Abstract
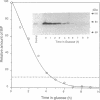
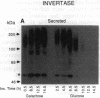
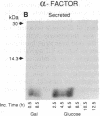
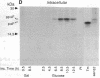
The endoplasmic reticulum of mammalian cells contains a heat shock protein of approximately 70 kDa (hsp70) termed binding protein BiP that is thought to promote the folding and subunit assembly of newly synthesized proteins. To study BiP function, we placed the BiP-encoding gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae under the control of a regulated promoter and examined the effects of BiP depletion. Reduction of BiP protein to about 15% of normal levels led to a profound reduction in secretion of alpha factor and invertase. At the same time, unglycosylated precursors of these proteins accumulated intracellularly. The predominant form of the invertase precursor had undergone signal sequence cleavage but accumulated as a soluble species in the cytosol. In contrast, the alpha-factor precursor was exclusively in the signal-uncleaved form. It sedimented with microsomal membranes and was exposed at the cytoplasmic face in a protease-resistant form. These findings suggest that, in yeast, BiP function is required for translocation of soluble proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum at a stage beyond the initial nascent chain-membrane association.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Böhni P. C., Deshaies R. J., Schekman R. W. SEC11 is required for signal peptide processing and yeast cell growth. J Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;106(4):1035–1042. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.4.1035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M., Botstein D. Two differentially regulated mRNAs with different 5' ends encode secreted with intracellular forms of yeast invertase. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90384-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshaies R. J., Schekman R. A yeast mutant defective at an early stage in import of secretory protein precursors into the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;105(2):633–645. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.2.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshaies R. J., Schekman R. SEC62 encodes a putative membrane protein required for protein translocation into the yeast endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):2653–2664. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.2653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorner A. J., Krane M. G., Kaufman R. J. Reduction of endogenous GRP78 levels improves secretion of a heterologous protein in CHO cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4063–4070. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn G. C., Chappell T. G., Rothman J. E. Peptide binding and release by proteins implicated as catalysts of protein assembly. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):385–390. doi: 10.1126/science.2756425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber R. E., Edwards L. A., Carne T. J. Studies on the mechanism of the iodination of tyrosine by lactoperoxidase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1381–1386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M., Davis R. W. Sequences that regulate the divergent GAL1-GAL10 promoter in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1440–1448. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius D., Schekman R., Thorner J. Glycosylation and processing of prepro-alpha-factor through the yeast secretory pathway. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):309–318. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90224-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassenbrock C. K., Garcia P. D., Walter P., Kelly R. B. Heavy-chain binding protein recognizes aberrant polypeptides translocated in vitro. Nature. 1988 May 5;333(6168):90–93. doi: 10.1038/333090a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machamer C. E., Doms R. W., Bole D. G., Helenius A., Rose J. K. Heavy chain binding protein recognizes incompletely disulfide-bonded forms of vesicular stomatitis virus G protein. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6879–6883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson R. C., Williams D. B., Moran L. A. An essential member of the HSP70 gene family of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is homologous to immunoglobulin heavy chain binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1159–1163. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normington K., Kohno K., Kozutsumi Y., Gething M. J., Sambrook J. S. cerevisiae encodes an essential protein homologous in sequence and function to mammalian BiP. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1223–1236. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90059-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. D., Misra L. M., Vogel J. P. KAR2, a karyogamy gene, is the yeast homolog of the mammalian BiP/GRP78 gene. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1211–1221. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90058-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothblatt J. A., Deshaies R. J., Sanders S. L., Daum G., Schekman R. Multiple genes are required for proper insertion of secretory proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum in yeast. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):2641–2652. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.2641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E. Polypeptide chain binding proteins: catalysts of protein folding and related processes in cells. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):591–601. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel J. P., Misra L. M., Rose M. D. Loss of BiP/GRP78 function blocks translocation of secretory proteins in yeast. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;110(6):1885–1895. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.6.1885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters M. G., Evans E. A., Blobel G. Prepro-alpha-factor has a cleavable signal sequence. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6209–6214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]