Fig. 2.
Use of oral contraceptives (versus non-use of hormonal contraception) and HIV acquisition, among 11 studies considered informative but with important limitations.
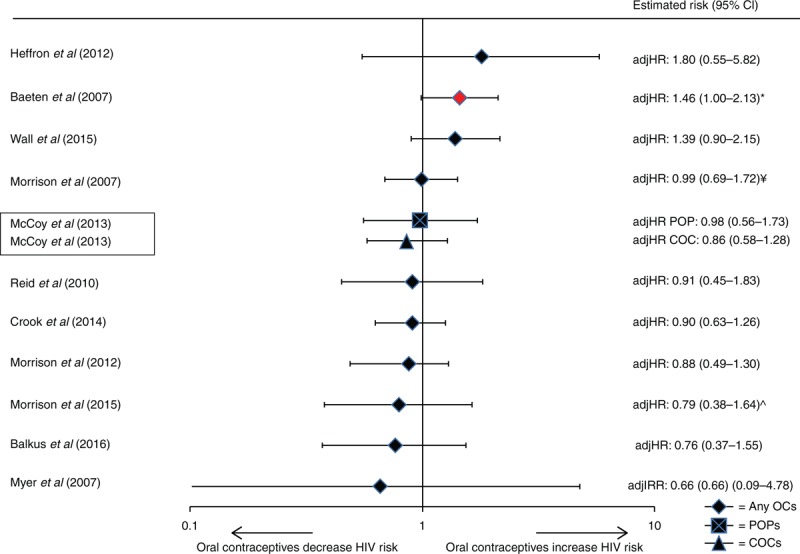
Error bars show 95% confidence intervals. Studies are arranged in order of decreasing magnitude of risk estimate, except if a single study disaggregated progestin-only pills and combined oral contraceptives, in which the case both estimates are adjacent (as indicated by a box around the study identifiers). Graph does not display estimates from marginal structural models. adjIRR, adjusted incidence risk ratio; adjHR, adjusted hazard ratio. ∗Analysis showed significant findings at P = 0.05 (marker also displayed in red). ^Unpublished estimates from a subanalysis of Morrison et al.[26] meta-analysis, restricted to pooled analysis using databases not previously used to publish estimates on hormonal contraceptive methods and HIV acquisition risk.
