Abstract
Large conductance Ca2+-activated K+ (BK) channels play essential roles in both excitable and non-excitable cells. For example, in chondrocytes, agonist-induced Ca2+ release from intracellular store activates BK channels, and this hyperpolarizes these cells, augments Ca2+ entry, and forms a positive feed-back mechanism for Ca2+ signaling and stimulation-secretion coupling. In the present study, functional roles of a newly identified splice variant in the BK channel α subunit (BKαΔe2) were examined in a human chondrocyte cell line, OUMS-27, and in a HEK293 expression system. Although BKαΔe2 lacks exon2, which codes the intracellular S0-S1 linker (Glu-127–Leu-180), significant expression was detected in several tissues from humans and mice. Molecular image analyses revealed that BKαΔe2 channels are not expressed on plasma membrane but can traffic to the plasma membrane after forming hetero-tetramer units with wild-type BKα (BKαWT). Single-channel current analyses demonstrated that BKα hetero-tetramers containing one, two, or three BKαΔe2 subunits are functional. These hetero-tetramers have a smaller single channel conductance and exhibit lower trafficking efficiency than BKαWT homo-tetramers in a stoichiometry-dependent manner. Site-directed mutagenesis of residues in exon2 identified Helix2 and the linker to S1 (Trp-158–Leu-180, particularly Arg-178) as an essential segment for channel function including voltage dependence and trafficking. BKαΔe2 knockdown in OUMS-27 chondrocytes increased BK current density and augmented the responsiveness to histamine assayed as cyclooxygenase-2 gene expression. These findings provide significant new evidence that BKαΔe2 can modulate cellular responses to physiological stimuli in human chondrocyte and contribute under pathophysiological conditions, such as osteoarthritis.
Keywords: alternative splicing, chondrocyte, fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET), molecular imaging, patch clamp, potassium channel, single molecule biophysics
Introduction
Changes in intracellular calcium concentration ([Ca2+]i) are essential elements of an intracellular second messenger for a wide variety of cellular functions. Large conductance Ca2+-activated K+ (BK)3 channels are widely expressed in both excitable and non-excitable mammalian cells. These BK currents strongly regulate essential physiological responses by hyperpolarizing the membrane potential (1). Each BK channel consists of pore-forming α subunits (BKα) arranged as tetramers that act in conjunction with tissue specific regulatory β and/or γ subunits (2). Functional diversity of BK channels can also be conferred by alternative splicing of either BKα or BKβ mRNA (3, 4). For example, the C terminus of the BKα subunit contains alternative splicing sites, C1 and C2 (3). A well documented splice variant of BKα is the stress-regulated exon (STREX), which can be induced by stress hormones such as corticoids (4). Dominant-negative forms of BKα subunit have also been discovered. The SV1 variant, which has an ER retention signal (CVLF motif) between the S0 and S1 region, can bind to wild-type BKα and prevent its translocation to PM (5). In addition, the hSloΔ579–664 variant lacks exon18, 19, and 23, coding the ER exit signal motif and, therefore, cannot traffic to the PM (3).
Articular cartilage consists mainly of chondrocytes and their secretion products that form the extracellular matrix (type-ΙΙ collagen and proteoglycans). Their ability to synthesize and release lubricants is essential for normal joint movement. Chondrocytes are exposed to a number of different stimuli including mechanical stress and osmotic and ionic changes in the synovial fluid (6). In response to these stimuli, chondrocytes alter the extracellular matrix to maintain homeostasis. Various types of ion channels are expressed in chondrocytes (7), where they regulate membrane potential and modulate [Ca2+]i (8). Changes in [Ca2+]i modulate chondrogenesis, proliferation, cell death (9), and baseline anabolic and catabolic activities in chondrocytes. Under pathophysiological conditions, such as osteoarthritis (OA), histamine release from resident mast cells enhances production of proinflammatory mediators and matrix degrading enzymes (matrix metalloproteinases). Histamine can also alter the proliferation of chondrocytes in articular joints. Specific spatial and temporal patterns of changes in [Ca2+]i are considered essential components of disease initiation and progression.
In a well studied model cell of the human chondrocyte, OUMS-27 cells, BK channels (as well as other Ca2+-activated K+ (KCa) channels) are functionally expressed. BK channels are involved in enhancement of histamine-induced Ca2+ influx after membrane hyperpolarization (8, 10). BK channels also act as mechano-sensing elements in chondrocytes, as judged by their sensitivity to hypo-osmotic challenges (11). The BK channel expression is up-regulated in patients with progressive OA (12). For these reasons, BK channels are thought to be involved in physiological and/or pathological regulation of chondrocyte function.
We have identified a novel BKα splice variant (BKαΔe2: AB524033.1) in OUMS-27 cells. The present study was undertaken to identify the molecular details of this novel variant and define its functional roles in chondrocytes. Our data demonstrate that this BKαΔe2 splice variant can negatively regulate functional expression of BK channels and modulate essential cellular functions, such as cyclooxygenase-2 (COX2) gene expression, in chondrocytes.
Results
Identification of a Novel Splice Variant of BKα
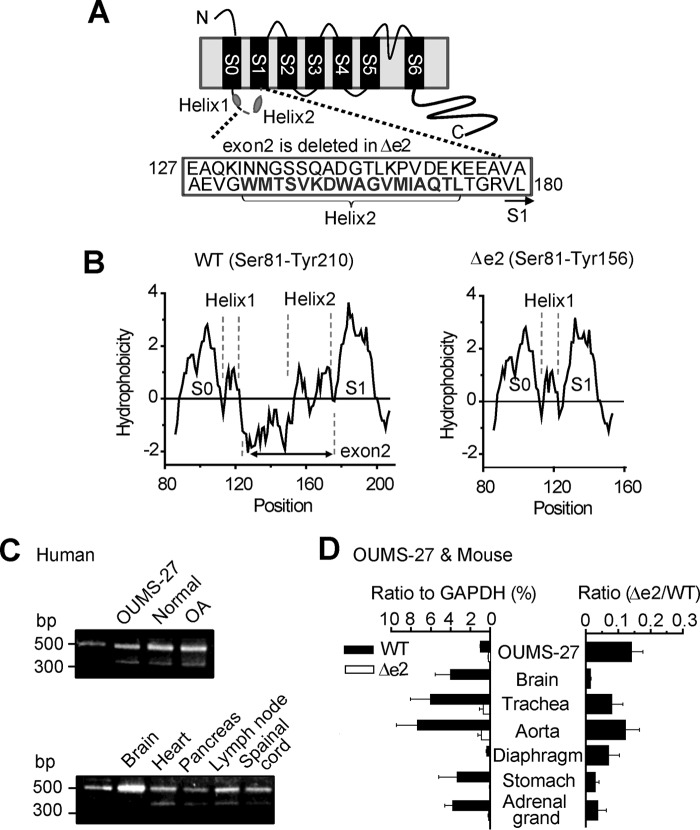
A novel splice variant of BKα, which is 54 amino acids shorter than wild-type BKα (BKαWT), was cloned (supplemental Fig. S1) from an OUMS-27 human chondrocyte cell line. This variant lacks a region encoded by exon2 (Glu127–Leu180) corresponding to the latter part of S0-S1 linker (Trp108–Arg178) and first two amino acid residues (Val179 and Leu180) of S1 segment (Val179–Ser199) (BKαΔe2, Fig. 1A). Recently NMR analysis revealed that the S0-S1 loop contains two short α-helix (Helix1 and Helix2) (13). As shown in Fig. 1B, the deletion of exon2 does not disrupt the overall hydrophobicity pattern of S1 segment of BKαΔe2. Instead, it alters hydrophilic region and the Helix2 in S0-S1 loop.
FIGURE 1.
The molecular schema and tissue distribution of BKαΔe2. A, schematic diagram of BKαΔe2. This splice variant lacks exon2, which codes approximately half of S0-S1 linker (C-terminal side) and first two residues (179VL180) in the S1 segment. B, hydrophobicity plots from the extracellular N terminus (Ser-81) to the S1-S2 loop (BKαWT: Tyr-210, BKαΔe2: Tyr-156) were described by Kyte and Doolittle hydropathy analysis using ProtScale done with the ExPASy Server. C, BKαΔe2 mRNA is expressed in (i) OUMS-27 cell line derived from human chondrosarcoma, (ii) articular cartilage from a healthy donor (Normal), and (iii) articular cartilage from a patient with OA, and (iv) other human tissues. The sizes of bands corresponding to BKαWT and BKαΔe2 are 514 bp and 352 bp, respectively. D, expression of BKαΔe2 mRNA in OUMS-27 cells and mouse tissues. mRNA levels of BKαWT (WT) and BKαΔe2 (Δe2) were normalized to GAPDH (left) using Q-PCR (n = 4). The amount of BKαΔe2 mRNA was normalized to that of BKαWT mRNA (right).
RT-PCR analysis establishes that this BKαΔe2-splice variant is expressed in OUMS-27 cells, human cartilage from both healthy and OA specimens (Fig. 1C, see supplemental Table S1 for primer information). Expression of BKαΔe2 mRNA has also been detected in other human tissues, such as heart and lymph node (Fig. 1C). In addition, quantitative real-time PCR (Q-PCR) analysis revealed relatively high expression of BKαΔe2 in OUMS-27, a well studied human chondrocyte cell line (relative expression to WT: 0.14 ± 0.03, n = 4) and trachea and aorta from mice (0.08 ± 0.03 and 0.12 ± 0.04, n = 4 each; Fig. 1D).
The BKαΔe2 Splice Variant Does Not Exhibit Ion Channel Function
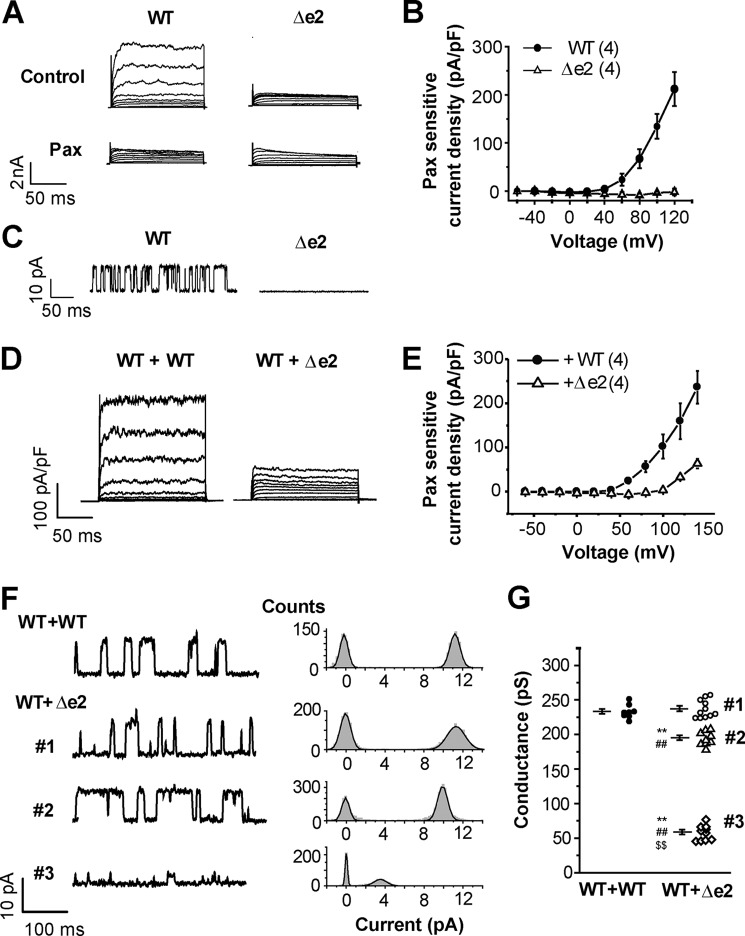
To evaluate whether BKαΔe2 can form functional channels, this transcript was labeled with a FLAG tag at its extracellular N terminus and also by mCherry (mCh) at the intracellular C terminus and then transiently expressed in HEK293 cells. BK-mediated currents were assessed using whole-cell patch clamp technique. When the pCa of pipette filling solution was 6.5, cells expressing BKαWT exhibited paxilline (Pax, a specific BK channel blocker)-sensitive currents; in contrast, BKαΔe2-transfected cells did not (Fig. 2, A and B). As shown in Fig. 2C, the unitary current amplitude (measured using inside-out patch clamp recordings) was 11.5 ± 0.9 pA at +50 mV (4 single channel recordings) in HEK293 cells expressing BKαWT, but no single channel current was detected from cells expressing BKαΔe2 (5 recordings).
FIGURE 2.
Co-expression of BKαΔe2 with BKαWT attenuates whole-cell currents and the single-channel conductance. A, whole-cell currents recorded from HEK293 cells expressing BKαWT or BKαΔe2 transcripts. To define the BK current component, a selective blocker 1 μm Pax was applied to these cells. B, electrophysiological data showing the relationship between Pax-sensitive current amplitude and activation voltage. The number of experiments is shown in parentheses. C, inside-out patch clamp recordings were used to measure single channel currents due to BKαWT or BKαΔe2 transcripts. D, whole-cell currents in HEK293 cells co-expressing WT-CFP and WT-mCh (WT+WT) or WT-CFP and Δe2-mCh (WT+Δe2). Cells were transfected with cDNA at a ratio (WT:Δe2) of 1:3. E, current-voltage relationships for the Pax-sensitive currents. F, single channel currents (left) and corresponding amplitude histograms of the currents (right) were obtained from cells expressing both WT and Δe2 at +50 mV. In control cells (WT+WT), these unitary currents show a single distribution pattern that peaks at 11.2 pA. In contrast, the amplitude histogram in WT+Δe2 forms three distinct groups (#1, 11.1 pA; #2, 9.7 pA; #3, 3.5 pA). Cells were transfected with cDNA at a ratio (WT:Δe2) of 1:1. G, single channel conductance in WT+WT (8 recordings from 8 patches) and WT+Δe2 (#1, #2, and #3, 30 recordings from 27 patches) are summarized. **, p < 0.01 versus WT+WT; ##, p < 0.01 versus #1; $$, p < 0.01 versus #2. See also supplemental Table S2.
Co-expression of BKαΔe2 Attenuates Whole-cell Currents and Reduces Single-channel BKαWT Conductance
Both whole-cell and inside-out path-clamp recordings were obtained using cells co-transfected with BKαWT and BKαΔe2. Whole-cell BKαWT currents were markedly attenuated by co-expression of BKαΔe2 (WT: Δe2 = 1:3) (Fig. 2, D and E, p < 0.01 at +100 mV).
Ratio-dependent inhibition by co-transfection of BKαΔe2 cDNA with BKαWT cDNA was examined using HEK293 cells. Constant amounts of BKαWT cDNA (50 ng) and variable amounts of BKαΔe2 cDNA (5, 50, and 150 ng, respectively) were applied for co-transfection to make cDNA ratio (WT:Δe2) 1:0.1, 1:1 and 1:3. HEK293 cells transfected with mock vector instead of BKαΔe2 cDNA (WT:Δe2 = 1:0) were used as a control (288.7 ± 35.9 pA/pF at +120 mV, 7 cells). As shown in supplemental Fig. S2, the co-transfection of BKαΔe2 cDNA with BKαWT cDNA suppressed the whole-cell BK channel currents in a ratio-dependent manner (BK channel currents at +120 mV: (1:0.1) 176.1 ± 37.5 pA/pF, 9 cells; (1:1) 97.6 ± 25.8 pA/pF, 7 cells; (1:3) 32.9 pA/pF ± 4.3 pA/pF, 5 cells; p < 0.05 versus control). Thus, application of only amount of BKαΔe2 cDNA actually reduced whole-cell BK channel currents. This result suggests that the relatively small ratio of BKαΔe2 mRNA in OUMS-27 cells (Fig. 1D) may be sufficient to substantially reduce BK channel currents.
Unitary currents through single BK channels in HEK293 cells co-expressing BKαWT-GFP (WT-GFP) and BKαWT-mCherry (WT-mCh) were similar to those in Fig. 2C. The averaged single channel conductance of WT-GFP+WT-mCh (WT+WT in Fig. 2, F and G, and supplemental Table S2) was 232.9 ± 3.5 pS (8 recordings, p > 0.05 versus non-labeled WT: 218.0 ± 8.1 pS, 7 recordings). On the other hand, in HEK293 cells co-expressing WT-GFP and BKαΔe2-mCherry (Δe2-mCh) the distribution of unitary current amplitude at +50 mV could be separated into three groups (WT+Δe2 #1, #2, and #3) (Fig. 2, F and G, and supplemental Table S2). The single channel conductance of WT+Δe2 #1 was 236.9 ± 3.9 pS (11 recordings, p > 0.05 versus WT+WT), and that of WT+Δe2 #2 and #3 was 194.7 ± 3.4 pS (9 recordings, p < 0.01 versus WT+WT and WT+Δe2 #1) and 56.6 ± 3.4 pS (10 recordings, p < 0.01 versus WT+WT, WT+Δe2 #1 and #2). The mean open time of WT+Δe2 #3 at +50 mV (4.1 ± 0.5 ms) was also significantly shorter than those of WT+WT (10.3 ± 1.4 ms, p < 0.05), WT+Δe2 #1 (11.7 ± 2.3 ms, p < 0.01) and #2 (13.3 ± 2.2 ms, p < 0.01).
In summary, BKαΔe2 can form hetero-tetramers with BKαWT that yield functional channels which have smaller single channel conductance and shorter mean open time than the corresponding homo-tetrameric BKαWT channels. Based on the conductance shown above, it is apparent that WT+Δe2 #1 corresponds to WT homo-tetramer. However, the stoichiometry in #2 and #3 is unclear.
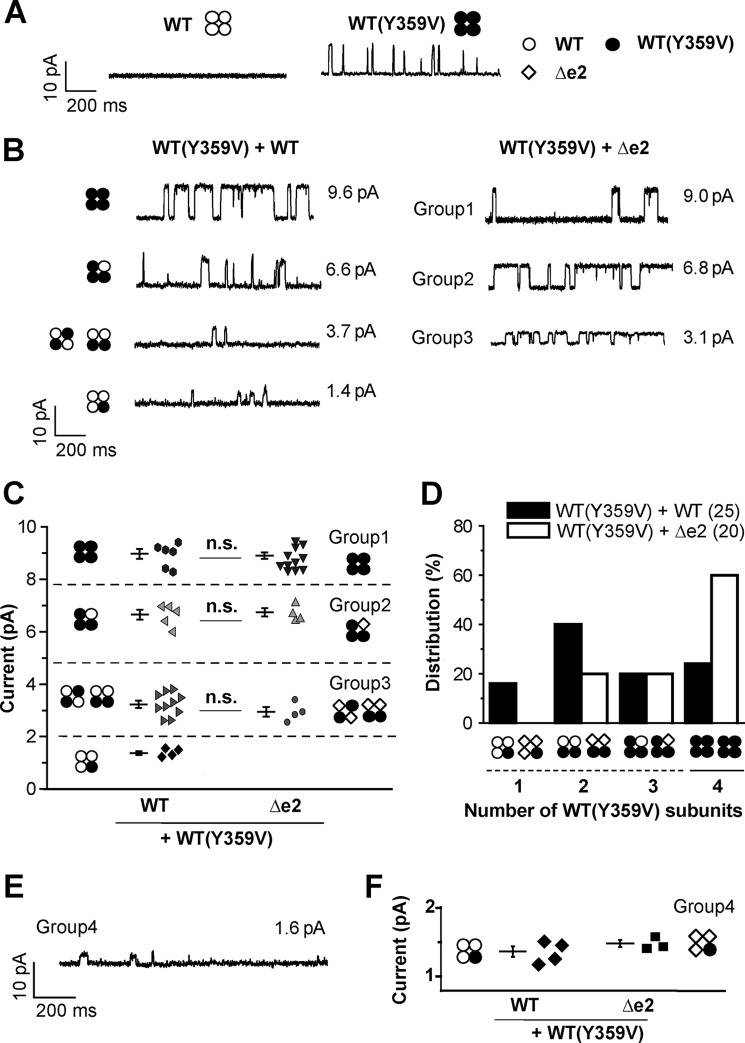
BKα Tetramer Containing One, Two, or Three BKαΔe2 Subunits in PM Can Permeate K+
The stoichiometry of functional BKαWT/BKαΔe2 hetero-tetramers was examined based on data from studies using tetraethylammonium (TEA, a BK channel blocker) as a pharmacological tool. It has been reported that when tyrosine residue at 359 in BKαWT is replaced with valine (BKαY359V), the resulting variant is insensitive to TEA (Fig. 3A) (14). When BKαY359V-mCh and BKαWT-GFP are co-expressed in HEK293 cells (WT(Y359V)+WT), unitary current amplitude in the presence of 2 mm TEA increased in approximate proportion to the number of BKαY359V subunits within a BKα tetramer (predicted number of WT(Y359V) and corresponding unitary currents in WT(Y359V)+WT: one and 1.4 ± 0.1 pA (4 recordings), two and 3.2 ± 0.1 pA (10 recordings), three and 6.6 ± 0.2 pA (5 recordings), four and 9.0 ± 0.2 pA (6 recordings) (Fig. 3, B and C, and supplemental Table S3) (14).
FIGURE 3.
BKα tetramer containing one, two, or three BKαΔe2 subunits in PM can permeate K+. A, single channel currents recorded in the presence of 2 mm TEA in the pipette solution. WT, WT(Y359V), and Δe2 subunits are presented by white circles, black circles, and white diamonds, respectively, in this figure. B, single channel currents recorded in cells expressing WT(Y359V)+WT (no mutation) (left) or cells expressing WT(Y359V)+Δe2 (right) at +50 mV in the presence of TEA. Cells were transfected with cDNA at a ratio (WT(Y359V):WT or WT(Y359V):Δe2) of 1:1. Each potential hetero-tetramer complex in a cell expressing WT(Y359V)+WT is also illustrated in the current traces. Note that unitary current distribution was divided into three distinct groups (Groups 1–3) in cells expressing WT(Y359V)+Δe2. C, scatter plots of the unitary current amplitude recorded in cells expressing WT(Y359V)+WT (25 recordings from 12 patches) or cells expressing WT(Y359V)+Δe2 (20 recordings from 16 patches). There was no significant difference in the distribution (p > 0.05 by F test) and mean value (n.s., p > 0.05 by t test) between the two types of cells. Predicted model of hetero- or homo-tetramer complexes are shown in both sides of the scatter plots. D, frequency distribution (%) of channels including the predicted number of WT(Y359V) within the single tetramer complex. Here the number of recordings that contained single channel currents due to each complex of BKα tetramer were counted. The total number of BKα tetramers within each patch could not be confirmed in this study. See “Experimental Procedures” for details. E, only when membrane patches were excised from cells exhibiting very strong fluorescence derived from Δe2-GFP, unitary currents smaller than 2 pA were detected. Cells were transfected with cDNA at a ratio (WT(Y359V)-mCh:Δe2-GFP) of 1:1. F, the unitary currents were compared with those of WT/WT(Y359V) = 3:1. There is no significant difference between the two groups (n = 4 in WT/WT(Y359V) and n = 3 in Δe2/WT(Y359V), p > 0.05). The data of WT/WT(Y359V) group here are the same as presented in C.
In cells co-expressing BKαY359V-mCh and BKαΔe2-GFP (WT(Y359V)+Δe2), unitary current distribution was divided into three groups (group 1: 8.9 ± 0.1 pA (12 recordings); group 2: 6.7 ± 0.2 pA (4 recordings); group 3: 2.9 ± 0.2 pA (4 recordings); Fig. 3, B and C, and supplemental Table S3). Then, it was examined to determine if the mean unitary currents of these three groups matched those of the corresponding groups in WT(Y359V)+WT cells, respectively (Fig. 3C). Statistical analyses denote distributions of single channel currents are equal between two groups having closest mean values (p > 0.05 by F-test). There is no significant difference (p > 0.05 by t test) between each set of three pairs.
The appearance rate of hetero-tetramers consisting of BKαY359V and BKαΔe2 (i.e. the sum of the 2:2 and 3:1 hetero-tetramers) was approximately 40%, significantly lower than the BKαY359V and BKαWT hetero-tetramers (1:3, 2:2, and 3:1, approximately 76%, indicated by the dashed line in Fig. 3D).
In addition, we found a small population of cells showing robust expression of BKαΔe2 judging from strong GFP fluorescence. Only when membrane patches were excised from some of these cells, small unitary currents corresponding to those of WT/WT(Y359V) = 3:1 were detected (1.5 ± 0.1 pA, 3 recordings, p > 0.05 versus 1.4 ± 0.1 pA of WT/WT(Y359V) = 3:1; Fig. 3, E and F). In summary, WT/Δe2 hetero-tetramers at the stoichiometry of 3:1, 2:2, and 1:3 are functional. WT+Δe2 #2 and #3 correspond to WT/Δe2 = 3:1 and WT/Δe2 = 2:2, respectively.
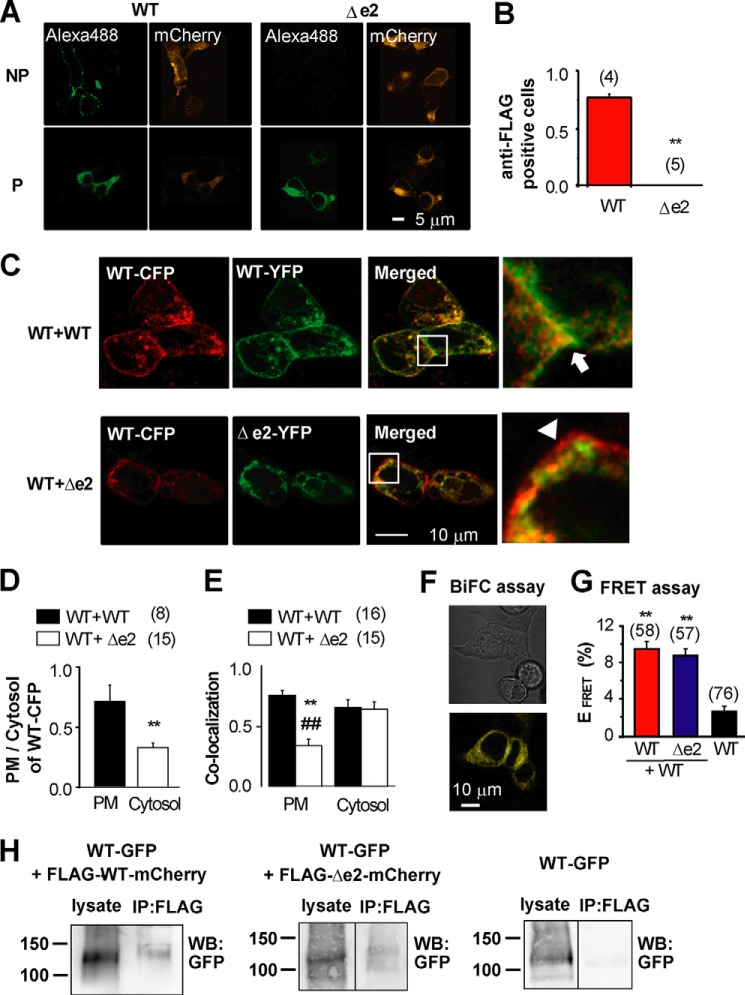
Molecular Imaging Shows Hetero-tetramer Formation of BKαΔe2 and BKαWT in PM
To complement and extend our electrophysiological findings, these same BKα hetero-tetramer complexes at the surface membrane were analyzed using confocal microscopy. A non-permeabilized (NP) labeling method was used to identify the BK channels that expressed well only in the surface membrane (PM) (3, 5). Because the N terminus of BKα is located in extracellular space (Fig. 1A), the N termini of both BKαWT and BKαΔe2 were fused with FLAG tag. In addition, the C termini were tagged with mCh. In HEK293 cells expressing BKαWT, the anti-FLAG antibody detected extracellular FLAG tag fused to BKαWT (Alexa488, Fig. 4A). The anti-FLAG antibody did not recognize FLAG tag conjugated to BKαΔe2; however, after membrane permeabilization, it did so. The ratio of anti-FLAG positive to mCh-positive cells, which indicates the efficiency of trafficking to PM, was ∼0.8 in cells expressing BKαWT. In contrast, this ratio was almost zero in cells expressing BKαΔe2 (Fig. 4B).
FIGURE 4.
The BKαΔe2 splice can prevent trafficking of BKαWT to the PM after hetero-tetramer formation. A, confocal images of WT and Δe2 stained with anti-FLAG antibody before (NP) and after (P) membrane permeabilization (Alexa488). Images of mCh fused to C termini are also shown (mCherry). B, the ratio of anti-FLAG positive cells to mCh-positive cells within regions of interest. **, p < 0.01. C, confocal images of cells co-expressing WT-CFP +WT-YFP (WT+WT: upper panel), and WT-CFP+Δe2-YFP (WT+Δe2: lower panel). In merged and expanded areas (enclosed by squares) in WT+WT, significant co-localization (yellow) at the PM is indicated by an arrow. In WT+Δe2, CFP fluorescence (red) rather than co-localization at the PM is indicated by an arrowhead. Cells were transfected with cDNA at a ratio (CFP:YFP) of 1:1. D, the ratio of fluorescence intensity of WT-CFP in PM to that of cytosol region. **, p < 0.01. E, co-localization ratio of WT-CFP in WT-CFP+WT-YFP (black column) or WT-CFP+Δe2-YFP (white) cells was analyzed in PM and Cytosol. **, p < 0.01 versus WT+WT in PM. ##, p < 0.01 versus WT+Δe2 in cytosol. F, BiFC assay was performed to detect direct coupling between WT and Δe2. A representative set of images from three independent experiments is presented. Cells were transfected with cDNA at a ratio (WT-VC155:Δe2-VN173) of 1:1. G, FRET analysis based on acceptor photobleaching was carried out using WT-YFP, Δe2-YFP, and WT-CFP. Cells were transfected with cDNA at a ratio (CFP:YFP) of 1:1. **, p < 0.01 versus WT-CFP alone. H, co-IP assay was performed using HEK293 cells expressing WT-GFP + FLAG-WT-mCh, WT-GFP + FLAG-Δe2-mCh, or only WT-GFP (for a negative control). Lysates were precipitated with anti-FLAG M2 antibody and blotted using the anti-GFP antibody. Similar results were obtained from three independent experiments. Cells were transfected with cDNA at a ratio (GFP:mCh) of 1:1.
When BKαWT transcripts labeled with either YFP or CFP were co-expressed in HEK293 cells, the WT-CFP/WT-YFP complex demonstrated distinct and significant co-localization along the PM (Fig. 4C). In contrast, when WT-CFP and Δe2-YFP were co-expressed, both the fraction of WT-CFP in PM versus cytosol (Fig. 4D) and the ratio of WT-CFP co-localized with Δe2-YFP in the PM (Fig. 4E) were much smaller than those in WT-CFP and WT-YFP co-expression, respectively. Moreover, WT-CFP was highly co-localized with BKαΔe2 only in the cytosol (Fig. 4E, p < 0.01 versus WT+WT in PM and WT+Δe2 in cytosol). Thus, hetero-tetramer formation of BKαΔe2 with BKαWT reduces the trafficking efficiency of these complexes to the PM.
Heteromeric BKα formation was also examined using a bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) assay (10) (Fig. 4F). As shown in Fig. 4F, Venus fluorescence was consistently detected in HEK293 cells that co-expressed BKαΔe2 and BKαWT tagged with N (VN173) and C (VC155) termini of Venus, respectively. To examine further the possible interactions between BKαWT and BKαΔe2, FRET analysis based on an acceptor photobleaching method was also carried out (Fig. 4G) (15, 16). FRET was observed consistently in cells that co-expressed WT-YFP and Δe2-CFP. The results from this co-immunoprecipitation (co-IP) assay also demonstrate molecular interaction between BKαΔe2 and BKαWT in HEK293 cells (Fig. 4H). In summary, our analysis shows that BKαΔe2 binds to both BKαWT and BKαΔe2 with similar affinity to form heteromeric molecular complexes. Importantly, however, hetero-tetramer formation of BKαWT with BKαΔe2 reduced the trafficking efficiency.
Molecular Imaging Reveals Stoichiometry of the BKαWT/BKαΔe2 Hetero-tetramer
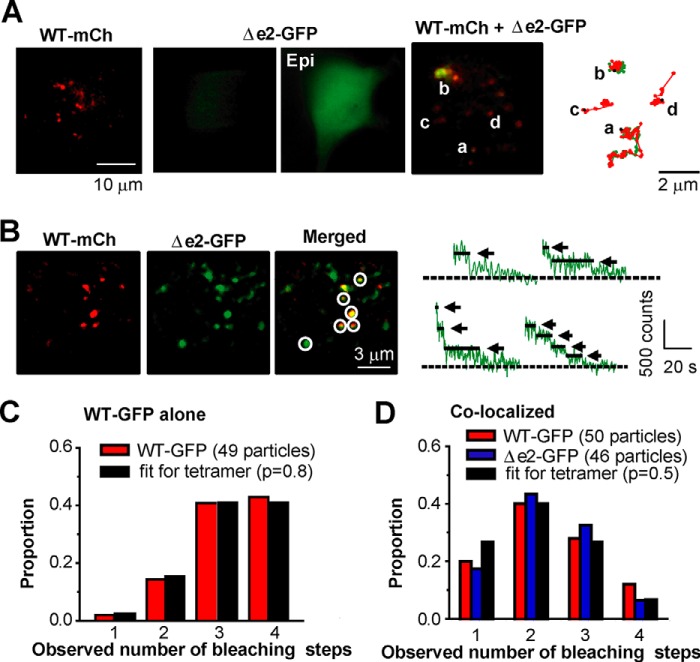
The stoichiometry of BKαWT/BKαΔe2 heteromeric channels was further examined by employing single molecule imaging methods based on TIRF microscopy (15, 17). Under TIRF illumination, the expression of only WT-mCh transcripts resulted in a distinct dotted pattern of signals (Fig. 5A). In contrast, expression of Δe2-GFP alone showed very weak fluorescence signals in the TIRF field, and it exhibited bright fluorescence under epifluorescence microscopy, suggesting mainly intracellular localization. When WT-mCh and Δe2-GFP were co-expressed, some of Δe2-GFP particles could be detected in the PM, where they were co-localized with WT-mCh particles. The combined signals due to mCh and GFP, detected as yellow particles, progressively moved together on the PM during 60-s measurements (Fig. 5A and see also the supplemental movie). This strongly suggests specific hetero-tetramer formation at or very near the PM.
FIGURE 5.
The BKαΔe2 splice variant can form hetero-tetramer with BKαWT. A, TIRF images from cells expressing WT-mCh, Δe2-GFP, or both (cells were transfected with cDNA at a ratio (WT-mCh:Δe2-GFP) of 1:1). Integrated fluorescence signals taken at 60 s (right). Signals from GFP or mCh are illustrated by green and red, respectively. Epi indicates an image obtained using epifluorescence microscopy. B, TIRF images of cells expressing WT-mCh and Δe2-GFP. Co-localized signals are indicated by circles. Traces of GFP fluorescence upon sequential excitation are shown in the right panels. Arrows and dotted lines denote bleaching steps and the basal levels, respectively. Cells were transfected with cDNA at a ratio (GFP:mCh) of 1:1. C, summary of frequency distributions of the number of WT-GFP bleaching steps measured in HEK293 cells transfected with WT-GFP and WT-mCh (49 spots from 6 cells). Here WT-GFP spots detected alone (not with WT-mCh) were analyzed. Note that the distribution is similar to theoretical frequency distribution assuming (i) WT-GFP homo-tetramers (n = 4) and (ii) the apparent probability of GFP being fluorescent (p) as 0.8 (fit for tetramer). D, frequency distributions of the number of bleaching steps in co-localizing WT-GFP (red) or Δe2-GFP (blue) (50 and 46 particles from 5 and 6 cells, respectively). Cells were transfected with cDNA at a ratio (GFP:mCh) of 1:1. Note that in both cases the distributions show the peaks at 2, and these were well fitted to the binomial distribution with n = 4 and p = 0.5.
The stoichiometry of these hetero-tetramers was also studied using molecular imaging, which quantified the “step down” decrease in fluorescent intensity (a single molecule GFP bleaching method) (15, 17). In this approach: two types of cells co-expressing WT-mCh and WT-GFP or expressing WT-mCh and Δe2-GFP were prepared by transfection of cDNA at a ratio of 1:1. Single spots of WT-GFP, which were detected alone (not with WT-mCh) in cells co-expressing WT-mCh and WT-GFP, displayed mainly 3 or 4 step bleaching (Fig. 5C). The population distribution of the data obtained from this bleaching step analysis was well fitted to the theoretical binomial distribution for a tetramer (n = 4), with the apparent probability of GFP being fluorescent during excitation (p) set at 0.80 (18) (see “Experimental Procedures”). This result provided evidence that each GFP spot contained single BKαWT tetramer under these conditions. In the secondary analysis, the pattern of bleaching of the GFP spots, which were detected by co-localization of mCh and GFP as yellow signals and assumed to represent heteromers of WT-mCh and Δe2-GFP (circles in Fig. 5B), was counted. Although these spots exhibited bleaching steps corresponding to one to four subunits, the population distribution peaked at two-step bleaching (Fig. 5D). Similarly, the presumed heteromer of WT-GFP and WT-mCh yielded a distribution that peaked at two steps. Both distributions were well fitted by binomial distribution, given n = 4 and apparent fluorescence probability p = 0.5. Here, p = 0.5 is based on the premise that two molecules (A and B) possess the same affinity between A-A, A-B, and B-B, when composing homo- or hetero-tetramer. It is notable that both distributions of WT-GFP/WT-mCh and Δe2-GFP/WT-mCh are peaked at two-step bleaching and well fitted to the theoretical distribution. These results suggest that binding affinity between Δe2-GFP and WT-mCh is comparable with that between WT-GFP and WT-mCh and support the finding by FRET shown in Fig. 4G. Taken together, BKαΔe2 can form tetramers with BKαWT at the stoichiometry of 1:3, 2:2, and 3:1.
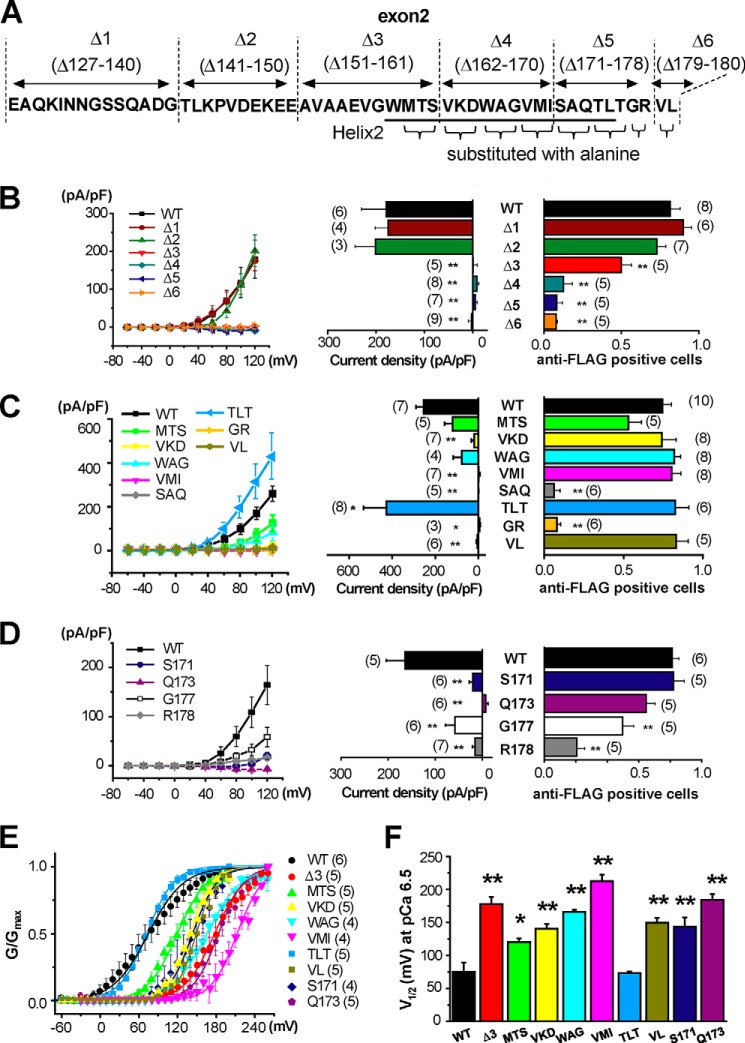
The Second Short α-Helix Region in S0-S1 Linker (Helix2) Is Responsible for Both the Cell Surface Expression and the Voltage Dependency
The region in exon2 that is responsible for surface expression was examined using site-directed mutagenesis (Fig. 6A and supplemental Table S4). Channel function and surface expression were measured based on whole-cell patch clamp recordings and anti-FLAG antibody imaging, respectively (see Fig. 2, A and B, Fig. 4, A and B, and supplemental Table S4). Mutants of Δ127–140 (Δ1) and Δ141–150 (Δ2) resulted in BK channel activity that were very similar to BKαWT. Mutations of Δ151–161 (Δ3) showed smaller but significant surface expression and only very little BK channel activity (n = 5). Other variants (Δ162–170 (Δ4), Δ171–178 (Δ5), or Δ179–180 (Δ6)) totally failed to generate BK currents and cell surface expression (Fig. 6B).
FIGURE 6.
Site-directed mutagenesis identified the region in exon2 that is responsible for the molecular/biophysical characteristics of BKαΔe2. A, diagram of the mutants selected for this study. B–D, current-voltage relationships of Pax-sensitive whole cell components obtained from cells that expressed mutants of Δ1-Δ6 (B), MTS, VKD, WAG, VMI, SAQ, TLT, GR, and VL (C) and S171, Q173, G177 and R178 (D) are shown (left). Current densities of Pax-sensitive component at +120 mV in cells expressing mutants are summarized (middle). The ratio of anti-FLAG-positive cells analyzed by NP labeling is illustrated as in Fig. 4B (right). See also supplemental Table S4. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01 versus WT by Dunnett's test. E, voltage dependence was examined in mutants that showed substantial reduction of current density without marked reduction of membrane trafficking, i.e. Δ3, MTS, VKD, WAG, VMI, TLT, VL, S171 and Q173. Intracellular Ca2+ level was fixed at pCa 6.5. Relationships between G/Gmax and voltage were fitted with Boltzmann equation. F, the values of half activation voltage (V1/2) of mutants were compared. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01 versus WT.
To examine this site-specific regulation further, eight sets of mutants were prepared by substitution of two or three sequential amino acids with alanine in the sequence from 159 to 180 (MTS, VKD, WAG, VMI, SAQ, TLT, GR, and VL in Fig. 6A). The variants of MTS, VKD, WAG, VMI, and VL showed significantly smaller whole-cell BK current. However, these mutants localized to the PM to a similar extent as BKαWT (Fig. 6C). Voltage dependence of these mutants was obtained from the activation curves at pCa 6.5 and compared by the half-activation voltage (V1/2) (see “Experimental Procedures”). As shown in Fig. 6E, the activation curves of Δ3, MTS, VKD, WAG, VMI, and VL showed substantial rightward shift in comparison with WT. Accordingly, V1/2 values were elevated (Fig. 6F and supplemental Table S5). For example, VMI showed PM expression comparable to WT but almost no current at +120 mV (Fig. 6C). The lack of current in VMI may be attributable to the marked shift of V1/2 to positive direction by +150 mV (Fig. 6F). As for the variant of TLT, whole-cell BK channel currents at pCa 6.5 were significantly increased. However, V1/2 at pCa 6.5 was similar to that of WT. All mutants in Fig. 6, E and F, possess significant Ca2+ sensitivity (supplemental Fig. S3 and Table S5).
On the other hand, SAQ and GR mutants exhibited neither surface expression nor BK currents (Fig. 6C). When Ser171 or Gln173 was substituted by alanine (S171 and Q173 in Fig. 6D, respectively), the PM expression was not altered, whereas the average current density significantly decreased (Fig. 6D). It is apparently due to the shift of V1/2 to depolarized potentials (Fig. 6, E and F). The Ala substitution of Gly177 or Arg178 (G177 and R178 in Fig. 6D, respectively) decreased both BK current and surface expression. In fact, Arg178 is a key amino acid for trafficking. Taken together, amino acids in the S0-S1 linker, especially the Helix2 (especially Ser171 and Gln173) and Helix2-S1 linker (Gly177 and Arg178), are necessary for both BKα trafficking to PM and channel function, including voltage dependence.
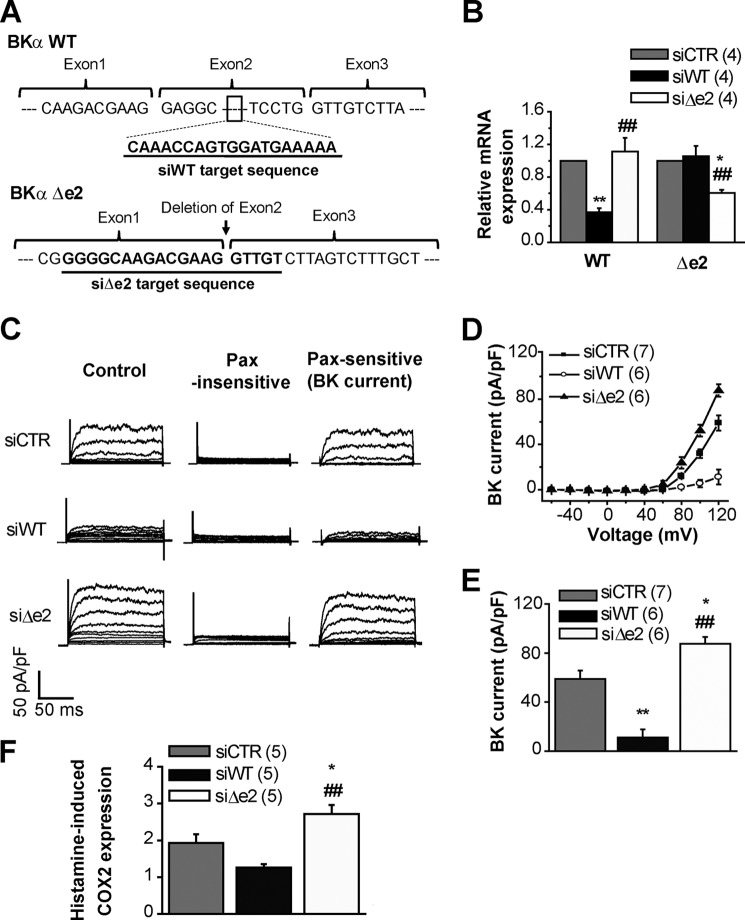
Knockdown of the BKαΔe2 Transcript Increased Histamine-induced COX2 Gene Expression
The final series of experiments revealed an important functional role of BKαΔe2 in OUMS-27 cells. siRNAs that targeted exon2 (siWT) and junction between exon1 and exon3 (siΔe2) were introduced to OUMS-27 cells (Fig. 7A). Similar methods were used to knockdown a short-type splice variant of ryanodine receptor type 3 in mouse myometrium (19). As shown in Fig. 7B, siWT and siΔe2 selectively reduced mRNA levels of BKαWT and BKαΔe2, respectively. Whole-cell BK channel current recordings from siRNA-treated cells (Fig. 7C) showed that: (i) siWT treatment significantly decreased BK channel currents in OUMS-27 cells, but (ii) siΔe2 significantly increased the currents (Control (siCTR): 59.0 ± 6.7 pA/pF, 7 cells; siWT: 11.2 ± 6.6 pA/pF, 6 cells; siΔe2: 87.6 ± 5.6 pA/pF, 6 cells; Fig. 7, D and E).
FIGURE 7.
Knockdown of BKαΔe2 increases histamine-induced COX2 expression in the OUMS-27 human chondrocyte cell line. A, schemata of siRNAs are shown. siWT is targeted to exon2, which does not exist in BKαΔe2. On the other hand, siΔe2 binds to the junctional region of exon1 and exon3 that does not reside in BKαWT. B, mRNA levels of BKαWT and BKαΔe2 in OUMS-27 cells treated with siCTR, siWT, or siΔe2. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01 versus siCTR; ##, p < 0.01 versus siWT. C, outward currents recorded in OUMS-27 cells treated with either siRNA. Currents recorded before (left) and after (middle) the application of 1 μm Pax and Pax sensitive-currents (BK current, right) are shown. D, whole-cell current-voltage relationship for Pax-sensitive currents. E, comparisons of these current densities at +120 mV. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01 versus siCTR; ##, p < 0.01 versus siWT. F, histamine-induced COX2 expression in siRNA-treated OUMS-27 cells evaluated by Q-PCR. Histamine (30 μm) was applied 48 h after the application of siRNA. After histamine treatment lasting 24 h, total RNA was extracted. COX2 mRNA expression is shown as the “relative COX2 level” compared with that in untreated groups. *, p < 0.05 versus siCTR; ##, p < 0.01 versus siWT.
Additional experiments further documented the functional significance of the splice variant. It is well known that histamine can enhance physiological responses in chondrocytes, such as increasing prostaglandin E (PGE) production (20). Accordingly, the effect of the same siRNAs that altered channel function was assessed in terms of the expression of COX2, an inducible enzyme for PGE2 production (Fig. 7F). Measurements based on Q-PCR showed that COX2 expression in OUMS-27 pretreated with 30 μm histamine for 24 h was ∼2× higher than that in untreated cells (siCTR normalized to untreated cells: 1.9 ± 0.2, n = 5). Importantly, siWT slightly decreased (siWT: 1.3 ± 0.1, n = 5), and siΔe2 significantly increased COX2 mRNA expression (siΔe2: 2.7 ± 0.3, n = 5).
Discussion
Main Findings
A new splice variant of BK channel α subunit (BKαΔe2) was cloned from OUMS-27, an accepted model of human chondrocytes. Our results suggest that this transcript has a significant role in articular joint function. It may also be the case under pathophysiological conditions, as this transcript is found in chondrocytes from osteoarthritis patients as well (Fig. 1C).
Homo-tetrameric BKαΔe2 transcripts cannot traffic to PM when transfected into HEK293 cells (Fig. 4, A and B). Electrophysiological (Figs. 2 and 3) and imaging (Figs. 4 and 5) analyses show that BKαΔe2 can form hetero-tetramers with BKαWT and are functionally expressed in PM. The affinity between BKαWT and BKαΔe2 for heteromerization is similar to that between BKαWT subunits based on FRET and GFP bleaching data (Figs. 4G and 5D). We note that hetero-tetramer complexes consisting of WT/Δe2 (at a ratio of 3:1, 2:2, or 1:3) can traffic to the PM, where functional BK channels are formed. Overall, the hetero-tetramerization of BKαΔe2 with BKαWT reduces both the efficiency of BKαWT trafficking to PM (Fig. 4) and the single channel functions (Figs. 2, 3, and 6). These effects occur in a stoichiometry-dependent manner.
Our analyses based on deletion mutants in exon2 (Δ1-Δ6) revealed that Helix 2 (especially Ser171 and Gln173), the adjacent linker to the S1 segment (Gly177 and Arg178), and a part of S1 segment are essential for the surface expression (Fig. 6). A short α-helix in the C terminus of BKαWT (1112DLIFCL1117) is known to function as an ER export motif (21). Indeed, intracellular BKαΔe2 was substantially co-localized with an ER marker (data not shown). Therefore, the Helix2 in S0-S1 linker may be involved in the mechanism for surface trafficking of BK channel via the interaction with a cargo recognition component (22) or an adaptor protein complex (23).
The deletion of exon2 affected not only the trafficking efficiency but also channel kinetics when it forms hetero-tetramers with BKαWT (Fig. 2, F and G). Deletion mutant (Δ3: Δ151–161) and mutants of alanine replacement (MTS, VKD, WAG, VMI, VL, Ser171 and Gln173) exhibited smaller BK current density even though their surface expression was comparable with that for BKαWT (Fig. 6, B–D). Analyses of voltage dependence revealed that voltage sensitivity of these mutants was markedly reduced (Fig. 6, E and F). It has been reported that Asp164 in the 162VKD164 forms a Mg2+ binding site, and Mg2+ binding is essential for interaction between voltage-sensor domain and cytoplasmic domain (RCK1) (24). This may be the reason why the mutation of 162VKD164 exhibits impaired voltage sensitivity. 159MTS161, 165WAG167, 168VMI170, Ser171, Gln173, and 179VL180 are located closely to Asp164 and, therefore, mutation in these residues may also affect Mg2+ binding and voltage dependence. Such effects could explain the observed smaller single channel conductance and shorter mean open time of WT/Δe2 BK channels (Fig. 2).
In this mutation assay some contradictions were observed. For example, deletion of 179VL180 (Δ6) prevents surface trafficking (Fig. 6B), whereas alanine replacement of 179VL180 (VL) does not affect surface trafficking (Fig. 6C). We assume that deletion of 179VL180 causes larger changes in the conformation of Helix2, Helix2-S1 linker, and/or S1 segment than Ala substitution. This conformational change in Δ6 may prevent Helix2 from binding to a cargo recognition protein. A similar explanation would be possible for discrepancy between Δ162–170 (Δ4) and mutants of Ala replacement in the region of Val162-Ile170.
When [Ca2+]i was increased to 10 μm (pCa 5.0, see supplemental Fig. S3 and Table S5), V1/2 of all mutants in Fig. 6, E and F, significantly decreased, whereas the sensitivity to Ca2+ was different among the mutants. Thus, Helix2 and adjacent regions may partially contribute to Ca2+ sensitivity (25).
Finally, the effects of single mutations of Ser171, Gln173, Gly177, and Arg178 should be emphasized. Both Ser171 and Gln173 exhibited a striking shift of V1/2 over +75 mV without the significant change in trafficking efficiency observed in SAQ. In contrast, Gly177 and Arg178 exhibited both reduced whole-cell BK channel currents and impaired trafficking efficiency. Arg178 may be a key amino acid in the linker between Helix2 and S1 segment to keep the Helix2 in the correct position or angle required for trafficking efficiency and channel activity. Taken together, it can be concluded that BKαΔe2 strongly inhibits BK channel function by two mechanisms; (i) preventing surface expression (Figs. 4 and 6) and (ii) reducing single channel activity by decreasing single channel conductance (Fig. 2) and voltage-sensitivity (Fig. 6).
Translational Significance of BK Channel Complexes
Inflammation in synovia of articular joints leads to an increase in mast cell migration, and these cells release pro-inflammatory mediators such as histamine, PGE2, IL-1, and TNF-α. Downstream actions of these agents can initiate the progressive degenerative diseases such as OA (26). In healthy articular cartilage, histamine binds to its type-1 receptor (H1R) and promotes cell proliferation. This is in part due to an increase in [Ca2+]i and related changes in DAG and in PKC activities. Notably, in cartilage from OA patients, expression levels of H1R and histidine decarboxylase are higher than normal (26). These changes may enhance H1R signaling and lead to increased PGE2 and metalloproteinase-3 (MMP-3) and -13 production (20) as well as cell proliferation (26). Histamine-mediated signaling pathway is involved in the inhibition of matrix production and resulting degeneration of articular cartilage under OA pathogenesis.
In the present study histamine promoted gene expression of COX2. Furthermore, the BKαΔe2 knockdown resulted in an increase in both BK channel current density and COX2 transcripts (Fig. 7). The COX2 transcription is regulated by several Ca2+-dependent factors (27). Overall our results suggest that an increase in [Ca2+]i can activate nuclear factor of activated T-cells (NFAT) and/or nuclear factor κB (NFκB), leading to COX2 transcription. Previously, we demonstrated in OUMS-27 cells that KCa channels (including the BK, intermediate and small conductance Ca2+-activated K+ (IK and SK) channels) are functionally expressed. Moreover, BK channels are essential for enhancement of histamine-induced Ca2+ influx, as the BK channel-mediated hyperpolarization of the resting membrane potential enhances Ca2+ influx (8). Here, we have shown that the BKαΔe2 knockdown can cause up-regulation of BK channel activity and membrane hyperpolarization and subsequently enhanced Ca2+ influx. This increase in [Ca2+]i may activate NFAT and/or NFκB and, thus, promote COX2 transcription.
The relative mRNA ratio of BKαΔe2 to BKαWT (WT:Δe2) was 1:0.14 in OUMS-27 cells (Fig. 1D). Experiments using HEK293 heterologous system actually showed that the amount of BKαΔe2 plasmid (1:0.1) reduced whole-cell BK channel currents by approximately 40% (supplemental Fig. S2). Moreover, co-transfection of BKαΔe2 cDNA inhibited whole-cell BK channel currents in a ratio-dependent manner. When mRNA ratio (WT:Δe2) is 1:0.14, the probability that BKα tetramer contains one or more BKαΔe2 subunits is calculated as approximately 41%. When siΔe2 reduces the BKαΔe2 mRNA level to 60% in OUMS-27, i.e. WT:Δe2 is 1:0.084, the probability that a BKα tetramer contains BKαΔe2 subunit(s) is approximately 28%. Thus, treatment with siΔe2 is thought to increase the occurrence of BKαWT homo-tetramers by 13% even if the increase in trafficking efficiency is not taken into account. In addition, the stoichiometric change from 1Δe2:3WT to 4WT increases the single channel conductance by ∼20% (Fig. 2). All these factors are considered to contribute to significant enhancement of whole-cell BK channel current amplitude. Thus, it is rather reasonable that siRNA knockdown of Δe2 substantially increases whole-cell BK channel current and COX-2 induction.
The expression level of BKα is up-regulated in OA patients (12). Similarly, immunohistochemical analysis demonstrated that BKα is up-regulated in the middle region of articular cartilage from OA animal models (28). We observed that inflammatory factors, such as IL-1β and TNF-α, modulate the mRNA levels of BKαΔe2 in OUMS-27 cells (data not shown). Thus, it is possible that changes in the expression of BKαΔe2 versus that of BKαWT (specifically, the regulation of the splicing) may be involved in the pathogenesis and/or progression of OA. The expressional changes in BKαWT and/or BKαΔe2 in chondrocytes of OA patients and the relevance of them to pathogenesis should be studied in future. An increase in [Ca2+]i is involved in development of OA by activating calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (29). Accordingly, the ion channels that modulate [Ca2+]i changes are critically important for the treatment of OA.
In summary, BKαΔe2, a newly identified splice variant of BK channels can significantly regulate human chondrocyte function under physiological and/or pathophysiological conditions. It does so by serving as a negative factor for trafficking to PM after formation of hetero-tetramers with BKαWT and also by regulating channel activity.
Experimental Procedures
Cell Culture, Human Tissue, and Animal Sources
HEK (human embryonic kidney) 293 and OUMS-27, the human chondrocyte cell line, were supplied from Japanese Collection of Research Bioresources Cell Bank and cultured as described previously (8–10). C57BL/6 mice were purchased from Japan SLC (Hamamatsu, Japan). Human articular cartilage from (i) a healthy individual and (ii) a patient with osteoarthritis was purchased from Articular Engineering (Northbrook, IL). All experiments were approved by the Ethics Committee of Nagoya City University and were conducted in accordance with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of the Japanese Pharmacological Society.
Electrophysiological Recordings
Electrophysiological studies were performed as described previously (16). When making whole-cell BK current measurements, the pipette solution contained 140 mm KCl, 2.8 mm MgCl2, 10 mm HEPES, 2 mm Na2ATP, 5 mm EGTA, and 3.15 mm CaCl2 (pCa 6.5). When the effect of increase in intracellular Ca2+ on mutants was examined, 4.93 mm CaCl2 was added to fix the intracellular Ca2+ concentration at 10 μm (pCa 5.0). The pH was adjusted to 7.2 with KOH. The extracellular solution had an ionic composition 137 mm NaCl, 5.9 mm KCl, 2.2 mm CaCl2, 1.2 mm MgCl2, 14 mm glucose, and 10 mm HEPES. The pH was adjusted to 7.4 with NaOH. Whole-cell BK currents were activated from a holding potential of −80 mV by applying 150-ms voltage steps, once every 10 s, to a voltage range between −60 and +120 or +140 mV in increments of 20 mV. The activation curve was made by plotting relative tail current amplitudes (G/Gmax) recorded at −60 or −30 mV against test potential ranging from −100 to +200 mV or from −60 mV to +260 mV. Obtained data were fitted with a Boltzmann relationship, G/Gmax = (1 + exp((V − V1/2)/S))−1, where V1/2, V, and S are the voltages required for half-maximum activation, membrane potential, and slope factor, respectively. Data were sampled at 10 kHz and filtered at 2 kHz. The BK channel-mediated current was defined as the 1 μm paxilline-sensitive current (15). The resistance of the pipette was 2–5 megaohms for whole-cell patch clamp configurations when filled with the pipette solutions.
Single BK channel current recordings were made using the inside-out patch clamp method. The compositions of solutions were as follows: pipette solution: (A) control measurements: 140 mm KCl, 1.2 mm MgCl2, 1.82 mm CaCl2, 5 mm EGTA (pCa 7.0), 14 mm d-glucose and 10 mm HEPES; (B) TEA-insensitive current recordings: 140 mm KCl, 1.2 mm MgCl2, 2.2 mm CaCl2, 5 mm EGTA (pCa 6.8), 14 mm d-glucose, 10 mm HEPES, and 2 mm TEA-Cl (pH 7.2 with KOH); bath solution: 140 mm KCl, 1.2 mm MgCl2, 3.15 mm CaCl2, 5 mm EGTA (pCa 6.5), 14 mm d-glucose, and 10 mm HEPES (pH 7.2 with KOH). All single-channel data were sampled at 5 kHz, filtered at 0.5 kHz, and recorded for 60 s after channel activity was stable. The data acquisition protocol was repeated at least three times for each preparation. All patches were voltage-clamped to 0 mV, and their unitary currents were activated by voltage steps to 50 mV. For single channel amplitude analysis, only patches containing fewer than two channel types were utilized. The unitary current amplitudes were obtained by fitting data with the Gaussian function. Single channel conductance was calculated from unitary currents at 0, 40, and 50 mV. In Figs. 2 and 3, the number of recordings that contained single channel currents due to each complex of BKα tetramer were counted. The total number of BKα tetramers within each patch could not be confirmed. The resistance of the pipette was 10–15 megaohms for inside-out patch clamp configurations when filled with the pipette solutions.
Plasmid Constructs and Transfection
The full-length of cDNA encoding the human KCNMA1 (BKαWT: NM_002247 and BKαΔe2: AB524033.1) were labeled with the FLAG tag and fluorescent proteins (using pEYFP-N1, pECFP-N1, pAcGFP1-N1, and pmCherry-N1 vectors from Clontech Laboratories, Mountain View, CA) at extracellular N and intracellular C termini, respectively. In the case of BiFC analysis, the C termini of BKα were labeled by fragments of N (1–173: VN173) or C (155–238: VC155) termini of Venus (10). pBiFC-VN173 and pBiFC-VC155 were gifts from Chang-Deng Hu (Addgene plasmid #22010 and #22011, respectively). HEK293 cells were transiently transfected with cDNA (total ∼2 μg) using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen). Experiments were preformed 12 to 72 h after transfection. All constructs were confirmed by DNA sequencing. The BKα mutants were generated by site-directed PCR.
Single Molecule Imaging
Single molecule imaging was performed using a TIRF imaging system with an objective lens (CFI Plan Apo TIRF 60×/1.45 or CFI Apo TIRF 100×/1.49, oil immersion; Nikon, Tokyo, Japan) as described previously (15). Data were collected with an EM-CCD camera and analyzed by AQUACOSMOS software (Hamamatsu Photonics, Hamamatsu, Japan). GFP- or mCh-fused protein targets were excited with a 488-nm argon laser (Spectra-Physics, Santa Clara, CA) or a 543-nm He/Ne laser (Melles Griot, Carlsbad, CA), respectively. GFP/mCh emission data were collected using a combination of dichroic mirrors and dual band-pass filters (505–530/570–660 nm; Omega Optical, Brattleboro, VT). The resolution of images was 105 nm per pixel (x-y) and <200 nm (z). All experiments were carried out at room temperature (25 °C).
FRET Analysis
The efficiency of FRET (EFRET) was evaluated based on the acceptor photobleaching method in which the emission of the donor fluorophore is compared before and after the photobleaching of the acceptor (15). CFP or YFP were excited using a 405-nm blue diode laser (Coherent, Santa Clarra, CA) or the 488-nm laser under the TIRF illumination. CFP-HQ (DM450/BA460–510; Nikon) and YFP-HQ (DM510/BA520–560; Nikon) filter cubes were used for collection of emission signal.
Single Molecule GFP Bleaching
The number of BKα subunits in the immediate vicinity of the plasma membrane of HEK293 cells was counted by observing the bleaching steps of GFP fused to channels in a single particle, as described previously (15, 17). Images were obtained in the order of mCh and GFP to avoid bleaching by cross-excitation. Images were acquired at 10 Hz for 100–120 s. Fluorescence intensity in a region of interest (ROI) (5 × 5 pixels) was calculated by subtracting the background in 24 pixels around the ROI. The number of bleaching steps was determined by eye from the fluorescence signal trace. The distributions of observed number of bleaching steps were compared with zero-truncated binomial distribution, P(x, n, p) = nCx px (1-p)n − x, where n is the number of subunits (n = 4 for tetramers), x is the observed number of bleaching steps, and p is the apparent probability for GFP fluorescence (30).
Non-permeabilized Labeling and Confocal Microscopy
FLAG tag fused to extracellular N terminus was immunostained using anti-FLAG M2 antibody (1:200, Sigma) (3, 5) for 2 h on ice. Primary antibodies were washed with PBS and fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 min at room temperature. After washing, cells were incubated with Alexa488-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG (1:500, Molecular Probes, Eugene, OR) for 1 h. Immunostained cells were observed using a laser scanning confocal fluorescent microscope (A1R, Nikon) and NIS Elements software (version 3.10, Nikon). The excitation wavelength from the multi-argon laser (MellesGriot) for Alexa488 was 488 nm, and the emission light was collected by a band-pass filter (500–530). mCh was excited at 543 nm, and fluorescence was measured using a filter cube (553–618). The ratio of anti-FLAG antibody-positive cells was calculated as the number of anti-FLAG-positive cells divided by that of mCh-positive cells within ROIs (1024 × 1024 pixel, 0.14 μm/pixel).
CFP or YFP were excited using the multi-argon laser (457 nm or 514 nm). CFP (BA465–500) and YFP (BA525–555) filter cubes were used for collection of emission signal.
Co-IP
Co-IP procedures were carried out using a Pierce co-immunoprecipitation kit according to the experimental manual supplied by Thermo Scientific (16). Briefly, HEK293 cells were lysed in IP lysis/wash buffer (0.025 m Tris, 0.15 m NaCl, 0.001 m EDTA, 1% Nonidet P-40, 5% glycerol (pH 7.4)) with a protease inhibitor mixture (Sigma). Homogenates were centrifuged (15, 000 × g, 30 min, 4 °C), and supernatant was precleared with control resin (1 h, 4 °C). Precleared lysates (∼0.5 mg of protein) were incubated with AminoLink Plus Coupling Resin, with which 10 μg of anti-FLAG M2 antibody was immobilized (overnight, 4 °C). The incubated lysates were washed with IP lysis/wash buffer, eluted with elution buffer, boiled with 5× sample buffer with 2-mercaptoehanol, and finally subjected to SDS-PAGE (10%). The blots were incubated with anti-GFP antibody (Living Colors Full-Length GFP Polyclonal Antibody; Clontech Laboratories) and then incubated with anti-rabbit horseradish peroxidase-conjugated IgG (Chemicon International, Temecula, CA). An enhanced chemiluminescence detection system (GE Healthcare) was used for getting images of the bound antibody. Resulting images were analyzed by a LAS-3000 device (Fujifilm, Tokyo, Japan).
RNA Extraction and Real-time PCR
Total RNA extraction from OUMS-27 cells, human articular cartilage and selected mouse tissues, and Q-PCR were performed as reported previously (8, 9). Human total RNA was purchased from BioChain (Newark, CA). The detail sequences of primers are presented in supplemental Table S1. All samples were run in triplicate. The efficiency of all primer pairs ranged from 90 to 110%. Transcriptional levels of BKαΔe2 are presented as relative expression to the endogenous standard, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), as illustrated in Fig. 1D. To compare the effects of siRNAs, transcript levels of BKα subunits and COX2 were analyzed by the ΔΔCt method (Fig. 7B and F).
siRNA Knockdown
siRNAs for BKαWT (siWT: 5′-CAAACCAGUGGAUGAAAAA-3′), BKαΔe2 (siΔe2: 5′-GGGGCAAGACGAAGGTTGT-3′), and Control (siCTR: medium GC duplex #3) were obtained from Invitrogen (Stealth RNAiTM). OUMS-27 cells were transfected with 200 nm concentrations of siRNA constructs and GFP plasmids using Nucleofector (Lonza, Basel, Switzerland). Cells were used for experiments 48–72 h after transfection. When COX2 expression was measured, DMEM medium containing 30 μm histamine was added to OUMS-27 cells 48 h after siRNA transfection. Cells were lysed 24 h after histamine application.
Statistics
All values are expressed as the mean ± S.E. The numbers of experiments in each protocol are shown in parentheses. Statistical significance between two groups was evaluated using Student's t test after F-test application. Tukey's test or Dunnett's test following one way analysis of variance was examined for statistical analyses among multiple groups.
Author Contributions
Y. S. designed the study, performed and analyzed experiments, and wrote the manuscript. S. O. cloned BKαΔe2 variant and provided technical assistance. H. Y. provided technical assistance and interpreted the data. W. R. G. interpreted the data and wrote the manuscript. Y. I. conceived and coordinated the study and wrote the manuscript. All authors reviewed the results and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Supplementary Material
This work was supported by Japan Society for the Promotion of Science KAKENHI Grants 26293021 and 15H01408 (to Y. I.), 26860059, 16H06215, and 16K15127 (to Y. S.), and 16K08278 (to H. Y.). This work was also supported by a grant-in-aid from Takeda Science Foundation (to Y. S.) and Salt Science Research Foundation Grant 1637 (to Y. S.). The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.

This article contains supplemental Figs. S1–S3, Tables S1–S5, and a movie.
- BK channel
- large conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel
- BiFC
- bimolecular fluorescence complementation
- COX2
- cyclooxygenase-2
- OA
- osteoarthritis
- Pax
- paxilline
- PM
- plasma membrane
- NP
- non-permeabilized
- TEA
- tetraethylammonium
- TIRF
- total internal reflection fluorescence
- Q-PCR
- quantitative real-time PCR
- mCh
- mCherry
- PGE
- prostaglandin E
- H1R
- histamine type-1 receptor
- YFP
- yellow fluorescent protein
- CFP
- cyan fluorescent protein
- ROI
- region of interest
- IP
- immunoprecipitation
- ER
- endoplasmic reticulum
- pF
- picofarads
- pS
- picosiemens.
References
- 1. Guéguinou M., Chantôme A., Fromont G., Bougnoux P., Vandier C., and Potier-Cartereau M. (2014) KCa and Ca2+ channels: the complex thought. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1843, 2322–2333 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Contreras G. F., Castillo K., Enrique N., Carrasquel-Ursulaez W., Castillo J. P., Milesi V., Neely A., Alvarez O., Ferreira G., González C., and Latorre R. (2013) A BK (Slo1) channel journey from molecule to physiology. Channels 7, 442–458 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Chen L., Jeffries O., Rowe I. C., Liang Z., Knaus H. G., Ruth P., and Shipston M. J. (2010) Membrane trafficking of large conductance calcium-activated potassium channels is regulated by alternative splicing of a transplantable, acidic trafficking motif in the RCK1-RCK2 linker. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 23265–23275 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Xie J., and McCobb D. P. (1998) Control of alternative splicing of potassium channels by stress hormones. Science 280, 443–446 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Zarei M. M., Eghbali M., Alioua A., Song M., Knaus H. G., Stefani E., and Toro L. (2004) An endoplasmic reticulum trafficking signal prevents surface expression of a voltage- and Ca2+-activated K+ channel splice variant. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101, 10072–10077 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Lewis R., Feetham C. H., and Barrett-Jolley R. (2011) Cell volume regulation in chondrocytes. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 28, 1111–1122 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Barrett-Jolley R., Lewis R., Fallman R., and Mobasheri A. (2010) The emerging chondrocyte channelome. Front Physiol. 1, 135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Funabashi K., Ohya S., Yamamura H., Hatano N., Muraki K., Giles W., and Imaizumi Y. (2010) Accelerated Ca2+ entry by membrane hyperpolarization due to Ca2+-activated K+ channel activation in response to histamine in chondrocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 298, C786–C797 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Kurita T., Yamamura H., Suzuki Y., Giles W. R., and Imaizumi Y. (2015) The ClC-7 chloride channel Is down-regulated by hypoosmotic stress in human chondrocytes. Mol. Pharmacol. 88, 113–120 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Inayama M., Suzuki Y., Yamada S., Kurita T., Yamamura H., Ohya S., Giles W. R., and Imaizumi Y. (2015) Orai1-Orai2 complex is involved in store-operated calcium entry in chondrocyte cell lines. Cell Calcium 57, 337–347 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Mobasheri A., Lewis R., Maxwell J. E., Hill C., Womack M., and Barrett-Jolley R. (2010) Characterization of a stretch-activated potassium channel in chondrocytes. J. Cell Physiol. 223, 511–518 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Karlsson C., Dehne T., Lindahl A., Brittberg M., Pruss A., Sittinger M., and Ringe J. (2010) Genome-wide expression profiling reveals new candidate genes associated with osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 18, 581–592 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Shi P., Li D., Lai C., Zhang L., and Tian C. (2013) Intracellular segment between transmembrane helices S0 and S1 of BK channel alpha subunit contains two amphipathic helices connected by a flexible loop. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 437, 408–412 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Niu X., and Magleby K. L. (2002) Stepwise contribution of each subunit to the cooperative activation of BK channels by Ca2+. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99, 11441–11446 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Suzuki Y., Yamamura H., Ohya S., and Imaizumi Y. (2013) Caveolin-1 facilitates the direct coupling between large conductance Ca2+-activated K+ (BKCa) and Cav1.2 Ca2+ channels and their clustering to regulate membrane excitability in vascular myocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 288, 36750–36761 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Suzuki Y., Yamamura H., Ohya S., and Imaizumi Y. (2013) Direct molecular interaction of caveolin-3 with KCa1.1 channel in living HEK293 cell expression system. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 430, 1169–1174 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Yamamura H., Ikeda C., Suzuki Y., Ohya S., and Imaizumi Y. (2012) Molecular assembly and dynamics of fluorescent protein-tagged single KCa1.1 channel in expression system and vascular smooth muscle cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 302, C1257–C1268 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Bharill S., Fu Z., Palty R., and Isacoff E. Y. (2014) Stoichiometry and specific assembly of Best ion channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 111, 6491–6496 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Dabertrand F., Morel J. L., Sorrentino V., Mironneau J., Mironneau C., and Macrez N. (2006) Modulation of calcium signalling by dominant negative splice variant of ryanodine receptor subtype 3 in native smooth muscle cells. Cell Calcium 40, 11–21 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Tetlow L. C., and Woolley D. E. (2002) Histamine stimulates matrix metalloproteinase-3 and -13 production by human articular chondrocytes in vitro. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 61, 737–740 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Kwon S. H., and Guggino W. B. (2004) Multiple sequences in the C terminus of MaxiK channels are involved in expression, movement to the cell surface, and apical localization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101, 15237–15242 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Grumbach Y., Bikard Y., Suaud L., Chanoux R. A., and Rubenstein R. C. (2014) ERp29 regulates epithelial sodium channel functional expression by promoting channel cleavage. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 307, C701–C709 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Ma D., Taneja T. K., Hagen B. M., Kim B. Y., Ortega B., Lederer W. J., and Welling P. A. (2011) Golgi export of the Kir2.1 channel is driven by a trafficking signal located within its tertiary structure. Cell 145, 1102–1115 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Yang H., Shi J., Zhang G., Yang J., Delaloye K., and Cui J. (2008) Activation of Slo1 BK channels by Mg2+ coordinated between the voltage sensor and RCK1 domains. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 15, 1152–1159 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Braun A. P., and Sy L. (2001) Contribution of potential EF hand motifs to the calcium-dependent gating of a mouse brain large conductance, calcium-sensitive K+ channel. J. Physiol. 533, 681–695 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Tetlow L. C., and Woolley D. E. (2005) Histamine, histamine receptors (H1 and H2), and histidine decarboxylase expression by chondrocytes of osteoarthritic cartilage: an immunohistochemical study. Rheumatol. Int. 26, 173–178 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Ding J., Li J., Xue C., Wu K., Ouyang W., Zhang D., Yan Y., and Huang C. (2006) Cyclooxygenase-2 induction by arsenite is through a nuclear factor of activated T-cell-dependent pathway and plays an antiapoptotic role in Beas-2B cells. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 24405–24413 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Lewis R., May H., Mobasheri A., and Barrett-Jolley R. (2013) Chondrocyte channel transcriptomics: do microarray data fit with expression and functional data? Channels 7, 459–467 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Sugita S., Hosaka Y., Okada K., Mori D., Yano F., Kobayashi H., Taniguchi Y., Mori Y., Okuma T., Chang S. H., Kawata M., Taketomi S., Chikuda H., Akiyama H., Kageyama R., Chung U. I., Tanaka S., Kawaguchi H., Ohba S., and Saito T. (2015) Transcription factor Hes1 modulates osteoarthritis development in cooperation with calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase 2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 112, 3080–3085 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Kitazawa M., Kubo Y., and Nakajo K. (2014) The stoichiometry and biophysical properties of the Kv4 potassium channel complex with K+ channel-interacting protein (KChIP) subunits are variable, depending on the relative expression level. J. Biol. Chem. 289, 17597–17609 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.