Abstract
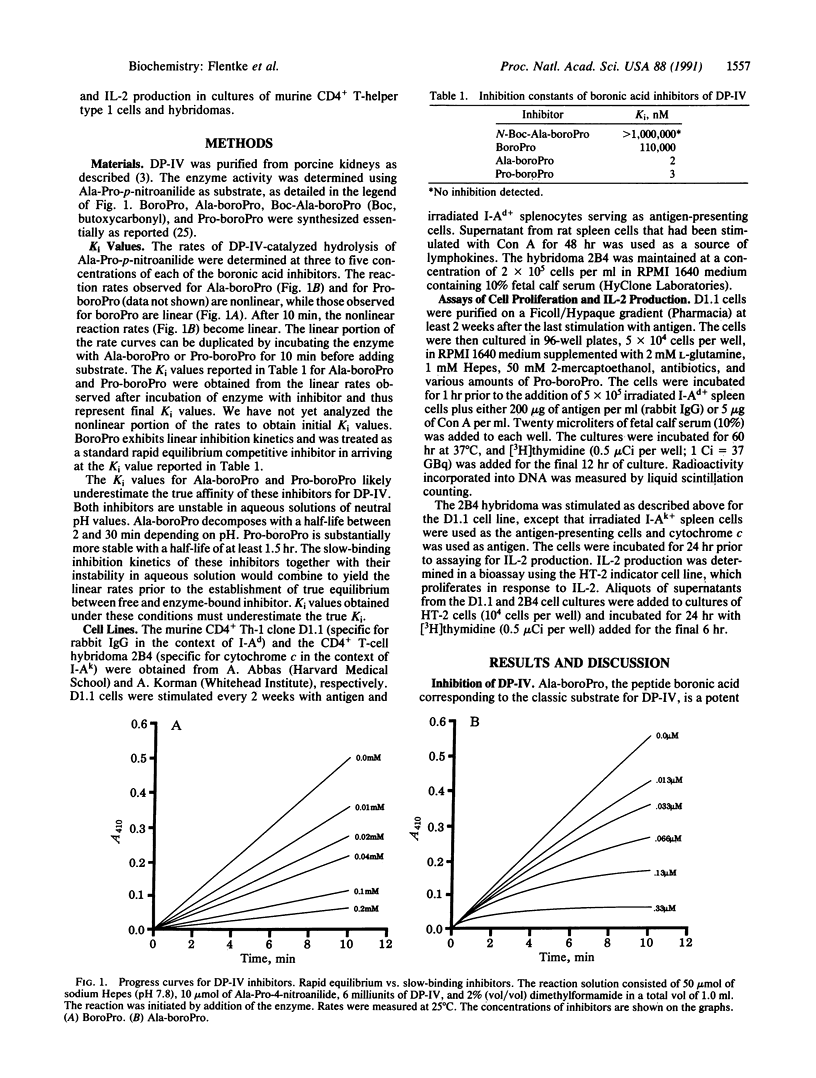
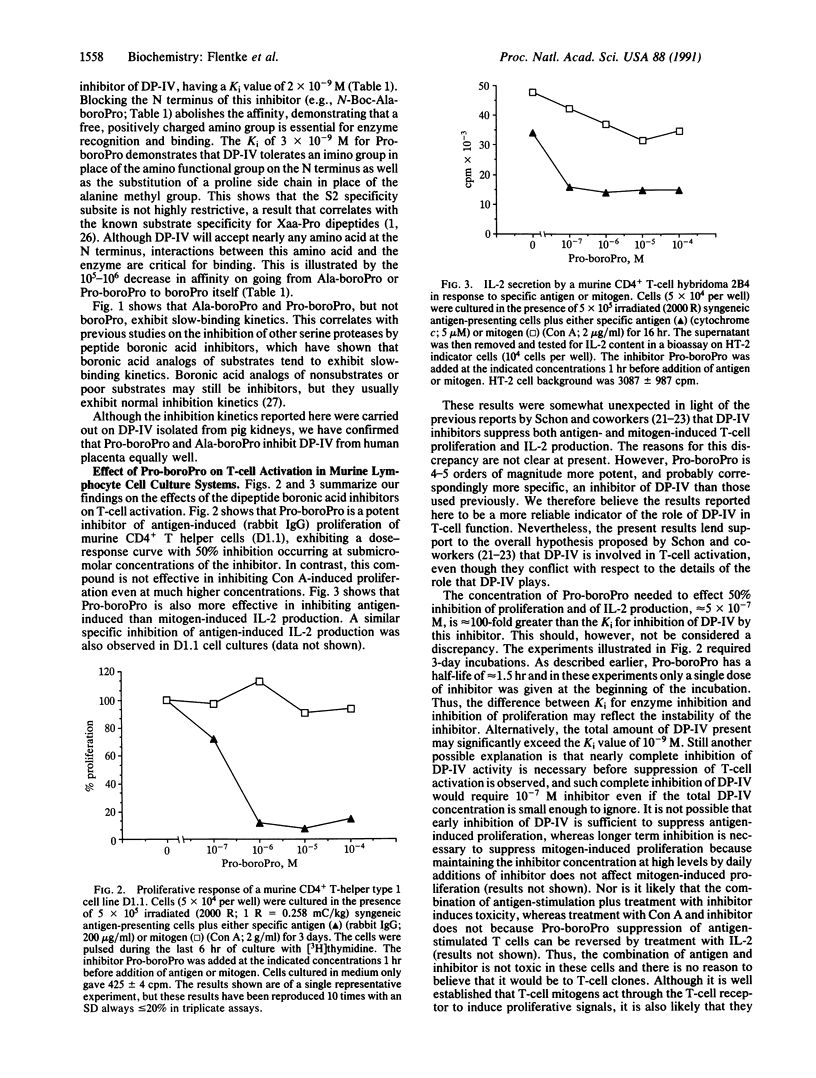
Dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DP-IV; dipeptidyl-peptide hydrolase, EC 3.4.14.5) is a serine protease with a specificity for cleaving Xaa-Pro dipeptides from polypeptides and proteins. It is found in a variety of mammalian cells and tissues, including those of lymphoid origin where it is found specifically on the surface of CD4+ T cells. Although the functional significance of this enzyme has not been established, a role in T-cell activation and immune regulation has been proposed. Here we report that Ala-boroPro and Pro-boroPro, where boroPro is the alpha-amino boronic acid analog of proline, are potent and specific inhibitors of DP-IV, having Ki values in the nanomolar range. Blocking the N terminus of Ala-boroPro abolishes the affinity of this inhibitor for DP-IV, while removal of the N-terminal residue, to give boroPro, reduces the affinity for DP-IV by 5 orders of magnitude. The dipeptide boronic acids exhibit slow-binding kinetics, while boroPro does not. We also report here that low concentrations of Pro-boroPro inhibit antigen-induced proliferation and interleukin 2 production in murine T-cell lines but do not inhibit the response of these T cells to the mitogen concanavalin A. These results indicate that DP-IV plays a role in antigen-induced, but not mitogen-induced, activation of T lymphocytes.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ansorge S., Schön E. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DP IV), a functional marker of the T lymphocyte system. Acta Histochem. 1987;82(1):41–46. doi: 10.1016/s0065-1281(87)80049-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachovchin W. W., Plaut A. G., Flentke G. R., Lynch M., Kettner C. A. Inhibition of IgA1 proteinases from Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Hemophilus influenzae by peptide prolyl boronic acids. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):3738–3743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boman H. C., Boman I. A., Andreu D., Li Z. Q., Merrifield R. B., Schlenstedt G., Zimmermann R. Chemical synthesis and enzymic processing of precursor forms of cecropins A and B. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5852–5860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caporale C., Fontanella A., Petrilli P., Pucci P., Molinaro M. F., Picone D., Auricchio S. Isolation and characterization of dipeptidyl peptidase IV from human meconium. Functional role of beta-casomorphins. FEBS Lett. 1985 May 20;184(2):273–277. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80621-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feller A. C., Heijnen C. J., Ballieux R. E., Parwaresch M. R. Enzymehistochemical staining of T mu lymphocytes for glycyl-proline-4-methoxy-beta-naphthylamide-peptidase (DAP IV). Br J Haematol. 1982 Jun;51(2):227–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman L. A., Downs T. R., Heimer E. P., Felix A. M. Dipeptidylpeptidase IV and trypsin-like enzymatic degradation of human growth hormone-releasing hormone in plasma. J Clin Invest. 1989 May;83(5):1533–1540. doi: 10.1172/JCI114049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman L. A., Downs T. R., Williams T. C., Heimer E. P., Pan Y. C., Felix A. M. Rapid enzymatic degradation of growth hormone-releasing hormone by plasma in vitro and in vivo to a biologically inactive product cleaved at the NH2 terminus. J Clin Invest. 1986 Oct;78(4):906–913. doi: 10.1172/JCI112679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossrau R. Cytochemistry of membrane proteases. Histochem J. 1985 Jul;17(7):737–771. doi: 10.1007/BF01003312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruber M., Scholz W., Flad H. D. Influence of human T lymphocytes identified by antibodies to dipeptidyl peptidase IV on differentiation of human B lymphocytes stimulated with Staphylococcus aureus Cowan I and pokeweed mitogen. Cell Immunol. 1988 May;113(2):423–434. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(88)90039-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanski C., Huhle T., Reutter W. Involvement of plasma membrane dipeptidyl peptidase IV in fibronectin-mediated adhesion of cells on collagen. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1985 Dec;366(12):1169–1176. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1985.366.2.1169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada M., Fukasawa K., Hiraoka B. Y., Mogi M., Barth A., Neubert K. Depth of side-chain pocket in the S2 subsite of dipeptidyl peptidase IV. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Aug 23;830(3):341–344. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(85)90293-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heins J., Welker P., Schönlein C., Born I., Hartrodt B., Neubert K., Tsuru D., Barth A. Mechanism of proline-specific proteinases: (I) Substrate specificity of dipeptidyl peptidase IV from pig kidney and proline-specific endopeptidase from Flavobacterium meningosepticum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 May 18;954(2):161–169. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(88)90067-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopsu-Havu V. K., Rintola P., Glenner G. G. A hog kidney aminopeptidase liberating N-terminal dipeptides. Partial purification and characteristics. Acta Chem Scand. 1968;22(1):299–308. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.22-0299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettner C. A., Bone R., Agard D. A., Bachovchin W. W. Kinetic properties of the binding of alpha-lytic protease to peptide boronic acids. Biochemistry. 1988 Oct 4;27(20):7682–7688. doi: 10.1021/bi00420a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreil G., Haiml L., Suchanek G. Stepwise cleavage of the pro part of promelittin by dipeptidylpeptidase IV. Evidence for a new type of precursor--product conversion. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Oct;111(1):49–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06073.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matoba S., Ogrydziak D. M. A novel location for dipeptidyl aminopeptidase processing sites in the alkaline extracellular protease of Yarrowia lipolytica. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6037–6043. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mentlein R., Heymann E., Scholz W., Feller A. C., Flad H. D. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV as a new surface marker for a subpopulation of human T-lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1984 Nov;89(1):11–19. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(84)90192-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto Y., Ganapathy V., Barlas A., Neubert K., Barth A., Leibach F. H. Role of dipeptidyl peptidase IV in uptake of peptide nitrogen from beta-casomorphin in rabbit renal BBMV. Am J Physiol. 1987 Apr;252(4 Pt 2):F670–F677. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.252.4.F670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollay C., Vilas U., Hutticher A., Kreil G. Isolation of a dipeptidyl aminopeptidase, a putative processing enzyme, from skin secretion of Xenopus laevis. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Oct 1;160(1):31–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09935.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita A., Chung Y. C., Freeman H. J., Erickson R. H., Sleisenger M. H., Kim Y. S. Intestinal assimilation of a proline-containing tetrapeptide. Role of a brush border membrane postproline dipeptidyl aminopeptidase IV. J Clin Invest. 1983 Aug;72(2):610–616. doi: 10.1172/JCI111009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Püschel G., Mentlein R., Heymann E. Isolation and characterization of dipeptidyl peptidase IV from human placenta. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Aug;126(2):359–365. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06788.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholz W., Mentlein R., Heymann E., Feller A. C., Ulmer A. J., Flad H. D. Interleukin 2 production by human T lymphocytes identified by antibodies to dipeptidyl peptidase IV. Cell Immunol. 1985 Jun;93(1):199–211. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90400-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schön E., Demuth H. U., Eichmann E., Horst H. J., Körner I. J., Kopp J., Mattern T., Neubert K., Noll F., Ulmer A. J. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV in human T lymphocytes. Impaired induction of interleukin 2 and gamma interferon due to specific inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase IV. Scand J Immunol. 1989 Feb;29(2):127–132. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1989.tb01108.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schön E., Jahn S., Kiessig S. T., Demuth H. U., Neubert K., Barth A., Von Baehr R., Ansorge S. The role of dipeptidyl peptidase IV in human T lymphocyte activation. Inhibitors and antibodies against dipeptidyl peptidase IV suppress lymphocyte proliferation and immunoglobulin synthesis in vitro. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Dec;17(12):1821–1826. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830171222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson B., Danielsen M., Staun M., Jeppesen L., Norén O., Sjöström H. An amphiphilic form of dipeptidyl peptidase IV from pig small-intestinal brush-border membrane. Purification by immunoadsorbent chromatography and some properties. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Oct 16;90(3):489–498. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12628.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf B., Fischer G., Barth A. Kinetische Untersuchungen an der Dipeptidyl-peptidase IV. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1978;37(3):409–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



