Figure 3.
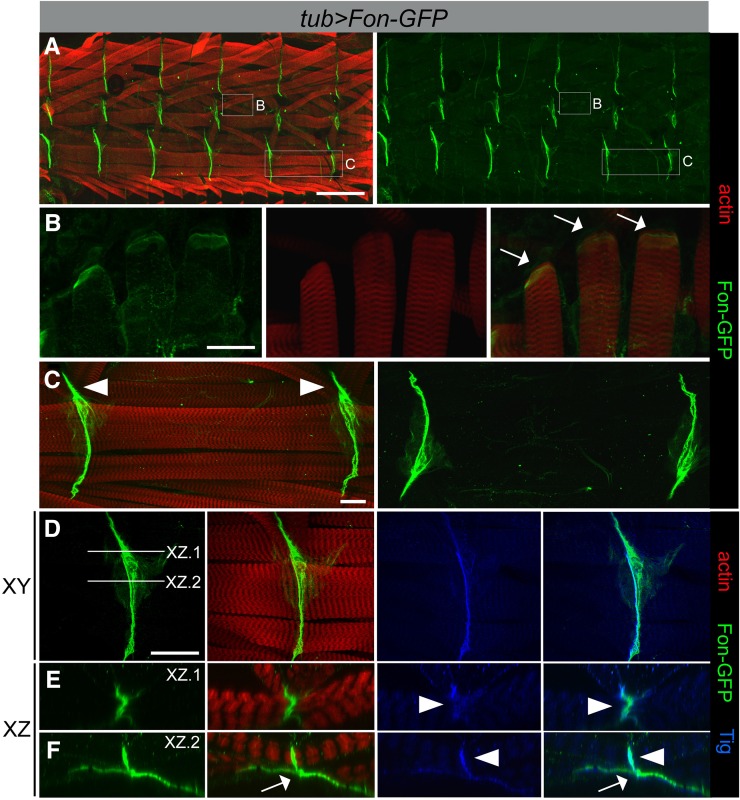
Fon accumulates at muscle attachment sites. (A–F) Ubiquitous expression of a Fon–GFP fusion protein (green) using the tubulin (tub)-Gal4 driver. Muscles are labeled with phalloidin (F-actin; red). Fon–GFP is enriched at the ends of attached myofibers at direct (muscle–cuticle; white arrows) and indirect (muscle–muscle; white arrowheads) attachments shown in a low magnification view of half a larval fillet (A) or in high magnification views (B–F). Fon–GFP weakly accumulates at the ends of lateral muscles at direct attachments (B) and is found at high levels between muscles at indirect attachment sites, such as the ventral muscles 6 and 7 (C–F). (D–F) The photographs in E and F represent the XZ plane of the lines indicated in D. Fon–GFP colocalizes with anti-Tig immunostaining (blue) at indirect attachments in regions of muscle-to-muscle contacts (E, arrowheads), but weakly within sites where muscles associate with the tendon cell (F, arrows), where Fon–GFP is more prominent. Bars, 200 µm for A; 50 µm for B and D; and 25 µm for C.