Abstract
Objectives
The maxillary sinus mucosa is reported to recover to preoperative sterility after sinus floor elevation. However, when drainage of maxillary sinus is impaired, recovery can be delayed and maxillary sinusitis can occur. Therefore, in this study, we investigated the correlations between anatomic variants that can interrupt the ostium of the maxillary sinus and incidence of complication after sinus lifting.
Materials and Methods
The subjects are 81 patients who underwent sinus lifting in Wonkwang University Dental Hospital (Iksan, Korea). Computed tomography (CT) images of the subjects were reviewed for presence of nasal septum deviation, anatomic variants of the middle turbinate, and Haller cells. Correlations between anatomic variations and occurrence of maxillary sinusitis were statistically analyzed.
Results
Patients with anatomic variants of ostio-meatal units, such as deviated nasal septum, concha bullosa or paradoxical curvature of the middle turbinate, or Haller cells, showed a higher rate of complication. However, only presence of Haller cell showed statistically significant.
Conclusion
Before sinus lifting, CT images are recommended to detect anatomic variants of the ostio-meatal complex. If disadvantageous anatomic variants are detected, the use of nasal decongestants should be considered to reduce the risk of postoperative sinusitis.
Keywords: Maxillary sinus, Sinus floor augmentation, Maxillary sinusitis, Anatomic variation, Ostio-meatal complex
I. Introduction
Maxillary sinus floor elevation is known as a reliable option to enable insertion of dental implants for patients with severe atrophy in the posterior area of the maxilla1. In spite of vague criteria for evaluation and diagnosis, maxillary sinusitis is the most common complication of this procedure2. This unpleasant complication can occur as a result of contamination of the maxillary sinus with oral or nasal pathogen or because of a lack of asepsis during the surgery3. However, obstruction of the ostium caused by postoperative swelling of the maxillary sinus mucosa can also be a source of this complication4.
Anatomical variants of the paranasal sinus and nasal cavity are commonly detected, with an estimated prevalence of 68%5. Some anatomic variants on the nasal cavity and ostium of maxillary sinus, such as deviated nasal septum, concha bullosa or paradoxical middle turbinate, bending of the uncinated process, and Haller cells, are very important because of their contribution to the blockage of ostio-meatal units. These anatomic variants can disturb the drainage and ventilation of the maxillary sinus and, thereby, can affect the risk of sinus mucosal disease6.
With maxillary sinus floor elevation, postoperative swelling of the Schneiderian membrane is an unavoidable sequela. Although the mucosa of the sinus membrane heals rapidly and recovers its homeostasis7, if the ostio-meatal complex is unfavorable due to anatomic variants, its healing can be delayed, and risk of sinusitis is increased.
In this study, we evaluated the computed tomography (CT) images of patients who had undergone sinus floor elevation and investigated the correlations between anatomic variants of the lateral nasal wall and maxillary sinus and risk of maxillary sinusitis after sinus floor elevation.
II. Materials and Methods
1. Subject
At the Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery in Wonkwang Dental Hospital (Iksan, Korea), we reviewed a total of 366 patients who had undergone sinus floor elevation from January 2009 to December 2015. Of these, 267 patients were excluded because of lack of adequate CT images with view of the ostio-meatal complex. Finally, 99 patients were included in this study.
2. Methods
Each CT image was reviewed by the author, investigating the presence of anatomic variants. The radiological assessments were used to detect conditions that could jeopardize the physiological maxillary ventilation and drainage functions, impairing the antral homeostasis, such as septal deviations, concha bullosa, paradoxical bending of the middle turbinate, or Haller cells.(Fig. 1, 2, 3, 4)
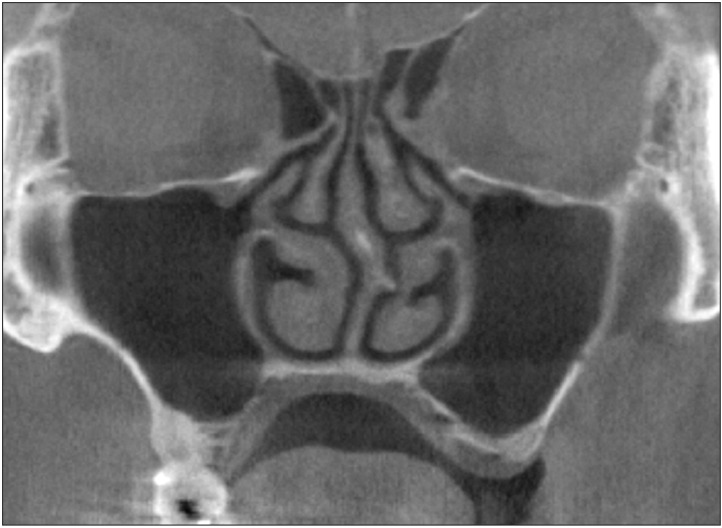
Fig. 1. Deviated nasal septum.
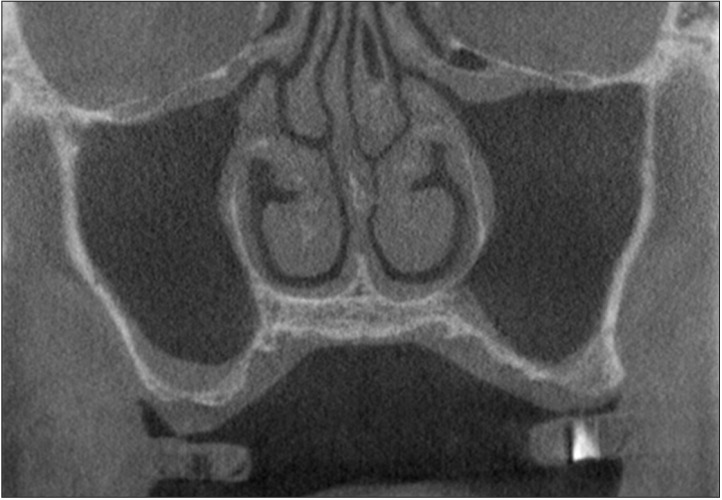
Fig. 2. Concha bullosa of middle turbinate and Haller cell on left.
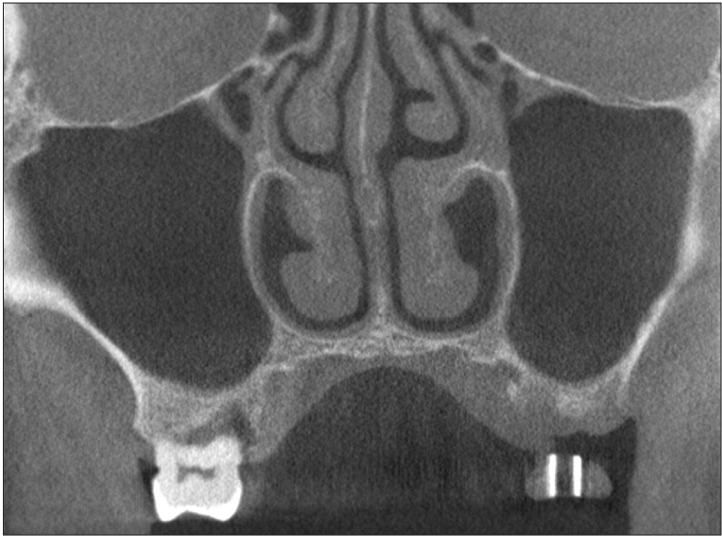
Fig. 3. Paradoxical curvature of left middle turbinate.
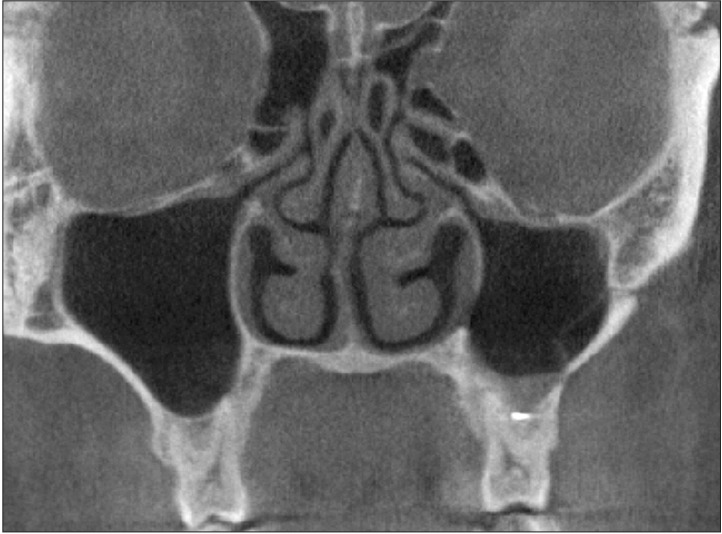
Fig. 4. Haller cell on left maxillary ostium.
Sinusitis is characterized by a typical triad of symptoms; nasal congestion or obstruction, pathological secretion, and headache8. However, these symptoms are extremely variable. Sinusitis is also suspected in patients complaining of pain or tenderness in the region of the sinus, in combination with mucopurulent rhinorrhea. A physical examination was performed after the sinus floor elevation procedure to assess the presence of maxillary sinusitis. In particular, the patients were assessed for development of any sign or symptom suggesting postoperative maxillary sinusitis, including nasal obstruction or a purulent nasal discharge, facial pain or tenderness, fever, or purulent oral discharge. In this study, the patients who experienced pain for longer than 2 weeks or nasal obstruction were considered to have complication after sinus floor elevation.
The statistical analysis was useful to assess the correlations between anatomic variants and the development of maxillary sinusitis. Correlations were evaluated using Fisher's exact test. A chi-square test was not appropriate for this data because the expected frequency was less than 5 for more than 25% of the cells in the contingency tables. Analysis was conducted using PASW Statistics version 18 (IBM Co., Armonk, NY, USA). Statistical significance was set at P<0.05.
III. Results
Of the 99 cases, 10 patients who underwent functional endoscopic surgery were excluded from this study. In addition, 8 cases in which the sinus membrane was perforated during the operation were excluded. Finally, the study group was composed of 81 cases, comprising 54 males (66.7%) and 27 females (33.3%) with a mean age of 51.48 years.(Table 1)
Table 1. Sex and age distributions (n=81).
| Patient | No. of patients (%) |
|---|---|
| Gender | |
| Male | 54 (66.7) |
| Female | 27 (33.3) |
| Age (yr) | |
| ≤30 | 4 (4.9) |
| 31–40 | 4 (4.9) |
| 41–50 | 23 (28.4) |
| 51–60 | 41 (50.6) |
| 61–70 | 9 (11.1) |
The operation was performed on the right side in 37 cases (45.7%) and on the left side in 44 cases (54.3%). In addition, 68 cases (84.0%) used the lateral window technique and 13 cases (16.1%) used the crestal approach.(Table 2) Simultaneous bone graft was conducted in 75 cases.
Table 2. Operation site and approach (n=81).
| Operation | No. of patients (%) |
|---|---|
| Operation site | |
| Right | 37 (45.7) |
| Left | 44 (54.3) |
| Approach | |
| Lateral window | 68 (84.0) |
| Crestal | 13 (16.1) |
In our study, 10 cases (12.4%) showed nasal septum deviation to the operation site. Concha bullosa or paradoxical curvature of the middle concha was discovered in 12 cases (14.8%), and Haller cells were identified in 30 cases (37.0%). (Table 3)
Table 3. Correlations between anatomic variations and postoperative sinusitis (n=81).
| Anatomic variants | Patient | Complication | OR (95% CI) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deviated nasal septum | 10 (12.4) | 2/10 (20.0) | 3.30 (0.55–19.89) | 0.206 |
| Concha bullosa or paradoxical curvature | 12 (14.8) | 2/12 (16.7) | 2.56 (0.44–15.03) | 0.276 |
| Haller cells | 30 (37.0) | 6/30 (20.0) | 12.50 (1.42–109.72) | 0.009 |
| Any anatomic variants | 37 (45.7) | 6/37 (16.2) | 8.32 (0.95–72.66) | 0.043 |
(OR: odds ratio, CI: confidence interval)
Values are presented as number (%) or OR (95% CI).
Among 81 cases, 7 cases that showed consistent pain for longer than 2 weeks or nasal discharge were considered to be demonstrating a complication.
Statistical analysis was performed to evaluate the correlations between each anatomical variant and prolonged healing after sinus floor elevation. Correlation of nasal septum deviation did not show a significant result (P=0.206), and neither did that of the middle concha (P=0.276). However, although most patients who showed variants of the middle concha showed nasal septum deviation, these cases were excluded from the nasal septum deviation group due to deviation direction. In this regard, we evaluated the relation between complication and variants on the nasal septum or middle concha, and its significance level was 0.070. Unlike other anatomical variants, correlations of Haller cells was statistically significant (P=0.009).
IV. Discussion
The ostio-meatal unit plays an important role in the development of maxillary sinusitis by impairment of the mucociliary clearance system9. If the patency of the ostio-meatal unit is interrupted, clearance of the maxillary sinus can be delayed, and this unfavorable event can increase the risk for development of sinusitis.
Given the close relationship between the Schneiderian membrane and the ostium of the maxillary sinus and the fact that inflammatory reaction after any surgical procedure is inevitable, surgeons must consider the risk of infectious sequelae after sinus floor elevation. Because of the temporary interference of ciliary activity caused by the traumatic elevation of the Schneiderian membrane, altered mucous composition and bacterial infection can occur10,11. After sinus floor elevation, the maxillary sinus may be filled with hematoma or seroma, requiring removal. However, a mild inflammatory reaction can occur as a normal physiological activity of the mucosal airway system12, and this swelling of the mucosa can lead to obstruction of the patency of the ostio-meatal unit. As a result, sinus floor elevation might compromise the physiological drainage of the maxillary sinus into the middle meatus by transient inflammatory swelling on the mucosa of the ostium or due to other mechanisms that can predispose the patient to acute maxillary sinusitis13 and possibly lead to bone graft loss.
Although a transient or persisting effect on the ciliated mucosa can be expected as a result of raising the mucosa of the maxillary sinus, the mucosal reaction has been reported to be negligible7. Fortunately, the maxillary sinus mucosa is capable of adapting adequately to the alteration following sinus floor elevation14,15. In particular, in healthy persons, drainage of the maxillary sinus did not seem to be impaired after the procedure12. This can explain why the incidence of maxillary sinusitis after sinus floor elevation in the literature is less than 1%16,17. Using generally accepted Ear, Nose, and Throat (ENT) criteria for diagnosing sinusitis, occurrence of maxillary sinusitis after sinus floor elevation has been reported at 1.3%13. Despite the low incidence of maxillary sinusitis after this procedure, there is still inherent risk of disturbing the physiology of the sinus. It is generally assumed that alteration of the maxillary sinus anatomy, such as elevation of the Schneiderian membrane with bulging or injured sinus mucosa, might impair the physiology of the maxillary sinus.
Even though sinus floor elevation is considered an efficacious procedure, surgeons should remember that this procedure may impair the physiology of the sinus mucosa and cause unpleasant complications. In spite of the prompt postoperative recovery of the maxillary mucosa with a rapid return to preoperative sterility, it must be pointed out that the sinus compliance, which represents the ability to recover normal maxillary sinus homeostasis after sinus floor elevation, depends on its baseline condition18.
Anatomical variants of the paranasal sinus and nasal cavity are commonly detected, with an estimated prevalence of 68%5. Because of their contribution to the blockage of ostiomeatal units, some anatomic variants on the lateral nasal wall, such as deviated nasal septum, concha bullosa or paradoxical middle turbinate, bending of the uncinated process, and Haller cells, are very important. These variants can interfere with drainage and ventilation of the maxillary sinus and, thereby, can affect the risk of sinus mucosal disease6. These variants and their relations with the ostium of the maxillary sinus can be easily detected on computed tomographic images19.
Theoretically, anatomical variants of the lateral nasal wall are likely to shift and alter ostio-meatal complex components, possibly resulting in obstruction of maxillary sinus mucous drainage19,20. Altered anatomic relations in the nasal cavity and ostio-meatal complex might be involved in sinus drainage impairment. Compromised maxillary sinus drainage is closely associated with a reduction of the maxillary ostium21. Previous studies on the function of this ostium have shown a reduced size of ostium diameter in cases of sinusitis22.
The nasal septum is an osseocartilaginous wall that divides the nasal cavity. In the junction of the nasal cartilage with the vomer, acute angulation can occur23, resulting in deviation of the nasal septum. Severe nasal septal deviation has been assumed to be related with sinusitis by interfering with the ostio-meatal complex19,24,25.
The term concha bullosa was first introduced by Zuckerlandl in 1862, as a pneumatization of the middle turbinate. Paradoxical curvature of the middle turbinate is known as a convexity pointing toward the middle meatus. These common anatomical variants might cause secondary deformity of the turbinate, followed by the risk of obstruction of the middle meatus and mucosal pathologies23,26.
Another common anatomic variant is the presence of infraorbital ethmoidal cells, also known as Haller cells, which can be found between the maxillary sinus and orbital floor. This is a clinically important anatomical variant because it has been assumed to be an etiologic factor in recurrent maxillary sinusitis due to reduction of the ostio-meatal complex27. In surprevious studies, the incidence of Haller cells was variable; from 6% to 45.1%5,23. A possible reason for this discrepancy is differences in criteria for diagnosing Haller cells or in the technique of CT scanning. In this study, the prevalence of Haller cells was 37.0%.
In this study, correlations of nasal septum deviation and middle concha variants with complications were not significant (P=0.206 and P=0.276, respectively). On the other hand, the correlation of Haller cells with complications was statistically significant (P=0.009). We concluded that this difference was due to regional proximity of Haller cells. Unlike other variants, Haller cells are located right above the ostium, and this proximity may contribute to reduction of the ostium after the operation. Another reason for this result is the small number of investigated cases. Unlike Haller cells, incidences of anatomic variants of nasal septum and middle concha were 12.4% and 14.8%, respectively. If the number of included cases was sufficient, these variants could have been found to be significant.
V. Conclusion
Considering the influence of anatomic variants of ostiomeatal complex, it is recommended that candidates for maxillary sinus floor elevation with any radiological or anamnestic evidence suggesting impaired maxillary sinus conditions should undergo an ENT evaluation that includes CT of the maxillofacial district28. If anatomic variants that might impair the patency of the maxillary sinus are detected, the surgeon should inform the patient of increased risk of postoperative sinusitis and consider the use of nasal decongestants as a prophylaxis.
Footnotes
Conflict of Interest: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
References
- 1.Raghoebar GM, Brouwer TJ, Reintsema H, Van Oort RP. Augmentation of the maxillary sinus floor with autogenous bone for the placement of endosseous implants: a preliminary report. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1993;51:1198–1203. doi: 10.1016/s0278-2391(10)80288-5. discussion 1203-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Doud Galli SK, Lebowitz RA, Giacchi RJ, Glickman R, Jacobs JB. Chronic sinusitis complicating sinus lift surgery. Am J Rhinol. 2001;15:181–186. doi: 10.2500/105065801779954120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Misch CM. The pharmacologic management of maxillary sinus elevation surgery. J Oral Implantol. 1992;18:15–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Drettner B. The permeability of the maxillary ostium. Acta Oto-Laryngologica. 1965;60:304–314. doi: 10.3109/00016486509127033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bolger WE, Butzin CA, Parsons DS. Paranasal sinus bony anatomic variations and mucosal abnormalities: CT analysis for endoscopic sinus surgery. Laryngoscope. 1991;101:56–64. doi: 10.1288/00005537-199101000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bayram M, Sirikci A, Bayazit YA. Important anatomic variations of the sinonasal anatomy in light of endoscopic surgery: a pictorial review. Eur Radiol. 2001;11:1991–1997. doi: 10.1007/s003300100858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Timmenga NM, Raghoebar GM, Liem RS, van Weissenbruch R, Manson WL, Vissink A. Effects of maxillary sinus floor elevation surgery on maxillary sinus physiology. Eur J Oral Sci. 2003;111:189–197. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0722.2003.00012.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Yonkers AJ. Sinusitis--inspecting the causes and treatment. Ear Nose Throat J. 1992;71:258–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Bertrand B, Eloy P. Relationship of chronic ethmoidal sinusitis, maxillary sinusitis, and ostial permeability controlled by sinusomanometry: statistical study. Laryngoscope. 1992;102:1281–1284. doi: 10.1288/00005537-199211000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Misch CE. Maxillary sinus augmentation for endosteal implants: organized alternative treatment plans. Int J Oral Implantol. 1987;4:49–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Zimbler MS, Lebowitz RA, Glickman R, Brecht LE, Jacobs JB. Antral augmentation, osseointegration, and sinusitis: the otolaryngologist's perspective. Am J Rhinol. 1998;12:311–316. doi: 10.2500/105065898780182381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Timmenga NM, Raghoebar GM, Boering G, van Weissenbruch R. Maxillary sinus function after sinus lifts for the insertion of dental implants. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1997;55:936–939. doi: 10.1016/s0278-2391(97)90063-x. discussion 940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Timmenga NM, Raghoebar GM, van Weissenbruch R, Vissink A. Maxillary sinusitis after augmentation of the maxillary sinus floor: a report of 2 cases. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2001;59:200–204. doi: 10.1053/joms.2001.20494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Stammberger H. Endoscopic endonasal surgery--concepts in treatment of recurring rhinosinusitis. Part II. Surgical technique. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1986;94:147–156. doi: 10.1177/019459988609400203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Jensen OT, Shulman LB, Block MS, Iacono VJ. Report of the sinus consensus conference of 1996. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1998;13(Suppl):11–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Bhattacharyya N. Bilateral chronic maxillary sinusitis after the sinus-lift procedure. Am J Otolaryngol. 1999;20:133–135. doi: 10.1016/s0196-0709(99)90022-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Zinner ID, Small SA. Sinus-lift graft: using the maxillary sinuses to support implants. J Am Dent Assoc. 1996;127:51–57. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.1996.0030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Torretta S, Mantovani M, Testori T, Cappadona M, Pignataro L. Importance of ENT assessment in stratifying candidates for sinus floor elevation: a prospective clinical study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2013;24:57–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2011.02371.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Laine FJ, Smoker WR. The ostiomeatal unit and endoscopic surgery: anatomy, variations, and imaging findings in inflammatory diseases. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1992;159:849–857. doi: 10.2214/ajr.159.4.1529853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Scribano E, Ascenti G, Cascio F, Racchiusa S, Salamone I. Computerized tomography in the evaluation of anatomic variations of the ostiomeatal complex. Radiol Med. 1993;86:195–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Aust R, Drettner B. The functional size of the human maxillary ostium in vivo. Acta Otolaryngol. 1974;78:432–435. doi: 10.3109/00016487409126376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Stierna P, Söderlund K, Hultman E. Chronic maxillary sinusitis. Energy metabolism in sinus mucosa and secretion. Acta Otolaryngol. 1991;111:135–143. doi: 10.3109/00016489109137364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Arslan H, Aydinlioğlu A, Bozkurt M, Egeli E. Anatomic variations of the paranasal sinuses: CT examination for endoscopic sinus surgery. Auris Nasus Larynx. 1999;26:39–48. doi: 10.1016/s0385-8146(98)00024-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Fadda GL, Rosso S, Aversa S, Petrelli A, Ondolo C, Succo G. Multiparametric statistical correlations between paranasal sinus anatomic variations and chronic rhinosinusitis. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2012;32:244–251. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Ameri AA, Eslambolchi A, Bakhshandeh H. Anatomic variants of paranasal sinuses and chronic sinusitis. Iran J Radiol. 2005;2:121–124. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Nouraei SA, Elisay AR, Dimarco A, Abdi R, Majidi H, Madani SA, et al. Variations in paranasal sinus anatomy: implications for the pathophysiology of chronic rhinosinusitis and safety of endoscopic sinus surgery. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2009;38:32–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Zinreich SJ, Kennedy DW, Rosenbaum AE, Gayler BW, Kumar AJ, Stammberger H. Paranasal sinuses: CT imaging requirements for endoscopic surgery. Radiology. 1987;163:769–775. doi: 10.1148/radiology.163.3.3575731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Pignataro L, Mantovani M, Torretta S, Felisati G, Sambataro G. ENT assessment in the integrated management of candidate for (maxillary) sinus lift. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2008;28:110–119. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]