Abstract
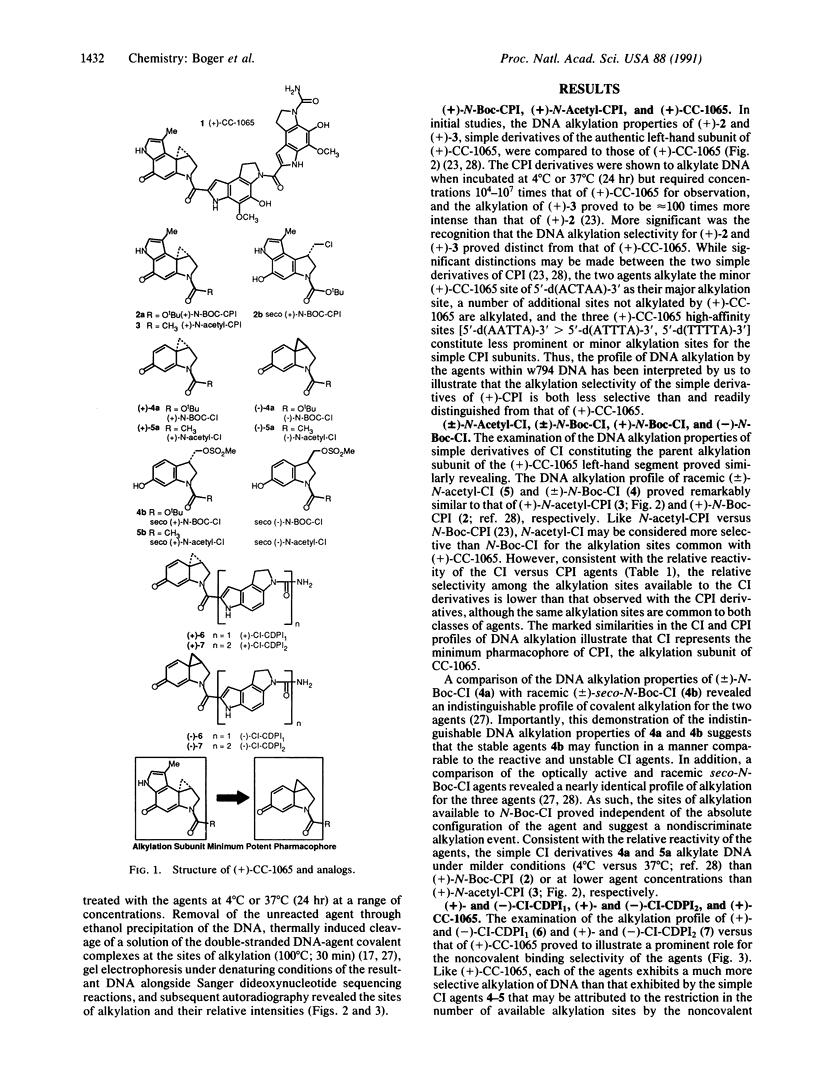
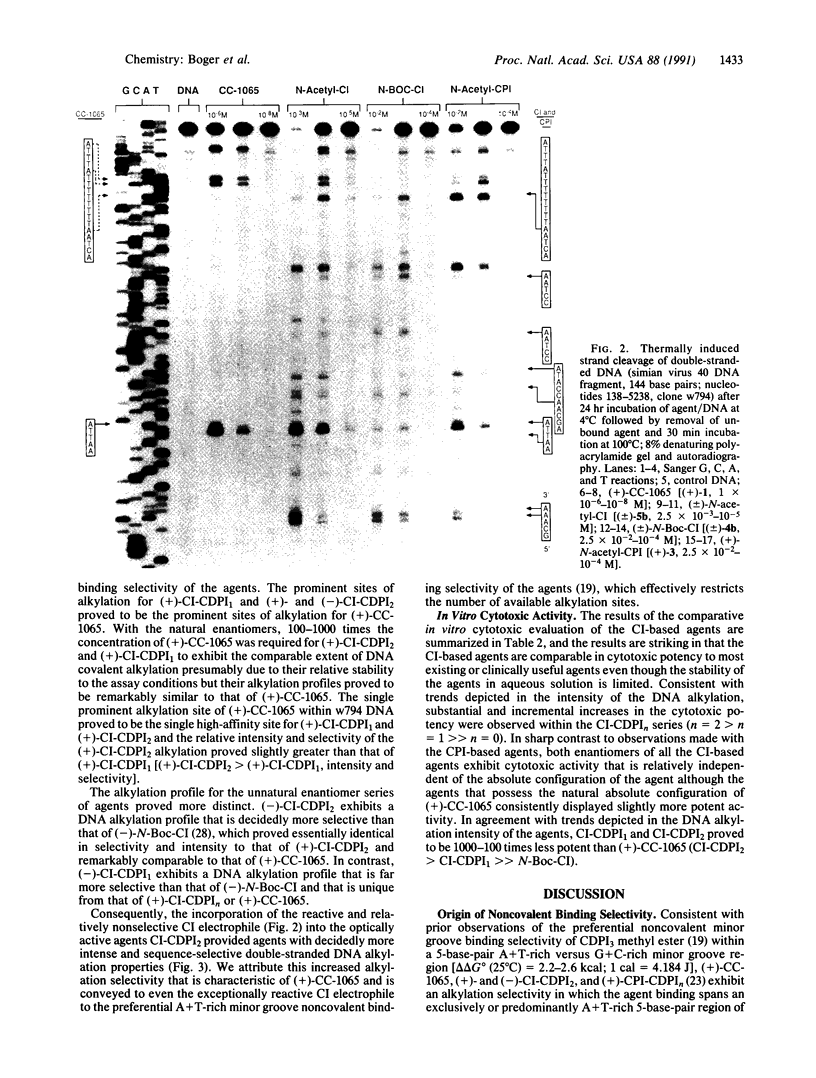
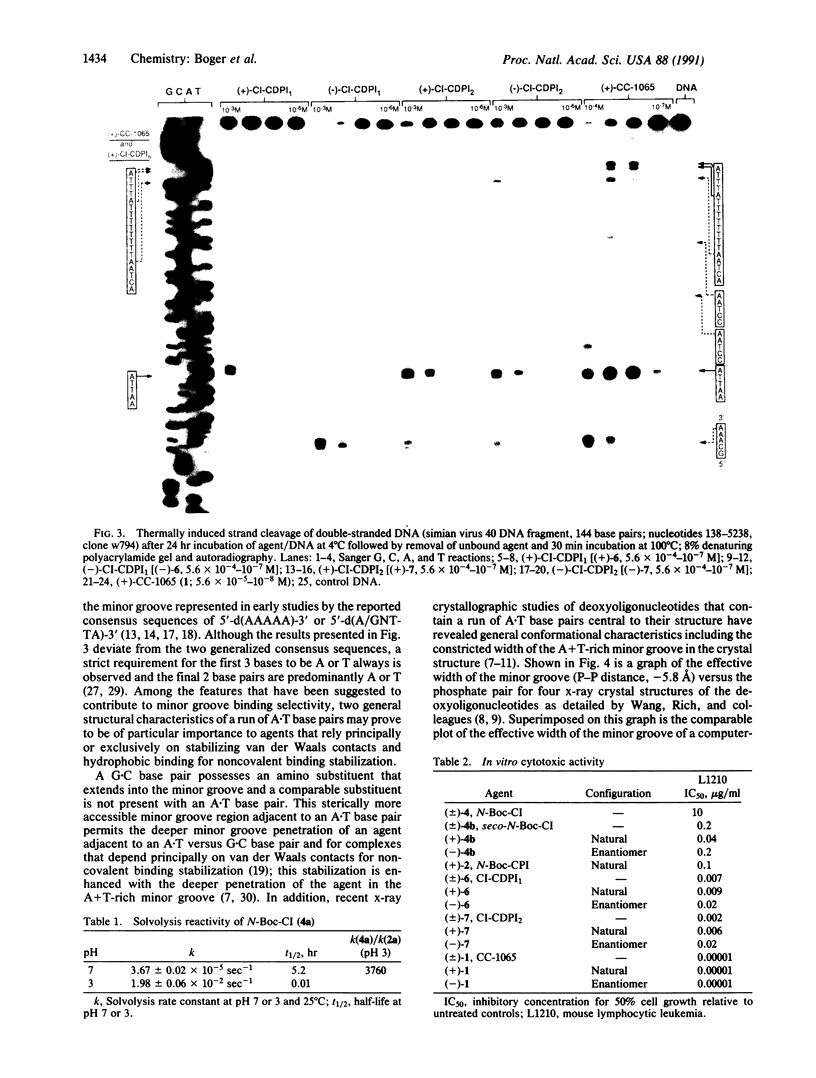
Studies on the structural origin of the DNA alkylation selectivity of the antitumor antibiotic (+)-CC-1065 are detailed. The sites of alkylation of double-stranded DNA were examined for simple derivatives of 7-methyl-1,2,8,8a-tetrahydrocycloprop[1,2-c]pyrrolo[3,2-e]indol- 4(5H)-one (CPI), (+)-CC-1065, and agents incorporating the parent 1,2,7,7a-tetrahydrocycloprop[1,2-c]indol-4-one (CI) left-hand subunit. The CI subunit of the agents is a much more reactive alkylating agent than the natural CPI alkylation subunit of CC-1065. Consequently, simple derivatives of CI were found to alkylate double-stranded DNA under milder conditions than were simple derivatives of CPI, and the marked similarities in the CI and CPI DNA alkylation profiles illustrate that CI represents the minimum pharmacophore of CPI. Comparisons of the DNA alkylation profiles of (+)-N-butyloxycarbonyl-CPI, (+)-N-acetyl-CPI, and (+)-CC-1065 revealed distinctions in the CPI and (+)-CC-1065 sites of alkylation, whereas the incorporation of the reactive CI electrophile into an analog of CC-1065 (CI-CDPI2) (CDPI, N3-carbamoyl-1,2-dihydro-3H-pyrrolo[3,2-e]indole-7-carboxylic acid) provided an agent that possesses the characteristic CC-1065 DNA alkylation profile (site selectivity and relative site intensity). These observations suggest that the noncovalent binding selectivity of the agents may restrict the number of available DNA alkylation sites and play a productive role in controlling the sequence-selective alkylation by effectively delivering the electrophile to A + T-rich minor groove regions of DNA possessing accessible adenine N-3 alkylation sites. In turn, the noncovalent binding selectivity may be derived from preferential binding within the narrower, sterically more accessible A + T-rich minor groove of double-stranded DNA.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambrose C., Rajadhyaksha A., Lowman H., Bina M. Locations of nucleosomes on the regulatory region of simian virus 40 chromatin. J Mol Biol. 1989 Nov 20;210(2):255–263. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90328-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boger D. L., Invergo B. J., Coleman R. S., Zarrinmayeh H., Kitos P. A., Thompson S. C., Leong T., McLaughlin L. W. A demonstration of the intrinsic importance of stabilizing hydrophobic binding and non-covalent van der Waals contacts dominant in the non-covalent CC-1065/B-DNA binding. Chem Biol Interact. 1990;73(1):29–52. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(90)90107-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coll M., Aymami J., van der Marel G. A., van Boom J. H., Rich A., Wang A. H. Molecular structure of the netropsin-d(CGCGATATCGCG) complex: DNA conformation in an alternating AT segment. Biochemistry. 1989 Jan 10;28(1):310–320. doi: 10.1021/bi00427a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coll M., Frederick C. A., Wang A. H., Rich A. A bifurcated hydrogen-bonded conformation in the d(A.T) base pairs of the DNA dodecamer d(CGCAAATTTGCG) and its complex with distamycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8385–8389. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dervan P. B. Design of sequence-specific DNA-binding molecules. Science. 1986 Apr 25;232(4749):464–471. doi: 10.1126/science.2421408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertzberg R. P., Dervan P. B. Cleavage of DNA with methidiumpropyl-EDTA-iron(II): reaction conditions and product analyses. Biochemistry. 1984 Aug 14;23(17):3934–3945. doi: 10.1021/bi00312a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley L. H., Lee C. S., McGovren J. P., Warpehoski M. A., Mitchell M. A., Kelly R. C., Aristoff P. A. Molecular basis for sequence-specific DNA alkylation by CC-1065. Biochemistry. 1988 May 17;27(10):3886–3892. doi: 10.1021/bi00410a054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson H. C., Finch J. T., Luisi B. F., Klug A. The structure of an oligo(dA).oligo(dT) tract and its biological implications. Nature. 1987 Nov 19;330(6145):221–226. doi: 10.1038/330221a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds V. L., McGovren J. P., Hurley L. H. The chemistry, mechanism of action and biological properties of CC-1065, a potent antitumor antibiotic. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1986 Mar;39(3):319–334. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.39.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds V. L., Molineux I. J., Kaplan D. J., Swenson D. H., Hurley L. H. Reaction of the antitumor antibiotic CC-1065 with DNA. Location of the site of thermally induced strand breakage and analysis of DNA sequence specificity. Biochemistry. 1985 Oct 22;24(22):6228–6237. doi: 10.1021/bi00343a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tullius T. D., Dombroski B. A., Churchill M. E., Kam L. Hydroxyl radical footprinting: a high-resolution method for mapping protein-DNA contacts. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:537–558. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55035-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke M. W., Hertzberg R. P., Dervan P. B. Map of distamycin, netropsin, and actinomycin binding sites on heterogeneous DNA: DNA cleavage-inhibition patterns with methidiumpropyl-EDTA.Fe(II). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5470–5474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warpehoski M. A., Hurley L. H. Sequence selectivity of DNA covalent modification. Chem Res Toxicol. 1988 Nov-Dec;1(6):315–333. doi: 10.1021/tx00006a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wing R., Drew H., Takano T., Broka C., Tanaka S., Itakura K., Dickerson R. E. Crystal structure analysis of a complete turn of B-DNA. Nature. 1980 Oct 23;287(5784):755–758. doi: 10.1038/287755a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]