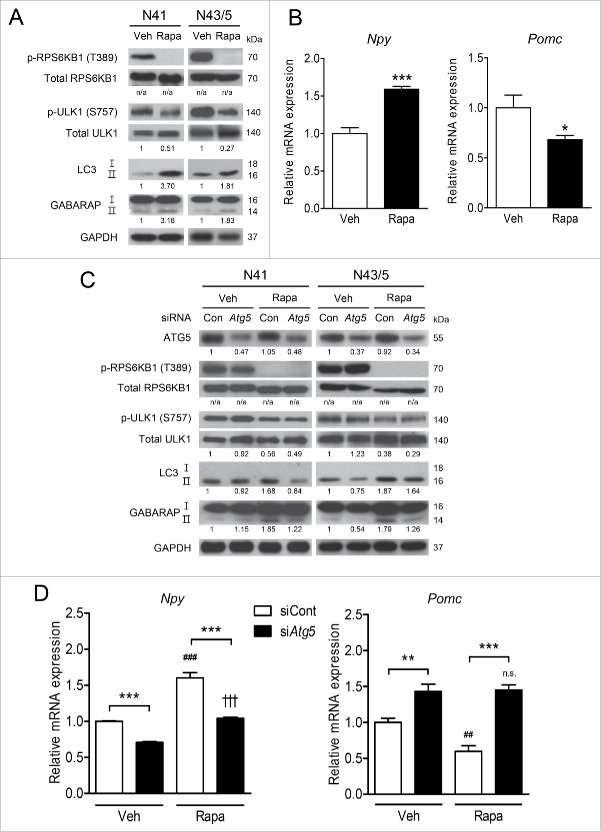
Figure 5.
Atg5 knockdown reduces rapamycin-induced neuropeptide mRNA levels. (A) N41 and N43/5 cells were treated with vehicle (Veh) for 4 h or with rapamycin (Rapa: 20 nM) for 1 h. The levels of p-RPS6KB1 (Thr389), total RPS6KB1, p-ULK1 (Ser757), total ULK1, LC3, GABARAP, and GAPDH were examined by immunoblotting. (B) The levels of Npy and Pomc mRNA in N41 cells treated with rapamycin for 4 h and in N43/5 cells treated for 1 h (*, p < 0.05; ***, p < 0.001 for Veh vs. Rapa; N41: n = 6, N43/5: n = 6 or 7). (C) Atg5 was knocked down using siRNAs and cells were treated with rapamycin for 4 h (N41) or 1h (N43/5). The levels of ATG5, p-SRP6KB1 (Thr389), total RPS6KB1, p-ULK1 (Ser757), total ULK1, LC3, GABARAP, and GAPDH were examined by immunoblotting. (D) The levels of Npy and Pomc mRNA in cells treated with rapamycin (N41, 4 h; N43/5, 1 h) after Atg5 knockdown using siRNAs (**, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001 for control siRNAs [siCont] vs. Atg5 siRNAs [siAtg5]; ##, p < 0.01; ###, p < 0.001 for Veh vs. Rapa in control siRNA groups; †††, p < 0.001; n.s. for Veh vs. Rapa in Atg5 siRNA groups; N41: n = 6, N43/5: n = 6). p-RPS6KB1 and p-ULK1 were normalized to corresponding total proteins. Other protein levels were normalized to GAPDH. Numbers under blots indicate relative quantitative mean values of independent replicates (A and C: n = 3). n/a: not applicable.