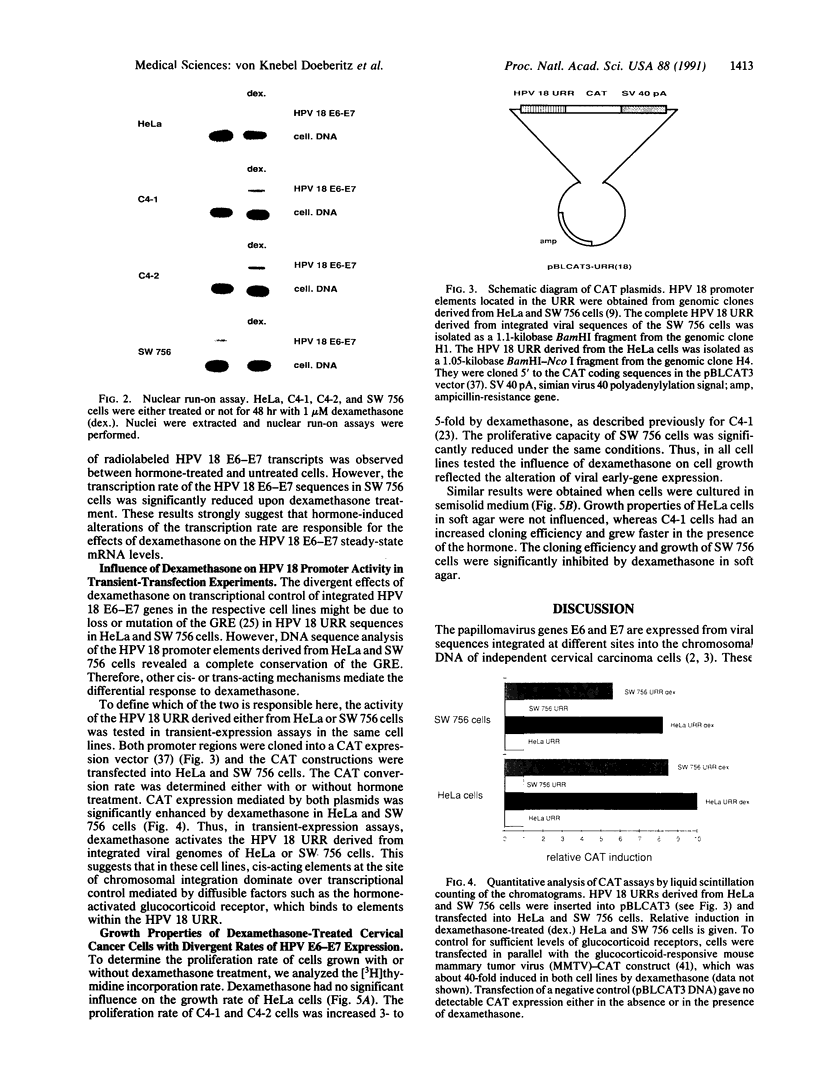
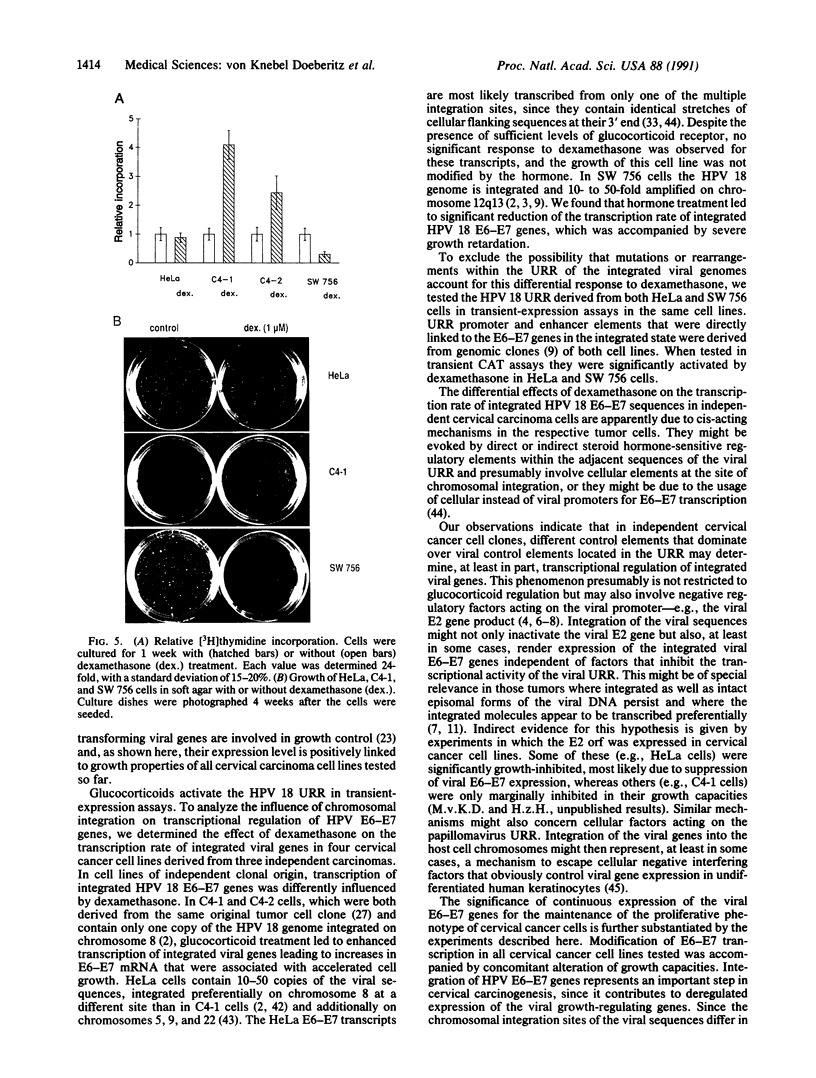
In most cervical carcinoma cells the E6 and E7 genes of specific human papillomaviruses are transcribed from viral sequences integrated into host cell chromosomes. Glucocorticoids activate the promoter elements of various human papillomaviruses in transient-expression assays. We have analyzed the effect of dexamethasone on the transcription rate of human papillomavirus 18 E6 and E7 genes integrated at different chromosomal sites in four cervical cancer cell lines. Dexamethasone led to an increase in the transcription rate of the integrated E6-E7 sequences in C4-1 and C4-2 cells but led to a decrease in SW 756 cells and did not affect the transcription rate in HeLa cells. However, when the viral promoter elements derived from HeLa or SW 756 cells, in which dexamethasone does not activate transcription of the integrated E6-E7 sequences, were tested in transient-expression assays within the same cell lines, dexamethasone consistently activated the viral promoter. It thus appears that dominant regulatory mechanisms presumably depending on the chromosomal integration site are able to override the response of the viral promoter to steroid hormones. The growth rate of all dexamethasone-treated cell lines correlated consistently with the expression of the papillomavirus E6 and E7 genes, supporting their role in the maintenance of the proliferative phenotype of cervical carcinoma cells. Since human papillomaviruses are integrated into the host cell genome at variable, presumably randomly selected chromosomal loci, regulatory mechanisms that influence viral gene expression, and hence cell growth, may differ among cancers of independent clonal origin.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AUERSPERG N., HAWRYLUK A. P. Chromosome observations on three epithelial-cell cultures derived from carcinomas of the human cervix. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1962 Mar;28:605–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Androphy E. J., Hubbert N. L., Schiller J. T., Lowy D. R. Identification of the HPV-16 E6 protein from transformed mouse cells and human cervical carcinoma cell lines. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):989–992. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04849.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. C., Phelps W. C., Lindgren V., Braun M. J., Gonda M. A., Howley P. M. Structural and transcriptional analysis of human papillomavirus type 16 sequences in cervical carcinoma cell lines. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):962–971. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.962-971.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedell M. A., Jones K. H., Grossman S. R., Laimins L. A. Identification of human papillomavirus type 18 transforming genes in immortalized and primary cells. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1247–1255. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1247-1255.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard B. A., Bailly C., Lenoir M. C., Darmon M., Thierry F., Yaniv M. The human papillomavirus type 18 (HPV18) E2 gene product is a repressor of the HPV18 regulatory region in human keratinocytes. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4317–4324. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4317-4324.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan W. K., Klock G., Bernard H. U. Progesterone and glucocorticoid response elements occur in the long control regions of several human papillomaviruses involved in anogenital neoplasia. J Virol. 1989 Aug;63(8):3261–3269. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.8.3261-3269.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cripe T. P., Haugen T. H., Turk J. P., Tabatabai F., Schmid P. G., 3rd, Dürst M., Gissmann L., Roman A., Turek L. P. Transcriptional regulation of the human papillomavirus-16 E6-E7 promoter by a keratinocyte-dependent enhancer, and by viral E2 trans-activator and repressor gene products: implications for cervical carcinogenesis. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3745–3753. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02709.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crook T., Storey A., Almond N., Osborn K., Crawford L. Human papillomavirus type 16 cooperates with activated ras and fos oncogenes in the hormone-dependent transformation of primary mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8820–8824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürst M., Croce C. M., Gissmann L., Schwarz E., Huebner K. Papillomavirus sequences integrate near cellular oncogenes in some cervical carcinomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):1070–1074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.1070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürst M., Gallahan D., Jay G., Rhim J. S. Glucocorticoid-enhanced neoplastic transformation of human keratinocytes by human papillomavirus type 16 and an activated ras oncogene. Virology. 1989 Dec;173(2):767–771. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90595-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman R. S., Bowen J. M., Leibovitz A., Pathak S., Siciliano M. J., Gallager H. S., Giovanella B. C. Characterization of a cell line (SW756) derived from a human squamous carcinoma of the uterine cervix. In Vitro. 1982 Aug;18(8):719–726. doi: 10.1007/BF02796428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser C. S., Simonsen C. C., Schilling J. W., Schimke R. T. Expression of abbreviated mouse dihydrofolate reductase genes in cultured hamster cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6522–6526. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gloss B., Bernard H. U., Seedorf K., Klock G. The upstream regulatory region of the human papilloma virus-16 contains an E2 protein-independent enhancer which is specific for cervical carcinoma cells and regulated by glucocorticoid hormones. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3735–3743. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02708.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inagaki Y., Tsunokawa Y., Takebe N., Nawa H., Nakanishi S., Terada M., Sugimura T. Nucleotide sequences of cDNAs for human papillomavirus type 18 transcripts in HeLa cells. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1640–1646. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1640-1646.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James G. K., Kalousek D. K., Auersperg N. Karyotypic analysis of two related cervical carcinoma cell lines that contain human papillomavirus type 18 DNA and express divergent differentiation. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1989 Mar;38(1):53–60. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(89)90165-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones H. W., Jr, McKusick V. A., Harper P. S., Wuu K. D. George Otto Gey. (1899-1970). The HeLa cell and a reappraisal of its origin. Obstet Gynecol. 1971 Dec;38(6):945–949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. F., Spalholz B. A., Howley P. M. A transcriptional repressor encoded by BPV-1 shares a common carboxy-terminal domain with the E2 transactivator. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):69–78. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90663-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazo P. A., DiPaolo J. A., Popescu N. C. Amplification of the integrated viral transforming genes of human papillomavirus 18 and its 5'-flanking cellular sequence located near the myc protooncogene in HeLa cells. Cancer Res. 1989 Aug 1;49(15):4305–4310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linial M., Gunderson N., Groudine M. Enhanced transcription of c-myc in bursal lymphoma cells requires continuous protein synthesis. Science. 1985 Dec 6;230(4730):1126–1132. doi: 10.1126/science.2999973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. CAT constructions with multiple unique restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5490–5490. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miksicek R., Borgmeyer U., Nowock J. Interaction of the TGGCA-binding protein with upstream sequences is required for efficient transcription of mouse mammary tumor virus. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1355–1360. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02375.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oltersdorf T., Seedorf K., Röwekamp W., Gissmann L. Identification of human papillomavirus type 16 E7 protein by monoclonal antibodies. J Gen Virol. 1987 Nov;68(Pt 11):2933–2938. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-11-2933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pater M. M., Pater A. Human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 sequences in carcinoma cell lines of the cervix. Virology. 1985 Sep;145(2):313–318. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90164-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popescu N. C., Amsbaugh S. C., DiPaolo J. A. Human papillomavirus type 18 DNA is integrated at a single chromosome site in cervical carcinoma cell line SW756. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1682–1685. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1682-1685.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popescu N. C., DiPaolo J. A., Amsbaugh S. C. Integration sites of human papillomavirus 18 DNA sequences on HeLa cell chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1987;44(1):58–62. doi: 10.1159/000132342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rungger D., Achermann H., Crippa M. Transcription of spacer sequences in genes coding for ribosomal RNA in Xenopus cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3957–3961. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider-Gädicke A., Schwarz E. Different human cervical carcinoma cell lines show similar transcription patterns of human papillomavirus type 18 early genes. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2285–2292. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04496.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz E., Freese U. K., Gissmann L., Mayer W., Roggenbuck B., Stremlau A., zur Hausen H. Structure and transcription of human papillomavirus sequences in cervical carcinoma cells. Nature. 1985 Mar 7;314(6006):111–114. doi: 10.1038/314111a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seedorf K., Oltersdorf T., Krämmer G., Röwekamp W. Identification of early proteins of the human papilloma viruses type 16 (HPV 16) and type 18 (HPV 18) in cervical carcinoma cells. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):139–144. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04731.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirasawa H., Tomita Y., Kubota K., Kasai T., Sekiya S., Takamizawa H., Simizu B. Detection of human papillomavirus type 16 DNA and evidence for integration into the cell DNA in cervical dysplasia. J Gen Virol. 1986 Sep;67(Pt 9):2011–2015. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-9-2011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirasawa H., Tomita Y., Kubota K., Kasai T., Sekiya S., Takamizawa H., Simizu B. Transcriptional differences of the human papillomavirus type 16 genome between precancerous lesions and invasive carcinomas. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):1022–1027. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.1022-1027.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirasawa H., Tomita Y., Sekiya S., Takamizawa H., Simizu B. Integration and transcription of human papillomavirus type 16 and 18 sequences in cell lines derived from cervical carcinomas. J Gen Virol. 1987 Feb;68(Pt 2):583–591. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-2-583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smotkin D., Wettstein F. O. Transcription of human papillomavirus type 16 early genes in a cervical cancer and a cancer-derived cell line and identification of the E7 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4680–4684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thierry F., Yaniv M. The BPV1-E2 trans-acting protein can be either an activator or a repressor of the HPV18 regulatory region. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3391–3397. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02662.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Knebel Doeberitz M., Koch S., Drzonek H., Zur Hausen H. Glucocorticoid hormones reduce the expression of major histocompatibility class I antigens on human epithelial cells. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Jan;20(1):35–40. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodworth C. D., Doniger J., DiPaolo J. A. Immortalization of human foreskin keratinocytes by various human papillomavirus DNAs corresponds to their association with cervical carcinoma. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):159–164. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.159-164.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee C., Krishnan-Hewlett I., Baker C. C., Schlegel R., Howley P. M. Presence and expression of human papillomavirus sequences in human cervical carcinoma cell lines. Am J Pathol. 1985 Jun;119(3):361–366. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Knebel Doeberitz M., Oltersdorf T., Schwarz E., Gissmann L. Correlation of modified human papilloma virus early gene expression with altered growth properties in C4-1 cervical carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 1988 Jul 1;48(13):3780–3786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- zur Hausen H. Intracellular surveillance of persisting viral infections. Human genital cancer results from deficient cellular control of papillomavirus gene expression. Lancet. 1986 Aug 30;2(8505):489–491. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90360-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- zur Hausen H. Papillomaviruses in anogenital cancer as a model to understand the role of viruses in human cancers. Cancer Res. 1989 Sep 1;49(17):4677–4681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]